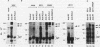Abstract
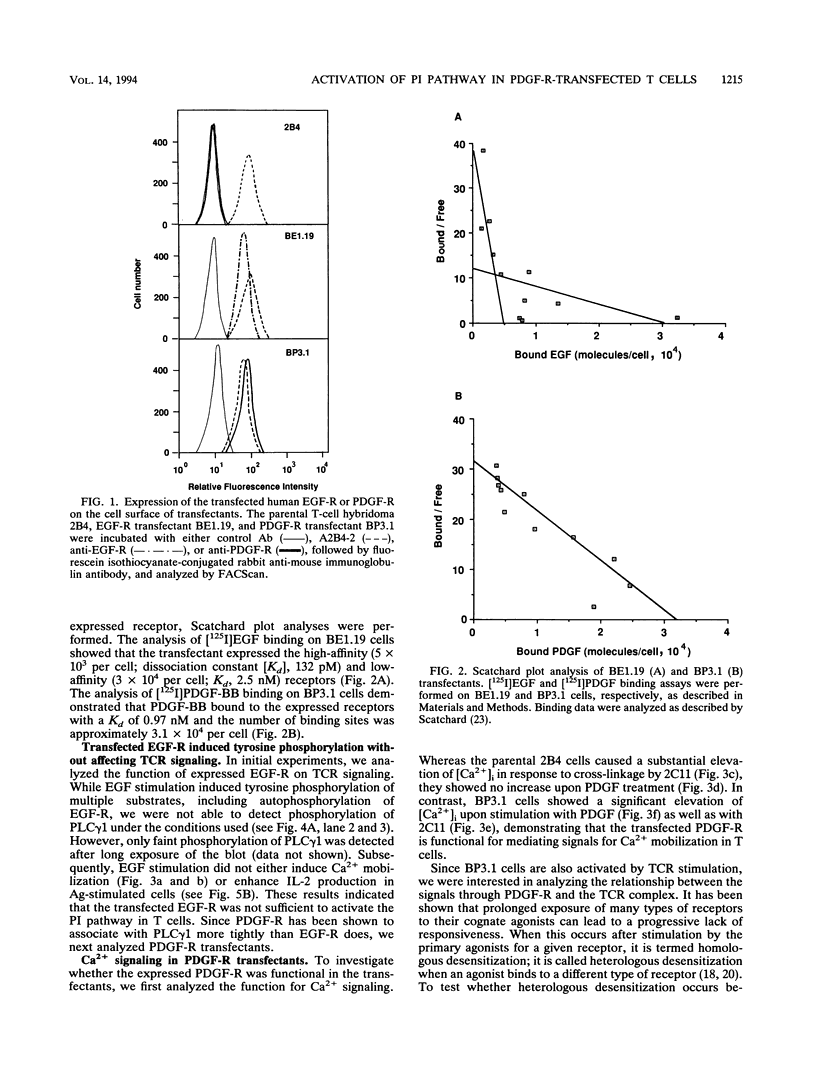
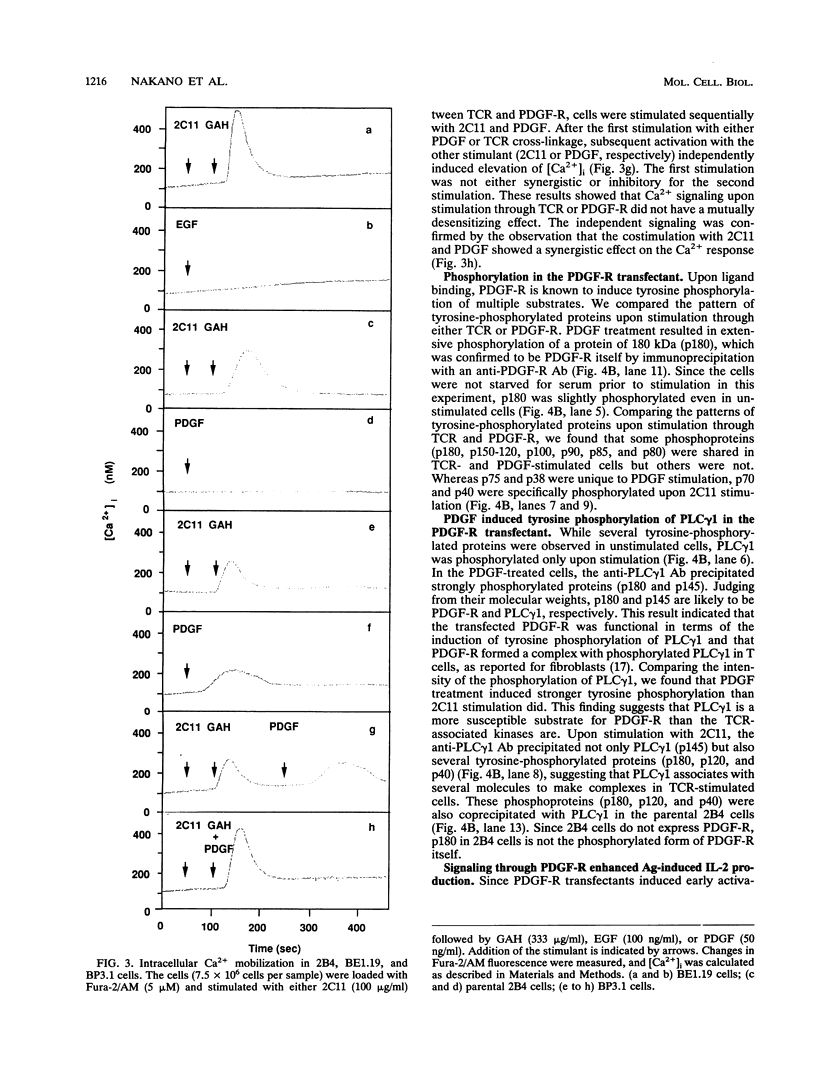
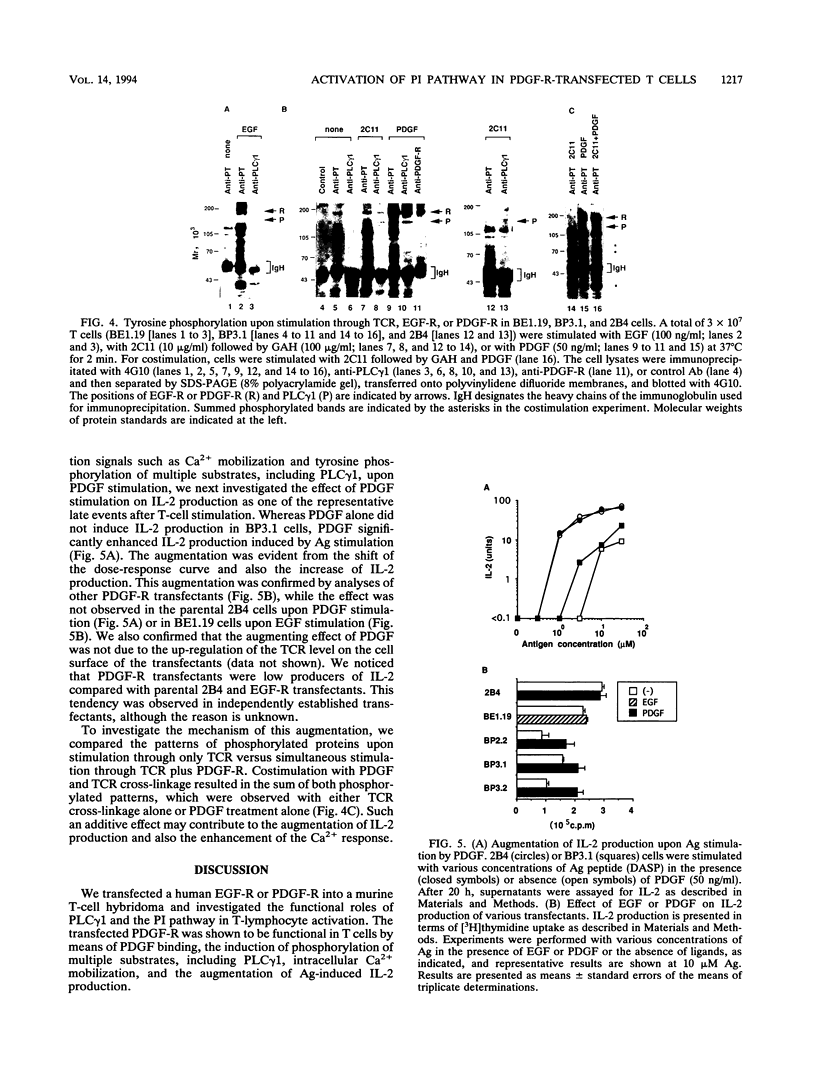
Phospholipase C-gamma 1 (PLC gamma 1) plays an important role in the signal transduction pathway by producing second messengers. However, the activation mechanism of PLC gamma 1 and the role of the phosphatidylinositol pathway for interleukin 2 (IL-2) production in T lymphocytes remain to be determined. To analyze the functional role of this pathway in T cells, we expressed an epidermal growth factor receptor (EGF) or platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) receptor (EGF-R or PDGF-R), both of which are known to directly activate PLC gamma 1 in fibroblasts, into a murine T-cell hybridoma. Both receptors were expressed on the cell surface and caused tyrosine phosphorylation of multiple substrates, including the receptor itself, upon ligand binding. While EGF stimulation did not either cause phosphorylation of PLC gamma 1 or induce Ca2+ mobilization in the EGF-R transfectant in this system, PDGF treatment induced tyrosine phosphorylation of PLC gamma 1 and Ca2+ mobilization in the PDGF-R transfectant. Stimulation through PDGF-R enhanced IL-2 production upon antigen stimulation of the transfectants, although PDGF treatment alone did not induce IL-2 production. These results suggest that activation of the phosphatidylinositol pathway affects the downstream pathway to IL-2 production but is not sufficient to produce IL-2 and that cooperation with signals from tyrosine kinase cascades is required for IL-2 production.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D., Koch C. A., Grey L., Ellis C., Moran M. F., Pawson T. Binding of SH2 domains of phospholipase C gamma 1, GAP, and Src to activated growth factor receptors. Science. 1990 Nov 16;250(4983):979–982. doi: 10.1126/science.2173144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashwell J. D., Cunningham R. E., Noguchi P. D., Hernandez D. Cell growth cycle block of T cell hybridomas upon activation with antigen. J Exp Med. 1987 Jan 1;165(1):173–194. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.1.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan A. C., Iwashima M., Turck C. W., Weiss A. ZAP-70: a 70 kd protein-tyrosine kinase that associates with the TCR zeta chain. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):649–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90598-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coggeshall K. M., McHugh J. C., Altman A. Predominant expression and activation-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma 2 in B lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5660–5664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta J. D., Granja C., Druker B., Lin L. L., Yunis E. J., Relias V. Phospholipase C-gamma 1 association with CD3 structure in T cells. J Exp Med. 1992 Jan 1;175(1):285–288. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.1.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desai D. M., Newton M. E., Kadlecek T., Weiss A. Stimulation of the phosphatidylinositol pathway can induce T-cell activation. Nature. 1990 Nov 1;348(6296):66–69. doi: 10.1038/348066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graber M., June C. H., Samelson L. E., Weiss A. The protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor herbimycin A, but not genistein, specifically inhibits signal transduction by the T cell antigen receptor. Int Immunol. 1992 Nov;4(11):1201–1210. doi: 10.1093/intimm/4.11.1201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansburg D., Fairwell T., Schwartz R. H., Appella E. The T lymphocyte response to cytochrome c. IV. Distinguishable sites on a peptide antigen which affect antigenic strength and memory. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):319–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick S. M., Matis L. A., Hecht T. T., Samelson L. E., Longo D. L., Heber-Katz E., Schwartz R. H. The fine specificity of antigen and Ia determinant recognition by T cell hybridoma clones specific for pigeon cytochrome c. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):141–152. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90020-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- June C. H., Fletcher M. C., Ledbetter J. A., Schieven G. L., Siegel J. N., Phillips A. F., Samelson L. E. Inhibition of tyrosine phosphorylation prevents T-cell receptor-mediated signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7722–7726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy I. C., June C. H., O'Shea J. J. Expression of the human epidermal growth factor receptor in a murine T-cell hybridoma. A transmembrane protein tyrosine kinase can synergize with the T-cell antigen receptor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4924–4929. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Samelson L. E. T cell antigen receptor activation pathways: the tyrosine kinase connection. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):875–878. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90310-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leo O., Foo M., Sachs D. H., Samelson L. E., Bluestone J. A. Identification of a monoclonal antibody specific for a murine T3 polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1374–1378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Rhee S. G., Felder S., Mervic M., Lyall R., Levitzki A., Ullrich A., Zilberstein A., Schlessinger J. EGF induces tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-II: a potential mechanism for EGF receptor signaling. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1101–1107. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90047-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisenhelder J., Hunter T. The SH2/SH3 domain-containing protein Nck is recognized by certain anti-phospholipase C-gamma 1 monoclonal antibodies, and its phosphorylation on tyrosine is stimulated by platelet-derived growth factor and epidermal growth factor treatment. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5843–5856. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisenhelder J., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G., Hunter T. Phospholipase C-gamma is a substrate for the PDGF and EGF receptor protein-tyrosine kinases in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1109–1122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar J. B., Rozengurt E. Heterologous desensitization of bombesin-induced mitogenesis by prolonged exposure to vasopressin: a post-receptor signal transduction block. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3204–3208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea J. J., Ashwell J. D., Bailey T. L., Cross S. L., Samelson L. E., Klausner R. D. Expression of v-src in a murine T-cell hybridoma results in constitutive T-cell receptor phosphorylation and interleukin 2 production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1741–1745. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosoff P. M., Mohan C. Unidirectional, heterologous desensitization of the pertussis toxin receptor by the CD3/TCR complex. J Immunol. 1992 Nov 15;149(10):3191–3199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samelson L. E., Germain R. N., Schwartz R. H. Monoclonal antibodies against the antigen receptor on a cloned T-cell hybrid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6972–6976. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samelson L. E., Phillips A. F., Luong E. T., Klausner R. D. Association of the fyn protein-tyrosine kinase with the T-cell antigen receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4358–4362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song J. G., Pfeffer L. M., Foster D. A. v-Src increases diacylglycerol levels via a type D phospholipase-mediated hydrolysis of phosphatidylcholine. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4903–4908. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley J. B., Gorczynski R., Huang C. K., Love J., Mills G. B. Tyrosine phosphorylation is an obligatory event in IL-2 secretion. J Immunol. 1990 Oct 1;145(7):2189–2198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman J. J., Merćep M., Saito T., Germain R. N., Bonvini E., Ashwell J. D. Dissociation of phosphoinositide hydrolysis and Ca2+ fluxes from the biological responses of a T-cell hybridoma. Nature. 1988 Aug 18;334(6183):625–628. doi: 10.1038/334625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl M. I., Olashaw N. E., Nishibe S., Rhee S. G., Pledger W. J., Carpenter G. Platelet-derived growth factor induces rapid and sustained tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma in quiescent BALB/c 3T3 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2934–2943. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]