Abstract
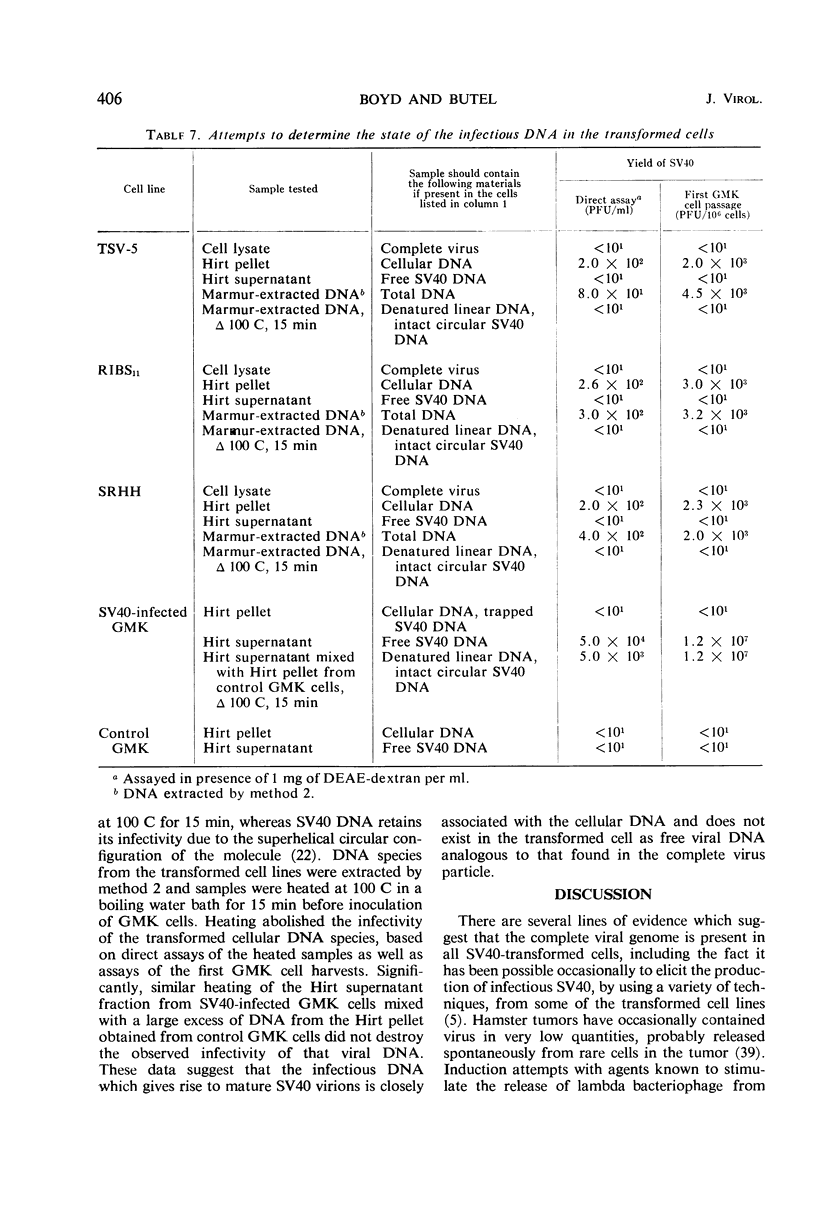
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) was extracted from virus-free simian virus 40 (SV40)-transformed hamster, mouse, and monkey cells and was inoculated into simian cells in the presence of diethylaminoethyl (DEAE)-dextran; infectious SV40 was recovered by using DNA from cell lines which fail to yield virus by the fusion technique as well as from cell lines which readily yield virus by fusion. The rescued virus was identified as SV40 by three methods: (i) neutralization of plaque formation by specific antiserum; (ii) induction of synthesis of viral-specific antigens detected by immunofluorescence; and (iii) presence of papovavirus particles seen by the electron microscope. Treatment of the transformed cell DNA with deoxyribonuclease or omission of the DEAE-dextran prevented the rescue of virus. Large amounts of transformed cell DNA were required (>10 μg/culture of 106 cells) to effect rescue of SV40 by passage through monkey cells. A linear response was obtained between the input of DNA with inocula between 10 and 45 μg of DNA/culture and the yield of SV40 recovered. Biological activity was demonstrable irregularly when the transformed cell DNA was assayed directly in the presence of DEAE-dextran. The DNA induced plaque formation in about 50% of the trials as well as the synthesis of SV40 tumor and viral antigens in rare simian cells. The infectious DNA appeared to be associated with cellular DNA. The infectivity was found in the pellet of precipitated DNA obtained by the Hirt technique and was inactivated by boiling for 15 min. These properties are characteristic of linear cellular DNA and not of free, circular SV40 DNA.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASHKENAZI A., MELNICK J. L. Tumorigencity of simian papovavirus SV40 and of virus-transformed cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1963 Jun;30:1227–1265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbanti-Brodano G., Swetly P., Koprowski H. Superinfection of simian virus 40-transformed permissive cells with simian virus 40. J Virol. 1970 Nov;6(5):644–651. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.5.644-651.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black P. H. The oncogenic DNA viruses: a review of in vitro transformation studies. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1968;22:391–426. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.22.100168.002135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butel J. S., Richardson L. S., Melnick J. L. Variation in properties of SV40-transformed simian cell lines detected by superinfection with SV40 and human adenoviruses. Virology. 1971 Dec;46(3):844–855. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90085-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butel J. S., Tevethia S. S., Melnick J. L. Oncogenicity and cell transformation by papovavirus SV40: the role of the viral genome. Adv Cancer Res. 1972;15:1–55. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60371-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butel J. S., Tevethia S. S., Nachtigal M. Malignant transformation in vitro by "non-oncogenic" variants of defective SV40 (PARA). J Immunol. 1971 Apr;106(4):969–974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassingena R., Tournier P. Mise en évidence d'un "répresseur" spéfique dans des cellules d'espèces différentes transformées par le virus SV 40. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1968 Dec 16;267(25):2251–2254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubbs D. R., Kit S., De Torres R. A., Anken M. Virogenic properties of bromodeoxyuridine-sensitive and bromodeoxyuridine-resistant simian virus 40-transformed mouse kidney cells. J Virol. 1967 Oct;1(5):968–979. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.5.968-979.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubbs D. R., Kit S. Isolation of defective lysogens from Simian virus 40-transformed mouse kidney cultures. J Virol. 1968 Nov;2(11):1272–1282. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.11.1272-1282.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell cultures. Science. 1959 Aug 21;130(3373):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3373.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelb L. D., Kohne D. E., Martin M. A. Quantitation of Simian virus 40 sequences in African green monkey, mouse and virus-transformed cell genomes. J Mol Biol. 1971 Apr 14;57(1):129–145. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90123-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber P. Studies on the transfer of subviral infectivity from SV40-induced hamster tumor cells to indicator cells. Virology. 1966 Apr;28(4):501–509. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90234-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham B. J., Ludwig H., Bronson D. L., Benyesh-Melnick M., Biswal N. Physicochemical properties of the DNA of herpes viruses. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 18;259(1):13–23. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90469-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS H., WATKINS J. F. HYBRID CELLS DERIVED FROM MOUSE AND MAN: ARTIFICIAL HETEROKARYONS OF MAMMALIAN CELLS FROM DIFFERENT SPECIES. Nature. 1965 Feb 13;205:640–646. doi: 10.1038/205640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOPPS H. E., BERNHEIM B. C., NISALAK A., TJIO J. H., SMADEL J. E. BIOLOGIC CHARACTERISTICS OF A CONTINUOUS KIDNEY CELL LINE DERIVED FROM THE AFRICAN GREEN MONKEY. J Immunol. 1963 Sep;91:416–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENSEN F. C., GIRARDI A. J., GILDEN R. V., KOPROWSKI H. INFECTION OF HUMAN AND SIMIAN TISSUE CULTURES WITH ROUS SARCOMA VIRUS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jul;52:53–59. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen F. C., Koprowski H. Absence of repressor in SV40-transformed cells. Virology. 1969 Apr;37(4):687–690. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90290-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KHERA K. S., ASHKENAZI A., RAPP F., MELNICK J. L. IMMUNITY IN HAMSTERS TO CELLS TRANSFORMED IN VITRO AND IN VIVO BY SV40. TESTS FOR ANTIGENIC RELATIONSHIP AMONG THE PAPOVAVIRUSES. J Immunol. 1963 Nov;91:604–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kit S., Brown M. Rescue of Simian Virus 40 from Cell Lines Transformed at High and at Low Input Multiplicities by Unirradiated or Ultraviolet-irradiated Virus. J Virol. 1969 Sep;4(3):226–230. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.3.226-230.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kit S., De Torres R. A., Dubbs D. R., Salvi M. L. Induction of cellular deoxyribonuleic acid synthesis by simian virus 40. J Virol. 1967 Aug;1(4):738–746. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.4.738-746.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kit S., Dubbs D. R., Somers K. Strategy of simian virus 40. In: strategy of the viral genome. Ciba Found Symp. 1971:229–265. doi: 10.1002/9780470719824.ch14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kit S., Kurimura T., Dubbs D. R. Transplantable mouse tumor line induced by injection of SV40-transformed mouse kidney cells. Int J Cancer. 1969 Jul 15;4(4):384–392. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910040403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kit S., Kurimura T., Salvi M. L., Dubbs D. R. Activation of infectious SV40 synthesis in transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1239–1246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koprowski H., Jensen F. C., Steplewski Z. Activation of production of infectious tumor virus SV40 in heterokaryon cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jul;58(1):127–133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. S., Oxman M. N., Henry P. H., Levin M. J., Diamandopoulos G. T., Enders J. F. Virus-specific deoxyribonucleic acid in simian virus 40-exposed hamster cells: correlation with S and T antigens. J Virol. 1970 Aug;6(2):199–207. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.2.199-207.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MELNICK J. L., KHERA K. S., RAPP F. PAPOVAVIRUS SV40: FAILURE TO ISOLATE INFECTIOUS VIRUS FROM TRANSFORMED HAMSTER CELLS SYNTHESIZING SV40-INDUCED ANTIGENS. Virology. 1964 Jul;23:430–432. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90267-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachtigal M., Melnick J. L., Butel J. S. Chromosomal changes in Syrian hamster cells transformed by simian virus 40 (SV40) and variants of defective SV40 (PARA). J Natl Cancer Inst. 1971 Jul;47(1):35–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neff J. M., Enders J. F. Poliovirus replication and cytopathogenicity in monolayer hamster cell cultures fused with beta propiolactone-inactivated Sendai virus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Jan;127(1):260–267. doi: 10.3181/00379727-127-32668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano J. S., McCutchan J. H., Vaheri A. Factors influencing the enhancement of the infectivity of poliovirus ribonucleic acid by diethylaminoethyl-dextran. J Virol. 1967 Oct;1(5):891–897. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.5.891-897.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPP F., BUTEL J. S., MELNICK J. L. VIRUS-INDUCED INTRANUCLEAR ANTIGEN IN CELLS TRANSFORMED BY PAPOVAVIRUS SV40. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Aug-Sep;116:1131–1135. doi: 10.3181/00379727-116-29472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp F., Pauluzzi S., Butel J. S. Variation in properties of plaque progeny of PARA (defective simian papovavirus 40)-adenovirus 7. J Virol. 1969 Nov;4(5):626–631. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.5.626-631.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp F., Trulock S. C. Susceptibility to superinfection of simian cells transformed by SV 40. Virology. 1970 Apr;40(4):961–970. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90142-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothschild H., Black P. H. Analysis of SV40-induced transformation of hamster kidney tissue in vitro. VII. Induction of SV40 virus from transformed hamster cell clones by various agents. Virology. 1970 Sep;42(1):251–256. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90264-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SABIN A. B., KOCH M. A. BEHAVIOR OF NONINFECTIOUS SV 40 VIRAL GENOME IN HAMSTER TUMOR CELLS: INDUCTION OF SYNTHESIS OF INFECTIOUS VIRUS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Sep;50:407–417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.3.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook J., Westphal H., Srinivasan P. R., Dulbecco R. The integrated state of viral DNA in SV40-transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1288–1295. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiroki K., Shimojo H. Transformation of green monkey kidney cells by SV40 genome: the establishment of transformed cell lines and the replication of human adenoviruses and SV40 in transformed cells. Virology. 1971 Jul;45(1):163–171. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90123-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Signer E. R. Lysogeny: the integration problem. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1968;22:451–488. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.22.100168.002315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. S., Gelb L. D., Martin M. A. Detection and quantitation of simian virus 40 genetic material in abortively transformed BALB-3T3 clones (mice-diploid cells-virus equivalents). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):152–156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki E., Shimojo H. A temperature-sensitive mutant of adenovirus 31, defective in viral deoxyribonucleic acid replication. Virology. 1971 Feb;43(2):488–494. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90320-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swetly P., Brodano G. B., Knowles B., Koprowski H. Response of simian virus 40-transformed cell lines and cell hybrids to superinfection with simian virus 40 and its deoxyribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1969 Oct;4(4):348–355. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.4.348-355.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TODARO G. J., GREEN H. SUCCESSIVE TRANSFORMATIONS OF AN ESTABLISHED CELL LINE BY POLYOMA VIRUS AND SV40. Science. 1965 Jan 29;147(3657):513–514. doi: 10.1126/science.147.3657.513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tournier P., Cassingena R., Wicker R., Coppey J., Suarez H. Etude du mécanisme de l'induction chez des cellules de hamster syrien transformées par le virus SV40. I. Propriétés d'une lignée cellulaire clonale. Int J Cancer. 1967 Mar 15;2(2):117–132. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910020207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J. F., Dulbecco R. Production of SV40 virus in heterokaryons of transformed and susceptible cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Oct;58(4):1396–1403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.4.1396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. C., Ephrussi B., Scaletta L. J. Loss of T-antigen from somatic hybrids between mouse cells and SV40-transformed human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Apr;59(4):1132–1135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.4.1132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. C. Further studies on loss of T-antigen from somatic hybrids between mouse cells and SV40-transformed human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 May;66(1):79–86. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westphal H., Dulbecco R. Viral DNA in polyoma- and SV40-transformed cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Apr;59(4):1158–1165. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.4.1158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


