Abstract
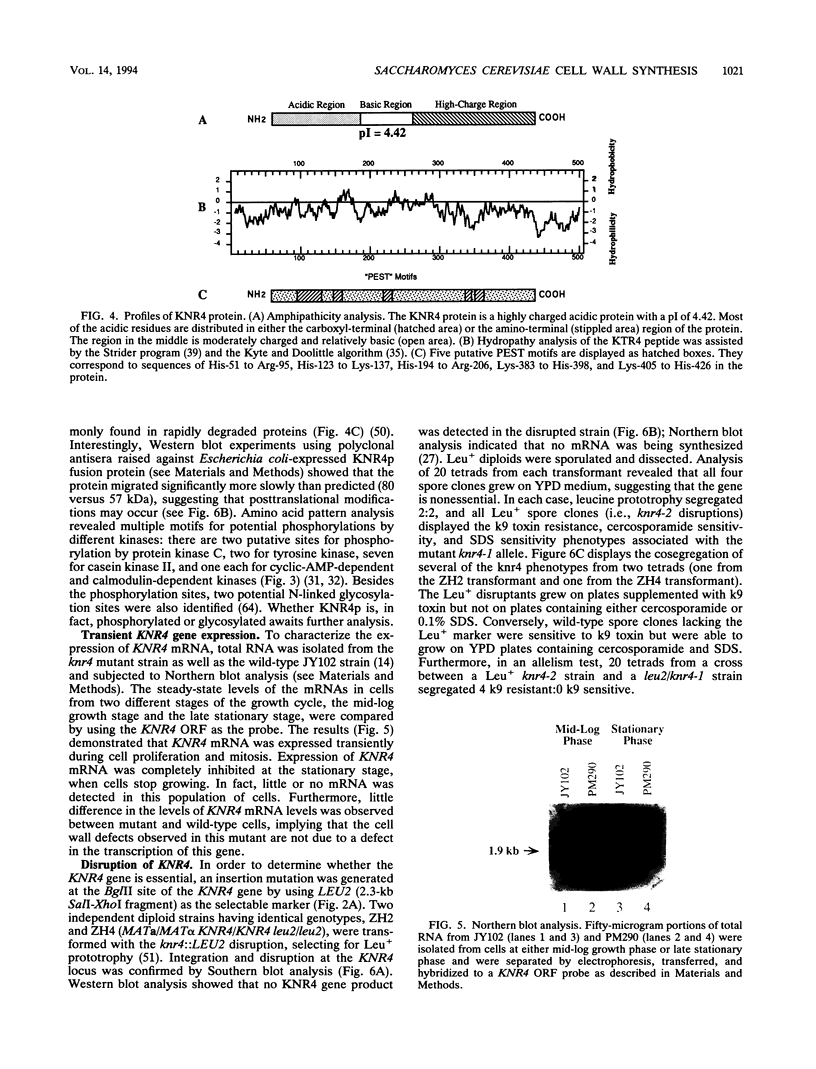
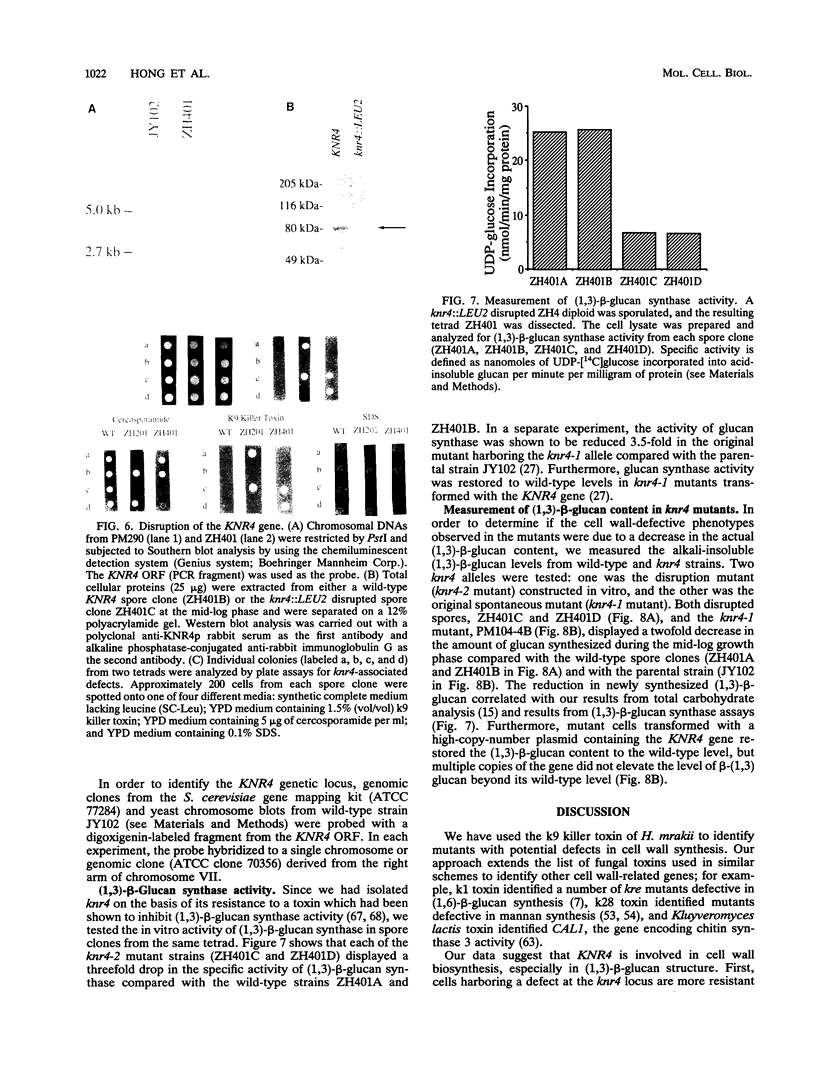
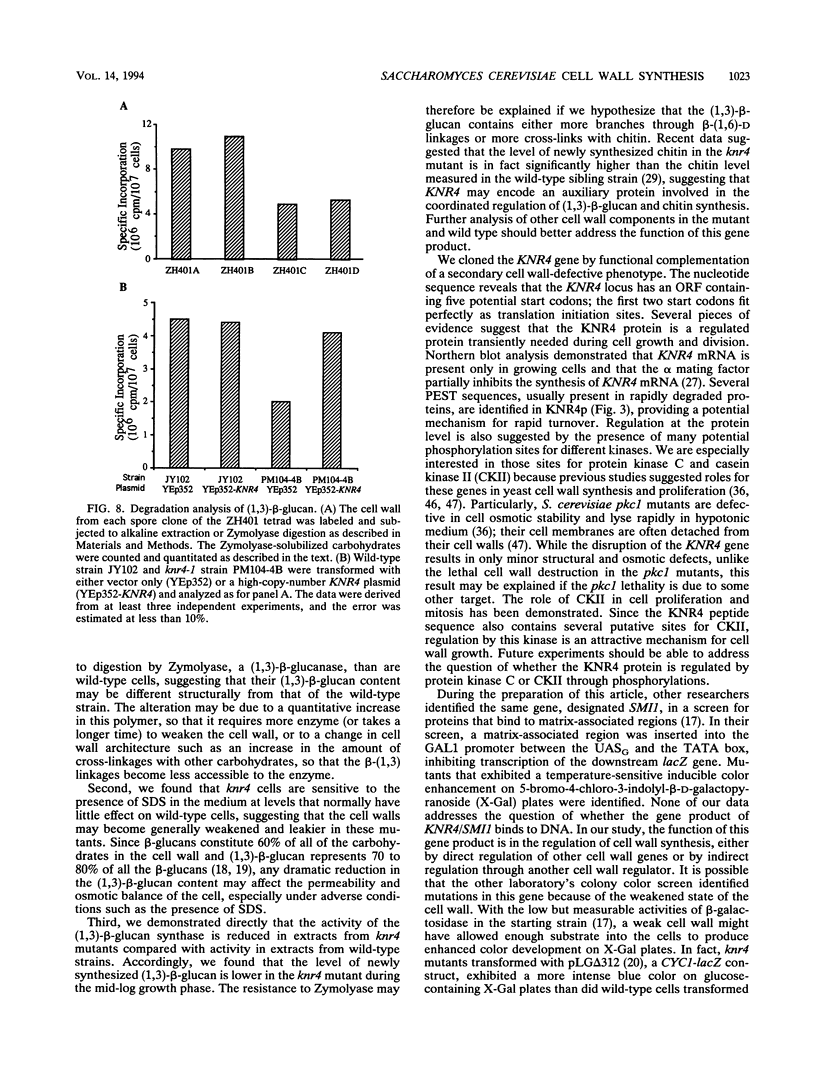
k9 killer toxin from Hansenula mrakii was used to select a number of resistant mutants from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Preliminary biochemical and genetic studies showed that some of them acquired structural defects in the cell wall. One of these mutants, the knr4-1 mutant, displays a number of cell wall defects, including osmotic sensitivity; sensitivity to cercosporamide, a known antifungal agent; and resistance to Zymolyase, a (1,3)-beta-glucanase. We report here the isolation and analysis of the KNR4 gene. DNA sequence analysis revealed an uninterrupted open reading frame which contains five potential start codons. The longest coding template encodes a protein of 505 amino acids with a calculated molecular mass of 57,044 Da. A data base search revealed 100% identity with a nuclear protein, SMI1p. Disruption of the KNR4 locus does not result in cell death; however, it leads to reduced levels of both (1,3)-beta-glucan synthase activity and (1,3)-beta-glucan content in the cell wall. The gene was mapped to the right arm of chromosome VII.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Al-Aidroos K., Bussey H. Chromosomal mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae affecting the cell wall binding site for killer factor. Can J Microbiol. 1978 Mar;24(3):228–237. doi: 10.1139/m78-041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacon J. S., Gordon A. H., Jones D., Taylor I. F., Webley D. M. The separation of beta-glucanases produced by Cytophaga johnsonii and their role in the lysis of yeast cell walls. Biochem J. 1970 Nov;120(1):67–78. doi: 10.1042/bj1200067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boone C., Sdicu A., Laroche M., Bussey H. Isolation from Candida albicans of a functional homolog of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae KRE1 gene, which is involved in cell wall beta-glucan synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Nov;173(21):6859–6864. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.21.6859-6864.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boone C., Sommer S. S., Hensel A., Bussey H. Yeast KRE genes provide evidence for a pathway of cell wall beta-glucan assembly. J Cell Biol. 1990 May;110(5):1833–1843. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.5.1833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. L., Kossaczka Z., Jiang B., Bussey H. A mutational analysis of killer toxin resistance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae identifies new genes involved in cell wall (1-->6)-beta-glucan synthesis. Genetics. 1993 Apr;133(4):837–849. doi: 10.1093/genetics/133.4.837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulawa C. E. CSD2, CSD3, and CSD4, genes required for chitin synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: the CSD2 gene product is related to chitin synthases and to developmentally regulated proteins in Rhizobium species and Xenopus laevis. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1764–1776. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulawa C. E., Osmond B. C. Chitin synthase I and chitin synthase II are not required for chitin synthesis in vivo in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7424–7428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabib E., Bowers B., Sburlati A., Silverman S. J. Fungal cell wall synthesis: the construction of a biological structure. Microbiol Sci. 1988 Dec;5(12):370–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabib E., Kang M. S. Fungal 1,3-beta-glucan synthase. Methods Enzymol. 1987;138:637–642. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)38057-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabib E., Roberts R., Bowers B. Synthesis of the yeast cell wall and its regulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:763–793. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.003555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carle G. F., Olson M. V. An electrophoretic karyotype for yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3756–3760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Botstein D. Two differentially regulated mRNAs with different 5' ends encode secreted with intracellular forms of yeast invertase. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90384-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dower W. J., Miller J. F., Ragsdale C. W. High efficiency transformation of E. coli by high voltage electroporation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):6127–6145. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.6127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishel B. R., Sperry A. O., Garrard W. T. Yeast calmodulin and a conserved nuclear protein participate in the in vivo binding of a matrix association region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5623–5627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleet G. H., Manners D. J. Isolation and composition of an alkali-soluble glucan from the cell walls of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 May;94(1):180–192. doi: 10.1099/00221287-94-1-180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Lalonde B., Gifford P., Alani E. Distinctly regulated tandem upstream activation sites mediate catabolite repression of the CYC1 gene of S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):503–511. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90243-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn S., Hoar E. T., Guarente L. Each of three "TATA elements" specifies a subset of the transcription initiation sites at the CYC-1 promoter of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8562–8566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartland R. P., Emerson G. W., Sullivan P. A. A secreted beta-glucan-branching enzyme from Candida albicans. Proc Biol Sci. 1991 Nov 22;246(1316):155–160. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1991.0138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J. E., Myers A. M., Koerner T. J., Tzagoloff A. Yeast/E. coli shuttle vectors with multiple unique restriction sites. Yeast. 1986 Sep;2(3):163–167. doi: 10.1002/yea.320020304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnen A., Hicks J. B., Fink G. R. Transformation of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1929–1933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman C. S., Winston F. A ten-minute DNA preparation from yeast efficiently releases autonomous plasmids for transformation of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1987;57(2-3):267–272. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang M. S., Cabib E. Regulation of fungal cell wall growth: a guanine nucleotide-binding, proteinaceous component required for activity of (1----3)-beta-D-glucan synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5808–5812. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp B. E., Pearson R. B. Protein kinase recognition sequence motifs. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Sep;15(9):342–346. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90073-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennelly P. J., Krebs E. G. Consensus sequences as substrate specificity determinants for protein kinases and protein phosphatases. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15555–15558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebl F., Tanner W. Molecular cloning of a cell wall exo-beta-1,3-glucanase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6259–6264. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6259-6264.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Possible role of flanking nucleotides in recognition of the AUG initiator codon by eukaryotic ribosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5233–5252. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D. E., Bartlett-Heubusch E. Mutants in the S. cerevisiae PKC1 gene display a cell cycle-specific osmotic stability defect. J Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;116(5):1221–1229. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.5.1221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manners D. J., Masson A. J., Patterson J. C., Björndal H., Lindberg B. The structure of a beta-(1--6)-D-glucan from yeast cell walls. Biochem J. 1973 Sep;135(1):31–36. doi: 10.1042/bj1350031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manners D. J., Masson A. J., Patterson J. C. The structure of a beta-(1 leads to 3)-D-glucan from yeast cell walls. Biochem J. 1973 Sep;135(1):19–30. doi: 10.1042/bj1350019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marck C. 'DNA Strider': a 'C' program for the fast analysis of DNA and protein sequences on the Apple Macintosh family of computers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 11;16(5):1829–1836. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.1829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLellan W. L., Jr, McDaniel L. E., Lampen J. O. Purification of phosphomannanase and its action on the yeast cell wall. J Bacteriol. 1970 Apr;102(1):261–270. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.1.261-270.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meaden P., Hill K., Wagner J., Slipetz D., Sommer S. S., Bussey H. The yeast KRE5 gene encodes a probable endoplasmic reticulum protein required for (1----6)-beta-D-glucan synthesis and normal cell growth. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):3013–3019. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.3013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molina M., Cenamor R., Nombela C. Exo-1,3-beta-glucanase activity in Candida albicans: effect of the yeast-to-mycelium transition. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Mar;133(3):609–617. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-3-609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebreda A. R., Villa T. G., Villanueva J. R., del Rey F. Cloning of genes related to exo-beta-glucanase production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: characterization of an exo-beta-glucanase structural gene. Gene. 1986;47(2-3):245–259. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90068-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padmanabha R., Chen-Wu J. L., Hanna D. E., Glover C. V. Isolation, sequencing, and disruption of the yeast CKA2 gene: casein kinase II is essential for viability in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4089–4099. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paravicini G., Cooper M., Friedli L., Smith D. J., Carpentier J. L., Klig L. S., Payton M. A. The osmotic integrity of the yeast cell requires a functional PKC1 gene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;12(11):4896–4905. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.11.4896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribas J. C., Diaz M., Duran A., Perez P. Isolation and characterization of Schizosaccharomyces pombe mutants defective in cell wall (1-3)beta-D-glucan. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(11):3456–3462. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.11.3456-3462.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roemer T., Bussey H. Yeast beta-glucan synthesis: KRE6 encodes a predicted type II membrane protein required for glucan synthesis in vivo and for glucan synthase activity in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11295–11299. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers S., Wells R., Rechsteiner M. Amino acid sequences common to rapidly degraded proteins: the PEST hypothesis. Science. 1986 Oct 17;234(4774):364–368. doi: 10.1126/science.2876518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- San Segundo P., Correa J., Vazquez de Aldana C. R., del Rey F. SSG1, a gene encoding a sporulation-specific 1,3-beta-glucanase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jun;175(12):3823–3837. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.12.3823-3837.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt M., Radler F. Mannoprotein of the yeast cell wall as primary receptor for the killer toxin of Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain 28. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Dec;133(12):3347–3354. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-12-3347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt M., Radler F. Molecular structure of the cell wall receptor for killer toxin KT28 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1988 May;170(5):2192–2196. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.5.2192-2196.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiota M., Nakajima T., Satoh A., Shida M., Matsuda K. Comparison of beta-glucan structures in a cell wall mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and the wild type. J Biochem. 1985 Nov;98(5):1301–1307. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sietsma J. H., Wessels J. G. Solubility of (1 leads to 3)-beta-D/(1 leads to 6)-beta-D-glucan in fungal walls: importance of presumed linkage between glucan and chitin. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Jul;125(1):209–212. doi: 10.1099/00221287-125-1-209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sietsma J. H., Wessels J. G. The occurrence of glucosaminoglycan in the wall of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Nov;136(11):2261–2265. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-11-2261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. The yeast his3 promoter contains at least two distinct elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7385–7389. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surarit R., Gopal P. K., Shepherd M. G. Evidence for a glycosidic linkage between chitin and glucan in the cell wall of Candida albicans. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Jun;134(6):1723–1730. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-6-1723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takita M. A., Castilho-Valavicius B. Absence of cell wall chitin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae leads to resistance to Kluyveromyces lactis killer toxin. Yeast. 1993 Jun;9(6):589–598. doi: 10.1002/yea.320090605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner W., Lehle L. Protein glycosylation in yeast. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Apr 27;906(1):81–99. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(87)90006-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
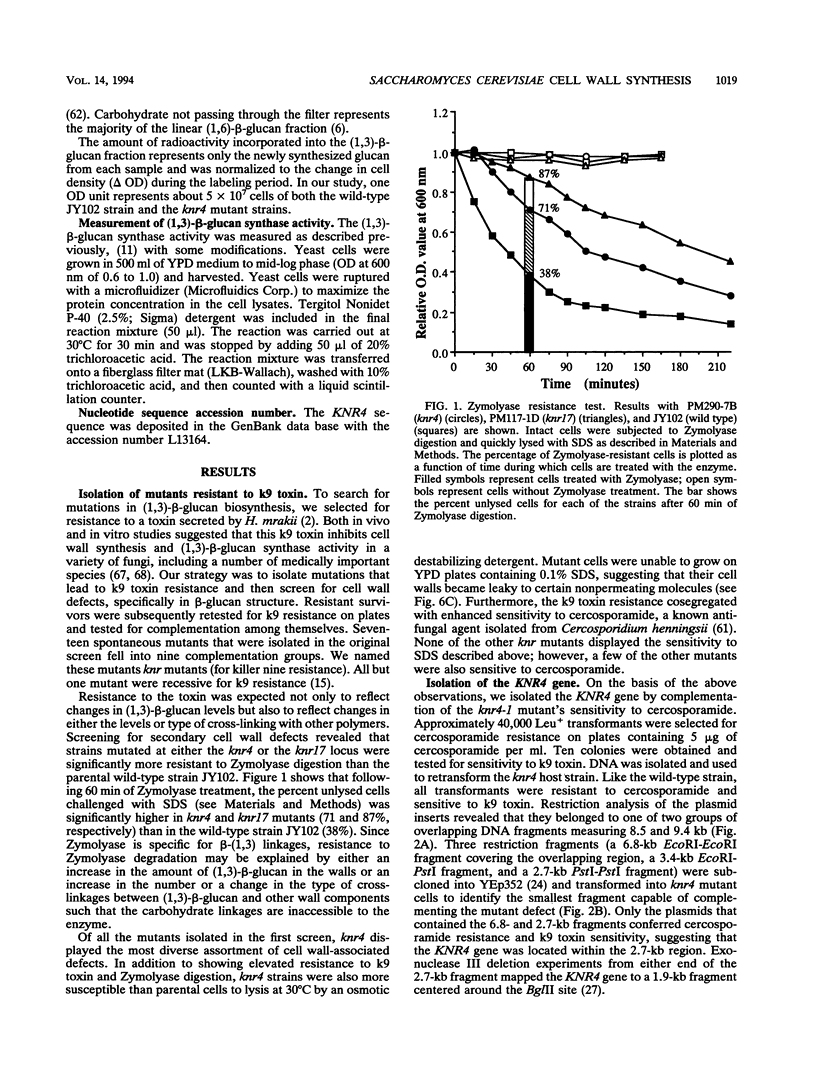
- Vazquez de Aldana C. R., Correa J., San Segundo P., Bueno A., Nebreda A. R., Mendez E., del Rey F. Nucleotide sequence of the exo-1,3-beta-glucanase-encoding gene, EXG1, of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1991 Jan 15;97(2):173–182. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90049-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Hiratani T., Hirata H., Imai M., Yamaguchi H. Killer toxin from Hansenula mrakii selectively inhibits cell wall synthesis in a sensitive yeast. FEBS Lett. 1986 Mar 3;197(1-2):50–54. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80296-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Uchida K., Hiratani T., Miyazaki T., Yagiu J., Yamaguchi H. In vitro activity of the killer toxin from yeast Hansenula mrakii against yeasts and molds. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1988 Mar;41(3):398–403. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.41.398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaret K. S., Sherman F. DNA sequence required for efficient transcription termination in yeast. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):563–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zlotnik H., Fernandez M. P., Bowers B., Cabib E. Saccharomyces cerevisiae mannoproteins form an external cell wall layer that determines wall porosity. J Bacteriol. 1984 Sep;159(3):1018–1026. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.3.1018-1026.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]