Abstract
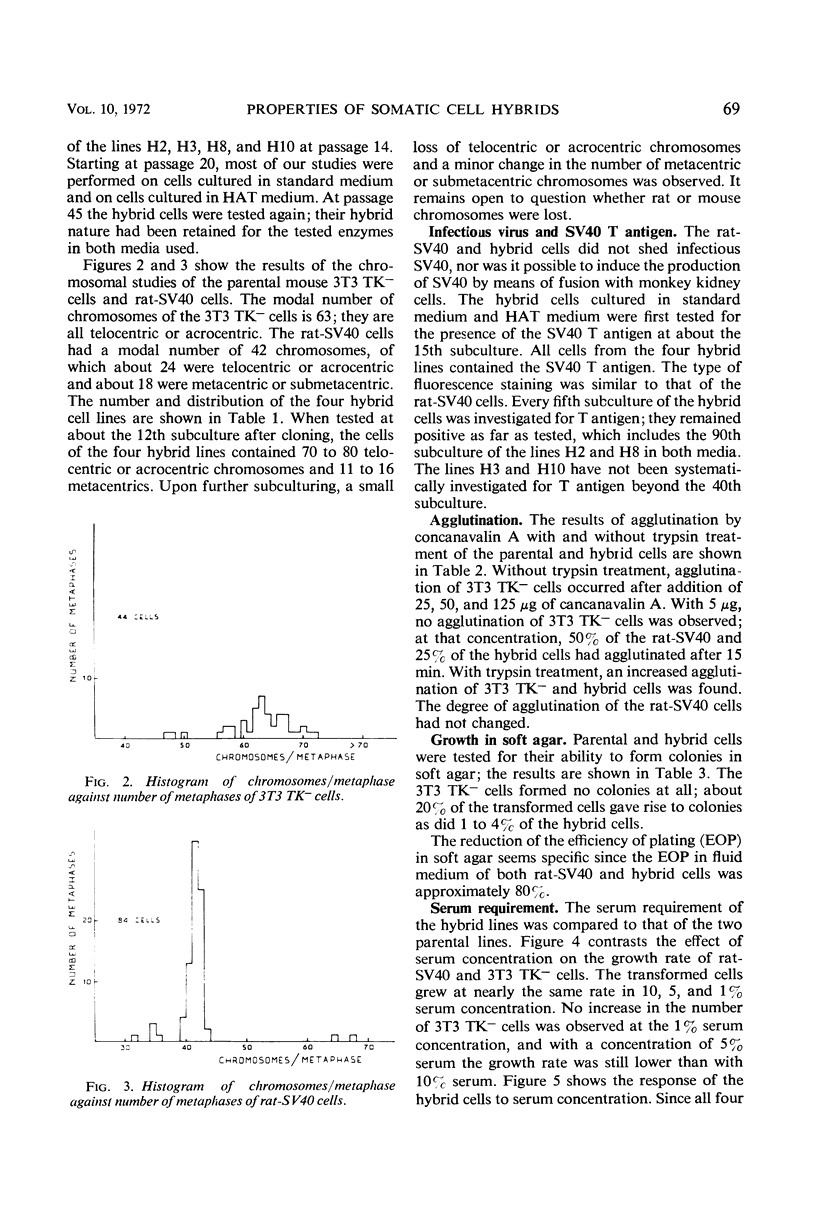
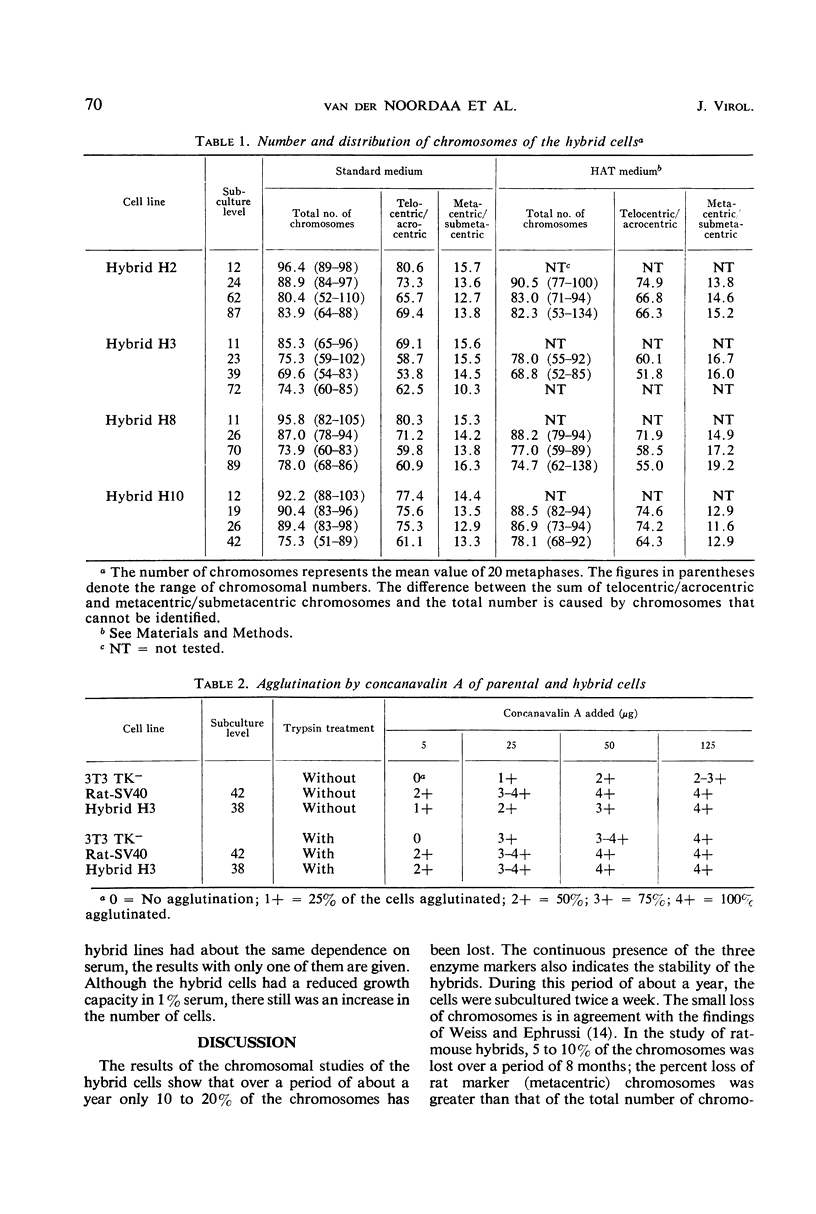
Hybrids between mouse cells and simian virus 40 (SV40)-transformed rat cells were made, and their properties and chromosome constitution were investigated over many generations. Their hybrid nature was confirmed by enzyme studies. During a period of 1 year a loss of 10 to 20% of the total number of chromosomes was observed. The SV40 tumor antigen was present and remained present in the hybrids. The parental and hybrid cells were studied for agglutination with concanavalin A, for growth in soft agar, and for serum requirement. These growth and surface characteristics of the transformed cells appeared in the hybrids.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basilico C., Wang R. Susceptibility to superinfection of hybrids between polyoma "transformed" BHK and "normal" 3T3 cells. Nat New Biol. 1971 Mar 24;230(12):105–107. doi: 10.1038/newbio230105a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Defendi V., Ephrussi B., Koprowski H., Yoshida M. C. Properties of hybrids between polyoma-transformed and normal mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Feb;57(2):299–305. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eagle H., Foley G. E., Koprowski H., Lazarus H., Levine E. M., Adams R. A. Growth characteristics of virus-transformed cells. Maximum population density, inhibition by normal cells, serum requirement, growth in soft agar, and xenogeneic transplantability. J Exp Med. 1970 Apr 1;131(4):863–879. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.4.863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inbar M., Sachs L. Interaction of the carbohydrate-binding protein concanavalin A with normal and transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Aug;63(4):1418–1425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.4.1418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTLEFIELD J. W. SELECTION OF HYBRIDS FROM MATINGS OF FIBROBLASTS IN VITRO AND THEIR PRESUMED RECOMBINANTS. Science. 1964 Aug 14;145(3633):709–710. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3633.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marin G., Littlefield J. W. Selection of morphologically normal cell lines from polyoma-transformed BHK21/13 hamster fibroblasts. J Virol. 1968 Jan;2(1):69–77. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.1.69-77.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meera Khan P. Enzyme electrophoresis on cellulose acetate gel: zymogram patterns in mgh-mouse and man--Chinese hamster somatic cell hybrids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Aug;145(2):470–483. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(71)80007-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neff J. M., Enders J. F. Poliovirus replication and cytopathogenicity in monolayer hamster cell cultures fused with beta propiolactone-inactivated Sendai virus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Jan;127(1):260–267. doi: 10.3181/00379727-127-32668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozanne B., Sambrook J. Binding of radioactively labelled concanavalin A and wheat germ agglutinin to normal and virus-transformed cells. Nat New Biol. 1971 Aug 4;232(31):156–160. doi: 10.1038/newbio232156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POPE J. H., ROWE W. P. DETECTION OF SPECIFIC ANTIGEN IN SV40-TRANSFORMED CELLS BY IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE. J Exp Med. 1964 Aug 1;120:121–128. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.2.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. C., Ephrussi B. Studies of Interspecific (Rat x Mouse) Somatic Hybrids. I. Isolation, Growth and Evolution of the Karyotype. Genetics. 1966 Nov;54(5):1095–1109. doi: 10.1093/genetics/54.5.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. C. Further studies on loss of T-antigen from somatic hybrids between mouse cells and SV40-transformed human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 May;66(1):79–86. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]