Abstract
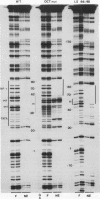
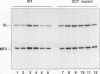
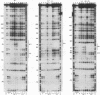
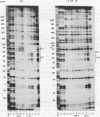
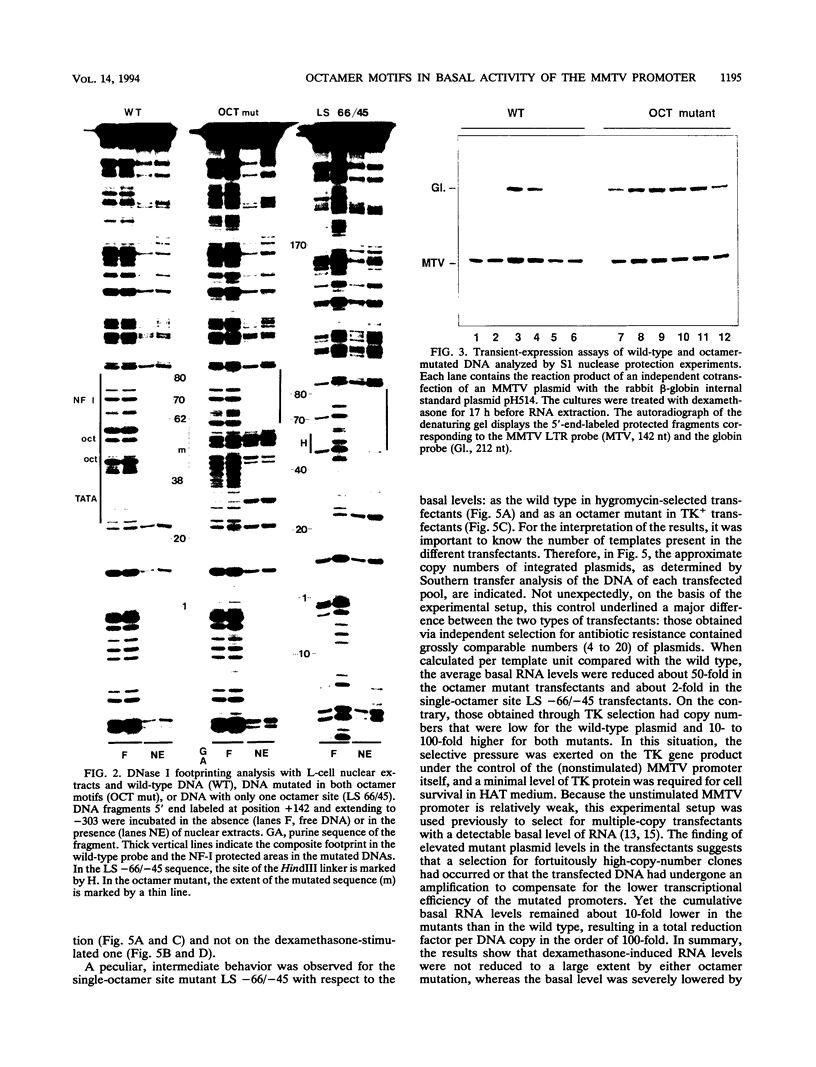
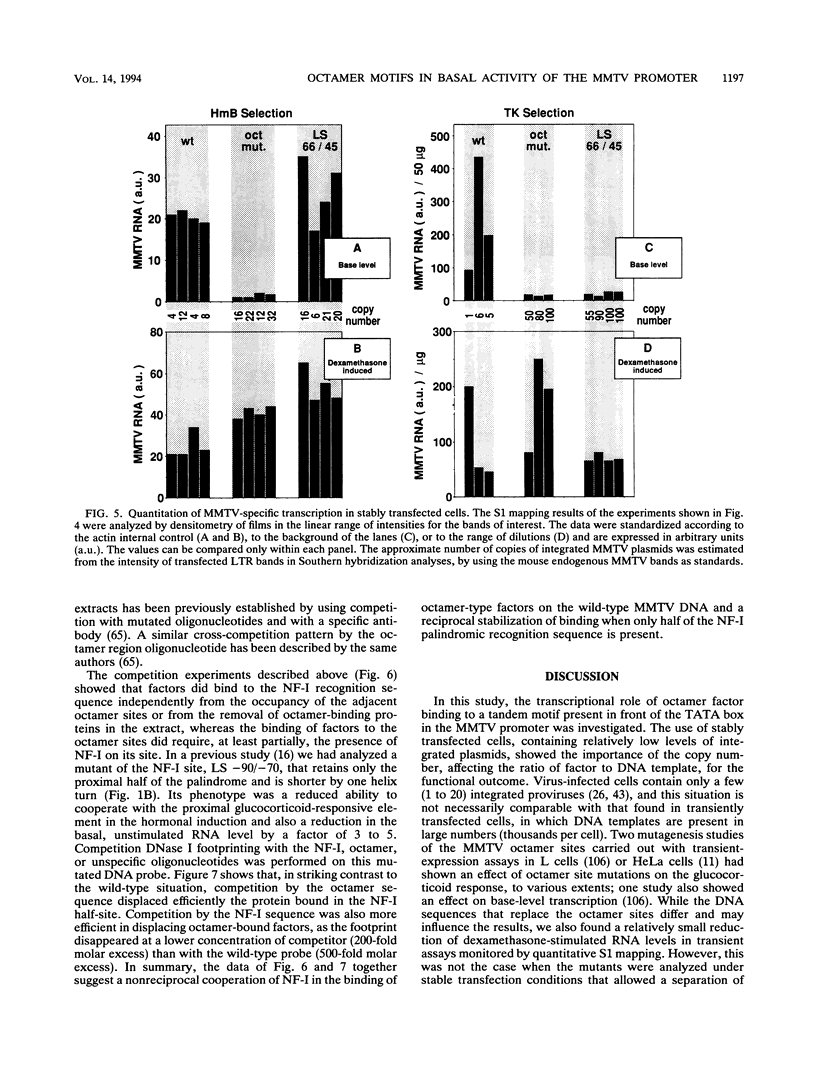
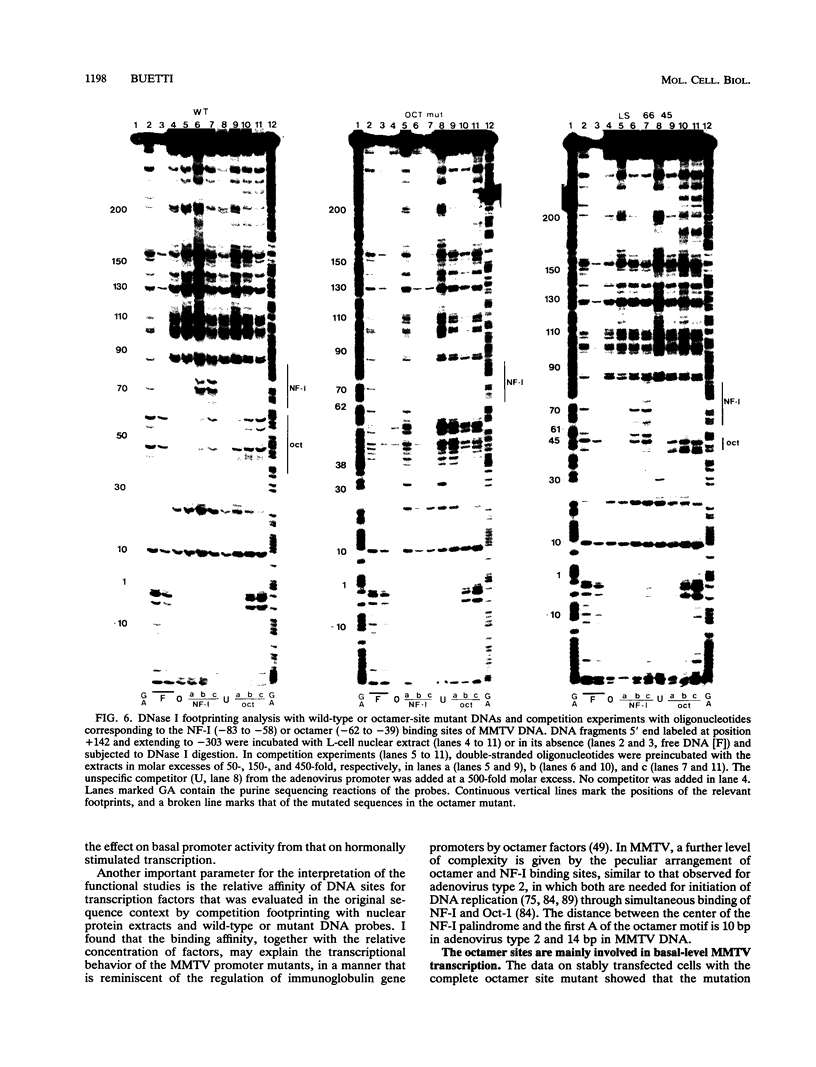
In the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter, a tandem of octamer motifs, recognized by ubiquitous and tissue-restricted Oct transcription factors, is located upstream of the TATA box and next to a binding site for the transcription factor nuclear factor I (NF-I). Their function was investigated with mutant long terminal repeats under different transfection conditions in mouse Ltk- cells and quantitative S1 nuclease mapping of the transcripts. In stable transfectants, which are most representative of the state of proviral DNA with respect to both number of integrated DNA templates and chromatin organization, a long terminal repeat mutant of both octamer sites showed an average 50-fold reduction of the basal transcription level, while the dexamethasone-stimulated level was unaffected. DNase I in vitro footprinting assays with L-cell nuclear protein extracts showed that the mutant DNA was unable to bind octamer factors but had a normal footprint in the NF-I site. I conclude that mouse mammary tumor virus employs the tandem octamer motifs of the viral promoter, recognized by the ubiquitous transcription factor Oct-1, for its basal transcriptional activity and the NF-I binding site, as previously shown, for glucocorticoid-stimulated transcription. A deletion mutant with only one octamer site showed a marked base-level reduction at high copy number but little reduction at low copies of integrated plasmids. The observed transcription levels may depend both on the relative ratio of transcription factors to DNA templates and on the relative affinity of binding sites, as determined by oligonucleotide competition footprinting.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acha-Orbea H., Shakhov A. N., Scarpellino L., Kolb E., Müller V., Vessaz-Shaw A., Fuchs R., Blöchlinger K., Rollini P., Billotte J. Clonal deletion of V beta 14-bearing T cells in mice transgenic for mammary tumour virus. Nature. 1991 Mar 21;350(6315):207–211. doi: 10.1038/350207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan G. F., Ing N. H., Tsai S. Y., Srinivasan G., Weigel N. L., Thompson E. B., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Synergism between steroid response and promoter elements during cell-free transcription. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 25;266(9):5905–5910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer T. K., Cordingley M. G., Wolford R. G., Hager G. L. Transcription factor access is mediated by accurately positioned nucleosomes on the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):688–698. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer T. K., Lefebvre P., Wolford R. G., Hager G. L. Transcription factor loading on the MMTV promoter: a bimodal mechanism for promoter activation. Science. 1992 Mar 20;255(5051):1573–1576. doi: 10.1126/science.1347958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball J. K., Diggelmann H., Dekaban G. A., Grossi G. F., Semmler R., Waight P. A., Fletcher R. F. Alterations in the U3 region of the long terminal repeat of an infectious thymotropic type B retrovirus. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2985–2993. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2985-2993.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerji J., Olson L., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific cellular enhancer is located downstream of the joining region in immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):729–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerji J., Rusconi S., Schaffner W. Expression of a beta-globin gene is enhanced by remote SV40 DNA sequences. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):299–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90413-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blochlinger K., Diggelmann H. Hygromycin B phosphotransferase as a selectable marker for DNA transfer experiments with higher eucaryotic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2929–2931. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohmann D., Keller W., Dale T., Schöler H. R., Tebb G., Mattaj I. W. A transcription factor which binds to the enhancers of SV40, immunoglobulin heavy chain and U2 snRNA genes. Nature. 1987 Jan 15;325(6101):268–272. doi: 10.1038/325268a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresnick E. H., Rories C., Hager G. L. Evidence that nucleosomes on the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter adopt specific translational positions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Feb 25;20(4):865–870. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.4.865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brüggemeier U., Kalff M., Franke S., Scheidereit C., Beato M. Ubiquitous transcription factor OTF-1 mediates induction of the MMTV promoter through synergistic interaction with hormone receptors. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):565–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90240-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brüggemeier U., Rogge L., Winnacker E. L., Beato M. Nuclear factor I acts as a transcription factor on the MMTV promoter but competes with steroid hormone receptors for DNA binding. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2233–2239. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07393.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buetti E., Diggelmann H. Cloned mouse mammary tumor virus DNA is biologically active in transfected mouse cells and its expression is stimulated by glucocorticoid hormones. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):335–345. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90129-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buetti E., Diggelmann H. Glucocorticoid regulation of mouse mammary tumor virus: identification of a short essential DNA region. EMBO J. 1983;2(8):1423–1429. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01601.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buetti E., Kühnel B., Diggelmann H. Dual function of a nuclear factor I binding site in MMTV transcription regulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 25;17(8):3065–3078. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.8.3065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buetti E., Kühnel B. Distinct sequence elements involved in the glucocorticoid regulation of the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter identified by linker scanning mutagenesis. J Mol Biol. 1986 Aug 5;190(3):379–389. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cato A. C., Henderson D., Ponta H. The hormone response element of the mouse mammary tumour virus DNA mediates the progestin and androgen induction of transcription in the proviral long terminal repeat region. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):363–368. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04763.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cato A. C., Miksicek R., Schütz G., Arnemann J., Beato M. The hormone regulatory element of mouse mammary tumour virus mediates progesterone induction. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2237–2240. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04490.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cato A. C., Skroch P., Weinmann J., Butkeraitis P., Ponta H. DNA sequences outside the receptor-binding sites differently modulate the responsiveness of the mouse mammary tumour virus promoter to various steroid hormones. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1403–1410. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02957.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalepakis G., Arnemann J., Slater E., Brüller H. J., Gross B., Beato M. Differential gene activation by glucocorticoids and progestins through the hormone regulatory element of mouse mammary tumor virus. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):371–382. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90157-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler V. L., Maler B. A., Yamamoto K. R. DNA sequences bound specifically by glucocorticoid receptor in vitro render a heterologous promoter hormone responsive in vivo. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):489–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90430-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi Y., Kappler J. W., Marrack P. A superantigen encoded in the open reading frame of the 3' long terminal repeat of mouse mammary tumour virus. Nature. 1991 Mar 21;350(6315):203–207. doi: 10.1038/350203a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciliberto G., Buckland R., Cortese R., Philipson L. Transcription signals in embryonic Xenopus laevis U1 RNA genes. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1537–1543. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03814.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. C., Shank P. R., Morris V. L., Cardiff R., Varmus H. E. Integration of the DNA of mouse mammary tumor virus in virus-infected normal and neoplastic tissue of the mouse. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):333–345. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordingley M. G., Riegel A. T., Hager G. L. Steroid-dependent interaction of transcription factors with the inducible promoter of mouse mammary tumor virus in vivo. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90429-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darbre P., Page M., King R. J. Androgen regulation by the long terminal repeat of mouse mammary tumor virus. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2847–2854. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudley J. P., Arfsten A., Hsu C. L., Kozak C., Risser R. Molecular cloning and characterization of mouse mammary tumor proviruses from a T-cell lymphoma. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):385–388. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.385-388.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkner F. G., Zachau H. G. Correct transcription of an immunoglobulin kappa gene requires an upstream fragment containing conserved sequence elements. Nature. 1984 Jul 5;310(5972):71–74. doi: 10.1038/310071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favaloro J., Treisman R., Kamen R. Transcription maps of polyoma virus-specific RNA: analysis by two-dimensional nuclease S1 gel mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):718–749. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher C., Heintz N., Roeder R. G. Purification and characterization of OTF-1, a transcription factor regulating cell cycle expression of a human histone H2b gene. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):773–781. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90100-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerster T., Matthias P., Thali M., Jiricny J., Schaffner W. Cell type-specificity elements of the immunoglobulin heavy chain gene enhancer. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1323–1330. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02371.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerster T., Roeder R. G. A herpesvirus trans-activating protein interacts with transcription factor OTF-1 and other cellular proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6347–6351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies S. D., Morrison S. L., Oi V. T., Tonegawa S. A tissue-specific transcription enhancer element is located in the major intron of a rearranged immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golovkina T. V., Chervonsky A., Dudley J. P., Ross S. R. Transgenic mouse mammary tumor virus superantigen expression prevents viral infection. Cell. 1992 May 15;69(4):637–645. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90227-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski K., Carneiro M., Schibler U. Tissue-specific in vitro transcription from the mouse albumin promoter. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):767–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouilleux F., Sola B., Couette B., Richard-Foy H. Cooperation between structural elements in hormono-regulated transcription from the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 11;19(7):1563–1569. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.7.1563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gowland P. L., Buetti E. Mutations in the hormone regulatory element of mouse mammary tumor virus differentially affect the response to progestins, androgens, and glucocorticoids. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3999–4008. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groner B., Hynes N. E. Number and location of mouse mammary tumor virus proviral DNA in mouse DNA of normal tissue and of mammary tumors. J Virol. 1980 Mar;33(3):1013–1025. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.3.1013-1025.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Günzburg W. H., Salmons B. Factors controlling the expression of mouse mammary tumour virus. Biochem J. 1992 May 1;283(Pt 3):625–632. doi: 10.1042/bj2830625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He X., Treacy M. N., Simmons D. M., Ingraham H. A., Swanson L. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Expression of a large family of POU-domain regulatory genes in mammalian brain development. Nature. 1989 Jul 6;340(6228):35–41. doi: 10.1038/340035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu C. L., Fabritius C., Dudley J. Mouse mammary tumor virus proviruses in T-cell lymphomas lack a negative regulatory element in the long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4644–4652. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4644-4652.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes N., van Ooyen A. J., Kennedy N., Herrlich P., Ponta H., Groner B. Subfragments of the large terminal repeat cause glucocorticoid-responsive expression of mouse mammary tumor virus and of an adjacent gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3637–3641. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemler I., Bucher E., Seipel K., Müller-Immerglück M. M., Schaffner W. Promoters with the octamer DNA motif (ATGCAAAT) can be ubiquitous or cell type-specific depending on binding affinity of the octamer site and Oct-factor concentration. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 25;19(2):237–242. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.2.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemler I., Schaffner W. Octamer transcription factors and the cell type-specificity of immunoglobulin gene expression. FASEB J. 1990 Mar;4(5):1444–1449. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.5.2407588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krol A., Lund E., Dahlberg J. E. The two embryonic U1 RNA genes of Xenopus laevis have both common and gene-specific transcription signals. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1529–1535. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03813.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutoh E., Strömstedt P. E., Poellinger L. Functional interference between the ubiquitous and constitutive octamer transcription factor 1 (OTF-1) and the glucocorticoid receptor by direct protein-protein interaction involving the homeo subdomain of OTF-1. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;12(11):4960–4969. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.11.4960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühnel B., Buetti E., Diggelmann H. Functional analysis of the glucocorticoid regulatory elements present in the mouse mammary tumor virus long terminal repeat. A synthetic distal binding site can replace the proximal binding domain. J Mol Biol. 1986 Aug 5;190(3):367–378. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTLEFIELD J. W. SELECTION OF HYBRIDS FROM MATINGS OF FIBROBLASTS IN VITRO AND THEIR PRESUMED RECOMBINANTS. Science. 1964 Aug 14;145(3633):709–710. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3633.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landolfi N. F., Capra J. D., Tucker P. W. Interaction of cell-type-specific nuclear proteins with immunoglobulin VH promoter region sequences. Nature. 1986 Oct 9;323(6088):548–551. doi: 10.1038/323548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laybourn P. J., Kadonaga J. T. Role of nucleosomal cores and histone H1 in regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Science. 1991 Oct 11;254(5029):238–245. doi: 10.1126/science.254.5029.238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. T., Prakash O., Klein D., Sarkar N. H. Structural alterations in the long terminal repeat of an acquired mouse mammary tumor virus provirus in a T-cell leukemia of DBA/2 mice. Virology. 1987 Jul;159(1):39–48. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90345-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefebvre P., Berard D. S., Cordingley M. G., Hager G. L. Two regions of the mouse mammary tumor virus long terminal repeat regulate the activity of its promoter in mammary cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2529–2537. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtsteiner S., Wuarin J., Schibler U. The interplay of DNA-binding proteins on the promoter of the mouse albumin gene. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):963–973. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90583-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopata M. A., Cleveland D. W., Sollner-Webb B. High level transient expression of a chloramphenicol acetyl transferase gene by DEAE-dextran mediated DNA transfection coupled with a dimethyl sulfoxide or glycerol shock treatment. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5707–5717. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majors J., Varmus H. E. A small region of the mouse mammary tumor virus long terminal repeat confers glucocorticoid hormone regulation on a linked heterologous gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5866–5870. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantei N., Boll W., Weissmann C. Rabbit beta-globin mRNA production in mouse L cells transformed with cloned rabbit beta-globin chromosomal DNA. Nature. 1979 Sep 6;281(5726):40–46. doi: 10.1038/281040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., Lienhard S., Jiricny J., De Robertis E. M. An enhancer-like sequence within the Xenopus U2 gene promoter facilitates the formation of stable transcription complexes. Nature. 1985 Jul 11;316(6024):163–167. doi: 10.1038/316163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meulia T., Diggelmann H. Tissue-specific factors and glucocorticoid receptors present in nuclear extracts bind next to each other in the promoter region of mouse mammary tumor virus. J Mol Biol. 1990 Dec 20;216(4):859–872. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(99)80006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalides R., Wagenaar E. Site-specific rearrangements in the long terminal repeat of extra mouse mammary tumor proviruses in murine T-cell leukemias. Virology. 1986 Oct 15;154(1):76–84. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90431-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalides R., Wagenaar E., Weijers P. Rearrangements in the long terminal repeat of extra mouse mammary tumor proviruses in T-cell leukemias of mouse strain GR result in a novel enhancer-like structure. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):823–830. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miksicek R., Borgmeyer U., Nowock J. Interaction of the TGGCA-binding protein with upstream sequences is required for efficient transcription of mouse mammary tumor virus. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1355–1360. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02375.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mink S., Härtig E., Jennewein P., Doppler W., Cato A. C. A mammary cell-specific enhancer in mouse mammary tumor virus DNA is composed of multiple regulatory elements including binding sites for CTF/NFI and a novel transcription factor, mammary cell-activating factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;12(11):4906–4918. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.11.4906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mink S., Ponta H., Cato A. C. The long terminal repeat region of the mouse mammary tumour virus contains multiple regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 25;18(8):2017–2024. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.8.2017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A. J., Alonso S., Guénet J. L., Buckingham M. E. Number and organization of actin-related sequences in the mouse genome. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 15;167(1):77–101. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mok E., Golovkina T. V., Ross S. R. A mouse mammary tumor virus mammary gland enhancer confers tissue-specific but not lactation-dependent expression in transgenic mice. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):7529–7532. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.7529-7532.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morley K. L., Toohey M. G., Peterson D. O. Transcriptional repression of a hormone-responsive promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):6973–6989. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.6973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosthaf L., Pawlita M., Gruss P. A viral enhancer element specifically active in human haematopoietic cells. Nature. 1985 Jun 13;315(6020):597–600. doi: 10.1038/315597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata K., Guggenheimer R. A., Enomoto T., Lichy J. H., Hurwitz J. Adenovirus DNA replication in vitro: identification of a host factor that stimulates synthesis of the preterminal protein-dCMP complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6438–6442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowock J., Borgmeyer U., Püschel A. W., Rupp R. A., Sippel A. E. The TGGCA protein binds to the MMTV-LTR, the adenovirus origin of replication, and the BK virus enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 25;13(6):2045–2061. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.6.2045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Goding C. R. Herpes simplex virus regulatory elements and the immunoglobulin octamer domain bind a common factor and are both targets for virion transactivation. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):435–445. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80036-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto K., Okazawa H., Okuda A., Sakai M., Muramatsu M., Hamada H. A novel octamer binding transcription factor is differentially expressed in mouse embryonic cells. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):461–472. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90597-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parslow T. G., Blair D. L., Murphy W. J., Granner D. K. Structure of the 5' ends of immunoglobulin genes: a novel conserved sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2650–2654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce J., Fee B. E., Toohey M. G., Peterson D. O. A mouse mammary tumor virus promoter element near the transcription initiation site. J Virol. 1993 Jan;67(1):415–424. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.1.415-424.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piña B., Brüggemeier U., Beato M. Nucleosome positioning modulates accessibility of regulatory proteins to the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):719–731. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90087-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M., Frame M. C., Campbell M. E. A complex formed between cell components and an HSV structural polypeptide binds to a viral immediate early gene regulatory DNA sequence. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):425–434. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruijn G. J., van Driel W., van Miltenburg R. T., van der Vliet P. C. Promoter and enhancer elements containing a conserved sequence motif are recognized by nuclear factor III, a protein stimulating adenovirus DNA replication. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3771–3778. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02712.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruijn G. J., van Driel W., van der Vliet P. C. Nuclear factor III, a novel sequence-specific DNA-binding protein from HeLa cells stimulating adenovirus DNA replication. Nature. 1986 Aug 14;322(6080):656–659. doi: 10.1038/322656a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruijn G. J., van Miltenburg R. T., Claessens J. A., van der Vliet P. C. Interaction between the octamer-binding protein nuclear factor III and the adenovirus origin of DNA replication. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3092–3102. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3092-3102.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richard-Foy H., Hager G. L. Sequence-specific positioning of nucleosomes over the steroid-inducible MMTV promoter. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2321–2328. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02507.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosales R., Vigneron M., Macchi M., Davidson I., Xiao J. H., Chambon P. In vitro binding of cell-specific and ubiquitous nuclear proteins to the octamer motif of the SV40 enhancer and related motifs present in other promoters and enhancers. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3015–3025. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02607.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld P. J., O'Neill E. A., Wides R. J., Kelly T. J. Sequence-specific interactions between cellular DNA-binding proteins and the adenovirus origin of DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):875–886. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross S. R., Hsu C. L., Choi Y., Mok E., Dudley J. P. Negative regulation in correct tissue-specific expression of mouse mammary tumor virus in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5822–5829. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruvkun G., Finney M. Regulation of transcription and cell identity by POU domain proteins. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):475–478. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90227-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Interaction of a gene-specific transcription factor with the adenovirus major late promoter upstream of the TATA box region. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidereit C., Beato M. Contacts between hormone receptor and DNA double helix within a glucocorticoid regulatory element of mouse mammary tumor virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3029–3033. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidereit C., Heguy A., Roeder R. G. Identification and purification of a human lymphoid-specific octamer-binding protein (OTF-2) that activates transcription of an immunoglobulin promoter in vitro. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):783–793. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90101-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R., Ruppert S., Suzuki N., Chowdhury K., Gruss P. New type of POU domain in germ line-specific protein Oct-4. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):435–439. doi: 10.1038/344435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro D. J., Sharp P. A., Wahli W. W., Keller M. J. A high-efficiency HeLa cell nuclear transcription extract. DNA. 1988 Jan-Feb;7(1):47–55. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Sen R., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. A nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence motif in transcriptional control elements of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):154–158. doi: 10.1038/319154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sive H. L., Heintz N., Roeder R. G. Multiple sequence elements are required for maximal in vitro transcription of a human histone H2B gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3329–3340. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudt L. M., Singh H., Sen R., Wirth T., Sharp P. A., Baltimore D. A lymphoid-specific protein binding to the octamer motif of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):640–643. doi: 10.1038/323640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern S., Tanaka M., Herr W. The Oct-1 homoeodomain directs formation of a multiprotein-DNA complex with the HSV transactivator VP16. Nature. 1989 Oct 19;341(6243):624–630. doi: 10.1038/341624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm R., Baumruker T., Franza B. R., Jr, Herr W. A 100-kD HeLa cell octamer binding protein (OBP100) interacts differently with two separate octamer-related sequences within the SV40 enhancer. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1147–1160. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theunissen H. J., Paardekooper M., Maduro L. J., Michalides R. J., Nusse R. Phorbol ester-inducible T-cell-specific expression of variant mouse mammary tumor virus long terminal repeats. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3466–3471. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3466-3471.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toohey M. G., Lee J. W., Huang M., Peterson D. O. Functional elements of the steroid hormone-responsive promoter of mouse mammary tumor virus. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4477–4488. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4477-4488.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsubura A., Inaba M., Imai S., Murakami A., Oyaizu N., Yasumizu R., Ohnishi Y., Tanaka H., Morii S., Ikehara S. Intervention of T-cells in transportation of mouse mammary tumor virus (milk factor) to mammary gland cells in vivo. Cancer Res. 1988 Nov 15;48(22):6555–6559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullman K. S., Flanagan W. M., Edwards C. A., Crabtree G. R. Activation of early gene expression in T lymphocytes by Oct-1 and an inducible protein, OAP40. Science. 1991 Oct 25;254(5031):558–562. doi: 10.1126/science.1683003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildeman A. G., Zenke M., Schatz C., Wintzerith M., Grundström T., Matthes H., Takahashi K., Chambon P. Specific protein binding to the simian virus 40 enhancer in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2098–2105. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagawa S., Tanaka H., Ishimoto A. Identification of a novel mammary cell line-specific enhancer element in the long terminal repeat of mouse mammary tumor virus, which interacts with its hormone-responsive element. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):526–531. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.526-531.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]