Abstract
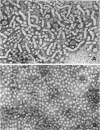
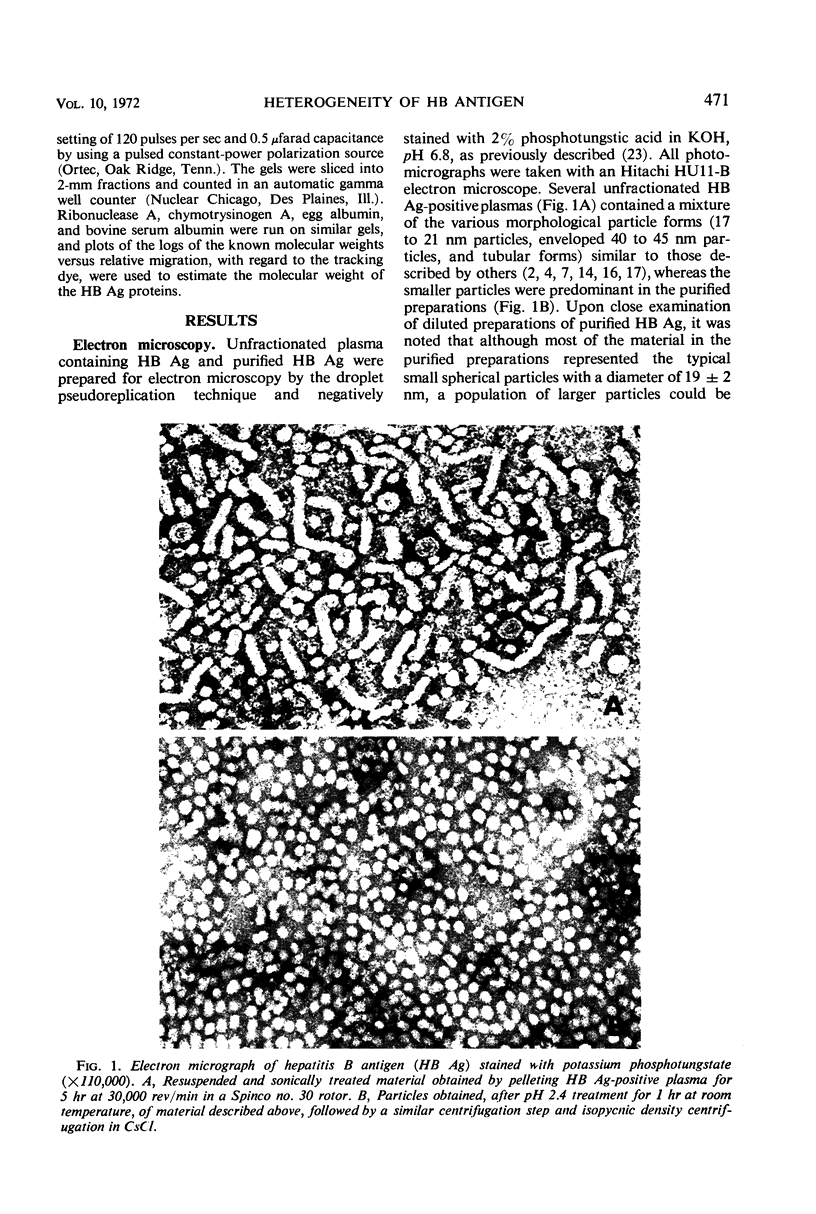
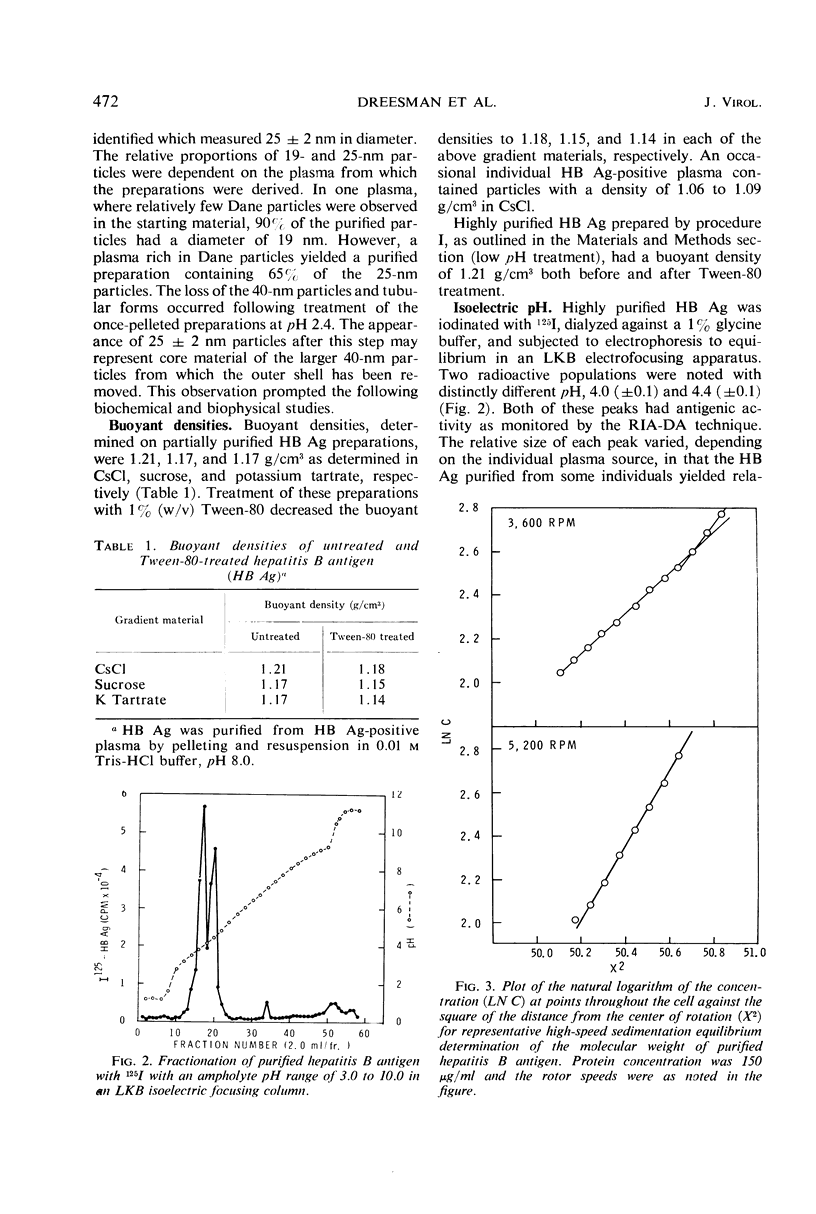
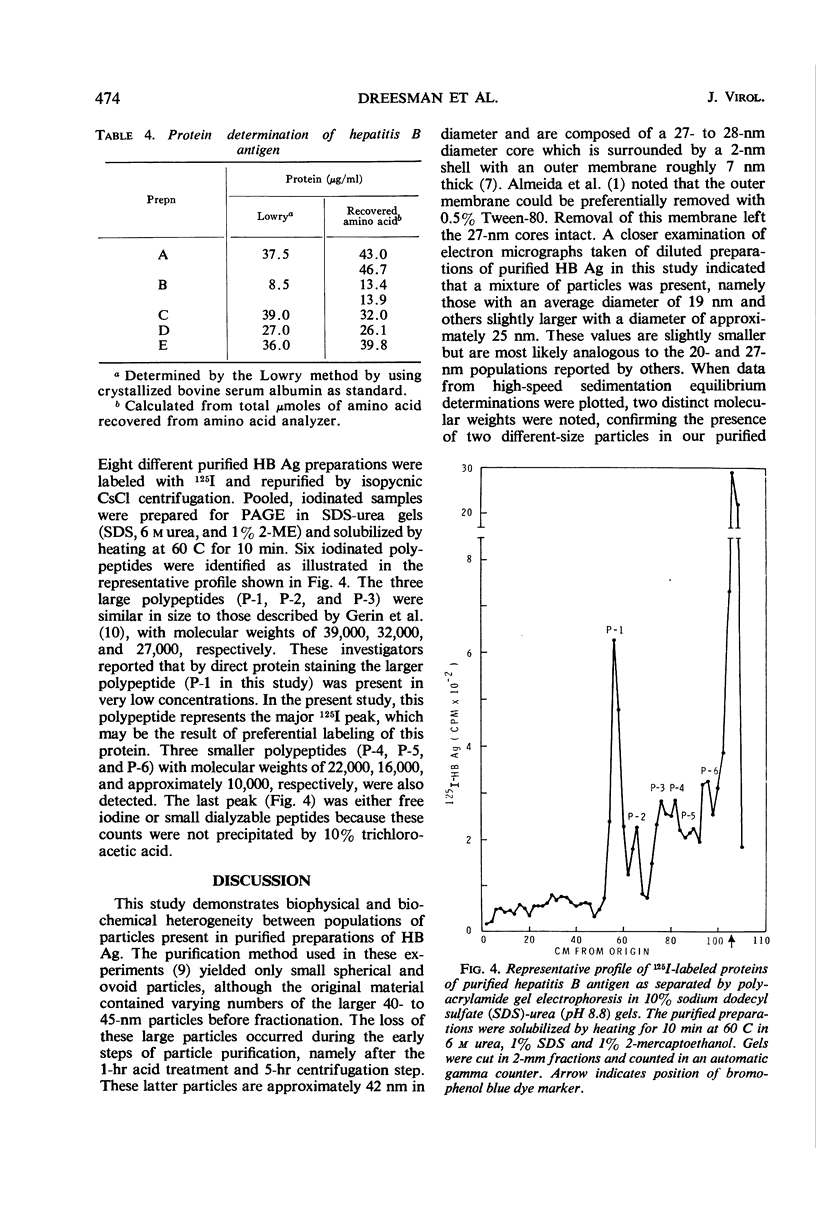
Hepatitis B antigen of the D (a+, d+, y−) subtype was purified from plasma of apparently healthy persons and from hepatitis patients. The original samples contained 20- and 42-nm particles and tubular forms (20-nm diameter). Ultracentrifugation during the purification procedure yielded pellets which were then treated at pH 2.4. Both the large, 42-nm Dane particles and the tubular forms were lost during the acid treatment of the pelleted particles, yielding a preparation containing a mixture of particles approximately 20 and 25 nm in diameter. This difference in size was substantiated in that two distinct molecular weights were calculated from high-speed equilibrium data, 3.6 × 106 and 4.5 × 106. Further heterogeneity was observed in that hepatitis B antigenic activity was present in purified particles with an isoelectric pH of 4.0 and also in those with a pH of 4.4. No significant differences were observed in the gross amino acid composition of purified antigen obtained from plasma of three different persons. 125I-labeled, purified antigen was found to contain six distinct polypeptides with molecular weights ranging from 10,000 to 39,000.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almeida J. D., Rubenstein D., Stott E. J. New antigen-antibody system in Australia-antigen-positive hepatitis. Lancet. 1971 Dec 4;2(7736):1225–1227. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90543-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almeida J. D., Waterson A. P. The morphology of virus-antibody interaction. Adv Virus Res. 1969;15:307–338. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3527(08)60878-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLUMBERG B. S. POLYMORPHISMS OF THE SERUM PROTEINS AND THE DEVELOPMENT OF ISO-PRECIPITINS IN TRANSFUSED PATIENTS. Bull N Y Acad Med. 1964 May;40:377–386. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer M. E., Blumberg B. S., Werner B. Particles associated with Australia antigen in the sera of patients with leukaemia, Down's Syndrome and hepatitis. Nature. 1968 Jun 15;218(5146):1057–1059. doi: 10.1038/2181057a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond H. E., Hall W. T. Separation and purification of hepatitis-associated antigen into morphologic types by zonal ultracentrifugation. J Infect Dis. 1972 Mar;125(3):263–268. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.3.263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dane D. S., Cameron C. H., Briggs M. Virus-like particles in serum of patients with Australia-antigen-associated hepatitis. Lancet. 1970 Apr 4;1(7649):695–698. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)90926-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreesman G. R., Hollinger F. B., McCombs R. M., Melnick J. L. Production of potent anti-Australia antigen sera of high specificity and sensitivity in goats. Infect Immun. 1972 Feb;5(2):213–221. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.2.213-221.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerin J. L., Holland P. V., Purcell R. H. Australia antigen: large-scale purification from human serum and biochemical studies of its proteins. J Virol. 1971 May;7(5):569–576. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.5.569-576.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H. B., Gocke D. J. An analysis of antibody response to Australia antigen in man. J Infect Dis. 1971 Apr;123(4):356–364. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.4.356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gust I. D., Cross G., Kaldor J., Ferris A. A. Virus-like particles in Australia-antigen-associated hepatitis. Lancet. 1970 May 2;1(7653):953–953. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)91082-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollinger F. B., Vorndam V., Dreesman G. R. Assay of Australia antigen and antibody employing double-antibody and solid-phase radioimmunoassay techniques and comparison with the passive hemagglutination methods. J Immunol. 1971 Oct;107(4):1099–1111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenson A. B., McCombs R. M., Sakurada N., Melnick J. L. Organ cultures inoculated with serum from a hepatitis patient with Au antigenemia. Exp Mol Pathol. 1970 Oct;13(2):217–230. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(70)90007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jokelainen P. T., Krohn K., Prince A. M., Finlayson N. D. Electrn microscopic observations on virus-like particles associated with SH antigen. J Virol. 1970 Nov;6(5):685–689. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.5.685-689.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim C. Y., Tilles J. G. Immunologic and electrophoretic heterogeneity of hepatitis-associated antigen. J Infect Dis. 1971 Jun;123(6):618–628. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.6.618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Bouvier G. L., McCollum R. W. Australia (hepatitis-associated) antigen: physicochemical and immunological characteristics. Adv Virus Res. 1970;16:357–396. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3527(08)60027-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Bouvier G. L. The heterogeneity of Australia antigen. J Infect Dis. 1971 Jun;123(6):671–675. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.6.671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levene C., Blumberg B. S. Additional specificities of Australia antigen and the possible identification of hepatitis carriers. Nature. 1969 Jan 11;221(5176):195–196. doi: 10.1038/221195a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCombs R. M., Melnick M. B., Brunschwig J. P. Biophysical studies of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):803–812. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.803-812.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raunio V. K., London W. T., Sutnick A. I., Millman I., Blumberg B. S. Specificities of human antibodies to Australia antigen. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Jun;134(2):548–557. doi: 10.3181/00379727-134-34833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sukeno N., Shirachi R., Yamaguchi J., Ishida N. Reduction and reoxidation of Australia antigen: loss and reconstitution of particle structure and antigenicity. J Virol. 1972 Jan;9(1):182–183. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.1.182-183.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers D. F., Maizel J. V., Jr, Darnell J. E., Jr Evidence for virus-specific noncapsid proteins in poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Aug;54(2):505–513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.2.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YPHANTIS D. A. EQUILIBRIUM ULTRACENTRIFUGATION OF DILUTE SOLUTIONS. Biochemistry. 1964 Mar;3:297–317. doi: 10.1021/bi00891a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckerman A. J., Baines P. M., Almeida J. D. Australia antigen as a marker of propagation of the serum hepatitis virus in liver cultures. Nature. 1972 Mar 10;236(5341):78–81. doi: 10.1038/236078a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]