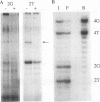
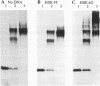
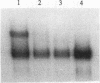
Abstract
The heat shock transcription factor (HSF) is a trimer that binds to DNA containing inverted repeats of the sequence nGAAn. HSF can bind DNA with the sequence nGAAnnTTCn or with the sequence nTTCnnGAAn, with little preference for either sequence over the other. However, (nGAAnnTTCn)2 is considerably less active as a heat shock response element (HSE) than is (nTTCnnGAAn)2. The electrophoretic mobilities of DNA-protein complexes and chemical cross-linking between protein monomers indicate that the sequence (nGAAnnTTCn)2 is capable of binding a single HSF trimer. In contrast, the sequence with higher biological activity, (nTTCnnGAAn)2, is capable of binding two trimers. Thus, the ability of four-nGAAn-element HSEs to bind one or two trimers depends on the permutation with which the elements are presented. A survey of naturally occurring HSEs shows the sequence (nTTCnnGAAn)2 to be the more prevalent. We suggest that the greater ability of one permutation over the other to bind two HSF trimers accounts for the initial identification of the naturally occurring heat shock consensus sequence as a region of dyad symmetry.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abravaya K., Myers M. P., Murphy S. P., Morimoto R. I. The human heat shock protein hsp70 interacts with HSF, the transcription factor that regulates heat shock gene expression. Genes Dev. 1992 Jul;6(7):1153–1164. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.7.1153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amin J., Ananthan J., Voellmy R. Key features of heat shock regulatory elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3761–3769. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amin J., Mestril R., Lawson R., Klapper H., Voellmy R. The heat shock consensus sequence is not sufficient for hsp70 gene expression in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):197–203. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson L. -O., Borg H., Mikaelsson M. Molecular weight estimations of proteins by electrophoresis in polyacrylamide gels of graded porosity. FEBS Lett. 1972 Feb 1;20(2):199–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80793-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baler R., Dahl G., Voellmy R. Activation of human heat shock genes is accompanied by oligomerization, modification, and rapid translocation of heat shock transcription factor HSF1. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2486–2496. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clos J., Westwood J. T., Becker P. B., Wilson S., Lambert K., Wu C. Molecular cloning and expression of a hexameric Drosophila heat shock factor subject to negative regulation. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):1085–1097. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90511-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen R. S., Meselson M. Periodic interactions of heat shock transcriptional elements. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):856–858. doi: 10.1038/332856a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elble R. A simple and efficient procedure for transformation of yeasts. Biotechniques. 1992 Jul;13(1):18–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellwood M. S., Craig E. A. Differential regulation of the 70K heat shock gene and related genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1454–1459. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Mason T. Heme regulates transcription of the CYC1 gene of S. cerevisiae via an upstream activation site. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1279–1286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90309-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobsen B. K., Pelham H. R. Constitutive binding of yeast heat shock factor to DNA in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):5040–5042. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.5040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. W. Tackling the protease problem in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:428–453. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94034-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopczynski J. B., Raff A. C., Bonner J. J. Translational readthrough at nonsense mutations in the HSF1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Sep;234(3):369–378. doi: 10.1007/BF00538696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu-Johnson H. N., Gartenberg M. R., Crothers D. M. The DNA binding domain and bending angle of E. coli CAP protein. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):995–1005. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90814-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto R. I. Cells in stress: transcriptional activation of heat shock genes. Science. 1993 Mar 5;259(5100):1409–1410. doi: 10.1126/science.8451637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. A regulatory upstream promoter element in the Drosophila hsp 70 heat-shock gene. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):517–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90249-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perisic O., Xiao H., Lis J. T. Stable binding of Drosophila heat shock factor to head-to-head and tail-to-tail repeats of a conserved 5 bp recognition unit. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):797–806. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90603-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabindran S. K., Haroun R. I., Clos J., Wisniewski J., Wu C. Regulation of heat shock factor trimer formation: role of a conserved leucine zipper. Science. 1993 Jan 8;259(5092):230–234. doi: 10.1126/science.8421783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuey D. J., Parker C. S. Binding of Drosophila heat-shock gene transcription factor to the hsp 70 promoter. Evidence for symmetric and dynamic interactions. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):7934–7940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater M. R., Craig E. A. Transcriptional regulation of an hsp70 heat shock gene in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1906–1916. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Nelson H. C. Trimerization of a yeast transcriptional activator via a coiled-coil motif. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):807–813. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90604-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Pelham H. R. Purification and characterization of a heat-shock element binding protein from yeast. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3035–3041. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02609.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topol J., Ruden D. M., Parker C. S. Sequences required for in vitro transcriptional activation of a Drosophila hsp 70 gene. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):527–537. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90110-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei R., Wilkinson H., Pfeifer K., Schneider C., Young R., Guarente L. Two or more copies of Drosophila heat shock consensus sequence serve to activate transcription in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 24;14(20):8183–8188. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.20.8183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westwood J. T., Clos J., Wu C. Stress-induced oligomerization and chromosomal relocalization of heat-shock factor. Nature. 1991 Oct 31;353(6347):822–827. doi: 10.1038/353822a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiederrecht G., Seto D., Parker C. S. Isolation of the gene encoding the S. cerevisiae heat shock transcription factor. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):841–853. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91197-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao H., Lis J. T. Germline transformation used to define key features of heat-shock response elements. Science. 1988 Mar 4;239(4844):1139–1142. doi: 10.1126/science.3125608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao H., Perisic O., Lis J. T. Cooperative binding of Drosophila heat shock factor to arrays of a conserved 5 bp unit. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):585–593. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90242-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]