Abstract
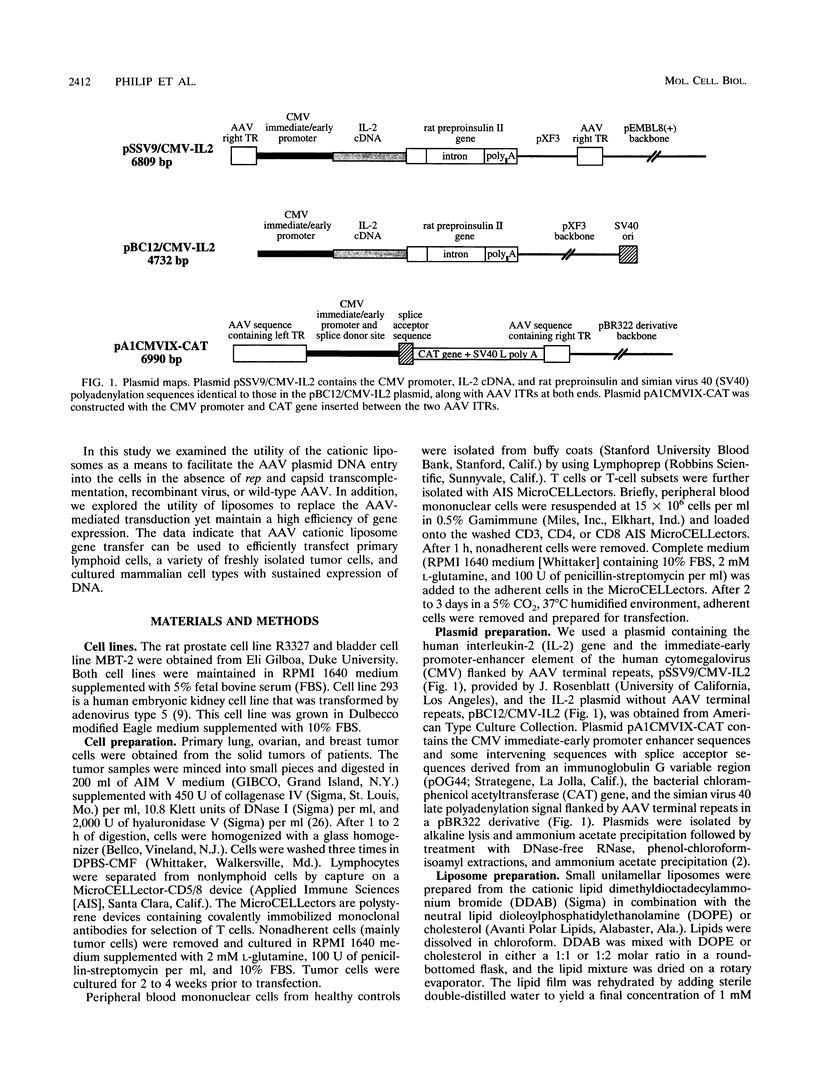
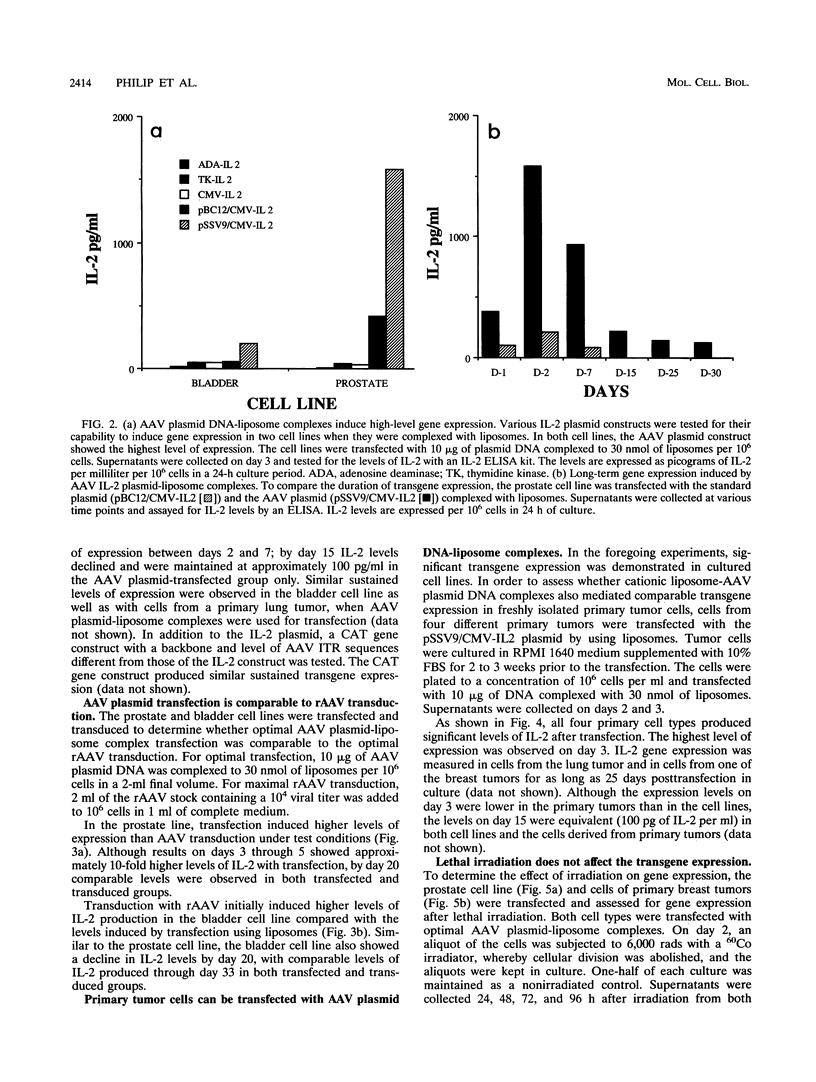
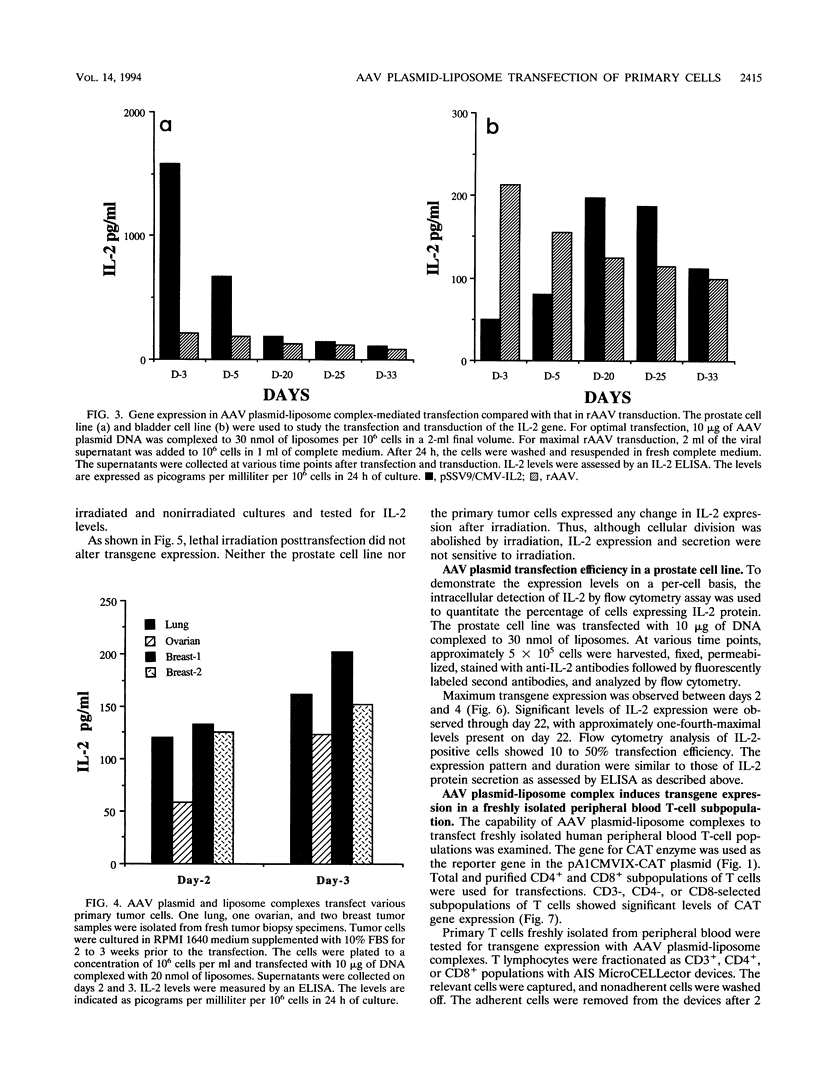
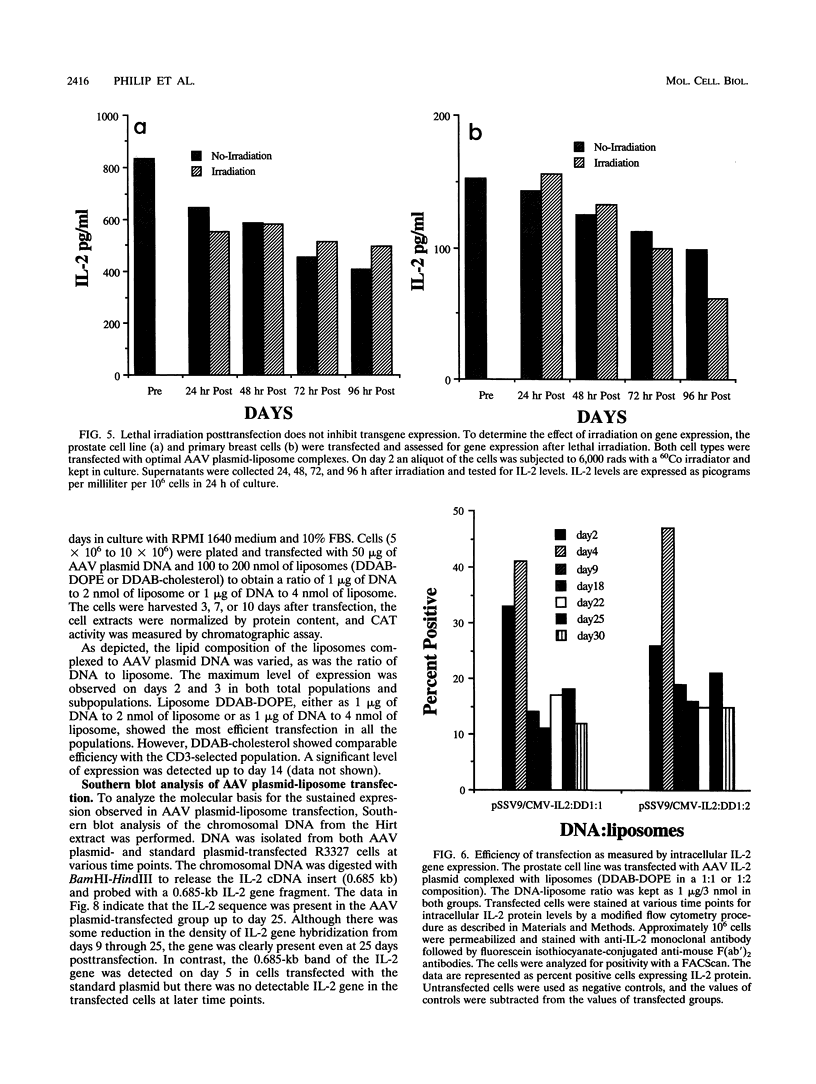
We have used cationic liposomes to facilitate adeno-associated virus (AAV) plasmid transfections of primary and cultured cell types. AAV plasmid DNA complexed with liposomes showed levels of expression several fold higher than those of complexes with standard plasmids. In addition, long-term expression (> 30 days) of the gene, unlike the transient expression demonstrated by typical liposome-mediated transfection with standard plasmids, was observed. Southern analysis of chromosomal DNA further substantiated the hypothesis that the long-term expression was due to the presence of the transgene in the AAV plasmid-transfected group and not in the standard plasmid-transfected group. AAV plasmid-liposome complexes induced levels of transgene expression comparable to those obtained by recombinant AAV transduction. Primary breast, ovarian, and lung tumor cells were transfectable with the AAV plasmid DNA-liposome complexes. Transfected primary and cultured tumor cells were able to express transgene product even after lethal irradiation. High-level gene expression was also observed in freshly isolated CD3+, CD4+, and CD8+ T cells from normal human peripheral blood. Transfection efficiency ranged from 10 to 50% as assessed by intracellular interleukin-2 levels in interleukin-2-transfected cells. The ability to express transgenes in primary tumor and lymphoid cells may be applied toward tumor vaccine studies and protocols which may eventually permit highly specific modulation of the cellular immune response in cancer and AIDS.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashktorab H., Srivastava A. Identification of nuclear proteins that specifically interact with adeno-associated virus type 2 inverted terminal repeat hairpin DNA. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):3034–3039. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.3034-3039.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debs R. J., Freedman L. P., Edmunds S., Gaensler K. L., Düzgünes N., Yamamoto K. R. Regulation of gene expression in vivo by liposome-mediated delivery of a purified transcription factor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10189–10192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimmock N. J. Review article initial stages in infection with animal viruses. J Gen Virol. 1982 Mar;59(Pt 1):1–22. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-59-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duc-Nguyen H. Enhancing effect of diethylaminoethyl-dextran on the focus-forming titer of a murine sarcoma virus (Harvey strain). J Virol. 1968 Jun;2(6):643–644. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.6.643-644.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faller D. V., Baltimore D. Liposome encapsulation of retrovirus allows efficient superinfection of resistant cell lines. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):269–272. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.269-272.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgner P. L., Gadek T. R., Holm M., Roman R., Chan H. W., Wenz M., Northrop J. P., Ringold G. M., Danielsen M. Lipofection: a highly efficient, lipid-mediated DNA-transfection procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7413–7417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedmann T. Progress toward human gene therapy. Science. 1989 Jun 16;244(4910):1275–1281. doi: 10.1126/science.2660259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Smiley J., Russell W. C., Nairn R. Characteristics of a human cell line transformed by DNA from human adenovirus type 5. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jul;36(1):59–74. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermonat P. L., Labow M. A., Wright R., Berns K. I., Muzyczka N. Genetics of adeno-associated virus: isolation and preliminary characterization of adeno-associated virus type 2 mutants. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):329–339. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.329-339.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermonat P. L., Muzyczka N. Use of adeno-associated virus as a mammalian DNA cloning vector: transduction of neomycin resistance into mammalian tissue culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6466–6470. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hug P., Sleight R. G. Liposomes for the transformation of eukaryotic cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jul 26;1097(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0925-4439(91)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Im D. S., Muzyczka N. Factors that bind to adeno-associated virus terminal repeats. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):3095–3104. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.3095-3104.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung T., Schauer U., Heusser C., Neumann C., Rieger C. Detection of intracellular cytokines by flow cytometry. J Immunol Methods. 1993 Feb 26;159(1-2):197–207. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(93)90158-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotin R. M., Siniscalco M., Samulski R. J., Zhu X. D., Hunter L., Laughlin C. A., McLaughlin S., Muzyczka N., Rocchi M., Berns K. I. Site-specific integration by adeno-associated virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2211–2215. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebkowski J. S., McNally M. M., Okarma T. B., Lerch L. B. Adeno-associated virus: a vector system for efficient introduction and integration of DNA into a variety of mammalian cell types. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):3988–3996. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.3988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malone R. W., Felgner P. L., Verma I. M. Cationic liposome-mediated RNA transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6077–6081. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philip R., Liggitt D., Philip M., Dazin P., Debs R. In vivo gene delivery. Efficient transfection of T lymphocytes in adult mice. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 5;268(22):16087–16090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Buonocore L., Whitt M. A. A new cationic liposome reagent mediating nearly quantitative transfection of animal cells. Biotechniques. 1991 Apr;10(4):520–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samulski R. J., Zhu X., Xiao X., Brook J. D., Housman D. E., Epstein N., Hunter L. A. Targeted integration of adeno-associated virus (AAV) into human chromosome 19. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3941–3950. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04964.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer-Ridder M., Wang Y., Hofschneider P. H. Liposomes as gene carriers: efficient transformation of mouse L cells by thymidine kinase gene. Science. 1982 Jan 8;215(4529):166–168. doi: 10.1126/science.7053567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder R. O., Im D. S., Muzyczka N. Evidence for covalent attachment of the adeno-associated virus (AAV) rep protein to the ends of the AAV genome. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):6204–6213. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.6204-6213.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart M. J., Plautz G. E., Del Buono L., Yang Z. Y., Xu L., Gao X., Huang L., Nabel E. G., Nabel G. J. Gene transfer in vivo with DNA-liposome complexes: safety and acute toxicity in mice. Hum Gene Ther. 1992 Jun;3(3):267–275. doi: 10.1089/hum.1992.3.3-267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stribling R., Brunette E., Liggitt D., Gaensler K., Debs R. Aerosol gene delivery in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11277–11281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topalian S. L., Muul L. M., Solomon D., Rosenberg S. A. Expansion of human tumor infiltrating lymphocytes for use in immunotherapy trials. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Aug 24;102(1):127–141. doi: 10.1016/s0022-1759(87)80018-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tratschin J. D., Miller I. L., Carter B. J. Genetic analysis of adeno-associated virus: properties of deletion mutants constructed in vitro and evidence for an adeno-associated virus replication function. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):611–619. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.611-619.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tratschin J. D., Miller I. L., Smith M. G., Carter B. J. Adeno-associated virus vector for high-frequency integration, expression, and rescue of genes in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3251–3260. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson T., Papahadjopoulos D., Taber R. Biological properties of poliovirus encapsulated in lipid vesicles: antibody resistance and infectivity in virus-resistant cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3471–3475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu N., Liggitt D., Liu Y., Debs R. Systemic gene expression after intravenous DNA delivery into adult mice. Science. 1993 Jul 9;261(5118):209–211. doi: 10.1126/science.7687073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




