Abstract
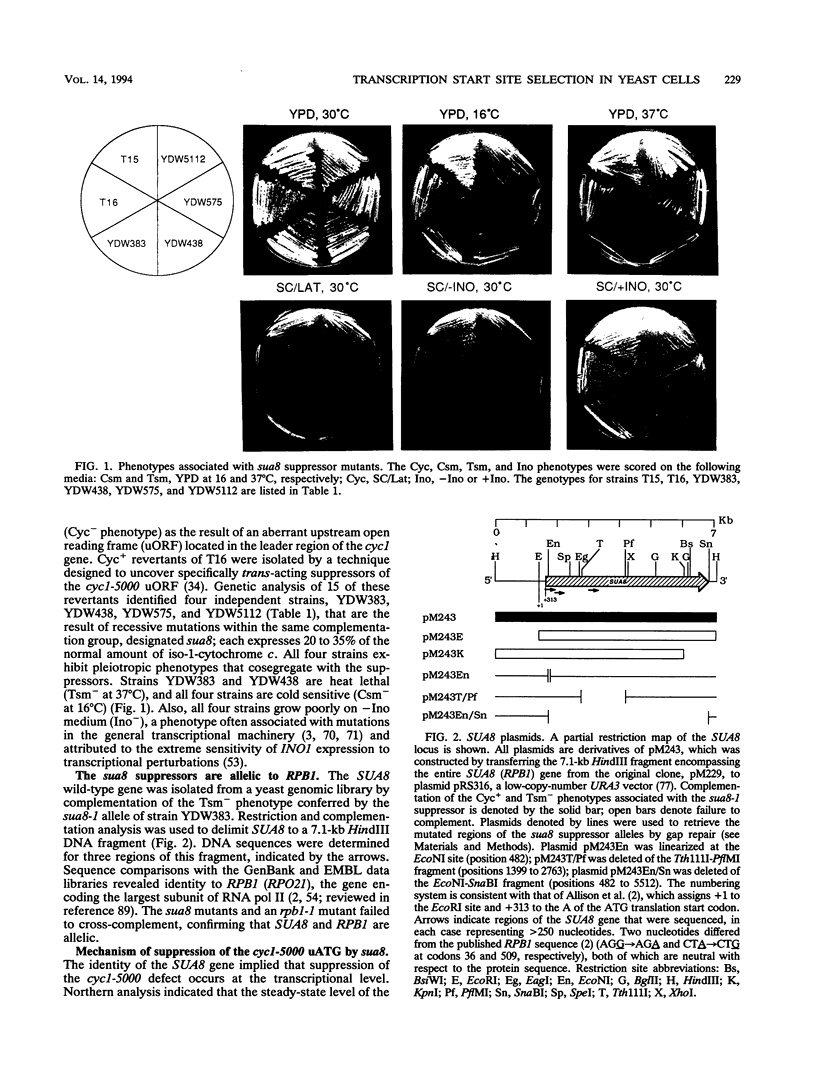
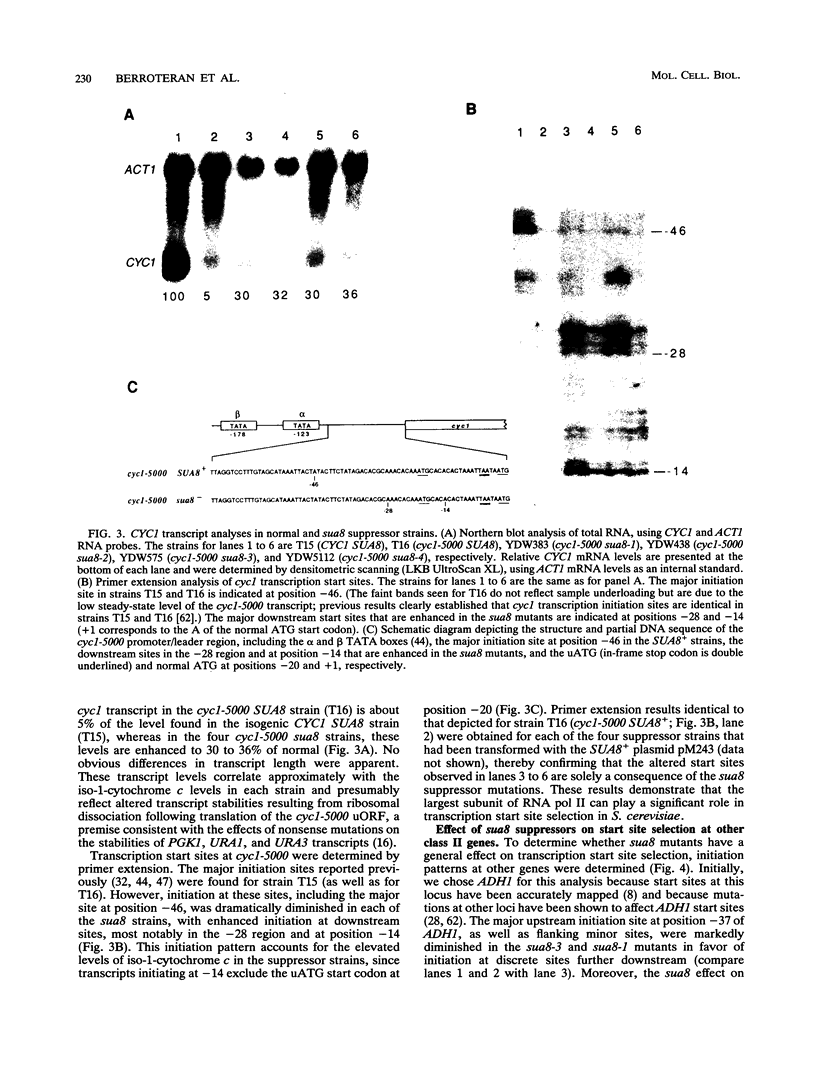
Mutations in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae sua8 gene were found to be suppressors of an aberrant ATG translation initiation codon in the leader region of the cyc1 gene. Analysis of cyc1 transcripts from sua8 mutants revealed that suppression is a consequence of diminished transcription initiation at the normal start sites in favor of initiation at downstream sites, including a site between the aberrant and normal ATG start codons. This effect is not cyc1 gene specific since initiation at other genes, including ADH1, CYC7, and HIS4, was similarly affected, although initiation at HIS3 and SPT15 was unaffected. The SUA8 gene was cloned and partially sequenced, revealing identity to RPB1, which encodes the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II. The sua8 suppressors are the result of single amino acid replacements of highly conserved residues. Three replacements were found either within or immediately preceding homology block D, and a fourth was found adjacent to homology block H, indicating that these regions play a role in defining start sites in vivo. Nearly identical effects on start site selection were observed for sua7 suppressors, which encode altered forms of TFIIB. Synthetic lethality was associated with double sua7 sua8 suppressor mutations, and recessive sua7 mutants failed to fully complement recessive sua8 mutants in heterozygous diploids (nonallelic noncomplementation). These data indicate that the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II and TFIIB are important determinants of transcription start site selection in S. cerevisiae and suggest that this function might be conferred by interaction between these two proteins.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahearn J. M., Jr, Bartolomei M. S., West M. L., Cisek L. J., Corden J. L. Cloning and sequence analysis of the mouse genomic locus encoding the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10695–10705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison L. A., Moyle M., Shales M., Ingles C. J. Extensive homology among the largest subunits of eukaryotic and prokaryotic RNA polymerases. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):599–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90117-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arndt K. T., Styles C. A., Fink G. R. A suppressor of a HIS4 transcriptional defect encodes a protein with homology to the catalytic subunit of protein phosphatases. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):527–537. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90576-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayer D. E., Dynan W. S. Simian virus 40 major late promoter: a novel tripartite structure that includes intragenic sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2021–2033. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barberis A., Müller C. W., Harrison S. C., Ptashne M. Delineation of two functional regions of transcription factor TFIIB. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5628–5632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaupain D., Eléouët J. F., Roméo P. H. Initiation of transcription of the erythroid promoter of the porphobilinogen deaminase gene is regulated by a cis-acting sequence around the cap site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6509–6515. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennetzen J. L., Hall B. D. The primary structure of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene for alcohol dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3018–3025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., Chambon P. In vivo sequence requirements of the SV40 early promotor region. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):304–310. doi: 10.1038/290304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berghöfer B., Kröckel L., Körtner C., Truss M., Schallenberg J., Klein A. Relatedness of archaebacterial RNA polymerase core subunits to their eubacterial and eukaryotic equivalents. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 25;16(16):8113–8128. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.16.8113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bielinska A., Krasnow S., Nabel G. J. NF-kappa B-mediated activation of the human immunodeficiency virus enhancer: site of transcriptional initiation is independent of the TATA box. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):4097–4100. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.4097-4100.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird D. M., Riddle D. L. Molecular cloning and sequencing of ama-1, the gene encoding the largest subunit of Caenorhabditis elegans RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4119–4130. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., LaCroute F., Fink G. R. A positive selection for mutants lacking orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase activity in yeast: 5-fluoro-orotic acid resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(2):345–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00330984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs M. R., Kadonaga J. T., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Purification and biochemical characterization of the promoter-specific transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):47–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3529394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. J. Messenger RNA stability in yeast. Yeast. 1989 Jul-Aug;5(4):239–257. doi: 10.1002/yea.320050405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski S., Hahn S., Guarente L., Sharp P. A. Five intermediate complexes in transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):549–561. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90578-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski S., Zhou H. A suppressor of TBP mutations encodes an RNA polymerase III transcription factor with homology to TFIIB. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):221–230. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90351-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski S., Zhou H. Functional domains of transcription factor TFIIB. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5633–5637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carcamo J., Buckbinder L., Reinberg D. The initiator directs the assembly of a transcription factor IID-dependent transcription complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 15;88(18):8052–8056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.18.8052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carcamo J., Maldonado E., Cortes P., Ahn M. H., Ha I., Kasai Y., Flint J., Reinberg D. A TATA-like sequence located downstream of the transcription initiation site is required for expression of an RNA polymerase II transcribed gene. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1611–1622. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W., Struhl K. Yeast mRNA initiation sites are determined primarily by specific sequences, not by the distance from the TATA element. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3273–3280. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04077.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colbert T., Hahn S. A yeast TFIIB-related factor involved in RNA polymerase III transcription. Genes Dev. 1992 Oct;6(10):1940–1949. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.10.1940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaway R. C., Conaway J. W. General initiation factors for RNA polymerase II. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:161–190. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.001113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corden J., Wasylyk B., Buchwalder A., Sassone-Corsi P., Kedinger C., Chambon P. Promoter sequences of eukaryotic protein-coding genes. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1406–1414. doi: 10.1126/science.6251548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cormack B. P., Struhl K. The TATA-binding protein is required for transcription by all three nuclear RNA polymerases in yeast cells. Cell. 1992 May 15;69(4):685–696. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90232-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fassler J. S., Winston F. Isolation and analysis of a novel class of suppressor of Ty insertion mutations in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1988 Feb;118(2):203–212. doi: 10.1093/genetics/118.2.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furter-Graves E. M., Furter R., Hall B. D. SHI, a new yeast gene affecting the spacing between TATA and transcription initiation sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):4121–4127. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.4121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furter-Graves E. M., Hall B. D. DNA sequence elements required for transcription initiation of the Schizosaccharomyces pombe ADH gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Sep;223(3):407–416. doi: 10.1007/BF00264447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gietz D., St Jean A., Woods R. A., Schiestl R. H. Improved method for high efficiency transformation of intact yeast cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Mar 25;20(6):1425–1425. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.6.1425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ha I., Roberts S., Maldonado E., Sun X., Kim L. U., Green M., Reinberg D. Multiple functional domains of human transcription factor IIB: distinct interactions with two general transcription factors and RNA polymerase II. Genes Dev. 1993 Jun;7(6):1021–1032. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.6.1021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn S., Hoar E. T., Guarente L. Each of three "TATA elements" specifies a subset of the transcription initiation sites at the CYC-1 promoter of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8562–8566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampsey M. A tester system for detecting each of the six base-pair substitutions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by selecting for an essential cysteine in iso-1-cytochrome c. Genetics. 1991 May;128(1):59–67. doi: 10.1093/genetics/128.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampsey M., Na J. G., Pinto I., Ware D. E., Berroteran R. W. Extragenic suppressors of a translation initiation defect in the cyc1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochimie. 1991 Dec;73(12):1445–1455. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90177-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hariharan N., Perry R. P. Functional dissection of a mouse ribosomal protein promoter: significance of the polypyrimidine initiator and an element in the TATA-box region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1526–1530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Healy A. M., Helser T. L., Zitomer R. S. Sequences required for transcriptional initiation of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae CYC7 genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3785–3791. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hekmatpanah D. S., Young R. A. Mutations in a conserved region of RNA polymerase II influence the accuracy of mRNA start site selection. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5781–5791. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnebusch A. G. Mechanisms of gene regulation in the general control of amino acid biosynthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Jun;52(2):248–273. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.2.248-273.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman C. S., Winston F. A ten-minute DNA preparation from yeast efficiently releases autonomous plasmids for transformation of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1987;57(2-3):267–272. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jokerst R. S., Weeks J. R., Zehring W. A., Greenleaf A. L. Analysis of the gene encoding the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II in Drosophila. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Jan;215(2):266–275. doi: 10.1007/BF00339727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Courey A. J., Ladika J., Tjian R. Distinct regions of Sp1 modulate DNA binding and transcriptional activation. Science. 1988 Dec 16;242(4885):1566–1570. doi: 10.1126/science.3059495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W. Z., Sherman F. Two types of TATA elements for the CYC1 gene of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):666–676. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil J. B., Smith M. Saccharomyces cerevisiae CYC1 mRNA 5'-end positioning: analysis by in vitro mutagenesis, using synthetic duplexes with random mismatch base pairs. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3545–3551. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil J. B., Smith M. Transcription initiation of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae iso-1-cytochrome c gene. Multiple, independent T-A-T-A sequences. J Mol Biol. 1986 Feb 5;187(3):363–378. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90439-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Means A. L., Farnham P. J. Transcription initiation from the dihydrofolate reductase promoter is positioned by HIP1 binding at the initiation site. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):653–661. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mémet S., Gouy M., Marck C., Sentenac A., Buhler J. M. RPA190, the gene coding for the largest subunit of yeast RNA polymerase A. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2830–2839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Na J. G., Pinto I., Hampsey M. Isolation and characterization of SUA5, a novel gene required for normal growth in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1992 Aug;131(4):791–801. doi: 10.1093/genetics/131.4.791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagawa F., Fink G. R. The relationship between the "TATA" sequence and transcription initiation sites at the HIS4 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8557–8561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawrath C., Schell J., Koncz C. Homologous domains of the largest subunit of eucaryotic RNA polymerase II are conserved in plants. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Aug;223(1):65–75. doi: 10.1007/BF00315798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikoloff D. M., Henry S. A. Genetic analysis of yeast phospholipid biosynthesis. Annu Rev Genet. 1991;25:559–583. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.25.120191.003015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonet M., Scafe C., Sexton J., Young R. Eucaryotic RNA polymerase conditional mutant that rapidly ceases mRNA synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1602–1611. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea-Greenfield A., Smale S. T. Roles of TATA and initiator elements in determining the start site location and direction of RNA polymerase II transcription. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):1391–1402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogden J. E., Stanway C., Kim S., Mellor J., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M. Efficient expression of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae PGK gene depends on an upstream activation sequence but does not require TATA sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4335–4343. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov YuA, Monastyrskaya G. S., Gubanov V. V., Guryev S. O., Salomatina I. S., Shuvaeva T. M., Lipkin V. M., Sverdlov E. D. The primary structure of E. coli RNA polymerase, Nucleotide sequence of the rpoC gene and amino acid sequence of the beta'-subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jul 10;10(13):4035–4044. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.13.4035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parvin J. D., Sharp P. A. DNA topology and a minimal set of basal factors for transcription by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):533–540. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90140-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C. L., Kruger W., Herskowitz I. A functional interaction between the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II and the negative regulator SIN1. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1135–1143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90268-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinto I., Na J. G., Sherman F., Hampsey M. cis- and trans-acting suppressors of a translation initiation defect at the cyc1 locus of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1992 Sep;132(1):97–112. doi: 10.1093/genetics/132.1.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinto I., Ware D. E., Hampsey M. The yeast SUA7 gene encodes a homolog of human transcription factor TFIIB and is required for normal start site selection in vivo. Cell. 1992 Mar 6;68(5):977–988. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90040-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. D., Novick P., Thomas J. H., Botstein D., Fink G. R. A Saccharomyces cerevisiae genomic plasmid bank based on a centromere-containing shuttle vector. Gene. 1987;60(2-3):237–243. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90232-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. Targeting, disruption, replacement, and allele rescue: integrative DNA transformation in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:281–301. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94022-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy A. L., Meisterernst M., Pognonec P., Roeder R. G. Cooperative interaction of an initiator-binding transcription initiation factor and the helix-loop-helix activator USF. Nature. 1991 Nov 21;354(6350):245–248. doi: 10.1038/354245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph H., Hinnen A. The yeast PHO5 promoter: phosphate-control elements and sequences mediating mRNA start-site selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1340–1344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHERMAN F., SLONIMSKI P. P. RESPIRATION-DEFICIENT MUTANTS OF YEAST. II. BIOCHEMISTRY. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jul 15;90:1–15. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs A. B., Davis R. W. The poly(A) binding protein is required for poly(A) shortening and 60S ribosomal subunit-dependent translation initiation. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):857–867. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90938-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scafe C., Chao D., Lopes J., Hirsch J. P., Henry S., Young R. A. RNA polymerase II C-terminal repeat influences response to transcriptional enhancer signals. Nature. 1990 Oct 4;347(6292):491–494. doi: 10.1038/347491a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scafe C., Martin C., Nonet M., Podos S., Okamura S., Young R. A. Conditional mutations occur predominantly in highly conserved residues of RNA polymerase II subunits. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1270–1275. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scafe C., Nonet M., Young R. A. RNA polymerase II mutants defective in transcription of a subset of genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1010–1016. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz M. C., Reeder R. H., Hahn S. Variants of the TATA-binding protein can distinguish subsets of RNA polymerase I, II, and III promoters. Cell. 1992 May 15;69(4):697–702. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90233-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto E., Shi Y., Shenk T. YY1 is an initiator sequence-binding protein that directs and activates transcription in vitro. Nature. 1991 Nov 21;354(6350):241–245. doi: 10.1038/354241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman F. Getting started with yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:3–21. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94004-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman F., Hicks J. Micromanipulation and dissection of asci. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:21–37. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94005-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Baltimore D. The "initiator" as a transcription control element. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Schmidt M. C., Berk A. J., Baltimore D. Transcriptional activation by Sp1 as directed through TATA or initiator: specific requirement for mammalian transcription factor IID. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4509–4513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stearns T., Botstein D. Unlinked noncomplementation: isolation of new conditional-lethal mutations in each of the tubulin genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1988 Jun;119(2):249–260. doi: 10.1093/genetics/119.2.249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Nucleotide sequence and transcriptional mapping of the yeast pet56-his3-ded1 gene region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 9;13(23):8587–8601. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.23.8587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschochner H., Sayre M. H., Flanagan P. M., Feaver W. J., Kornberg R. D. Yeast RNA polymerase II initiation factor e: isolation and identification as the functional counterpart of human transcription factor IIB. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11292–11296. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke M. W., Roeder R. G., Sawadogo M. Physical analysis of transcription preinitiation complex assembly on a class II gene promoter. Science. 1988 Sep 9;241(4871):1335–1338. doi: 10.1126/science.3413495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston F., Chaleff D. T., Valent B., Fink G. R. Mutations affecting Ty-mediated expression of the HIS4 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1984 Jun;107(2):179–197. doi: 10.1093/genetics/107.2.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woychik N. A., McKune K., Lane W. S., Young R. A. Yeast RNA polymerase II subunit RPB11 is related to a subunit shared by RNA polymerase I and III. Gene Expr. 1993;3(1):77–82. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L., Berk A. J. Transcriptional activation by the pseudorabies virus immediate early protein requires the TATA box element in the adenovirus 2 E1B promoter. Virology. 1988 Nov;167(1):318–322. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90089-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano R., Yura T. Suppression of the Escherichia coli rpoH opal mutation by ribosomes lacking S15 protein. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1712–1717. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1712-1717.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A. RNA polymerase II. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:689–715. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.003353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalkin H., Paluh J. L., van Cleemput M., Moye W. S., Yanofsky C. Nucleotide sequence of Saccharomyces cerevisiae genes TRP2 and TRP3 encoding bifunctional anthranilate synthase: indole-3-glycerol phosphate synthase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3985–3992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawel L., Reinberg D. Advances in RNA polymerase II transcription. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;4(3):488–495. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenzie-Gregory B., Khachi A., Garraway I. P., Smale S. T. Mechanism of initiator-mediated transcription: evidence for a functional interaction between the TATA-binding protein and DNA in the absence of a specific recognition sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):3841–3849. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.3841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]