Abstract
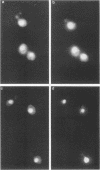
The transition from G1 to S phase of the cell cycle in Saccharomyces cerevisiae requires the activity of the Ubc3 (Cdc34) ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme. S. cerevisiae cells lacking a functional UBC3 (CDC34) gene are able to execute the Start function that initiates the cell cycle but fail to form a mitotic spindle or enter S phase. The Ubc3 (Cdc34) enzyme has previously been shown to catalyze the attachment of multiple ubiquitin molecules to model substrates, suggesting that the role of this enzyme in cell cycle progression depends on its targeting an endogenous protein(s) for degradation. In this report, we demonstrate that the Ubc3 (Cdc34) protein is itself a substrate for both ubiquitination and phosphorylation. Immunochemical localization of the gene product to the nucleus renders it likely that the relevant substrates similarly reside within the nucleus.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmair A., Finley D., Varshavsky A. In vivo half-life of a protein is a function of its amino-terminal residue. Science. 1986 Oct 10;234(4773):179–186. doi: 10.1126/science.3018930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum P., Yip C., Goetsch L., Byers B. A yeast gene essential for regulation of spindle pole duplication. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5386–5397. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bram R. J., Kornberg R. D. Specific protein binding to far upstream activating sequences in polymerase II promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):43–47. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers B., Goetsch L. Duplication of spindle plaques and integration of the yeast cell cycle. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:123–131. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciechanover A., DiGiuseppe J. A., Bercovich B., Orian A., Richter J. D., Schwartz A. L., Brodeur G. M. Degradation of nuclear oncoproteins by the ubiquitin system in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):139–143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohmen R. J., Madura K., Bartel B., Varshavsky A. The N-end rule is mediated by the UBC2(RAD6) ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7351–7355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutcher S. K., Hartwell L. H. The role of S. cerevisiae cell division cycle genes in nuclear fusion. Genetics. 1982 Feb;100(2):175–184. doi: 10.1093/genetics/100.2.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finley D., Chau V. Ubiquitination. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:25–69. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.000325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsburg S. L., Nurse P. Cell cycle regulation in the yeasts Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:227–256. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.001303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glotzer M., Murray A. W., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin is degraded by the ubiquitin pathway. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):132–138. doi: 10.1038/349132a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebl M. G., Yochem J., Jentsch S., McGrath J. P., Varshavsky A., Byers B. The yeast cell cycle gene CDC34 encodes a ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme. Science. 1988 Sep 9;241(4871):1331–1335. doi: 10.1126/science.2842867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. L. The mechanism and functions of ATP-dependent proteases in bacterial and animal cells. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Jan 15;203(1-2):9–23. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb19822.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda D. K., Bachmair A., Wünning I., Tobias J. W., Lane W. S., Varshavsky A. Universality and structure of the N-end rule. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16700–16712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas A. L., Reback P. B., Chau V. Ubiquitin conjugation by the yeast RAD6 and CDC34 gene products. Comparison to their putative rabbit homologs, E2(20K) AND E2(32K). J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 15;266(8):5104–5112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H. Macromolecule synthesis in temperature-sensitive mutants of yeast. J Bacteriol. 1967 May;93(5):1662–1670. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.5.1662-1670.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H. Three additional genes required for deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):966–974. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.966-974.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K. M., Clark C. D., Botstein D. Subcellular localization of yeast CDC46 varies with the cell cycle. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12B):2252–2263. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12b.2252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hereford L. M., Hartwell L. H. Sequential gene function in the initiation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae DNA synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1974 Apr 15;84(3):445–461. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90451-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochstrasser M., Ellison M. J., Chau V., Varshavsky A. The short-lived MAT alpha 2 transcriptional regulator is ubiquitinated in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4606–4610. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jentsch S., McGrath J. P., Varshavsky A. The yeast DNA repair gene RAD6 encodes a ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme. Nature. 1987 Sep 10;329(6135):131–134. doi: 10.1038/329131a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jentsch S. The ubiquitin-conjugation system. Annu Rev Genet. 1992;26:179–207. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.26.120192.001143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koerner T. J., Hill J. E., Myers A. M., Tzagoloff A. High-expression vectors with multiple cloning sites for construction of trpE fusion genes: pATH vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:477–490. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94036-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolman C. J., Toth J., Gonda D. K. Identification of a portable determinant of cell cycle function within the carboxyl-terminal domain of the yeast CDC34 (UBC3) ubiquitin conjugating (E2) enzyme. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):3081–3090. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05380.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konopka J. B., Jenness D. D., Hartwell L. H. The C-terminus of the S. cerevisiae alpha-pheromone receptor mediates an adaptive response to pheromone. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):609–620. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer A. N., Wilkinson K. D. Detection, resolution, and nomenclature of multiple ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal esterases from bovine calf thymus. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 10;28(1):166–172. doi: 10.1021/bi00427a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney J. D., Chang F., Heintz N., Cross F. R. Negative regulation of FAR1 at the Start of the yeast cell cycle. Genes Dev. 1993 May;7(5):833–843. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.5.833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll T., Tebb G., Surana U., Robitsch H., Nasmyth K. The role of phosphorylation and the CDC28 protein kinase in cell cycle-regulated nuclear import of the S. cerevisiae transcription factor SWI5. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):743–758. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90118-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K. A. FAR-reaching discoveries about the regulation of START. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1117–1120. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90404-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizawa M., Okazaki K., Furuno N., Watanabe N., Sagata N. The 'second-codon rule' and autophosphorylation govern the stability and activity of Mos during the meiotic cell cycle in Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2433–2446. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05308.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski M. The multicatalytic proteinase complex, a major extralysosomal proteolytic system. Biochemistry. 1990 Nov 13;29(45):10289–10297. doi: 10.1021/bi00497a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plon S. E., Leppig K. A., Do H. N., Groudine M. Cloning of the human homolog of the CDC34 cell cycle gene by complementation in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 15;90(22):10484–10488. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.22.10484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechsteiner M. Natural substrates of the ubiquitin proteolytic pathway. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):615–618. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90104-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. D., Broach J. R. Cloning genes by complementation in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:195–230. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffner M., Werness B. A., Huibregtse J. M., Levine A. J., Howley P. M. The E6 oncoprotein encoded by human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 promotes the degradation of p53. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1129–1136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90409-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J. C., Guarente L. Vectors for expression of cloned genes in yeast: regulation, overproduction, and underproduction. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:373–388. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94028-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seufert W., Jentsch S. Ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes UBC4 and UBC5 mediate selective degradation of short-lived and abnormal proteins. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):543–550. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08141.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanklin J., Jabben M., Vierstra R. D. Red light-induced formation of ubiquitin-phytochrome conjugates: Identification of possible intermediates of phytochrome degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):359–363. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon G., Raboy B., Parag H. A., Dimitrovsky D., Kulka R. G. RAD6 gene product of Saccharomyces cerevisiae requires a putative ubiquitin protein ligase (E3) for the ubiquitination of certain proteins. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15890–15894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver E. T., Gwozd T. J., Ptak C., Goebl M., Ellison M. J. A chimeric ubiquitin conjugating enzyme that combines the cell cycle properties of CDC34 (UBC3) and the DNA repair properties of RAD6 (UBC2): implications for the structure, function and evolution of the E2s. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):3091–3098. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05381.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver P. A., Chiang A., Sadler I. Mutations that alter both localization and production of a yeast nuclear protein. Genes Dev. 1988 Jun;2(6):707–717. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.6.707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung P., Berleth E., Pickart C., Prakash S., Prakash L. Yeast RAD6 encoded ubiquitin conjugating enzyme mediates protein degradation dependent on the N-end-recognizing E3 enzyme. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2187–2193. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07754.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyers M., Tokiwa G., Nash R., Futcher B. The Cln3-Cdc28 kinase complex of S. cerevisiae is regulated by proteolysis and phosphorylation. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1773–1784. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05229.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. R. Labeling of RNA and phosphoproteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:423–428. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94033-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. H., Green S. R., Barker D. G., Dumas L. B., Johnston L. H. The CDC8 transcript is cell cycle regulated in yeast and is expressed coordinately with CDC9 and CDC21 at a point preceding histone transcription. Exp Cell Res. 1987 Jul;171(1):223–231. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90265-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiebel F. F., Kunau W. H. The Pas2 protein essential for peroxisome biogenesis is related to ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes. Nature. 1992 Sep 3;359(6390):73–76. doi: 10.1038/359073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zioncheck T. F., Harrison M. L., Geahlen R. L. Purification and characterization of a protein-tyrosine kinase from bovine thymus. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15637–15643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]