Abstract
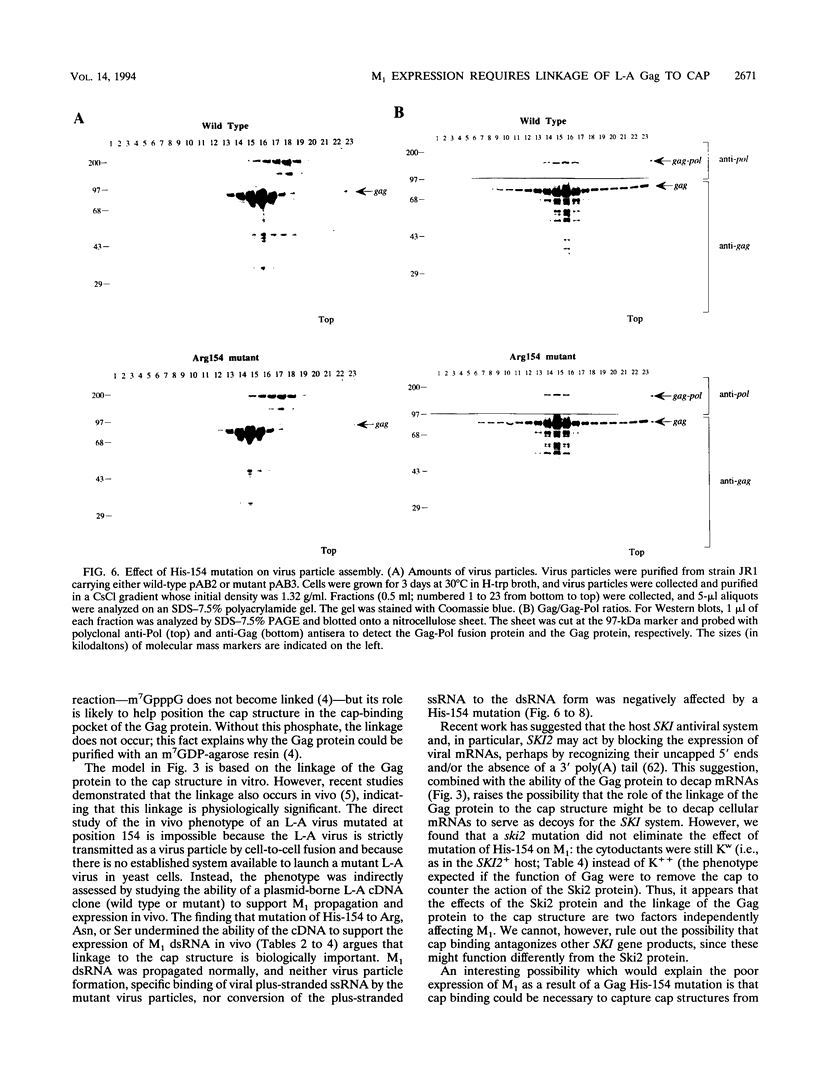
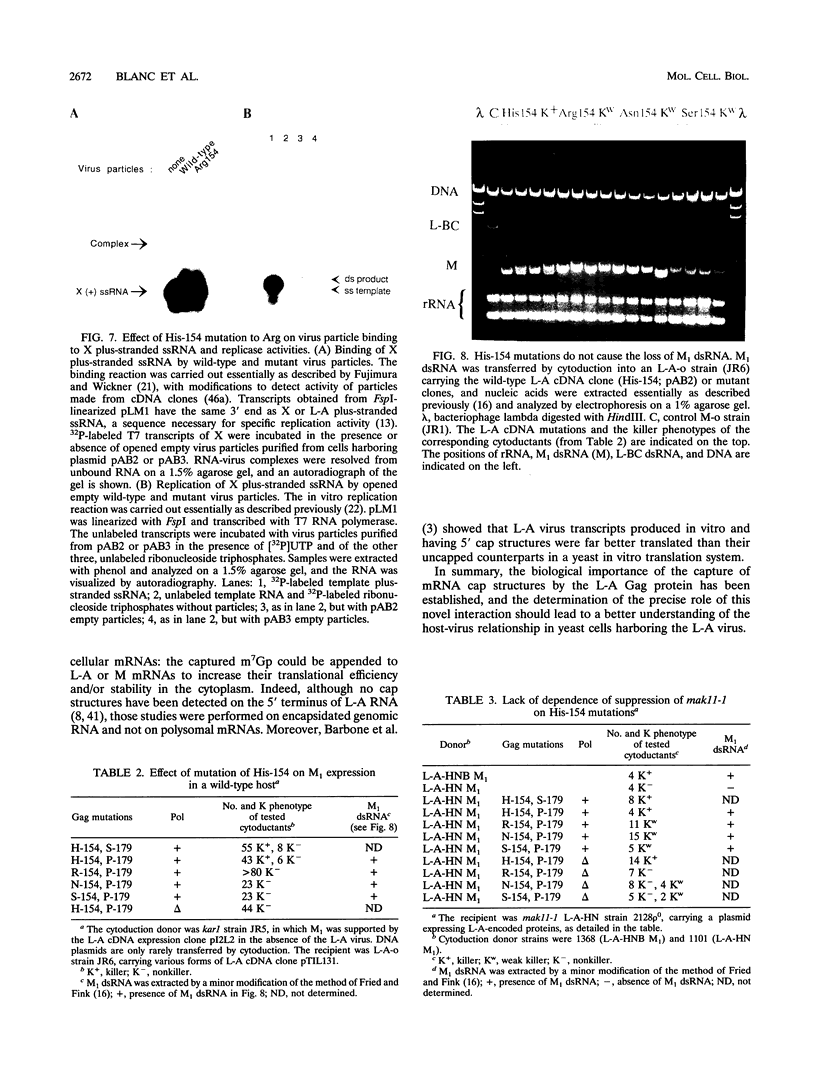
The coat protein (Gag) of the double-stranded RNA virus L-A was previously shown to form a covalent bond with the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs. Here, we identify the linkage as a phosphoroimidazole bond between the alpha phosphate of the cap structure and a nitrogen in the Gag protein His-154 imidazole side chain. Mutations of His-154 abrogate the ability of Gag to bind to the cap structure, without affecting cap recognition, in vivo virus particle formation from an L-A cDNA clone, or in vitro specific binding and replication of plus-stranded single-stranded RNA. However, genetic analyses demonstrate that His-154 is essential for M1 satellite virus expression.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ball S. G., Tirtiaux C., Wickner R. B. Genetic Control of L-a and L-(Bc) Dsrna Copy Number in Killer Systems of SACCHAROMYCES CEREVISIAE. Genetics. 1984 Jun;107(2):199–217. doi: 10.1093/genetics/107.2.199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbone F. P., Williams T. L., Leibowitz M. J. Yeast killer virus transcription initiation in vitro. Virology. 1992 Mar;187(1):333–337. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90323-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanc A., Goyer C., Sonenberg N. The coat protein of the yeast double-stranded RNA virus L-A attaches covalently to the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;12(8):3390–3398. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.8.3390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boone C., Bussey H., Greene D., Thomas D. Y., Vernet T. Yeast killer toxin: site-directed mutations implicate the precursor protein as the immunity component. Cell. 1986 Jul 4;46(1):105–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90864-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braam-Markson J., Jaudon C., Krug R. M. Expression of a functional influenza viral cap-recognizing protein by using a bovine papilloma virus vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4326–4330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruenn J., Keitz B. The 5' ends of yeast killer factor RNAs are pppGp. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Oct;3(10):2427–2436. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.10.2427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinman J. D., Icho T., Wickner R. B. A -1 ribosomal frameshift in a double-stranded RNA virus of yeast forms a gag-pol fusion protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):174–178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edery I., Sonenberg N. Cap-dependent RNA splicing in a HeLa nuclear extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7590–7594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esteban R., Fujimura T., Wickner R. B. Internal and terminal cis-acting sites are necessary for in vitro replication of the L-A double-stranded RNA virus of yeast. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):947–954. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03456.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esteban R., Wickner R. B. A deletion mutant of L-A double-stranded RNA replicates like M1 double-stranded RNA. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1278–1285. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1278-1285.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esteban R., Wickner R. B. A new non-mendelian genetic element of yeast that increases cytopathology produced by M1 double-stranded RNA in ski strains. Genetics. 1987 Nov;117(3):399–408. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.3.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried H. M., Fink G. R. Electron microscopic heteroduplex analysis of "killer" double-stranded RNA species from yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4224–4228. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura T., Esteban R., Esteban L. M., Wickner R. B. Portable encapsidation signal of the L-A double-stranded RNA virus of S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):819–828. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90125-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura T., Esteban R., Wickner R. B. In vitro L-A double-stranded RNA synthesis in virus-like particles from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4433–4437. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura T., Ribas J. C., Makhov A. M., Wickner R. B. Pol of gag-pol fusion protein required for encapsidation of viral RNA of yeast L-A virus. Nature. 1992 Oct 22;359(6397):746–749. doi: 10.1038/359746a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura T., Wickner R. B. Gene overlap results in a viral protein having an RNA binding domain and a major coat protein domain. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):663–671. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90225-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura T., Wickner R. B. Interaction of two cis sites with the RNA replicase of the yeast L-A virus. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2708–2713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura T., Wickner R. B. Replicase of L-A virus-like particles of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. In vitro conversion of exogenous L-A and M1 single-stranded RNAs to double-stranded form. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):454–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgiev O., Mous J., Birnstiel M. L. Processing and nucleo-cytoplasmic transport of histone gene transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8539–8551. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyer C., Altmann M., Lee H. S., Blanc A., Deshmukh M., Woolford J. L., Jr, Trachsel H., Sonenberg N. TIF4631 and TIF4632: two yeast genes encoding the high-molecular-weight subunits of the cap-binding protein complex (eukaryotic initiation factor 4F) contain an RNA recognition motif-like sequence and carry out an essential function. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;13(8):4860–4874. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.8.4860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyer C., Altmann M., Trachsel H., Sonenberg N. Identification and characterization of cap-binding proteins from yeast. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7603–7610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamm J., Mattaj I. W. Monomethylated cap structures facilitate RNA export from the nucleus. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):109–118. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90292-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannig E. M., Williams T. L., Leibowitz M. J. The internal polyadenylate tract of yeast killer virus M1 double-stranded RNA is variable in length. Virology. 1986 Jul 15;152(1):149–158. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90380-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart R. P., McDevitt M. A., Nevins J. R. Poly(A) site cleavage in a HeLa nuclear extract is dependent on downstream sequences. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):677–683. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90240-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Icho T., Wickner R. B. The MAK11 protein is essential for cell growth and replication of M double-stranded RNA and is apparently a membrane-associated protein. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1467–1475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Icho T., Wickner R. B. The double-stranded RNA genome of yeast virus L-A encodes its own putative RNA polymerase by fusing two open reading frames. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):6716–6723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izaurralde E., Stepinski J., Darzynkiewicz E., Mattaj I. W. A cap binding protein that may mediate nuclear export of RNA polymerase II-transcribed RNAs. J Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;118(6):1287–1295. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.6.1287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebe R. J., Harriss J. V., Sharp Z. D., Douglas M. G. A general method for polyethylene-glycol-induced genetic transformation of bacteria and yeast. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):333–341. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90238-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarska M. M., Padgett R. A., Sharp P. A. Recognition of cap structure in splicing in vitro of mRNA precursors. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):731–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90268-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Maniatis T., Ruskin B., Green M. R. Normal and mutant human beta-globin pre-mRNAs are faithfully and efficiently spliced in vitro. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):993–1005. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinac B., Zhu H., Kubalski A., Zhou X. L., Culbertson M., Bussey H., Kung C. Yeast K1 killer toxin forms ion channels in sensitive yeast spheroplasts and in artificial liposomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6228–6232. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto Y., Fishel R., Wickner R. B. Circular single-stranded RNA replicon in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7628–7632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto Y., Sarkar G., Sommer S. S., Wickner R. B. A yeast antiviral protein, SKI8, shares a repeated amino acid sequence pattern with beta-subunits of G proteins and several other proteins. Yeast. 1993 Jan;9(1):43–51. doi: 10.1002/yea.320090106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto Y., Wickner R. B. Yeast 20 S RNA replicon. Replication intermediates and encoded putative RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12779–12783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemeroff M. E., Bruenn J. A. Initiation by the yeast viral transcriptase in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6785–6787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno M., Kataoka N., Shimura Y. A nuclear cap binding protein from HeLa cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):6989–6995. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.6989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patzelt E., Blaas D., Kuechler E. CAP binding proteins associated with the nucleus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 10;11(17):5821–5835. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.17.5821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee S. K., Icho T., Wickner R. B. Structure and nuclear localization signal of the SKI3 antiviral protein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast. 1989 May-Jun;5(3):149–158. doi: 10.1002/yea.320050304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads R. E. Cap recognition and the entry of mRNA into the protein synthesis initiation cycle. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Feb;13(2):52–56. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads R. E. Regulation of eukaryotic protein synthesis by initiation factors. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 15;268(5):3017–3020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribas J. C., Wickner R. B. RNA-dependent RNA polymerase consensus sequence of the L-A double-stranded RNA virus: definition of essential domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2185–2189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley S. P., Sommer S. S., Wickner R. B. Superkiller mutations in Saccharomyces cerevisiae suppress exclusion of M2 double-stranded RNA by L-A-HN and confer cold sensitivity in the presence of M and L-A-HN. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;4(4):761–770. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.4.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Cousiño N., Esteban L. M., Esteban R. Molecular cloning and characterization of W double-stranded RNA, a linear molecule present in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Identification of its single-stranded RNA form as 20 S RNA. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12772–12778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozen F., Sonenberg N. Identification of nuclear cap specific proteins in HeLa cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 25;15(16):6489–6500. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.16.6489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Krainer A. R., Maniatis T., Green M. R. Excision of an intact intron as a novel lariat structure during pre-mRNA splicing in vitro. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):317–331. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90553-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer S. S., Wickner R. B. Gene disruption indicates that the only essential function of the SKI8 chromosomal gene is to protect Saccharomyces cerevisiae from viral cytopathology. Virology. 1987 Mar;157(1):252–256. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90338-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer S. S., Wickner R. B. Yeast L dsRNA consists of at least three distinct RNAs; evidence that the non-Mendelian genes [HOK], [NEX] and [EXL] are on one of these dsRNAs. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):429–441. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90136-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N. Cap-binding proteins of eukaryotic messenger RNA: functions in initiation and control of translation. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1988;35:173–207. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60614-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toh-E A., Guerry P., Wickner R. B. Chromosomal superkiller mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1978 Dec;136(3):1002–1007. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.3.1002-1007.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valle R. P., Wickner R. B. Elimination of L-A double-stranded RNA virus of Saccharomyces cerevisiae by expression of gag and gag-pol from an L-A cDNA clone. J Virol. 1993 May;67(5):2764–2771. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.5.2764-2771.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner R. B., Icho T., Fujimura T., Widner W. R. Expression of yeast L-A double-stranded RNA virus proteins produces derepressed replication: a ski- phenocopy. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):155–161. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.155-161.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner R. B., Toh-e A. [HOK], a new yeast non-Mendelian trait, enables a replication-defective killer plasmid to be maintained. Genetics. 1982 Feb;100(2):159–174. doi: 10.1093/genetics/100.2.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widner W. R., Wickner R. B. Evidence that the SKI antiviral system of Saccharomyces cerevisiae acts by blocking expression of viral mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):4331–4341. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.4331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Peña P., Barros F., Gascón S., Lazo P. S., Ramos S. Effect of yeast killer toxin on sensitive cells of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 25;256(20):10420–10425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]