Abstract
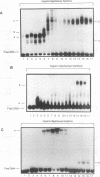
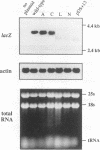
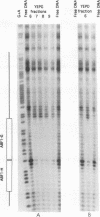
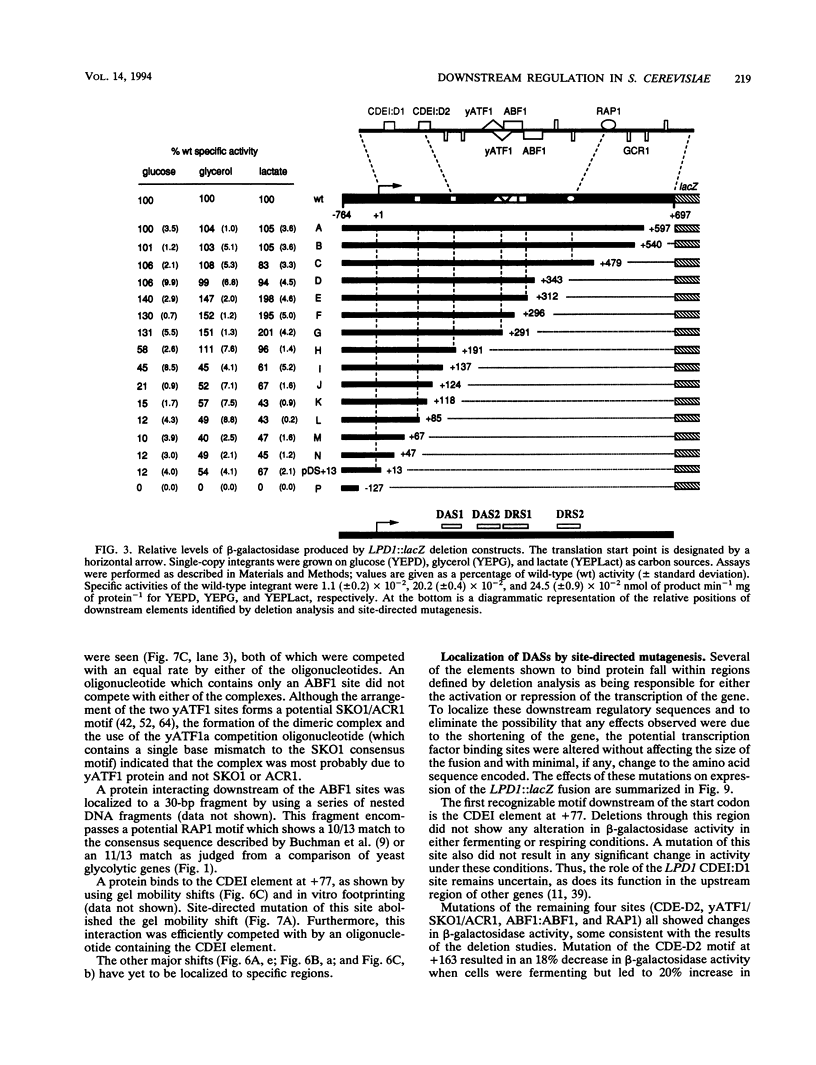
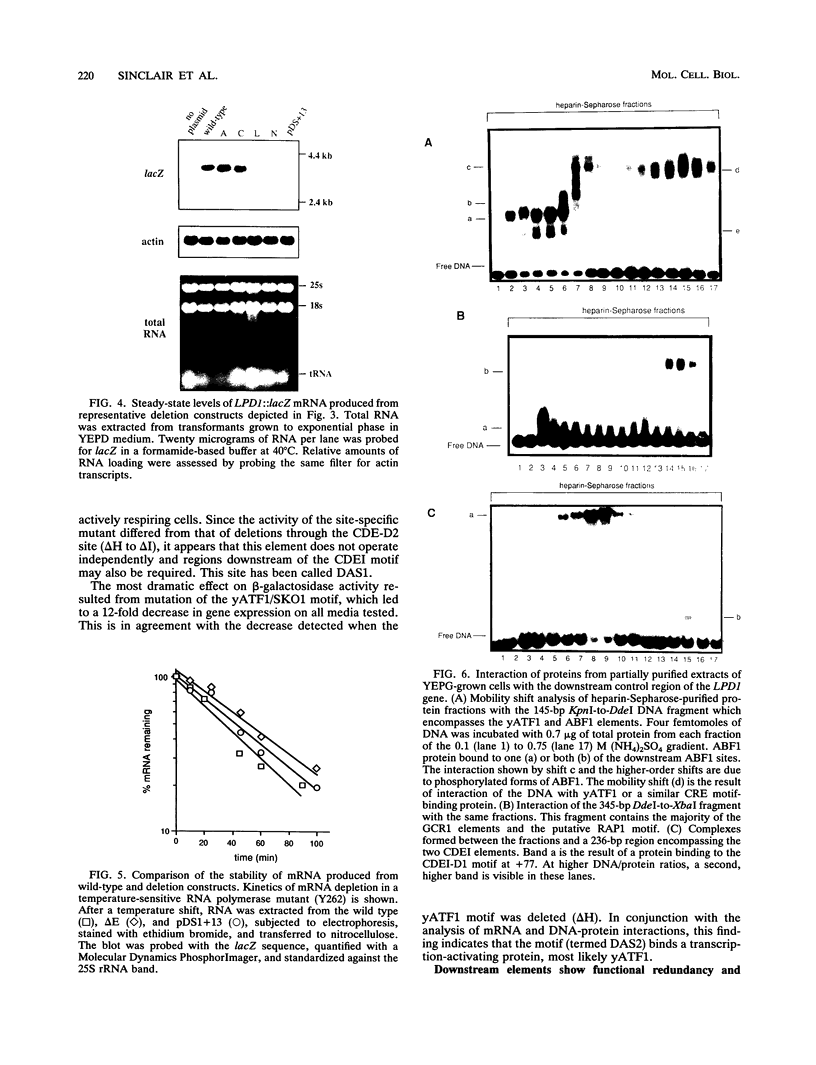
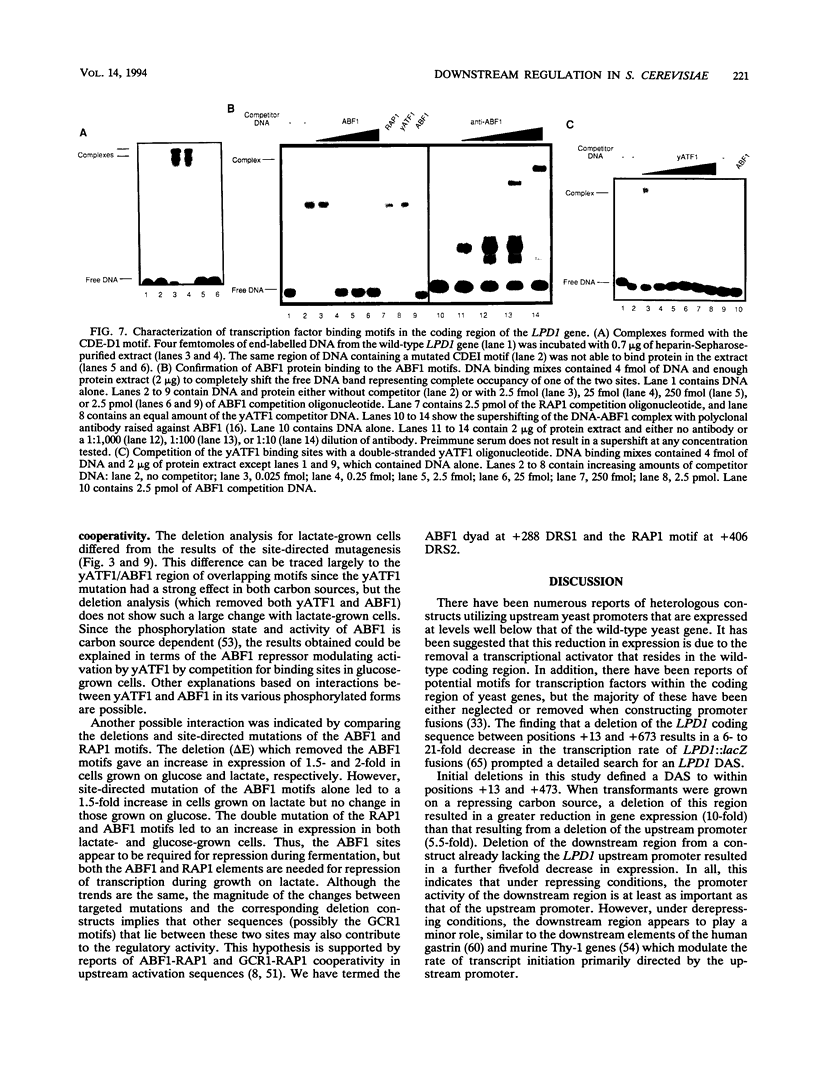
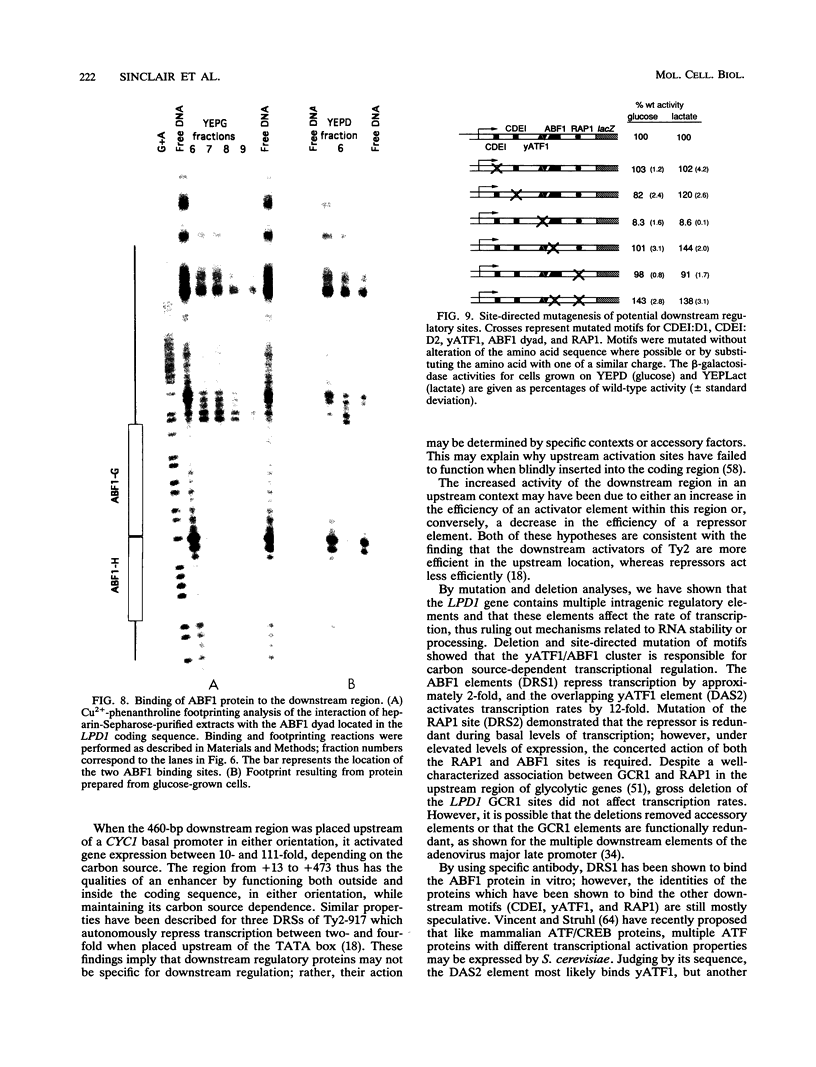
Though widely recognized in higher eukaryotes, the regulation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae genes transcribed by RNA polymerase II by proteins that bind within the coding sequence remains largely speculative. We have shown for the LPD1 gene, encoding lipoamide dehydrogenase, that the coding sequence between +13 and +469 activated gene expression of an LPD1::lacZ fusion by up to sixfold in the presence of the upstream promoter. This downstream region, inserted upstream of a promoterless CYC1::lacZ fusion, activated gene expression in a carbon source-dependent manner by a factor of 15 to 111, independent of orientation. Deletion and mutational analysis identified two downstream activation sites (DAS1 and DAS2) and two downstream repressor sites (DRS1 and DRS2) that influence the rate of LPD1 transcription rather than mRNA degradation or translation. Activation from the DAS1 region (positions +137 to +191), encompassing a CDEI-like element, is twofold under derepressive conditions. Activation from DAS2 (+291 to +296), a CRE-like motif, is 12-fold for both repressed and derepressed states. DRS1, a pair of adjacent and opposing ABF1 sites (+288 to +313), is responsible for a 1.3- to 2-fold repression of transcription, depending on the carbon source. DRS1 requires the concerted action of DRS2 (a RAP1 motif at position +406) for repression of transcription only when the gene is induced. Gel mobility shift analysis and in vitro footprinting have shown that proteins bind in vitro to these downstream elements.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes C. A., Johnston G. C., Singer R. A. Expression of lacZ gene fusions affects downstream transcription in yeast. Gene. 1991 Jul 31;104(1):47–54. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90463-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benen J. A., Van Berkel W. J., Van Dongen W. M., Müller F., De Kok A. Molecular cloning and sequence determination of the lpd gene encoding lipoamide dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas fluorescens. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Jul;135(7):1787–1797. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-7-1787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bettany A. J., Moore P. A., Cafferkey R., Bell L. D., Goodey A. R., Carter B. L., Brown A. J. 5'-secondary structure formation, in contrast to a short string of non-preferred codons, inhibits the translation of the pyruvate kinase mRNA in yeast. Yeast. 1989 May-Jun;5(3):187–198. doi: 10.1002/yea.320050308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman S. B., Zaman Z., Collinson L. P., Brown A. J., Dawes I. W. Positive regulation of the LPD1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae by the HAP2/HAP3/HAP4 activation system. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Jan;231(2):296–303. doi: 10.1007/BF00279803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brindle P. K., Holland J. P., Willett C. E., Innis M. A., Holland M. J. Multiple factors bind the upstream activation sites of the yeast enolase genes ENO1 and ENO2: ABFI protein, like repressor activator protein RAP1, binds cis-acting sequences which modulate repression or activation of transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4872–4885. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman A. R., Lue N. F., Kornberg R. D. Connections between transcriptional activators, silencers, and telomeres as revealed by functional analysis of a yeast DNA-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5086–5099. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns G., Brown T., Hatter K., Sokatch J. R. Sequence analysis of the lpdV gene for lipoamide dehydrogenase of branched-chain-oxoacid dehydrogenase of Pseudomonas putida. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jan 15;179(1):61–69. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14521.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. Y., Hitzeman R. A. Human, yeast and hybrid 3-phosphoglycerate kinase gene expression in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 26;15(2):643–660. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.2.643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Della Seta F., Treich I., Buhler J. M., Sentenac A. ABF1 binding sites in yeast RNA polymerase genes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):15168–15175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson J. R., Dawes I. W. The catabolism of branched-chain amino acids occurs via 2-oxoacid dehydrogenase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Gen Microbiol. 1992 Oct;138(10):2029–2033. doi: 10.1099/00221287-138-10-2029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diffley J. F., Stillman B. Similarity between the transcriptional silencer binding proteins ABF1 and RAP1. Science. 1989 Nov 24;246(4933):1034–1038. doi: 10.1126/science.2511628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farabaugh P. J., Vimaladithan A., Türkel S., Johnson R., Zhao H. Three downstream sites repress transcription of a Ty2 retrotransposon in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2081–2090. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farabaugh P., Liao X. B., Belcourt M., Zhao H., Kapakos J., Clare J. Enhancer and silencerlike sites within the transcribed portion of a Ty2 transposable element of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4824–4834. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher F., Goding C. R. Single amino acid substitutions alter helix-loop-helix protein specificity for bases flanking the core CANNTG motif. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):4103–4109. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05503.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsburg S. L., Guarente L. Mutational analysis of upstream activation sequence 2 of the CYC1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a HAP2-HAP3-responsive site. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):647–654. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulton A. M., Rathjen P. D., Kingsman S. M., Kingsman A. J. Upstream and downstream transcriptional control signals in the yeast retrotransposon, TY. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 24;16(12):5439–5458. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.12.5439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gietz D., St Jean A., Woods R. A., Schiestl R. H. Improved method for high efficiency transformation of intact yeast cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Mar 25;20(6):1425–1425. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.6.1425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L. Yeast promoters and lacZ fusions designed to study expression of cloned genes in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:181–191. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemilä H. Lipoamide dehydrogenase of Staphylococcus aureus: nucleotide sequence and sequence analysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Dec 2;1129(1):119–123. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90225-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet J., Cottrelle P., Cool M., Vignais M. L., Thiele D., Marck C., Buhler J. M., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. A general upstream binding factor for genes of the yeast translational apparatus. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3539–3547. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04114.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huie M. A., Scott E. W., Drazinic C. M., Lopez M. C., Hornstra I. K., Yang T. P., Baker H. V. Characterization of the DNA-binding activity of GCR1: in vivo evidence for two GCR1-binding sites in the upstream activating sequence of TPI of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2690–2700. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jentoft J. E., Shoham M., Hurst D., Patel M. S. A structural model for human dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase. Proteins. 1992 Sep;14(1):88–101. doi: 10.1002/prot.340140110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. H., Jones N. C. Mammalian cAMP-responsive element can activate transcription in yeast and binds a yeast factor(s) that resembles the mammalian transcription factor ANF. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2176–2180. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsman S. M., Kingsman A. J., Dobson M. J., Mellor J., Roberts N. A. Heterologous gene expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 1985;3:377–416. doi: 10.1080/02648725.1985.10647819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D., Lorch Y. Irresistible force meets immovable object: transcription and the nucleosome. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):833–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90354-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer B., Kramer W., Fritz H. J. Different base/base mismatches are corrected with different efficiencies by the methyl-directed DNA mismatch-repair system of E. coli. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):879–887. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90283-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwabara M. D., Sigman D. S. Footprinting DNA-protein complexes in situ following gel retardation assays using 1,10-phenanthroline-copper ion: Escherichia coli RNA polymerase-lac promoter complexes. Biochemistry. 1987 Nov 17;26(23):7234–7238. doi: 10.1021/bi00397a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambrechts M. G., Pretorius I. S., Sollitti P., Marmur J. Primary structure and regulation of a glucoamylase-encoding gene (STA2) in Saccharomyces diastaticus. Gene. 1991 Apr;100:95–103. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90354-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong K., Lee W., Berk A. J. High-level transcription from the adenovirus major late promoter requires downstream binding sites for late-phase-specific factors. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):51–60. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.51-60.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. S., Green M. R. Identification and purification of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae protein with the DNA binding specificity of mammalian activating transcription factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):109–113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Wang J. C. Supercoiling of the DNA template during transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7024–7027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellor J., Dobson M. J., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M. A transcriptional activator is located in the coding region of the yeast PGK gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 11;15(15):6243–6259. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.15.6243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellor J., Rathjen J., Jiang W., Barnes C. A., Dowell S. J. DNA binding of CPF1 is required for optimal centromere function but not for maintaining methionine prototrophy in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 11;19(11):2961–2969. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.11.2961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers A. M., Tzagoloff A., Kinney D. M., Lusty C. J. Yeast shuttle and integrative vectors with multiple cloning sites suitable for construction of lacZ fusions. Gene. 1986;45(3):299–310. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nehlin J. O., Carlberg M., Ronne H. Yeast SKO1 gene encodes a bZIP protein that binds to the CRE motif and acts as a repressor of transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Oct 25;20(20):5271–5278. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.20.5271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonet M., Scafe C., Sexton J., Young R. Eucaryotic RNA polymerase conditional mutant that rapidly ceases mRNA synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1602–1611. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otulakowski G., Robinson B. H. Isolation and sequence determination of cDNA clones for porcine and human lipoamide dehydrogenase. Homology to other disulfide oxidoreductases. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17313–17318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purvis I. J., Loughlin L., Bettany A. J., Brown A. J. Translation and stability of an Escherichia coli beta-galactosidase mRNA expressed under the control of pyruvate kinase sequences in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):7963–7974. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raleigh E. A., Murray N. E., Revel H., Blumenthal R. M., Westaway D., Reith A. D., Rigby P. W., Elhai J., Hanahan D. McrA and McrB restriction phenotypes of some E. coli strains and implications for gene cloning. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 25;16(4):1563–1575. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.4.1563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J., Reid G. A., Dawes I. W. The nucleotide sequence of the LPD1 gene encoding lipoamide dehydrogenase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: comparison between eukaryotic and prokaryotic sequences for related enzymes and identification of potential upstream control sites. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 May;134(5):1131–1139. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-5-1131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruet A., Camier S., Smagowicz W., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. Isolation of a class C transcription factor which forms a stable complex with tRNA genes. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):343–350. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01809.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt M. E., Brown T. A., Trumpower B. L. A rapid and simple method for preparation of RNA from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 25;18(10):3091–3092. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.10.3091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott E. W., Baker H. V. Concerted action of the transcriptional activators REB1, RAP1, and GCR1 in the high-level expression of the glycolytic gene TPI. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):543–550. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellers J. W., Vincent A. C., Struhl K. Mutations that define the optimal half-site for binding yeast GCN4 activator protein and identify an ATF/CREB-like repressor that recognizes similar DNA sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5077–5086. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silve S., Rhode P. R., Coll B., Campbell J., Poyton R. O. ABF1 is a phosphoprotein and plays a role in carbon source control of COX6 transcription in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):4197–4208. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.4197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spanopoulou E., Giguere V., Grosveld F. The functional domains of the murine Thy-1 gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2216–2228. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanway C., Mellor J., Ogden J. E., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M. The UAS of the yeast PGK gene contains functionally distinct domains. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):6855–6873. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.6855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenlund A., Botchan M. R. The E2 trans-activator can act as a repressor by interfering with a cellular transcription factor. Genes Dev. 1990 Jan;4(1):123–136. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.1.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens P. E., Lewis H. M., Darlison M. G., Guest J. R. Nucleotide sequence of the lipoamide dehydrogenase gene of Escherichia coli K12. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Oct 3;135(3):519–527. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07683.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Genetic properties and chromatin structure of the yeast gal regulatory element: an enhancer-like sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7865–7869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Promoters, activator proteins, and the mechanism of transcriptional initiation in yeast. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):295–297. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90277-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theill L. E., Wiborg O., Vuust J. Cell-specific expression of the human gastrin gene: evidence for a control element located downstream of the TATA box. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4329–4336. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tornow J., Santangelo G. M. Efficient expression of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae glycolytic gene ADH1 is dependent upon a cis-acting regulatory element (UASRPG) found initially in genes encoding ribosomal proteins. Gene. 1990 May 31;90(1):79–85. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90441-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Türkel S., Farabaugh P. J. Interspersion of an unusual GCN4 activation site with a complex transcriptional repression site in Ty2 elements of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2091–2103. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vettakkorumakankav N. N., Stevenson K. J. Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase from Haloferax volcanii: gene cloning, complete primary structure, and comparison to other dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenases. Biochem Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;70(8):656–663. doi: 10.1139/o92-101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent A. C., Struhl K. ACR1, a yeast ATF/CREB repressor. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5394–5405. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaman Z., Brown A. J., Dawes I. W. A 3' transcriptional enhancer within the coding sequence of a yeast gene encoding the common subunit of two multi-enzyme complexes. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Jan;6(2):239–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb02005.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawel L., Reinberg D. Advances in RNA polymerase II transcription. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;4(3):488–495. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]