Abstract
A combination of autozygosity mapping and exome sequencing identified a null mutation in SLC24A4 in a family with hypomineralized amelogenesis imperfect a (AI), a condition in which tooth enamel formation fails. SLC24A4 encodes a calcium transporter upregulated in ameloblasts during the maturation stage of amelogenesis. Screening of further AI families identified a missense mutation in the ion-binding site of SLC24A4 expected to severely diminish or abolish the ion transport function of the protein. Furthermore, examination of previously generated Slc24a4 null mice identified a severe defect in tooth enamel that reflects impaired amelogenesis. These findings support a key role for SLC24A4 in calcium transport during enamel formation.
Main Text
The formation of dental enamel (amelogenesis) results in the hardest, most mineralized tissue in the body. Amelogenesis is completed before tooth eruption and thereafter it has no capacity for cellular repair. Mature enamel consists almost exclusively of highly organized, calcium hydroxyapatite (Ca10[PO4]6[OH]2) crystals, which form in a discrete extracellular compartment within the developing tooth.1 Ameloblasts, the enamel forming cells within the enamel organ, secrete an organic matrix and regulate the mineralization of enamel via several mechanisms that include the secretion of matrix proteins, which act as potential modulators of crystal growth, temporospatial control of protease secretion to sequentially degrade matrix proteins, removal of degraded protein from the enamel matrix, and control of mineral ion transport to accommodate secondary crystal growth during the maturation stage of enamel development.2
Failure of amelogenesis presents clinically as amelogenesis imperfecta (AI [MIM %104530]), a genetically and phenotypically heterogeneous group of inherited conditions with a prevalence ranging from 1/700 to 1/14,000.3,4 AI may be classified as either hypoplastic AI, in which the enamel volume is diminished, or hypomineralized AI, characterized by variable degrees of incomplete mineralization of the enamel matrix, typically with a near-normal enamel matrix volume prior to posteruptive changes and premature failure. The negative psychological impact of AI on affected individuals and their families can be profound and the dental treatment required is challenging.5
Mutations in genes encoding enamel matrix proteins6,7 and mutations in genes encoding proteases that digest enamel matrix proteins8,9 have been identified as causes of AI. However, little is known about the function of genes identified in recent genetic studies.10–17 Surprisingly, considering the essential role for calcium transport across the enamel organ in amelogenesis,18 to date no known calcium transport proteins have been implicated in the pathogenesis of AI.
We identified a consanguineous family (AI-112) from Pakistan segregating autosomal-recessive hypomineralized AI in the absence of other health problems (Figure 1; Figure 2A). The study was performed according to the principles of the declaration of Helsinki with ethical approval and family participation following informed consent.
Figure 1.
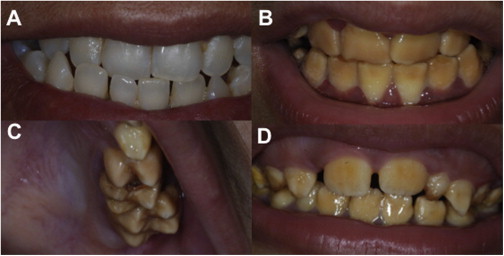
Clinical Dental Phenotypes Due to SLC24A Mutations
(A–C) Family AI-112 from Pakistan. The heterozygous (carrier) (III.2 in Figure 2) has teeth with a normal appearance (A) that contrasts with the yellow-brown discoloration and increased opacity of the enamel observed in her niece with erupted permanent teeth (B) (IV.5 in Figure 2). The enamel volume is within normal limits in all teeth with normal crown morphology and cusp patterns evident in the teeth illustrated (C) (IV.6), although affected teeth are susceptible to premature enamel loss.
(D) Family AI-131 from Pakistan. The appearances of the affected teeth are similar to those for AI-112 as illustrated in individual IV.4 in Figure 2 with posteruptive changes leading to premature enamel loss.
Figure 2.
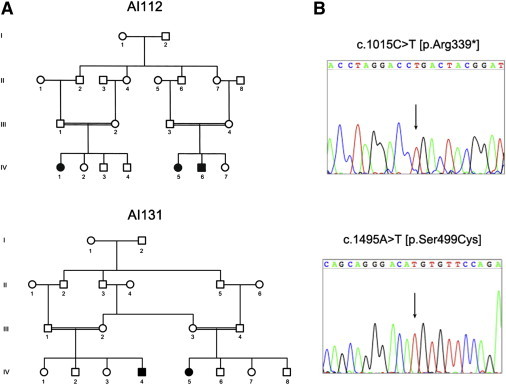
Family Pedigrees and SLC24A4 Mutations
(A) Pedigrees of families AI-112 and AI-131.
(B) Representative electropherograms of SLC24A4 mutations discovered in family AI-112 and AI-131.
Individuals IV:1, IV:5, and IV:6 were analyzed using Affymetrix 6.0 SNP microarrays and common regions of homozygosity identified using AutoSNPa.19 Five regions of homozygosity spanning approximately 16 Mb were identified (see Table S1 available online), none of which overlapped with previously published AI loci. We therefore performed exome sequencing on DNA from individual IV:5 using a SureSelect All Exon V4 reagent (Agilent Technologies, Edinburgh UK). Three micrograms of genomic DNA were processed according to the Agilent SureSelect Library Prep protocol. Sequencing was performed using a 150 bp paired-end protocol on an Illumina MiSeq sequencer. The resulting sequence reads were aligned to the human reference sequence (GRCh37) using Novoalign software (Novocraft Technologies, Selangor, Malaysia). This alignment was processed in the SAM/BAM format20 using Picard and The Genome Analysis Toolkit (GATK)21,22 java programs in order to correct alignments around indel sites and mark potential PCR duplicates. Following postprocessing and duplicate removal a mean depth of 25.55 reads was achieved for targeted exons in our homozygous regions with 94.5% of these bases covered by at least 5 reads.
Indel and single nucleotide variants within the candidate regions were called in the VCF format using the Unified Genotyper function of GATK. A total of 1,163 variants passing standard GATK filters were identified in these regions (Table S1). Using the dbSNP135 database at NCBI we filtered variants present in dbSNP129 or with a minor allele frequency equal to or greater than 1%. We also removed variants present in ten non-AI in-house exome data sets from individuals also originating from Pakistan. This left 102 variants with only 3 variants predicted to have an effect on gene function (i.e., nonsynonymous variants, exonic insertions or deletions, or variants at splice consensus sites). Of these three variants a missense (NM_001261835.1:c.1954G>A [p.Gly652Arg]) in BZRAP1 (MIM 610764) was called as heterozygous and therefore not considered a candidate for a disease-causing mutation for this recessively inherited condition. We were therefore left with two rare homozygous variants: one missense change (NM_016186.2:c.1260T>G [p.Phe420Leu]) in SERPINA10 (MIM 605271) and a nonsense change (NM_153646.3:c.1015C>T [p.Arg339∗]) in SLC24A4 (MIM 609840). While the missense variant in SERPINA10 was predicted as “possibly damaging” by Polyphen-223, with a score of 0.770 under the HumVar model, truncating mutations in SERPINA10 have been previously associated with susceptibility to venous thrombosis with an incidence of between 3.0% and 4.4% in cohorts of individuals with venous thromboembolic disease.24,25 Moreover, one member of such a cohort was reported to have a homozygous nonsense variant in SERPINA10 with no additional pathologies.25 We therefore discounted this variant as a potential pathogenic factor for AI in this family.
The remaining variant introduces a premature termination codon in coding exon 11 of 17 of SLC24A4 and would therefore be expected to lead to nonsense-mediated decay (NMD). Even in the absence of NMD, the mutant protein would miss the final 284 residues of the 622 amino acid wild-type protein, lack one of the sodium/calcium exchanger domains (PFAM Family Na_Ca_ex [PF01699]) critical to the ion transport function of the protein, and almost certainly be nonfunctional. We confirmed segregation of this mutation in the AI-112 family and absence in 170 ethnically matched controls by Sanger sequencing. Examination of exome alignments from 70 Gujarati Indian samples from the 1000 Genomes Project26 also confirmed absence of this variant. In addition, this variant was confirmed to be absent in existing 1000 Genomes Project variant call files.
We investigated a panel of 37 further individuals with AI from diverse ethnic backgrounds by Sanger sequencing the coding regions and intron-exon boundaries of SLC24A4 (primers shown in Table S2). Sequencing identified a homozygous missense variant in a family from Pakistan (AI-131, Figure 2A) converting a serine residue to cysteine at position 499 of the protein (c.1495A>T [p.Ser499Cys], Figure 3). Substitution of this residue, which shows a high degree of evolutionarily conservation in SLC24A4 orthologs (Figure 4), was predicted as “probably damaging” by Polyphen-2 with a score of 0.997 under the HumVar model. We also confirmed absence of this mutation in 170 ethnically matched control samples and in 1000 genomes data sets as above.
Figure 3.
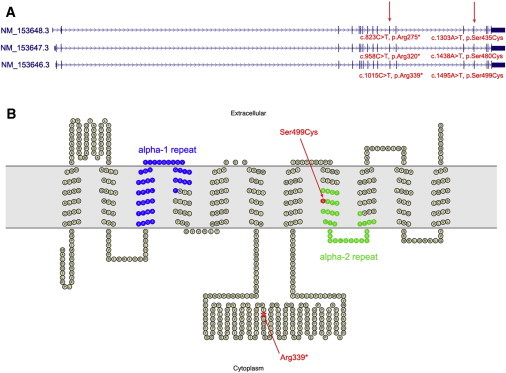
Structure of SLC24A4 and the Encoded Protein
(A) The three human RefSeq SLC24A4 transcripts are shown with the position of mutations discovered in AI-112 and AI-131 marked.
(B) Predicted topology of full-length SLC24A4 (corresponding to transcript NM_153646.3) as generated by the TMHMM38 program and drawn using TOPO2. Altered residues corresponding to residues affected by SLC24A4 mutations in family AI-112 and AI-131 are shown in red. The conserved alpha repeats which form the ion binding pockets of the transporter are shown in blue and green. The extracellular membrane is shown in gray.
Figure 4.
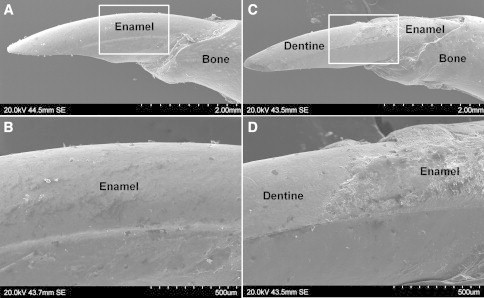
Scanning Electron Microscopy of Mandibular Incisors from Wild-Type and Slc24a4 Knockout Mice
(A) SEM shows the typical mouse incisor morphology of a wild-type mouse where the labial surface of the tooth is completely covered with a smooth layer of enamel. The incisal tip shows the characteristic chisel-like biting edge characteristic of rodents.
(B) Higher magnification of the boxed area in (A) showing the smooth unbroken enamel surface.
(C) SEM of the incisor from a Slc24a4 knockout mouse. Enamel is only present near the cervical margin where the tooth erupts from the mandibular bone. Enamel is missing from the remainder of the tooth (reflecting premature failure) and the underlying dentine surface is exposed. The incisal tip, comprising only softer dentine, is blunted.
(D) Higher magnification of the boxed area in (C) showing the affected enamel to be irregular and poorly mineralized compared to wild-type enamel.
SLC24A4 encodes a member of the potassium-dependent sodium/calcium exchanger family27 (SLC24A) containing five members. SLC24A6, while originally thought to be part of this family, was reclassified as belonging to a unique branch of the calcium/cation antiporter superfamily on the basis of phylogenetic28 and substrate specificity studies.29 The potassium-dependent sodium/calcium exchangers share significant homology with the three members of the potassium-independent sodium/calcium exchanger family (SLC8A). These proteins share a common topology with eleven predicted transmembrane helices including two conserved clusters of five transmembrane helices connected by a divergent cytoplasmic loop (Figure 3B). These transmembrane regions comprise the sodium/calcium exchanger domains and each contains a highly conserved region of 30–40 amino acids referred to as the alpha-1 and alpha-2 repeats respectively. The alpha-1 and alpha-2 repeats associate to form the ion-binding pockets of these transporters.30 Ser499 lies in the alpha-2 repeat region of SLC24A4 and is highly conserved in SLC24A4 orthologs (Figure S1). To further investigate the evolutionary conservation of this residue, we retrieved the protein sequences for members of the potassium-dependent sodium/calcium exchanger and potassium-independent sodium/calcium exchanger families from Homologene and performed a multiple sequence alignment with ClustalX.31 This analysis showed the Ser499 residue to be conserved in all the sodium/calcium exchangers identified (Figure S2). Furthermore, scanning mutagenesis experiments performed on SLC8A132 (MIM 182305) and SLC24A233,34 (MIM 609838) have shown that substitution of this same residue results in a dramatic decrease in transporter activity compared to wild-type. Indeed, the experiments performed on SLC24A2 showed that substitution with cysteine, the same substitution observed in AI-131, reduced the transport activity to less than 20% of wild-type33 or completely abolished transport activity34 depending on the cell type used in overexpression experiments. We therefore conclude that the Ser499Cys substitution observed in family AI-131 is likely to lead to severely impaired transport function of the encoded protein.
The identification of two mutations expected to lead to either loss or severe impairment of SLC24A4 function by exome sequencing of one family and Sanger sequencing of a further 37 AI individuals of diverse ethnic origins suggests that variants in SLC24A4 are an infrequent cause of AI. However, because both variants were identified in families of Pakistani origin from a total of 15 Pakistani families screened, it is possible that variants in SLC24A4 are a more frequent cause of AI in this population.
SLC24A4 has been shown to control response termination kinetics and adaptation of the olfactory response in mice through the study of Slc24a4 knockout mice,35 but teeth of these animals had not been previously examined. Samples from two 6-month-old Slc24a4−/− mice were available to study alongside two samples from wild-type mice born within 11 days of the knockout animals examined. Examination of mouse incisors by scanning electron microscopy identified gross enamel defects in the Slc24a4−/− samples compared to wild-type samples indicative of failed enamel mineralization (Figure 4). Neither of the families identified with mutations in SLC24A4 have been tested for deficits in olfactory response.
A recent transcriptome study of developing rat enamel has demonstrated that Slc24a4 mRNA is expressed in the enamel organ during amelogenesis where it is strongly upregulated during the maturation stage.36 SLC24A4 localizes to the apical ends of ameloblasts37 where it is well situated to mediate calcium transport between the ameloblasts and the mineralizing enamel in order to facilitate crystal growth. The observation of SLC24A4 mutations in individuals with AI together with the identification of severe enamel defects in Slc24a4−/− mice provide further evidence that SLC24A4 is a key component of calcium transport during enamel formation. Further characterization of Slc24a4−/− mice will provide further insight into mechanisms of calcium transport during amelogenesis.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the families for participating in this study. This work was supported by grants from The Wellcome Trust (to A.J.M., H.J., Y.R., and C.F.I. grant # 082448 and S.J.B. grant #093113), the Sir Jules Thorn Award for Biomedical Research (to C.A.J. and C.F.I. grant #JTA/09) and National Institute of Health (to H.Z. grant # DC007395).
Supplemental Data
Web Resources
The URLs for data presented herein are as follows:
1000 Genomes, http://browser.1000genomes.org/index.html
AutoSNPa, http://dna.leeds.ac.uk/autosnpa/
Homologene, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/homologene
Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.omim.org
PolyPhen-2, http://genetics.bwh.harvard.edu/pph2/
TOPO2, Transmembrane protein display software, http://www.sacs.ucsf.edu/TOPO2/
UCSC Genome Browser, http://genome.ucsc.edu/
References
- 1.Simmer J.P., Fincham A.G. Molecular mechanisms of dental enamel formation. Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med. 1995;6:84–108. doi: 10.1177/10454411950060020701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Smith C.E. Cellular and chemical events during enamel maturation. Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med. 1998;9:128–161. doi: 10.1177/10454411980090020101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Witkop C.J., Sauk J.J. Heritable defects of enamel. In: Prescott G., Stewart R., editors. Oral Facial Genetics. CV Mosby Company; St Louis: 1976. pp. 151–226. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bäckman B., Holm A.K. Amelogenesis imperfecta: prevalence and incidence in a northern Swedish county. Community Dent. Oral Epidemiol. 1986;14:43–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0528.1986.tb01493.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Coffield K.D., Phillips C., Brady M., Roberts M.W., Strauss R.P., Wright J.T. The psychosocial impact of developmental dental defects in people with hereditary amelogenesis imperfecta. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2005;136:620–630. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.2005.0233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Lagerström M., Dahl N., Nakahori Y., Nakagome Y., Bäckman B., Landegren U., Pettersson U. A deletion in the amelogenin gene (AMG) causes X-linked amelogenesis imperfecta (AIH1) Genomics. 1991;10:971–975. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90187-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Rajpar M.H., Harley K., Laing C., Davies R.M., Dixon M.J. Mutation of the gene encoding the enamel-specific protein, enamelin, causes autosomal-dominant amelogenesis imperfecta. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2001;10:1673–1677. doi: 10.1093/hmg/10.16.1673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hart P.S., Hart T.C., Michalec M.D., Ryu O.H., Simmons D., Hong S., Wright J.T. Mutation in kallikrein 4 causes autosomal recessive hypomaturation amelogenesis imperfecta. J. Med. Genet. 2004;41:545–549. doi: 10.1136/jmg.2003.017657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kim J.W., Simmer J.P., Hart T.C., Hart P.S., Ramaswami M.D., Bartlett J.D., Hu J.C. MMP-20 mutation in autosomal recessive pigmented hypomaturation amelogenesis imperfecta. J. Med. Genet. 2005;42:271–275. doi: 10.1136/jmg.2004.024505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.El-Sayed W., Parry D.A., Shore R.C., Ahmed M., Jafri H., Rashid Y., Al-Bahlani S., Al Harasi S., Kirkham J., Inglehearn C.F., Mighell A.J. Mutations in the beta propeller WDR72 cause autosomal-recessive hypomaturation amelogenesis imperfecta. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009;85:699–705. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2009.09.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.O’Sullivan J., Bitu C.C., Daly S.B., Urquhart J.E., Barron M.J., Bhaskar S.S., Martelli-Júnior H., dos Santos Neto P.E., Mansilla M.A., Murray J.C. Whole-Exome sequencing identifies FAM20A mutations as a cause of amelogenesis imperfecta and gingival hyperplasia syndrome. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2011;88:616–620. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.04.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kim J.W., Lee S.K., Lee Z.H., Park J.C., Lee K.E., Lee M.H., Park J.T., Seo B.M., Hu J.C., Simmer J.P. FAM83H mutations in families with autosomal-dominant hypocalcified amelogenesis imperfecta. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2008;82:489–494. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2007.09.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Parry D.A., Mighell A.J., El-Sayed W., Shore R.C., Jalili I.K., Dollfus H., Bloch-Zupan A., Carlos R., Carr I.M., Downey L.M. Mutations in CNNM4 cause Jalili syndrome, consisting of autosomal-recessive cone-rod dystrophy and amelogenesis imperfecta. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009;84:266–273. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2009.01.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Polok B., Escher P., Ambresin A., Chouery E., Bolay S., Meunier I., Nan F., Hamel C., Munier F.L., Thilo B. Mutations in CNNM4 cause recessive cone-rod dystrophy with amelogenesis imperfecta. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009;84:259–265. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2009.01.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Mory A., Dagan E., Illi B., Duquesnoy P., Mordechai S., Shahor I., Romani S., Hawash-Moustafa N., Mandel H., Valente E.M. A nonsense mutation in the human homolog of Drosophila rogdi causes Kohlschutter-Tonz syndrome. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012;90:708–714. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.03.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Schossig A., Wolf N.I., Fischer C., Fischer M., Stocker G., Pabinger S., Dander A., Steiner B., Tönz O., Kotzot D. Mutations in ROGDI Cause Kohlschütter-Tönz Syndrome. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012;90:701–707. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.02.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Parry D.A., Brookes S.J., Logan C.V., Poulter J.A., El-Sayed W., Al-Bahlani S., Al Harasi S., Sayed J., Raïf M., Shore R.C. Mutations in C4orf26, encoding a peptide with in vitro hydroxyapatite crystal nucleation and growth activity, cause amelogenesis imperfecta. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012;91:565–571. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.07.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hubbard M.J. Calcium transport across the dental enamel epithelium. Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med. 2000;11:437–466. doi: 10.1177/10454411000110040401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Carr I.M., Flintoff K.J., Taylor G.R., Markham A.F., Bonthron D.T. Interactive visual analysis of SNP data for rapid autozygosity mapping in consanguineous families. Hum. Mutat. 2006;27:1041–1046. doi: 10.1002/humu.20383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Li H., Handsaker B., Wysoker A., Fennell T., Ruan J., Homer N., Marth G., Abecasis G., Durbin R., 1000 Genome Project Data Processing Subgroup The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics. 2009;25:2078–2079. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.McKenna A., Hanna M., Banks E., Sivachenko A., Cibulskis K., Kernytsky A., Garimella K., Altshuler D., Gabriel S., Daly M., DePristo M.A. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: a MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010;20:1297–1303. doi: 10.1101/gr.107524.110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.DePristo M.A., Banks E., Poplin R., Garimella K.V., Maguire J.R., Hartl C., Philippakis A.A., del Angel G., Rivas M.A., Hanna M. A framework for variation discovery and genotyping using next-generation DNA sequencing data. Nat. Genet. 2011;43:491–498. doi: 10.1038/ng.806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Adzhubei I.A., Schmidt S., Peshkin L., Ramensky V.E., Gerasimova A., Bork P., Kondrashov A.S., Sunyaev S.R. A method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nat. Methods. 2010;7:248–249. doi: 10.1038/nmeth0410-248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Van de Water N., Tan T., Ashton F., O’Grady A., Day T., Browett P., Ockelford P., Harper P. Mutations within the protein Z-dependent protease inhibitor gene are associated with venous thromboembolic disease: a new form of thrombophilia. Br. J. Haematol. 2004;127:190–194. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2004.05189.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Corral J., González-Conejero R., Soria J.M., González-Porras J.R., Pérez-Ceballos E., Lecumberri R., Roldán V., Souto J.C., Miñano A., Hernández-Espinosa D. A nonsense polymorphism in the protein Z-dependent protease inhibitor increases the risk for venous thrombosis. Blood. 2006;108:177–183. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-08-3249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Abecasis G.R., Altshuler D., Auton A., Brooks L.D., Durbin R.M., Gibbs R.A., Hurles M.E., McVean G.A., 1000 Genomes Project Consortium A map of human genome variation from population-scale sequencing. Nature. 2010;467:1061–1073. doi: 10.1038/nature09534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Li X.F., Kraev A.S., Lytton J. Molecular cloning of a fourth member of the potassium-dependent sodium-calcium exchanger gene family, NCKX4. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:48410–48417. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M210011200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Cai X., Lytton J. The cation/Ca(2+) exchanger superfamily: phylogenetic analysis and structural implications. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2004;21:1692–1703. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msh177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Palty R., Ohana E., Hershfinkel M., Volokita M., Elgazar V., Beharier O., Silverman W.F., Argaman M., Sekler I. Lithium-calcium exchange is mediated by a distinct potassium-independent sodium-calcium exchanger. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:25234–25240. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M401229200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Iwamoto T., Uehara A., Imanaga I., Shigekawa M. The Na+/Ca2+ exchanger NCX1 has oppositely oriented reentrant loop domains that contain conserved aspartic acids whose mutation alters its apparent Ca2+ affinity. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:38571–38580. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M003788200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Larkin M.A., Blackshields G., Brown N.P., Chenna R., McGettigan P.A., McWilliam H., Valentin F., Wallace I.M., Wilm A., Lopez R. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics. 2007;23:2947–2948. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btm404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Nicoll D.A., Hryshko L.V., Matsuoka S., Frank J.S., Philipson K.D. Mutation of amino acid residues in the putative transmembrane segments of the cardiac sarcolemmal Na+-Ca2+ exchanger. J. Biol. Chem. 1996;271:13385–13391. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.23.13385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Winkfein R.J., Szerencsei R.T., Kinjo T.G., Kang K., Perizzolo M., Eisner L., Schnetkamp P.P. Scanning mutagenesis of the alpha repeats and of the transmembrane acidic residues of the human retinal cone Na/Ca-K exchanger. Biochemistry. 2003;42:543–552. doi: 10.1021/bi026982x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kang K.J., Kinjo T.G., Szerencsei R.T., Schnetkamp P.P. Residues contributing to the Ca2+ and K+ binding pocket of the NCKX2 Na+/Ca2+-K+ exchanger. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:6823–6833. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M407933200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Stephan A.B., Tobochnik S., Dibattista M., Wall C.M., Reisert J., Zhao H. The Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchanger NCKX4 governs termination and adaptation of the mammalian olfactory response. Nat. Neurosci. 2012;15:131–137. doi: 10.1038/nn.2943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Lacruz R.S., Smith C.E., Bringas P., Jr., Chen Y.B., Smith S.M., Snead M.L., Kurtz I., Hacia J.G., Hubbard M.J., Paine M.L. Identification of novel candidate genes involved in mineralization of dental enamel by genome-wide transcript profiling. J. Cell. Physiol. 2012;227:2264–2275. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Hu P., Lacruz R.S., Smith C.E., Smith S.M., Kurtz I., Paine M.L. Expression of the Sodium/Calcium/Potassium Exchanger, NCKX4, in Ameloblasts. Cells Tissues Organs. 2012;196:501–509. doi: 10.1159/000337493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Sonnhammer E.L., von Heijne G., Krogh A. A hidden Markov model for predicting transmembrane helices in protein sequences. Proc. Int. Conf. Intell. Syst. Mol. Biol. 1998;6:175–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


