Abstract
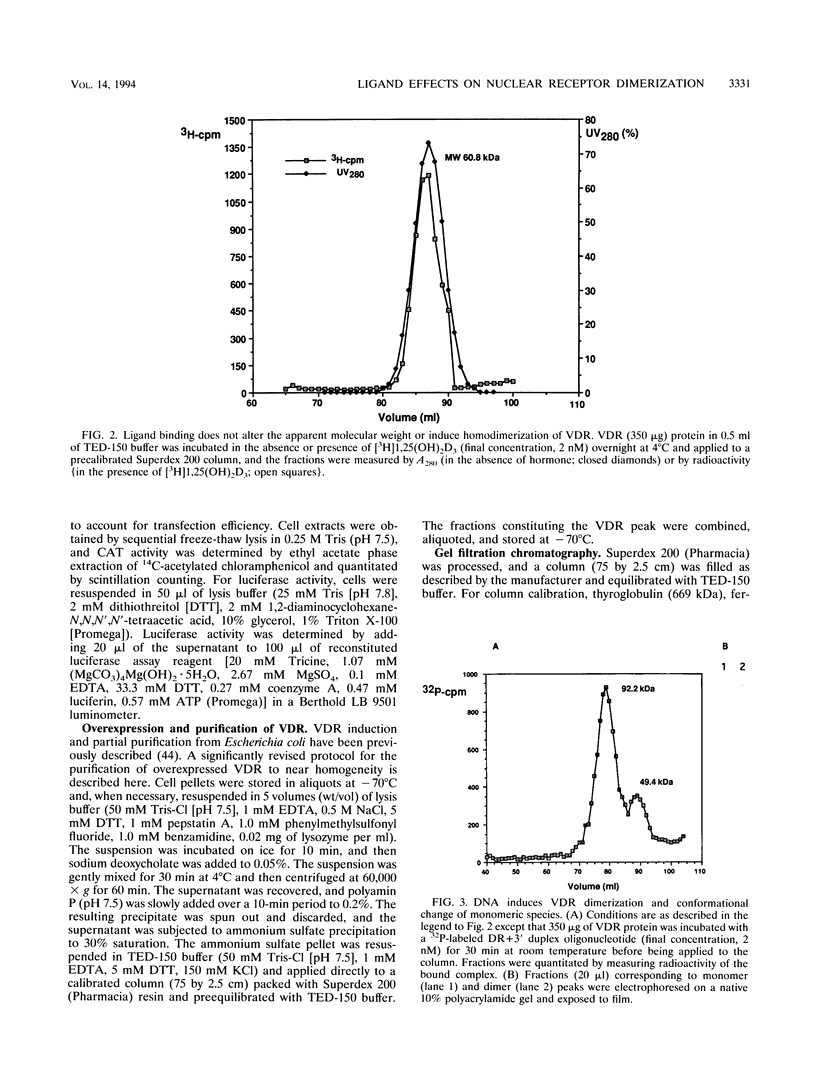
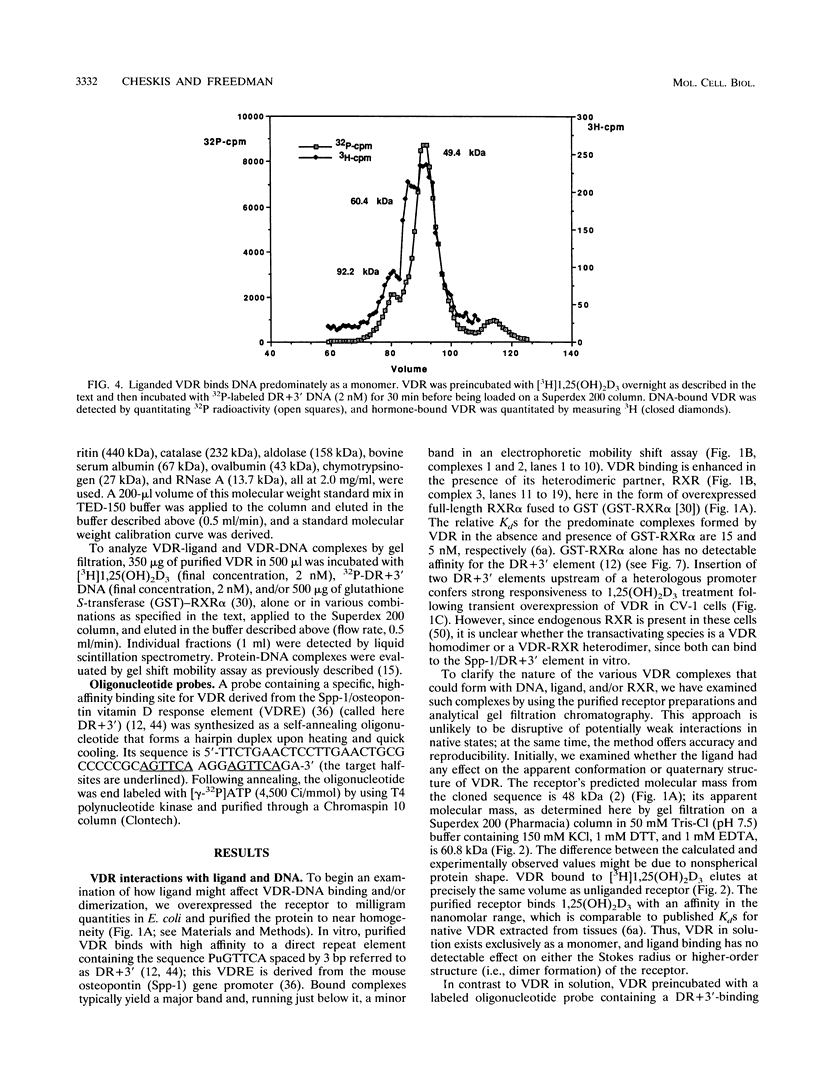
Protein dimerization facilitates cooperative, high-affinity interactions with DNA. Nuclear hormone receptors, for example, bind either as homodimers or as heterodimers with retinoid X receptors (RXR) to half-site repeats that are stabilized by protein-protein interactions mediated by residues within both the DNA- and ligand-binding domains. In vivo, ligand binding among the subfamily of steroid receptors unmasks the nuclear localization and DNA-binding domains from a complex with auxiliary factors such as the heat shock proteins. However, the role of ligand is less clear among nuclear receptors, since they are constitutively localized to the nucleus and are presumably associated with DNA in the absence of ligand. In this study, we have begun to explore the role of the ligand in vitamin D3 receptor (VDR) function by examining its effect on receptor homodimer and heterodimer formation. Our results demonstrate that VDR is a monomer in solution; VDR binding to a specific DNA element leads to the formation of a homodimeric complex through a monomeric intermediate. We find that 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3, the ligand for VDR, decreases the amount of the DNA-bound VDR homodimer complex. It does so by significantly decreasing the rate of conversion of DNA-bound monomer to homodimer and at the same time enhancing the dissociation of the dimeric complex. This effectively stabilizes the bound monomeric species, which in turn serves to favor the formation of a VDR-RXR heterodimer. The ligand for RXR, 9-cis retinoic acid, has the opposite effect of destabilizing the heterodimeric-DNA complex. These results may explain how a nuclear receptor can bind DNA constitutively but still act to regulate transcription in a fully hormone-dependent manner.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson M. L., Nordström K., Demczuk S., Harbers M., Vennström B. Thyroid hormone alters the DNA binding properties of chicken thyroid hormone receptors alpha and beta. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Sep 25;20(18):4803–4810. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.18.4803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker A. R., McDonnell D. P., Hughes M., Crisp T. M., Mangelsdorf D. J., Haussler M. R., Pike J. W., Shine J., O'Malley B. W. Cloning and expression of full-length cDNA encoding human vitamin D receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3294–3298. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkenstam A., Vivanco Ruiz M. M., Barettino D., Horikoshi M., Stunnenberg H. G. Cooperativity in transactivation between retinoic acid receptor and TFIID requires an activity analogous to E1A. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):401–412. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90443-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bugge T. H., Pohl J., Lonnoy O., Stunnenberg H. G. RXR alpha, a promiscuous partner of retinoic acid and thyroid hormone receptors. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1409–1418. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05186.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlberg C., Bendik I., Wyss A., Meier E., Sturzenbecker L. J., Grippo J. F., Hunziker W. Two nuclear signalling pathways for vitamin D. Nature. 1993 Feb 18;361(6413):657–660. doi: 10.1038/361657a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalman F. C., Koenig R. J., Perdew G. H., Massa E., Pratt W. B. In contrast to the glucocorticoid receptor, the thyroid hormone receptor is translated in the DNA binding state and is not associated with hsp90. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):3615–3618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalman F. C., Sturzenbecker L. J., Levin A. A., Lucas D. A., Perdew G. H., Petkovitch M., Chambon P., Grippo J. F., Pratt W. B. Retinoic acid receptor belongs to a subclass of nuclear receptors that do not form "docking" complexes with hsp90. Biochemistry. 1991 Jun 4;30(22):5605–5608. doi: 10.1021/bi00236a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawell S. E., Lees J. A., White R., Parker M. G. Characterization and colocalization of steroid binding and dimerization activities in the mouse estrogen receptor. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):953–962. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90343-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fondell J. D., Roy A. L., Roeder R. G. Unliganded thyroid hormone receptor inhibits formation of a functional preinitiation complex: implications for active repression. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7B):1400–1410. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7b.1400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman B. M., Yang C. R., Au M., Casanova J., Ghysdael J., Samuels H. H. A domain containing leucine-zipper-like motifs mediate novel in vivo interactions between the thyroid hormone and retinoic acid receptors. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Oct;3(10):1610–1626. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-10-1610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman L. P., Arce V., Perez Fernandez R. DNA sequences that act as high affinity targets for the vitamin D3 receptor in the absence of the retinoid X receptor. Mol Endocrinol. 1994 Mar;8(3):265–273. doi: 10.1210/mend.8.3.8015545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman L. P., Luisi B. F., Korszun Z. R., Basavappa R., Sigler P. B., Yamamoto K. R. The function and structure of the metal coordination sites within the glucocorticoid receptor DNA binding domain. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):543–546. doi: 10.1038/334543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman L. P., Luisi B. F. On the mechanism of DNA binding by nuclear hormone receptors: a structural and functional perspective. J Cell Biochem. 1993 Feb;51(2):140–150. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240510205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman L. P., Towers T. L. DNA binding properties of the vitamin D3 receptor zinc finger region. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Dec;5(12):1815–1826. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-12-1815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godowski P. J., Rusconi S., Miesfeld R., Yamamoto K. R. Glucocorticoid receptor mutants that are constitutive activators of transcriptional enhancement. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):365–368. doi: 10.1038/325365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall B. L., Smit-McBride Z., Privalsky M. L. Reconstitution of retinoid X receptor function and combinatorial regulation of other nuclear hormone receptors in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 1;90(15):6929–6933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.6929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heery D. M., Zacharewski T., Pierrat B., Gronemeyer H., Chambon P., Losson R. Efficient transactivation by retinoic acid receptors in yeast requires retinoid X receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):4281–4285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.4281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Härd T., Kellenbach E., Boelens R., Maler B. A., Dahlman K., Freedman L. P., Carlstedt-Duke J., Yamamoto K. R., Gustafsson J. A., Kaptein R. Solution structure of the glucocorticoid receptor DNA-binding domain. Science. 1990 Jul 13;249(4965):157–160. doi: 10.1126/science.2115209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ing N. H., Beekman J. M., Tsai S. Y., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Members of the steroid hormone receptor superfamily interact with TFIIB (S300-II). J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):17617–17623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliewer S. A., Umesono K., Mangelsdorf D. J., Evans R. M. Retinoid X receptor interacts with nuclear receptors in retinoic acid, thyroid hormone and vitamin D3 signalling. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):446–449. doi: 10.1038/355446a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar V., Chambon P. The estrogen receptor binds tightly to its responsive element as a ligand-induced homodimer. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):145–156. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurokawa R., Yu V. C., När A., Kyakumoto S., Han Z., Silverman S., Rosenfeld M. G., Glass C. K. Differential orientations of the DNA-binding domain and carboxy-terminal dimerization interface regulate binding site selection by nuclear receptor heterodimers. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7B):1423–1435. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7b.1423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann J. M., Jong L., Fanjul A., Cameron J. F., Lu X. P., Haefner P., Dawson M. I., Pfahl M. Retinoids selective for retinoid X receptor response pathways. Science. 1992 Dec 18;258(5090):1944–1946. doi: 10.1126/science.1335166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann J. M., Zhang X. K., Graupner G., Lee M. O., Hermann T., Hoffmann B., Pfahl M. Formation of retinoid X receptor homodimers leads to repression of T3 response: hormonal cross talk by ligand-induced squelching. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7698–7707. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leid M., Kastner P., Lyons R., Nakshatri H., Saunders M., Zacharewski T., Chen J. Y., Staub A., Garnier J. M., Mader S. Purification, cloning, and RXR identity of the HeLa cell factor with which RAR or TR heterodimerizes to bind target sequences efficiently. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):377–395. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90478-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luisi B. F., Xu W. X., Otwinowski Z., Freedman L. P., Yamamoto K. R., Sigler P. B. Crystallographic analysis of the interaction of the glucocorticoid receptor with DNA. Nature. 1991 Aug 8;352(6335):497–505. doi: 10.1038/352497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald P. N., Dowd D. R., Nakajima S., Galligan M. A., Reeder M. C., Haussler C. A., Ozato K., Haussler M. R. Retinoid X receptors stimulate and 9-cis retinoic acid inhibits 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3-activated expression of the rat osteocalcin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5907–5917. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Umesono K., Kliewer S. A., Borgmeyer U., Ong E. S., Evans R. M. A direct repeat in the cellular retinol-binding protein type II gene confers differential regulation by RXR and RAR. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):555–561. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks M. S., Hallenbeck P. L., Nagata T., Segars J. H., Appella E., Nikodem V. M., Ozato K. H-2RIIBP (RXR beta) heterodimerization provides a mechanism for combinatorial diversity in the regulation of retinoic acid and thyroid hormone responsive genes. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1419–1435. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05187.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell D. P., Pike J. W., Drutz D. J., Butt T. R., O'Malley B. W. Reconstitution of the vitamin D-responsive osteocalcin transcription unit in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3517–3523. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miner J. N., Yamamoto K. R. Regulatory crosstalk at composite response elements. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Nov;16(11):423–426. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90168-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto T., Suzuki S., DeGroot L. J. High affinity and specificity of dimeric binding of thyroid hormone receptors to DNA and their ligand-dependent dissociation. Mol Endocrinol. 1993 Feb;7(2):224–231. doi: 10.1210/mend.7.2.8469235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Vogel R. L., Craig A. M., Prahl J., DeLuca H. F., Denhardt D. T. Identification of a DNA sequence responsible for binding of the 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptor and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 enhancement of mouse secreted phosphoprotein 1 (SPP-1 or osteopontin) gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9995–9999. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- När A. M., Boutin J. M., Lipkin S. M., Yu V. C., Holloway J. M., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G. The orientation and spacing of core DNA-binding motifs dictate selective transcriptional responses to three nuclear receptors. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1267–1279. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90021-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel L., Abate C., Curran T. Altered protein conformation on DNA binding by Fos and Jun. Nature. 1990 Oct 11;347(6293):572–575. doi: 10.1038/347572a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann T., Rangarajan P. N., Umesono K., Evans R. M. Determinants for selective RAR and TR recognition of direct repeat HREs. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7B):1411–1422. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7b.1411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Salser S. J., Yamamoto K. R. A movable and regulable inactivation function within the steroid binding domain of the glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):1073–1080. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90122-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privalsky M. L., Sharif M., Yamamoto K. R. The viral erbA oncogene protein, a constitutive repressor in animal cells, is a hormone-regulated activator in yeast. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1277–1286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90423-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saatcioglu F., Deng T., Karin M. A novel cis element mediating ligand-independent activation by c-ErbA: implications for hormonal regulation. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1095–1105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90319-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Evans R. M. Cross-coupling of signal transduction pathways: zinc finger meets leucine zipper. Trends Genet. 1991 Nov-Dec;7(11-12):377–381. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90259-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sone T., Kerner S., Pike J. W. Vitamin D receptor interaction with specific DNA. Association as a 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3-modulated heterodimer. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 5;266(34):23296–23305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towers T. L., Luisi B. F., Asianov A., Freedman L. P. DNA target selectivity by the vitamin D3 receptor: mechanism of dimer binding to an asymmetric repeat element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6310–6314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umesono K., Murakami K. K., Thompson C. C., Evans R. M. Direct repeats as selective response elements for the thyroid hormone, retinoic acid, and vitamin D3 receptors. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1255–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90020-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson T. E., Fahrner T. J., Milbrandt J. The orphan receptors NGFI-B and steroidogenic factor 1 establish monomer binding as a third paradigm of nuclear receptor-DNA interaction. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5794–5804. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrange O., Eriksson P., Perlmann T. The purified activated glucocorticoid receptor is a homodimer. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):5253–5259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen P. M., Sugawara A., Chin W. W. Triiodothyronine (T3) differentially affects T3-receptor/retinoic acid receptor and T3-receptor/retinoid X receptor heterodimer binding to DNA. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):23248–23252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu V. C., Delsert C., Andersen B., Holloway J. M., Devary O. V., När A. M., Kim S. Y., Boutin J. M., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G. RXR beta: a coregulator that enhances binding of retinoic acid, thyroid hormone, and vitamin D receptors to their cognate response elements. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1251–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90301-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. K., Hoffmann B., Tran P. B., Graupner G., Pfahl M. Retinoid X receptor is an auxiliary protein for thyroid hormone and retinoic acid receptors. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):441–446. doi: 10.1038/355441a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. K., Lehmann J., Hoffmann B., Dawson M. I., Cameron J., Graupner G., Hermann T., Tran P., Pfahl M. Homodimer formation of retinoid X receptor induced by 9-cis retinoic acid. Nature. 1992 Aug 13;358(6387):587–591. doi: 10.1038/358587a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







