Abstract
Quality management in clinical microbiology began in the 1960s. Both government and professional societies introduced programs for proficiency testing and laboratory inspection and accreditation. Many laboratory scientists and pathologists were independently active and creative in expanding efforts to monitor and improve practices. The initial emphasis was placed on intralaboratory process. Later, attention was shifted to physician ordering, specimen collection, reporting, and use of information. Quality management in the laboratory depends in large part on the monitoring of indicators that provide some evidence of how laboratory resources are being used and how the information benefits patient care. Continuous quality improvement should be introduced. This consists of a more thorough assessment of doing the right things versus the wrong things in terms of customer demand and satisfaction and studying the cumulative effect of error when responsibility is passed from one person to another. Prevention of error is accomplished more through effective training and continuing education than through surveillance. Also, this system will force more conscious attention to meeting the expectations of the many customers that must be satisfied by laboratory services, including patients, physicians, third-party payers, and managed-care organizations.
Full text
PDF






















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman V. P., Pritchard R. C. External quality assurance in microbiology. The programme of the Royal College of Pathologists of Australasia. Pathology. 1984 Jul;16(3):235–239. doi: 10.3109/00313028409068529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ackerman V. P., Pritchard R. C., Groot Obbink D. J., Bradbury R., Lee A. Reporting practices of microbiology laboratories. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Sep;33(9):830–835. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.9.830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ackerman V. P., Pritchard R. C., Obbink D. J., Bradbury R., Lee A. Consumer survey on microbiology reports. Lancet. 1979 Jan 27;1(8109):199–202. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90593-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albright R. E., Jr, Graham C. B., 3rd, Christenson R. H., Schell W. A., Bledsoe M. C., Emlet J. L., Mears T. P., Reller L. B., Schneider K. A. Issues in cerebrospinal fluid management. Acid-fast bacillus smear and culture. Am J Clin Pathol. 1991 Mar;95(3):418–423. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/95.3.418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson M. D., Bor D. H. Blood cultures. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Feb;106(2):246–253. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-106-2-246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arpi M., Bentzon M. W., Jensen J., Frederiksen W. Importance of blood volume cultured in the detection of bacteremia. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1989 Sep;8(9):838–842. doi: 10.1007/BF02185857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachner P. Quality assurance of the analytic process: pre- and postanalytic variation. Clin Lab Med. 1986 Dec;6(4):613–623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barr J. T. Quality laboratory service and cost containment: are the two incompatible. Am J Med Technol. 1979 Jul;45(7):613–614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry A. L., Bernsohn K. L. The role of quality control in the clinical bacteriology laboratory. Am J Med Technol. 1968 Apr;34(4):195–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry A. L., Feeney K. L. Quality control in bacteriology through media monitoring. Am J Med Technol. 1967 Sep-Oct;33(5):387–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett R. C. A plea for clinical relevance in medical microbiology. Am J Clin Pathol. 1974 Jun;61(6):867–872. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/61.6.867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett R. C. Bacteriologic surveillance of long-term-catheterized patients. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Feb;25(2):464–465. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.2.464-465.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett R. C. Cost containment in microbiology. Clin Lab Med. 1985 Dec;5(4):761–791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett R. C. Making optimum use of the microbiology laboratory. I. Use of the laboratory. JAMA. 1982 Feb 12;247(6):857–859. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett R. C. Making optimum use of the microbiology laboratory. II. Urine, respiratory, wound, and cervicovaginal exudate. JAMA. 1982 Mar 5;247(9):1336–1338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett R. C. Making optimum use of the microbiology laboratory. III. Aids of antimicrobial therapy. JAMA. 1982 Apr 2;247(13):1868–1871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett R. C., Quintiliani R. D., Nightingale C. H., Platt D., Crowe H., Grotz R., Orlando R., Strycharz C., Tetreault J., Lerer T. Effect of including recommendations for antimicrobial therapy in microbiology laboratory reports. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1991 Mar-Apr;14(2):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(91)90051-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett R. C., Rutz C. A., Konopacki N. Cost effectiveness of quality control in bacteriology. Am J Clin Pathol. 1982 Feb;77(2):184–190. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/77.2.184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett R. C., Rutz C. Processing control and cost in bacteriology. Am J Clin Pathol. 1980 Sep;74(3):287–296. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/74.3.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett R. C., Tetreault J., Evers J., Officer J., Derench J. Quality assurance of gram-stained direct smears. Am J Clin Pathol. 1979 Dec;72(6):984–989. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/72.6.984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett R. C., Treiber N. Clinical significance of mixed bacterial cultures of urine. Am J Clin Pathol. 1984 Sep;82(3):319–322. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/82.3.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
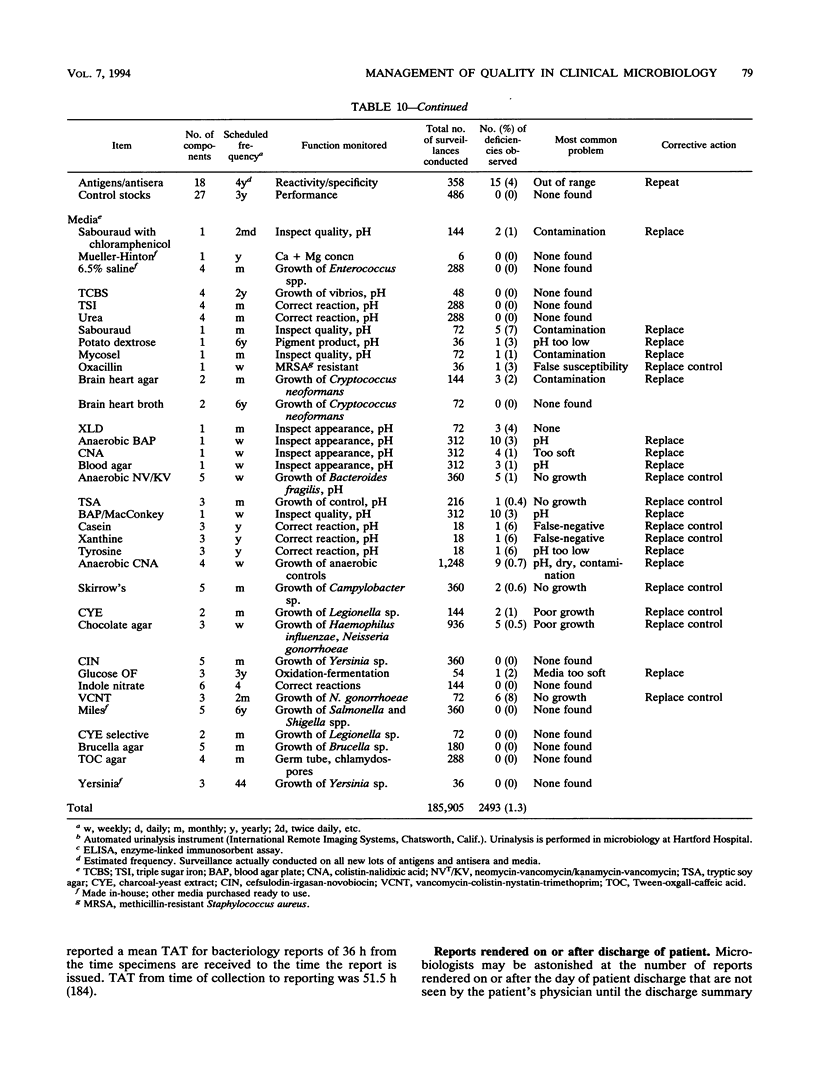
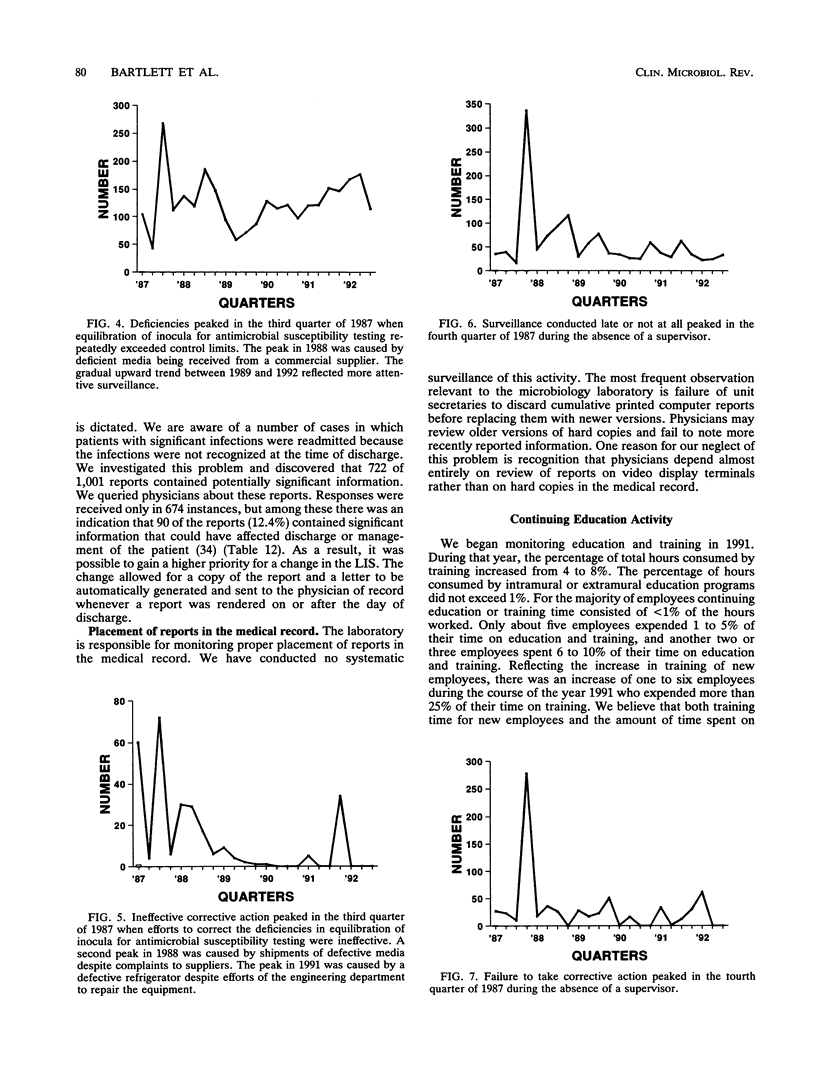
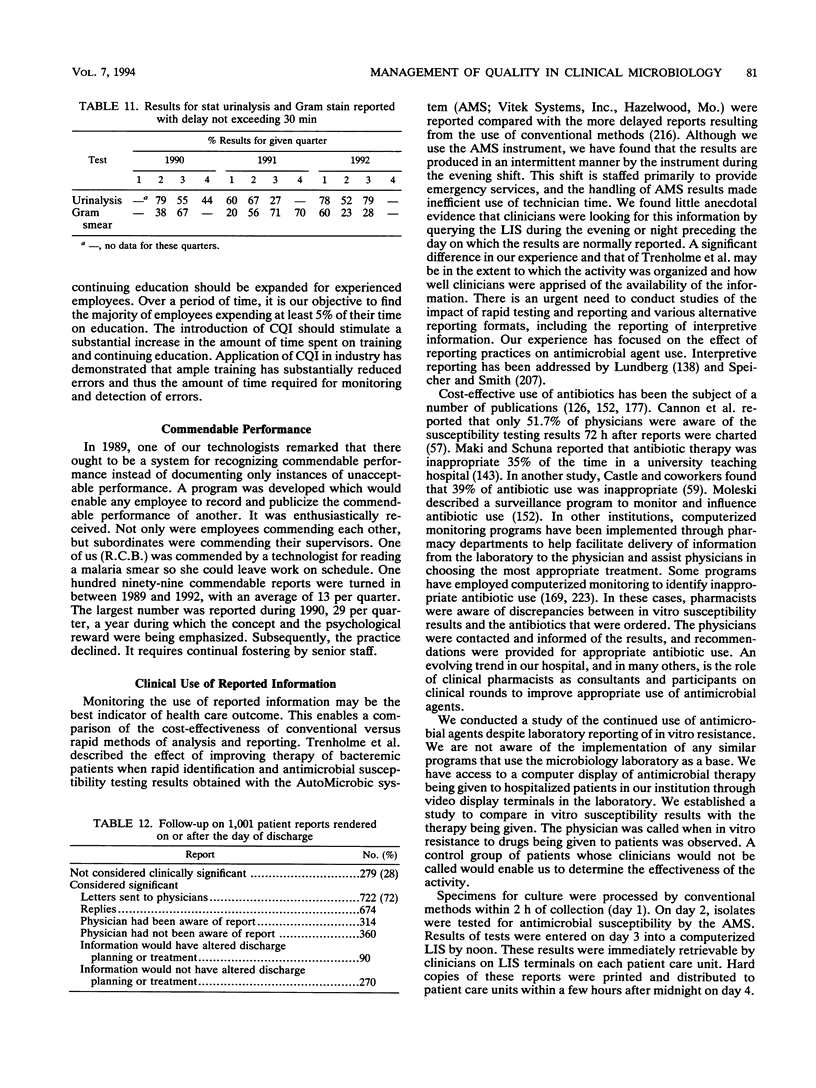
- Bartlett R. C. Trends in quality management. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1990 Nov;114(11):1126–1130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartola J. Painless office laboratory regulation. Prim Care. 1986 Dec;13(4):605–615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates D. W., Cook E. F., Goldman L., Lee T. H. Predicting bacteremia in hospitalized patients. A prospectively validated model. Ann Intern Med. 1990 Oct 1;113(7):495–500. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-113-7-495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates D. W., Goldman L., Lee T. H. Contaminant blood cultures and resource utilization. The true consequences of false-positive results. JAMA. 1991 Jan 16;265(3):365–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates D. W., Lee T. H. Rapid classification of positive blood cultures. Prospective validation of a multivariate algorithm. JAMA. 1992 Apr 8;267(14):1962–1966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belsey R., Baer D. M. Proficiency of office microbiology testing. Clin Lab Med. 1986 Jun;6(2):345–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belyus P. S., Burgess T. E., Walsh P. R. Quality assurance in a large reference laboratory. Clin Lab Med. 1986 Dec;6(4):745–754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berwick D. M. Continuous improvement as an ideal in health care. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jan 5;320(1):53–56. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198901053200110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black W. A., Dorse S. E. A regional quality control program in microbiology. II. Advantages of simulated clinical specimens. Am J Clin Pathol. 1976 Aug;66(2):407–415. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/66.2.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black W. A., Dorse S. E., Whitby J. L. A regional quality control program in microbiology. I. Administrative aspects. Am J Clin Pathol. 1976 Aug;66(2):401–406. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/66.2.401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boone D. J. Evaluating laboratory performance. Historical and governmental perspectives. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1988 Apr;112(4):354–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman R. A., Bowman J. M., Arrow S. A., Riley T. V. Selective criteria for the microbiological examination of faecal specimens. J Clin Pathol. 1992 Sep;45(9):838–839. doi: 10.1136/jcp.45.9.838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branson D. Problems and errors in the clinical microbiology laboratory. Am J Med Technol. 1966 Nov-Dec;32(6):349–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braunstein H. Quality control in microbiology: a review and bibliography. Clin Lab Med. 1986 Dec;6(4):649–674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campo L., Mylotte J. M. Use of microbiology reports by physicians in prescribing antimicrobial agents. Am J Med Sci. 1988 Dec;296(6):392–398. doi: 10.1097/00000441-198812000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson D. J. Cost effectiveness of laboratory improvement programs: the viewpoint from the private sector. Health Lab Sci. 1977 Jul;14(3):199–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castle M., Wilfert C. M., Cate T. R., Osterhout S. Antibiotic use at Duke University Medical Center. JAMA. 1977 Jun 27;237(26):2819–2822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicchetti D. V., Keitges P., Barnett R. N. How many is enough? A statistical study of proficiency testing of syphilis serology specimens. Health Lab Sci. 1974 Oct;11(4):299–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crane S. C. Regulatory considerations in the establishment and expansion of office-based laboratories. Med Clin North Am. 1987 Jul;71(4):733–749. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)30839-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawley R., Belsey R., Brock D., Baer D. M. Regulation of physicians' office laboratories. The Idaho experience. JAMA. 1986 Jan 17;255(3):374–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunha B. A., Gurevich I., Tafuro P. Cost-effective utilization of microbiology data. Hosp Physician. 1986 Nov;22(11):19–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damron D. J., Warren J. W., Chippendale G. R., Tenney J. H. Do clinical microbiology laboratories report complete bacteriology in urine from patients with long-term urinary catheters? J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Sep;24(3):400–404. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.3.400-404.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derman H., Dorsey D. B. The pathology of regulation. Clin Lab Med. 1991 Sep;11(3):793–802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolan C. T. A summary of the 1972 mycology proficiency testing survey of the College of American Pathologists. Am J Clin Pathol. 1974 Jun;61(6):990–993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donabedian A. Evaluating the quality of medical care. Milbank Mem Fund Q. 1966 Jul;44(3 Suppl):166–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donabedian A. The quality of care. How can it be assessed? JAMA. 1988 Sep 23;260(12):1743–1748. doi: 10.1001/jama.260.12.1743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorsey D. B. Evolving concepts of quality in laboratory practice. A historical overview of quality assurance in clinical laboratories. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1989 Dec;113(12):1329–1334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doubilet P., Weinstein M. C., McNeil B. J. Use and misuse of the term "cost effective" in medicine. N Engl J Med. 1986 Jan 23;314(4):253–256. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198601233140421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckworth J. K. Proficiency testing. Its role in a voluntary clinical Laboratory Accreditation Program. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1988 Apr;112(4):346–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edinger S. E. The Medicare and Clinical Laboratories Improvement Act of 1967 proficiency testing requirements and its relationship to the private sector. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1988 Apr;112(4):357–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrmeyer S. S., Laessig R. H. An evaluation of the ability of proficiency testing programs to determine intralaboratory performance. Peer group statistics vs clinical usefulness limits. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1988 Apr;112(4):444–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilers R. J. Total quality control for the medical laboratory. South Med J. 1969 Nov;62(11):1362–1365. doi: 10.1097/00007611-196911000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estevez E. G. A program for in-house proficiency testing in clinical microbiology. Am J Med Technol. 1980 Feb;46(2):102–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferraro M. J. Potential impact of rapid microbiology tests in the prospective payment era. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1985 Nov;3(6 Suppl):65S–71S. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(85)90055-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finn A. F., Jr, Valenstein P. N., Burke M. D. Alteration of physicians' orders by nonphysicians. JAMA. 1988 May 6;259(17):2549–2552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer P. M., Addison L. A., Koneman E. W., Crowley J. Education and the physician's office laboratory. JAMA. 1986 Mar 21;255(11):1464–1467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs P. C., Dolan C. T. Summary and analysis of the mycology proficiency testing survey results of the College of American Pathologists. 1976-1979. Am J Clin Pathol. 1981 Oct;76(4 Suppl):538–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavan T. L. A summary of the bacteriology portion of the 1972 basic, comprehensive, and special, College of American Pathologists (CAP) Quality Evaluation Program. Am J Clin Pathol. 1974 Jun;61(6):971–979. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavan T. L., King J. W. An evaluation of the microbiology portions of the 1969 basic, comprehensive, and special College of American Pathologists proficiency testing surveys. Am J Clin Pathol. 1970 Sep;54(3):514–520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glasser L., Bosley G. S., Boring J. R., 3rd A systematic program of quality control in clinical microbiology. Am J Clin Pathol. 1971 Sep;56(3):379–383. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/56.3.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin C. W., 3rd, Cook E. C., Mehaffey M. A. Centers for Disease Control performance evaluation program in bacteriology: 1980 to 1985 review. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Dec;24(6):1004–1012. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.6.1004-1012.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin C. W., 3rd, Mehaffey M. A., Cook E. C., Blumer S. O., Podeszwik P. A. Relationship between performance in three of the Centers for Disease Control microbiology proficiency testing programs and the number of actual patient specimens tested by participating laboratories. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Feb;23(2):246–250. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.2.246-250.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross P. A., Van Antwerpen C. L., Hess W. A., Reilly K. A. Use and abuse of blood cultures: program to limit use. Am J Infect Control. 1988 Jun;16(3):114–117. doi: 10.1016/0196-6553(88)90048-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruft H. Evaluation of mycobacteriology laboratories: the acid-fast smear. Health Lab Sci. 1978 Oct;15(4):215–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halstead E. G., Jr, Quevedo R. A., Gingerich W. H. A quality control program for the bacteriology laboratory. Am J Med Technol. 1971 Jan;37(1):15–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond H. C. Federal regulation of clinical laboratories. A prospective public policy analysis. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1988 Apr;112(4):363–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding H. B. Quality control in microbiology. II. Hosp Top. 1965 Nov;43(11):79–85. doi: 10.1080/00185868.1965.9954597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley R. M., Markowitz M. A., Komaroff A. L. The expense of testing in a teaching hospital: the predominant role of high-cost tests. Am J Public Health. 1989 Oct;79(10):1389–1391. doi: 10.2105/ajph.79.10.1389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heineman H. S., Chawla J. K., Lopton W. M. Misinformation from sputum cultures without microscopic examination. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Nov;6(5):518–527. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.5.518-527.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoke C. H., Jr, Batt J. M., Mirrett S., Cox R. L., Reller L. B. False-positive Gram-stained smears. JAMA. 1979 Feb 2;241(5):478–480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howanitz P. J. Quality assurance measurements in departments of pathology and laboratory medicine. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1990 Nov;114(11):1131–1135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howanitz P. J., Steindel S. J. Intralaboratory performance and laboratorians' expectations for stat turnaround times. A College of American Pathologists Q-Probes study of four cerebrospinal fluid determinations. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1991 Oct;115(10):977–983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howanitz P. J. Use of proficiency test performance to determine clinical laboratory director qualifications. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1988 Apr;112(4):349–353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howanitz P. J., Walker K., Bachner P. Quantification of errors in laboratory reports. A quality improvement study of the College of American Pathologists' Q-Probes program. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1992 Jul;116(7):694–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howie J. Medical microbiology for patient and community. J Clin Pathol. 1972 Nov;25(11):921–926. doi: 10.1136/jcp.25.11.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg H. D. Is cost effective ordering of microbiology tests for infection control possible? Infect Control. 1985 Oct;6(10):425–427. doi: 10.1017/s0195941700063530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
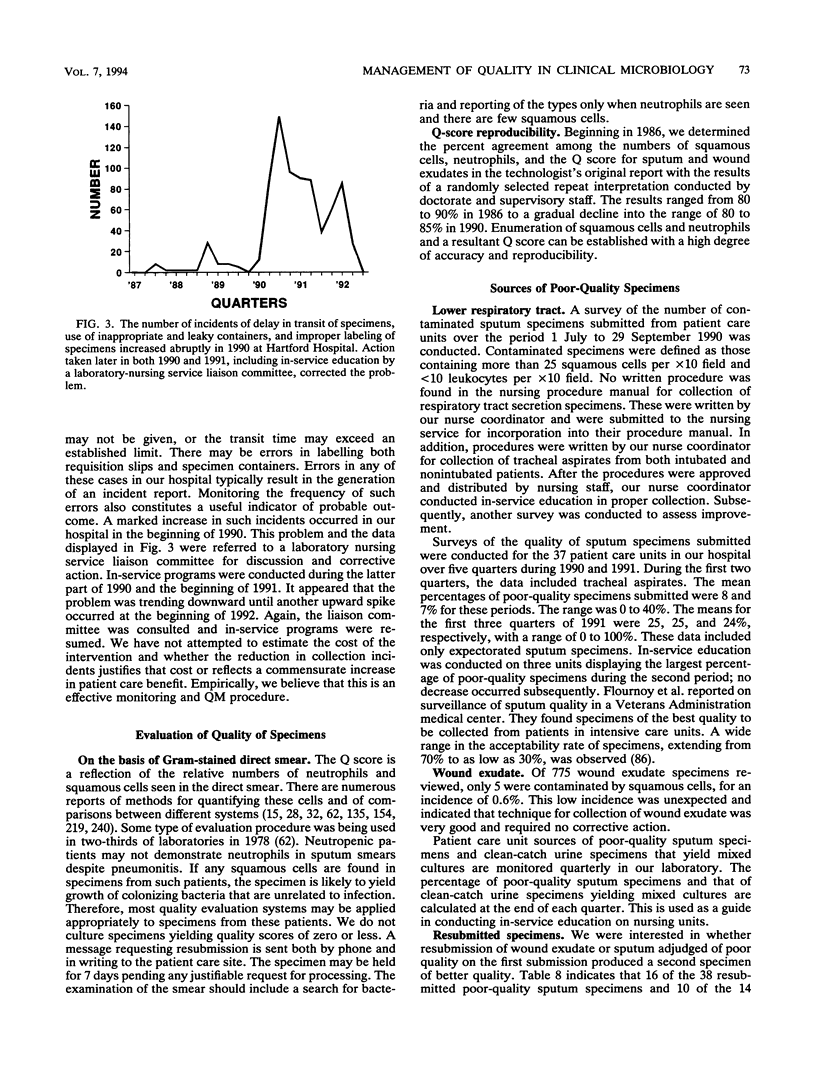
- Jefferson H., Dalton H. P., Escobar M. R., Allison M. J. Transportation delay and the microbiological quality of clinical specimens. Am J Clin Pathol. 1975 Nov;64(5):689–693. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/64.5.689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. N., Edson D. C. Antibiotic susceptibility testing accuracy. Review of the College of American Pathologists Microbiology Survey, 1972-1983. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1985 Jul;109(7):595–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
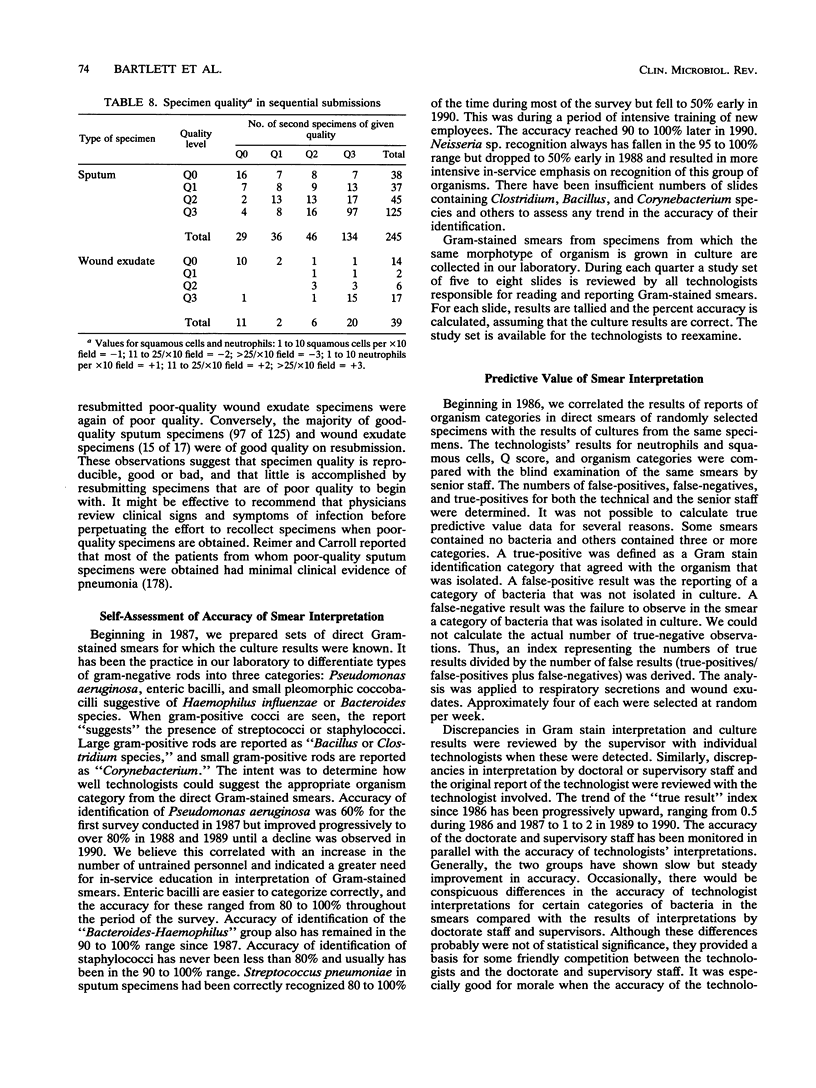
- Jones R. N., Edson D. C. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing trends and accuracy in the United States. A review of the College of American Pathologists Microbiology Surveys, 1972-1989. Microbiology Resource Committee of the College of American Pathologists. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1991 May;115(5):429–436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. N., Edson D. C., Gilmore B. F. Contemporary quality control practices for antimicrobial susceptibility tests: a report from the microbiology portion of the College of American Pathologists (CAP) surveys program. Am J Clin Pathol. 1983 Oct;80(4 Suppl):622–625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. N., Edson D. C., Marymont J. V. Evaluations of antimicrobial susceptibility test proficiency by the College of American Pathologists Survey program. A clarification of quality control recommendations. Am J Clin Pathol. 1982 Aug;78(2):168–172. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/78.2.168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. N., Edson D. C. Special topics in antimicrobial susceptibility testing: test accuracy against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, pneumococci, and the sensitivity of beta-lactamase methods. Am J Clin Pathol. 1983 Oct;80(4 Suppl):609–614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. N., Edson D. C. The identification and antimicrobial susceptibility testing of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, 1980-1987. Results from the College of American Pathologists Microbiology Surveys Program. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1988 May;112(5):485–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles R. C., Gilmore B. F. Quality control of agar diffusion susceptibility tests. Data from the Quality Assurance Service Microbiology Program of the College of American Pathologists. Am J Clin Pathol. 1981 Oct;76(4 Suppl):590–596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koepke J. A., Klee G. G. The process of quality assurance. Quality indicators in clinical pathology. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1990 Nov;114(11):1136–1139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer F., Modilevsky T., Waliany A. R., Leedom J. M., Barnes P. F. Delayed diagnosis of tuberculosis in patients with human immunodeficiency virus infection. Am J Med. 1990 Oct;89(4):451–456. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(90)90375-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunin C. M. The responsibility of the infectious disease community for the optimal use of antimicrobial agents. J Infect Dis. 1985 Mar;151(3):388–398. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.3.388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacher D. A. Predictive value derived from likelihood ratios: a superior technic to interpret quantitative laboratory results. Am J Clin Pathol. 1987 May;87(5):673–676. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/87.5.673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laessig R. H., Ehrmeyer S. S., Hassemer D. J. Quality control and quality assurance. Clin Lab Med. 1986 Jun;6(2):317–327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laessig R. H., Ehrmeyer S. S. Proficiency testing programs--promises, progress, and problems. A 40-year prospective. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1988 Apr;112(4):329–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamanna A. Controlli di qualità in batteriologia. Ann Sclavo. 1977 Jul-Aug;19(4):610–621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassen J., Sandven P. External quality assessment for clinical microbiology in Norway 1985. NIPH Ann. 1986 Jun;9(1):23–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassen J., Sandven P. External quality assessment for clinical microbiology in Norway 1986-1987. NIPH Ann. 1988 Jun;11(1):29–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A., McLean S. The laboratory report: a problem in communication between clinician and microbiologist? Med J Aust. 1977 Dec 24;2(26-27):858–860. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1977.tb107716.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
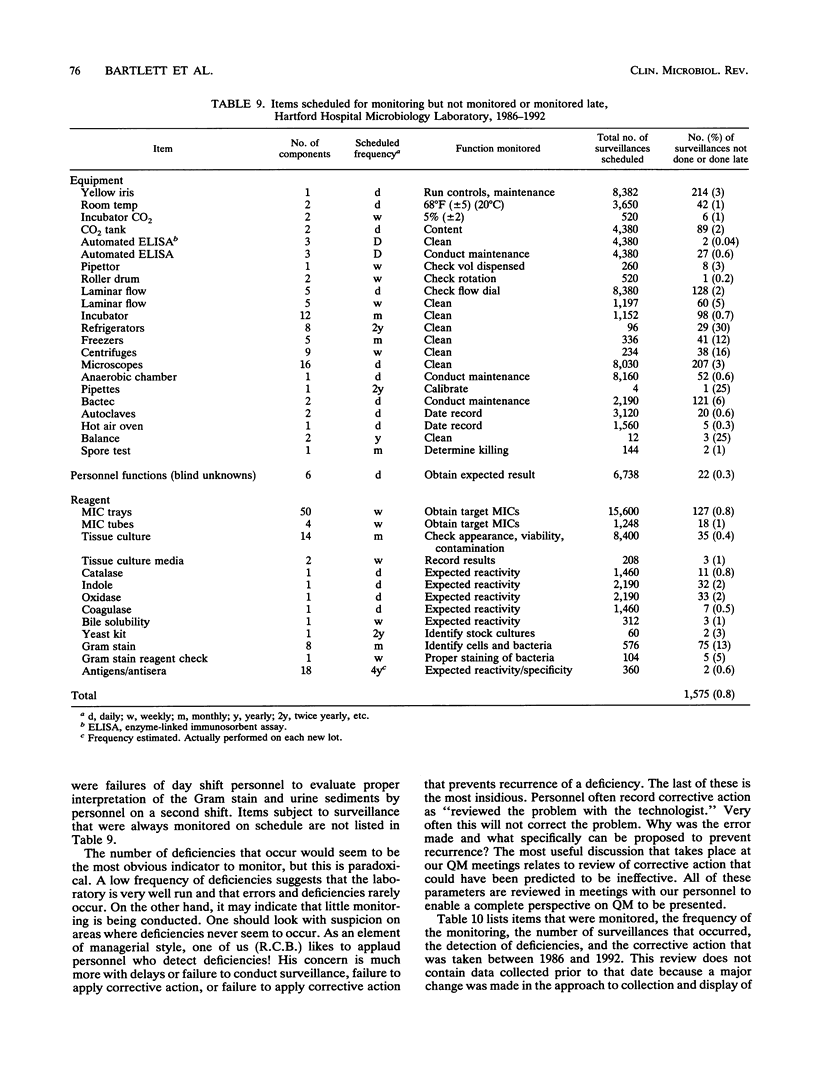
- Lentino J. R., Lucks D. A. Nonvalue of sputum culture in the management of lower respiratory tract infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 May;25(5):758–762. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.5.758-762.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomas J., Anderson G. M., Domnick-Pierre K., Vayda E., Enkin M. W., Hannah W. J. Do practice guidelines guide practice? The effect of a consensus statement on the practice of physicians. N Engl J Med. 1989 Nov 9;321(19):1306–1311. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198911093211906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longberry J., Del Polito G. A. The Clinical Laboratory Improvement Act: a retrospective view. Am J Med Technol. 1981 Mar;47(3):205–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
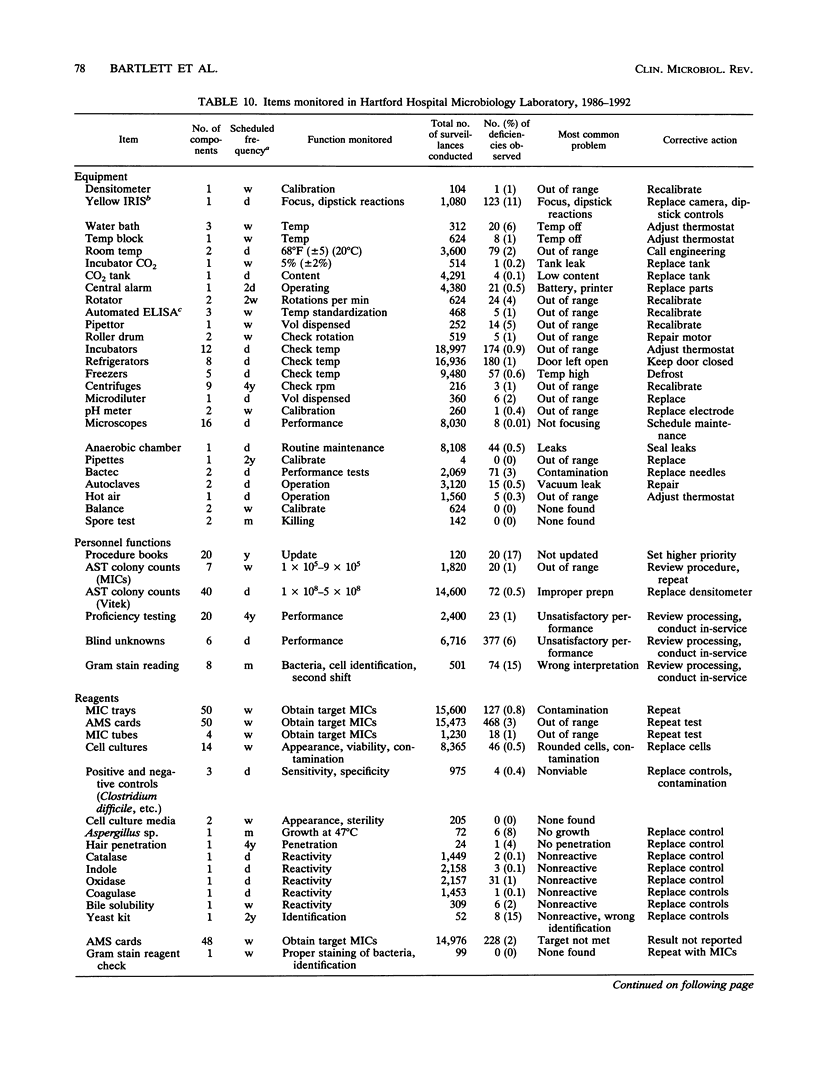
- Lundberg G. D. The reporting of laboratory data interpretations: to omit or commit? JAMA. 1980 Apr 18;243(15):1554–1555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunz M. E., Castleberry B. M., James K., Stahl J. The impact of the quality of laboratory staff on the accuracy of laboratory results. JAMA. 1987 Jul 17;258(3):361–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lányi B., Czirók E. Bacteriological proficiency testing in Hungarian clinical microbiology laboratories. Acta Microbiol Hung. 1990;37(4):379–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maki D. G., Schuna A. A. A study of antimicrobial misuse in a university hospital. Am J Med Sci. 1978 May-Jun;275(3):271–282. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197805000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manek N., Napier Rees E. Audit of catheter urine culture requests. J Clin Pathol. 1992 Jan;45(1):79–79. doi: 10.1136/jcp.45.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks J. Notes on the organization of tuberculosis bacteriology and its quality control. Tubercle. 1975 Sep;56(3):219–226. doi: 10.1016/0041-3879(75)90055-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. J. Quality assurance and clinical microbiology. Med Lab Sci. 1983 Jul;40(3):269–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizrachi H. H., Valenstein P. N. Randomized trial interpreting sputum quality in a clinical laboratory. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Dec;25(12):2327–2329. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.12.2327-2329.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moleski R. J., Andriole V. T. Role of the infectious disease specialist in containing costs of antibiotics in the hospital. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 May-Jun;8(3):488–493. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.3.488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris A. J., Wilson M. L., Reller L. B. Application of rejection criteria for stool ovum and parasite examinations. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Dec;30(12):3213–3216. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.12.3213-3216.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray P. R., Washington J. A. Microscopic and baceriologic analysis of expectorated sputum. Mayo Clin Proc. 1975 Jun;50(6):339–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagel J. G., Kunz L. J. Needless retesting of quality-assured, commercially prepared culture media. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Jul;26(1):31–37. doi: 10.1128/am.26.1.31-37.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neff J. C., Speicher C. E. CLIA '88. More misguided regulation, or a promise of quality? Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1992 Jul;116(7):679–680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C. Cost effective blood cultures--is it possible or impossible to modify behavior? Infect Control. 1986 Jan;7(1):32–33. doi: 10.1017/s0195941700063773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyiendo J., Kilbourn J. P. Cost-effective clinical microbiology. Am J Med Technol. 1979 May;45(5):393–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor M. How to evaluate medical laboratories. Med Sect Proc. 1989:103–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Dell C. Benchmarking. Building on received wisdom. Healthc Forum J. 1993 Jan-Feb;36(1):17-8, 20-1. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orsi A., De Mayo E., Morgantetti F. The Italian experience of quality control in microbiology. Quad Sclavo Diagn. 1984 Jun;20(2):203–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paris M. Cost and quality control of laboratory services: the New York City medicaid centralized laboratory proposal. Med Care. 1976 Sep;14(9):777–793. doi: 10.1097/00005650-197609000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedler S. J., Bint A. J. Survey of users' attitudes to their local microbiology laboratory. J Clin Pathol. 1991 Jan;44(1):6–9. doi: 10.1136/jcp.44.1.6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry J. L., Miller G. R. Quality control slide for potassium hydroxide and cellufluor fungal preparations. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jun;27(6):1411–1412. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.6.1411-1412.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry S. F., Campbell C. K., Snell J. J. Mycology quality assessment: United Kingdom national scheme. J Clin Pathol. 1989 May;42(5):531–535. doi: 10.1136/jcp.42.5.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestotnik S. L., Evans R. S., Burke J. P., Gardner R. M., Classen D. C. Therapeutic antibiotic monitoring: surveillance using a computerized expert system. Am J Med. 1990 Jan;88(1):43–48. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(90)90126-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersdorf R. G., Sherris J. C. Methods and significance of in vitro testing of bacterial sensitivity to drugs. Am J Med. 1965 Nov;39(5):766–779. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(65)90096-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen K. F. Methods for internal quality control in the mycobacteriology laboratory. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1983 Nov;255(4):503–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips G., Senior B. W., McEwan H. Use of telephone enquiries to a microbiology laboratory as a proxy measure of reporting efficiency. J Clin Pathol. 1992 Mar;45(3):250–253. doi: 10.1136/jcp.45.3.250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porres J. M. Quality control in microbiology. I. Utilization of reference laboratory data. Am J Clin Pathol. 1974 Sep;62(3):407–411. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/62.3.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porres J. M. Quality control in microbiology. II. The need for standards. Am J Clin Pathol. 1974 Sep;62(3):412–419. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/62.3.412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard R. C. A medical microbiology quality assurance programme. Malays J Pathol. 1987 Aug;9:9–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quintiliani R., Cooper B. W., Briceland L. L., Nightingale C. H. Economic impact of streamlining antibiotic administration. Am J Med. 1987 Apr 27;82(4A):391–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Report of the Ad Hoc Committee on Medical Microbiology Laboratory Utilization; State of Connecticut, Department of Health. Conn Med. 1975 Aug;39(8):499-501, 503-5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds S. M. Nonmicrobial alternative to reagent quality control testing. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Nov;16(5):836–839. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.5.836-839.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts-Thomson P., McEvoy R., Gale R., Jovanovich S., Bradley J. Quality assurance of immunodiagnostic tests in Australasia. Pathology. 1991 Apr;23(2):125–129. doi: 10.3109/00313029109060810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodewald L. E., Woodin K. A., Szilâgyi P. G., Arvan D. A., Raubertas R. F., Powell K. R. Relevance of common tests of cerebrospinal fluid in screening for bacterial meningitis. J Pediatr. 1991 Sep;119(3):363–369. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)82046-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers S., Bywater M. J., Reeves D. S. Audit of turn-around times in a microbiology laboratory. J Clin Pathol. 1991 Mar;44(3):257–258. doi: 10.1136/jcp.44.3.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer M. Health department's role in improving operations of clinical laboratories. Public Health Rep. 1966 Jan;81(1):71–74. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer M., Widelock D., Blatt S., Wilson E. The clinical laboratory improvement program in New York City. I. Methods of evaluation and results of performance tests. Health Lab Sci. 1967 Apr;4(2):72–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer M., Widelock D., May P. S., Blatt S., Wilson M. E. The clinical laboratory improvement program in New York City. II. Progress after five years of experience. Health Lab Sci. 1970 Oct;7(4):242–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalla W. O., Hearn T. L., Taylor R. N., Eavenson E., Valdiserri R. O., Essien J. D. CDC's Model Performance Evaluation Program: assessment of the quality of laboratory performance for HIV-1 antibody testing. Public Health Rep. 1990 Mar-Apr;105(2):167–171. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schifman R. B., Strand C. L., Braun E., Louis-Charles A., Spark R. P., Fried M. L. Solitary blood cultures as a quality assurance indicator. Qual Assur Util Rev. 1991 Winter;6(4):132–137. doi: 10.1177/0885713x9100600406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanholtzer C. J., Peterson L. R. Laboratory quality assurance testing of microbiologic media from commercial sources. Am J Clin Pathol. 1987 Aug;88(2):210–215. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/88.2.210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel D. L., Edelstein P. H., Nachamkin I. Inappropriate testing for diarrheal diseases in the hospital. JAMA. 1990 Feb 16;263(7):979–982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skendzel L. P. How physicians use laboratory tests. JAMA. 1978 Mar 13;239(11):1077–1080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. P., Sandlin C. Quality control in bacteriology. Am J Med Technol. 1969 Sep;35(9):531–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. W. Identification of fecal parasites in the Special Parasitology Survey of the College of American Pathologists. Am J Clin Pathol. 1979 Aug;72(2 Suppl):371–373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. W. Parasitology proficiency testing in the Quality Evaluation Programs of the College of American Pathologists. Am J Clin Pathol. 1974 Jun;61(6):994–998. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snell J. J., Brown D. F. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: a trial organised as part of the United Kingdom national external quality assessment scheme for microbiology. J Clin Pathol. 1988 Jan;41(1):97–102. doi: 10.1136/jcp.41.1.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snell J. J., Brown D. F., Gardner P. S. An antibiotic susceptibility testing trial organised as part of the United Kingdom national external microbiological quality assessment scheme. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Nov;35(11):1169–1176. doi: 10.1136/jcp.35.11.1169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snell J. J., De Mello J. V., Gardner P. S. The United Kingdom national microbiological quality assessment scheme. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Jan;35(1):82–93. doi: 10.1136/jcp.35.1.82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snell J. J., De Mello J. V., Phua T. J. Errors in bacteriological techniques: results from the United Kingdom national external quality assessment scheme for microbiology. Med Lab Sci. 1986 Oct;43(4):344–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snell J. J. United Kingdom National External Quality Assessment Scheme for Microbiology. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Oct;4(5):464–467. doi: 10.1007/BF02014425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommers H. M. Mycobacterial proficiency testing in the Quality Evaluation Programs of the College of American Pathologists, 1972. Am J Clin Pathol. 1974 Jun;61(6):980–989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speicher C. E., Smith J. W. Helping physicians use laboratory tests. Clin Lab Med. 1985 Dec;5(4):653–663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speicher C. E., Smith J. W., Jr Interpretive reporting in clinical pathology. JAMA. 1980 Apr 18;243(15):1556–1560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunderman F. W. Forty-five years of proficiency testing. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 1991 Mar-Apr;21(2):143–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. N., Fulford K. M. Assessment of laboratory improvement by the Center for Disease Control Diagnostic Immunology Proficiency Testing Program. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Feb;13(2):356–368. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.2.356-368.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson R. B., Jr, File T. M., Jr, Burgoon R. A. Repeat antimicrobial susceptibility testing of identical isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 May;27(5):1108–1111. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.5.1108-1111.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson R. B., Jr, File T. M., Jr, Tan J. S., Evans B. L. Yield, clinical significance, and cost of a combination BACTEC plus Septi-Chek blood culture system. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 May;25(5):819–823. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.5.819-823.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillett H. E., Crone P. B. Quality control of the isolation rate of pathogens in medical microbiology laboratories. J Hyg (Lond) 1976 Dec;77(3):359–367. doi: 10.1017/s002217240005573x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trenholme G. M., Kaplan R. L., Karakusis P. H., Stine T., Fuhrer J., Landau W., Levin S. Clinical impact of rapid identification and susceptibility testing of bacterial blood culture isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jun;27(6):1342–1345. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.6.1342-1345.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tydeman J., Morrison J. I., Harwick D. F., Cassidy P. A. The cost of quality control procedures in the clinical laboratory. Am J Clin Pathol. 1982 May;77(5):528–533. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/77.5.528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenstein P. N., Emancipator K. Sensitivity, specificity, and reproducibility of four measures of laboratory turnaround time. Am J Clin Pathol. 1989 Apr;91(4):452–457. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/91.4.452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenstein P., Leiken A., Lehmann C. Test-ordering by multiple physicians increases unnecessary laboratory examinations. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1988 Mar;112(3):238–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Scoy R. E. Bacterial sputum cultures. A clinician's viewpoint. Mayo Clin Proc. 1977 Jan;52(1):39–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Seggern R. L. Culture and antibiotic monitoring service in a community hospital. Am J Hosp Pharm. 1987 Jun;44(6):1358–1362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washington J. A., 2nd, Ilstrup D. M. Blood cultures: issues and controversies. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Sep-Oct;8(5):792–802. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.5.792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washington J. A., 2nd The clinical microbiology laboratory. Utilization and cost-effectiveness. Am J Med. 1985 Jun 28;78(6B):8–16. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(85)90357-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts N. B. Medical relevance of laboratory tests. A clinical perspective. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1988 Apr;112(4):379–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitby J. L., Black W. A., Richardson H., Wood D. E. System for laboratory proficiency testing in bacteriology: organisation and impact on microbiology laboratories in health care facilities funded by the Ontario Government. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Jan;35(1):94–100. doi: 10.1136/jcp.35.1.94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildermann R. F., Schneider K. A. Regulatory and legal influences on physicians' office laboratories. JAMA. 1986 Jul 11;256(2):252–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. E., Faur Y. C., Schaefler S., Weitzman I., Weisburd M. H., Schaeffer M. Proficiency testing in clinical microbiology: the New York City Program. Mt Sinai J Med. 1977 Jan-Feb;44(1):142–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkelman J. W. Less utilization of the clinical laboratory produces disproportionately small true cost reductions. Hum Pathol. 1984 Jun;15(6):499–501. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(84)80002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkelman J. W. Quantitative analysis of cost-savings strategies in the clinical laboratory. Clin Lab Med. 1985 Dec;5(4):635–651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong E. T. Cost-effective use of laboratory tests: a joint responsibility of clinicians and laboratorians. Clin Lab Med. 1985 Dec;5(4):665–672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong E. T., Lincoln T. L. Ready! Fire! . . . Aim! An inquiry into laboratory test ordering. JAMA. 1983 Nov 11;250(18):2510–2513. doi: 10.1001/jama.250.18.2510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong E. T., Nelson J. M. Quality assurance and the clinical laboratory. JAMA. 1988 May 6;259(17):2584–2585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong L. K., Barry A. L., Horgan S. M. Comparison of six different criteria for judging the acceptability of sputum specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Oct;16(4):627–631. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.4.627-631.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood R. J., Durham T. M. Reproducibility of serological titers. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jun;11(6):541–545. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.6.541-545.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D., Byers J. F. Quality control recording methods in microbiology. Am J Med Technol. 1973 Mar;39(3):79–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward R. S., Medoff G., Smith M. D., Gray J. L., 3rd Antibiotic cost savings from formulary restrictions and physician monitoring in a medical-school-affiliated hospital. Am J Med. 1987 Nov;83(5):817–823. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(87)90636-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worman H. J. Excessive use of urine cultures for inpatients. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Jul;107(1):115–116. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-107-1-115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yannelli B., Gurevich I., Schoch P. E., Cunha B. A. Yield of stool cultures, ova and parasite tests, and Clostridium difficile determinations in nosocomial diarrheas. Am J Infect Control. 1988 Dec;16(6):246–249. doi: 10.1016/s0196-6553(88)80003-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


