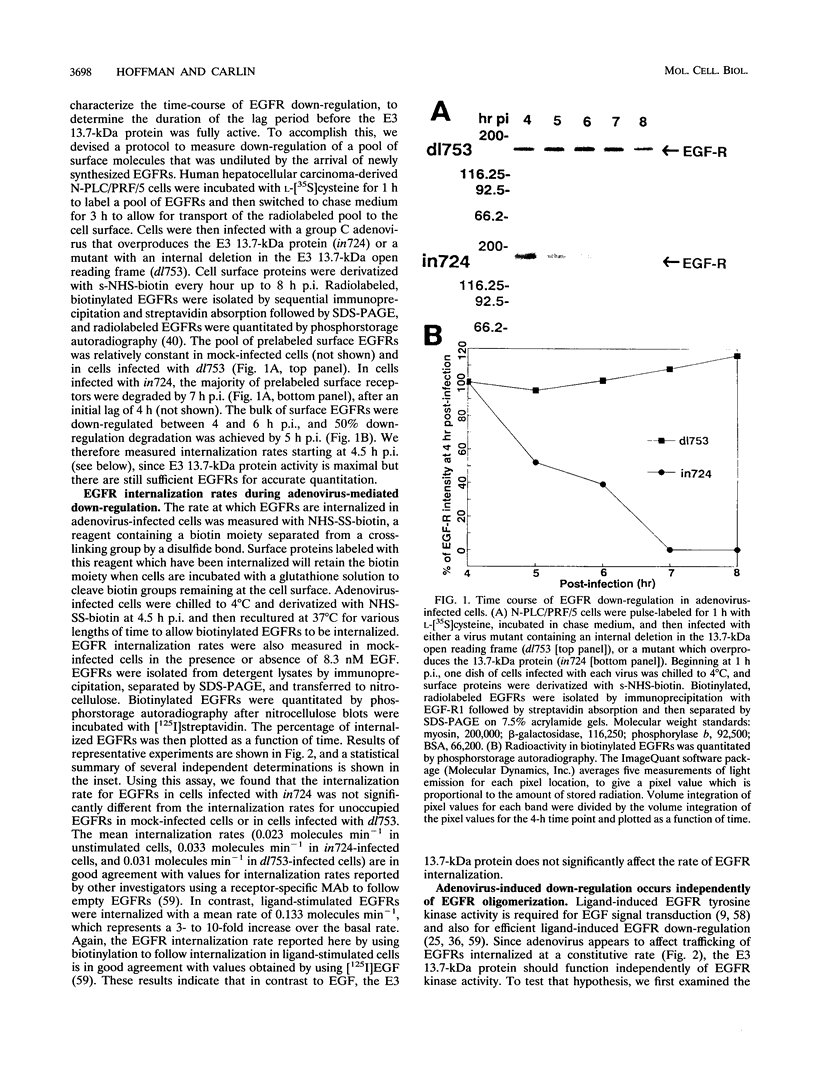
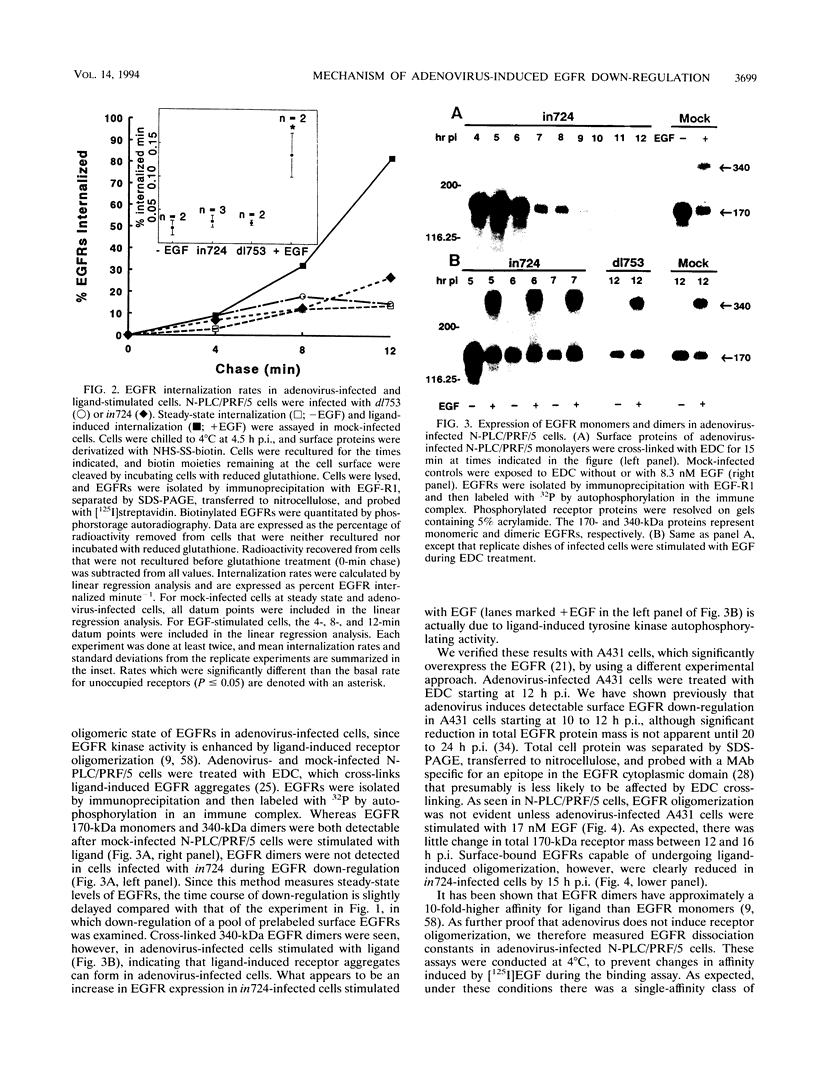
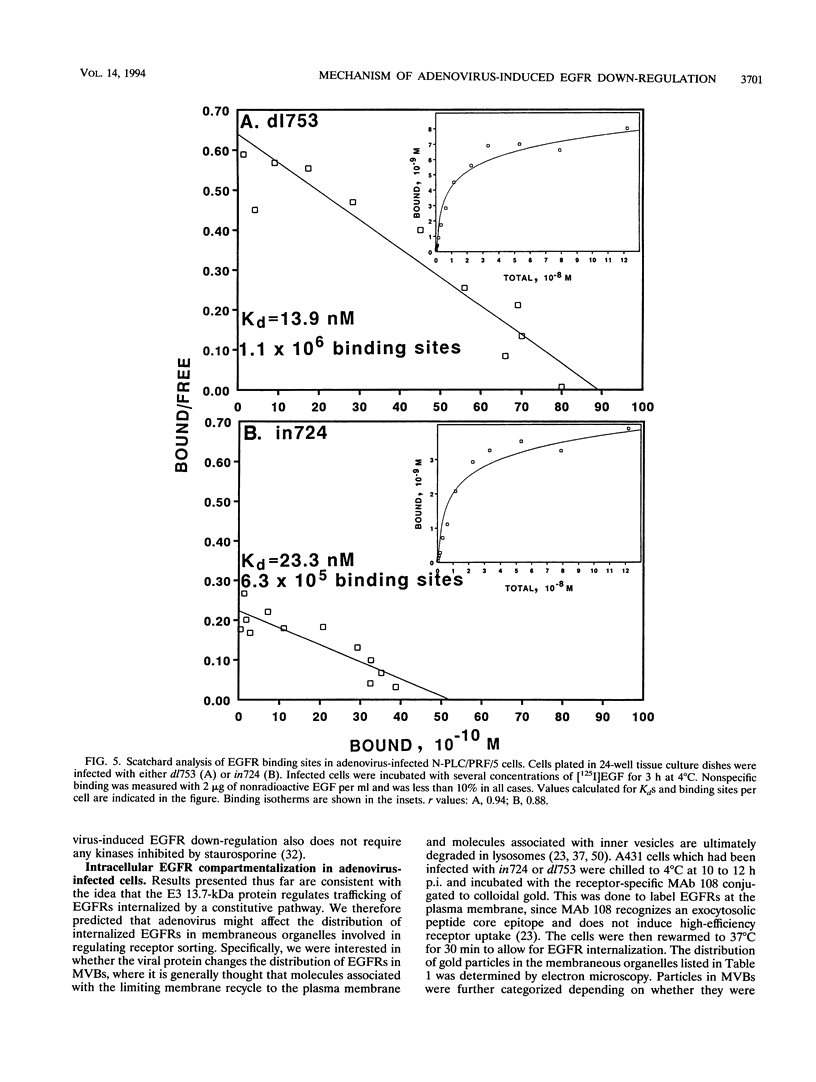
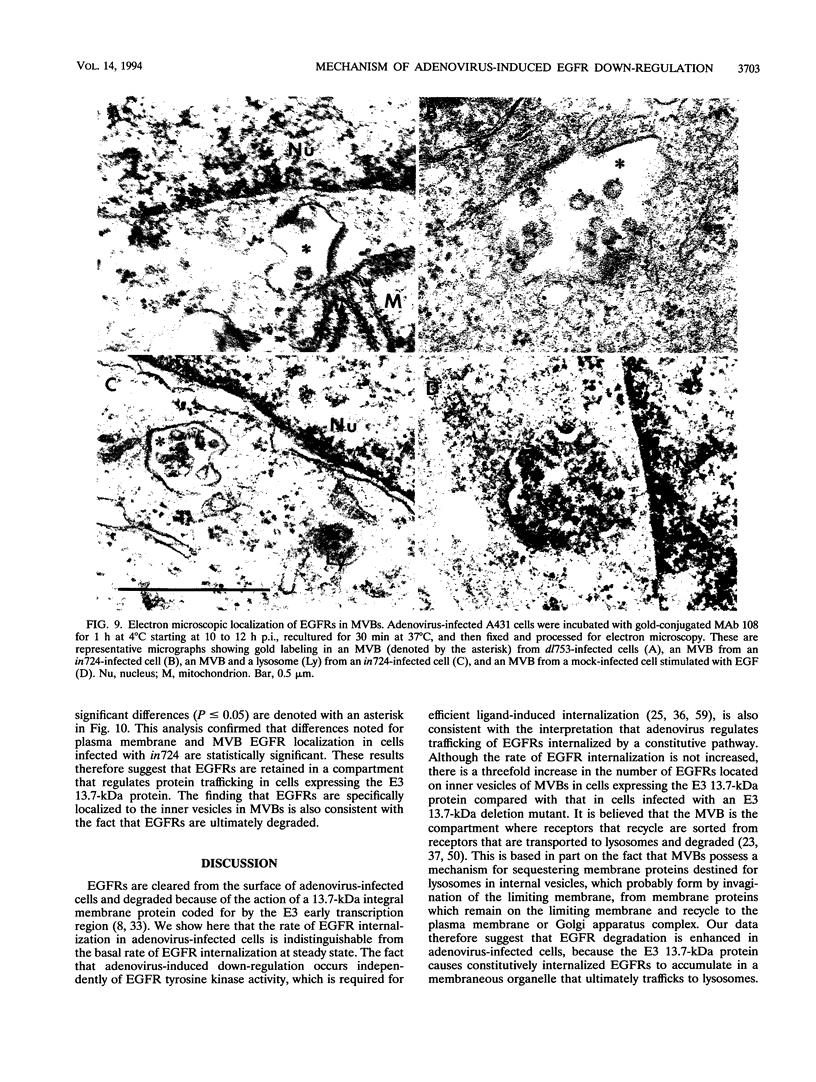
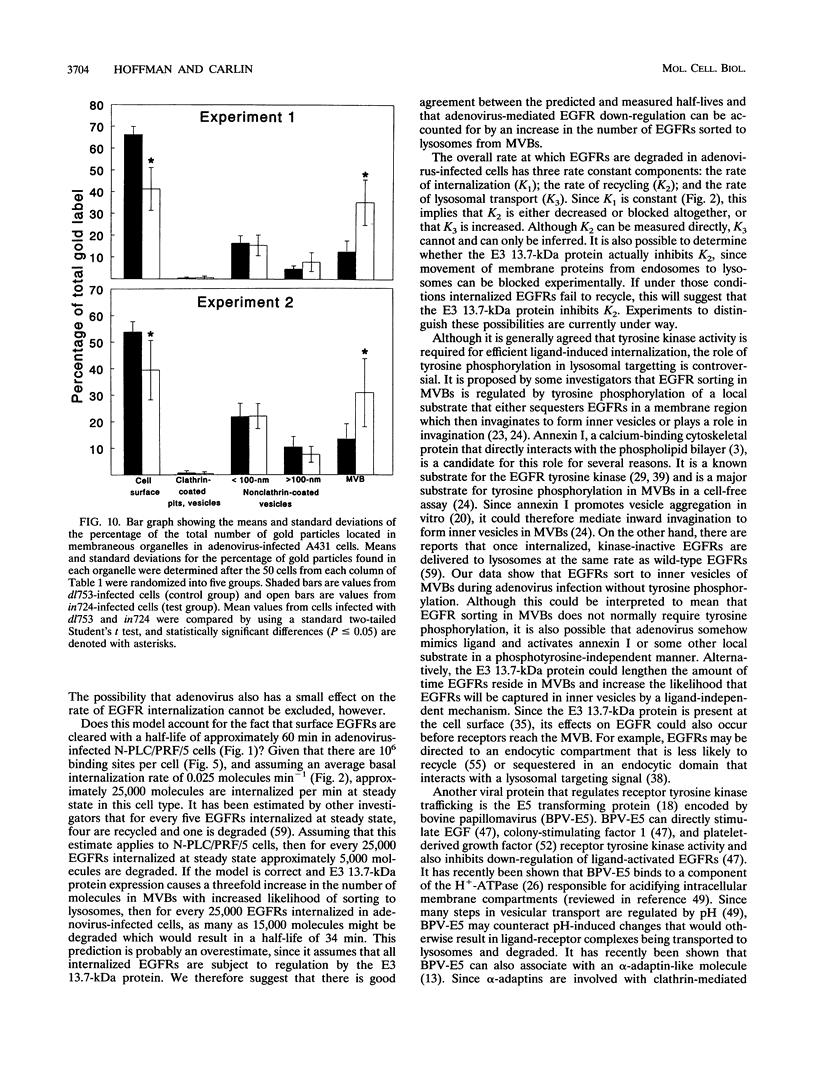
Abstract
We have previously identified and characterized an integral membrane protein coded for by the early transcription region 3 (E3) of human group C adenoviruses that down-regulates the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). The goal of this study was to characterize the early receptor trafficking events leading to enhanced EGFR degradation in adenovirus-infected cells. Specifically, we wished to determine whether adenovirus increases the rate of EGFR internalization or alters the subcellular compartmentalization of internalized EGFRs. Once the optimal time for measuring early trafficking events was determined, surface EGFRs were labeled with a cleavable biotin reagent to measure internalization rates and with a receptor-specific monoclonal antibody (MAb) conjugated to colloidal gold for intracellular localization studies. We first showed that the rate of EGFR internalization in adenovirus-infected cells is indistinguishable from the constitutive internalization rate for unoccupied EGFRs. The possibility that the E3 protein can affect trafficking of EGFRs internalized at a low constitutive rate was further supported by studies showing that adenovirus-mediated down-regulation occurs independently of EGFR oligomerization and intrinsic EGFR tyrosine kinase activity, which are required for efficient ligand-induced internalization. Other tyrosine kinases inhibited by genistein are also not required for adenovirus-induced down-regulation. When the intracellular localization of EGFRs during adenovirus-mediated down-regulation was examined by electron microscopy, there was a threefold increase in the number of EGFRs localized to multivesicular bodies. The multivesicular body has been proposed to be important for regulating intracellular membrane protein sorting, since trafficking patterns for receptors that recycle and receptors that are degraded diverge in this organelle. These data therefore suggest that adenovirus may enhance EGFR degradation by causing constitutively internalized EGFRs to accumulate in a prelysosomal compartment. This is the first example of a mechanism that efficiently down-regulates EGFR without significantly increasing the rate of internalization or that does not require EGFR tyrosine kinase activity. Since viral proteins often mimic or modify a host counterpart, this suggests that there are normal physiological conditions when receptor destruction without tyrosine signalling is beneficial.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyama T., Ishida J., Nakagawa S., Ogawara H., Watanabe S., Itoh N., Shibuya M., Fukami Y. Genistein, a specific inhibitor of tyrosine-specific protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5592–5595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arsenis G., Hayes G. R., Livingston J. N. Insulin receptor cycling and insulin action in the rat adipocyte. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2202–2207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwood R. A., Ernst J. D. Characterization of Ca2(+)-dependent phospholipid binding, vesicle aggregation and membrane fusion by annexins. Biochem J. 1990 Feb 15;266(1):195–200. doi: 10.1042/bj2660195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Auger K. R., Carpenter C., Duckworth B., Graziani A., Kapeller R., Soltoff S. Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):281–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90639-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlin C. R., Knowles B. B. Biosynthesis of the epidermal growth factor receptor in human epidermoid carcinoma-derived A431 cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7902–7908. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlin C. R., Knowles B. B. Identity of human epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor with glycoprotein SA-7: evidence for differential phosphorylation of the two components of the EGF receptor from A431 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):5026–5030. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.5026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlin C. R., Simon D., Mattison J., Knowles B. B. Expression and biosynthetic variation of the epidermal growth factor receptor in human hepatocellular carcinoma-derived cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):25–34. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlin C. R., Tollefson A. E., Brady H. A., Hoffman B. L., Wold W. S. Epidermal growth factor receptor is down-regulated by a 10,400 MW protein encoded by the E3 region of adenovirus. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):135–144. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90179-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G. Receptors for epidermal growth factor and other polypeptide mitogens. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:881–914. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. P., Kao J. P., Lazar C. S., Walsh B. J., Wells A., Wiley H. S., Gill G. N., Rosenfeld M. G. Ligand-induced internalization and increased cell calcium are mediated via distinct structural elements in the carboxyl terminus of the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 5;266(34):23467–23470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W. S., Lazar C. S., Lund K. A., Welsh J. B., Chang C. P., Walton G. M., Der C. J., Wiley H. S., Gill G. N., Rosenfeld M. G. Functional independence of the epidermal growth factor receptor from a domain required for ligand-induced internalization and calcium regulation. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):33–43. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90867-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen B. D., Lowy D. R., Schiller J. T. The conserved C-terminal domain of the bovine papillomavirus E5 oncoprotein can associate with an alpha-adaptin-like molecule: a possible link between growth factor receptors and viral transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;13(10):6462–6468. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.10.6462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Countaway J. L., Northwood I. C., Davis R. J. Mechanism of phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor at threonine 669. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10828–10835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Fiore P. P., Pierce J. H., Kraus M. H., Segatto O., King C. R., Aaronson S. A. erbB-2 is a potent oncogene when overexpressed in NIH/3T3 cells. Science. 1987 Jul 10;237(4811):178–182. doi: 10.1126/science.2885917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMaio D., Guralski D., Schiller J. T. Translation of open reading frame E5 of bovine papillomavirus is required for its transforming activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1797–1801. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebner R., Derynck R. Epidermal growth factor and transforming growth factor-alpha: differential intracellular routing and processing of ligand-receptor complexes. Cell Regul. 1991 Aug;2(8):599–612. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.8.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst J. D., Hoye E., Blackwood R. A., Mok T. L. Identification of a domain that mediates vesicle aggregation reveals functional diversity of annexin repeats. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 15;266(11):6670–6673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabricant R. N., De Larco J. E., Todaro G. J. Nerve growth factor receptors on human melanoma cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):565–569. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felder S., LaVin J., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Kinetics of binding, endocytosis, and recycling of EGF receptor mutants. J Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;117(1):203–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.1.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felder S., Miller K., Moehren G., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Hopkins C. R. Kinase activity controls the sorting of the epidermal growth factor receptor within the multivesicular body. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):623–634. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90474-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Futter C. E., Felder S., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A., Hopkins C. R. Annexin I is phosphorylated in the multivesicular body during the processing of the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;120(1):77–83. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Chen W. S., Lazar C. S., Walton G. M., Zokas L. M., Rosenfeld M. G., Gill G. N. Ligand-induced endocytosis of the EGF receptor is blocked by mutational inactivation and by microinjection of anti-phosphotyrosine antibodies. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):675–684. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90405-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Tack B., Powell M. A. Calpactins: two distinct Ca++-regulated phospholipid- and actin-binding proteins isolated from lung and placenta. J Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;104(3):503–511. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.3.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. J., Finbow M. E., Andresson T., McLean P., Smith K., Bubb V., Schlegel R. Bovine papillomavirus E5 oncoprotein binds to the 16K component of vacuolar H(+)-ATPases. Nature. 1991 Jul 25;352(6333):347–349. doi: 10.1038/352347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S. A., Kelly R. B. Low density lipoprotein receptor and cation-independent mannose 6-phosphate receptor are transported from the cell surface to the Golgi apparatus at equal rates in PC12 cells. J Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;117(1):47–55. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullick W. J., Marsden J. J., Whittle N., Ward B., Bobrow L., Waterfield M. D. Expression of epidermal growth factor receptors on human cervical, ovarian, and vulval carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1986 Jan;46(1):285–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen S. H., Sandvig K., van Deurs B. The preendosomal compartment comprises distinct coated and noncoated endocytic vesicle populations. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(4):731–741. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.4.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heisermann G. J., Wiley H. S., Walsh B. J., Ingraham H. A., Fiol C. J., Gill G. N. Mutational removal of the Thr669 and Ser671 phosphorylation sites alters substrate specificity and ligand-induced internalization of the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):12820–12827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman B. L., Takishima K., Rosner M. R., Carlin C. Adenovirus and protein kinase C have distinct molecular requirements for regulating epidermal growth factor receptor trafficking. J Cell Physiol. 1993 Dec;157(3):535–543. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041570313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman B. L., Ullrich A., Wold W. S., Carlin C. R. Retrovirus-mediated transfer of an adenovirus gene encoding an integral membrane protein is sufficient to down regulate the receptor for epidermal growth factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5521–5524. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P., Rajakumar P., Hoffman B., Heuertz R., Wold W. S., Carlin C. R. Evidence for intracellular down-regulation of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor during adenovirus infection by an EGF-independent mechanism. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):197–203. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.197-203.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P., Yaffe M. B., Hoffman B. L., Yei S., Wold W. S., Carlin C. Characterization of the adenovirus E3 protein that down-regulates the epidermal growth factor receptor. Evidence for intermolecular disulfide bonding and plasma membrane localization. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13480–13487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honegger A. M., Dull T. J., Felder S., Van Obberghen E., Bellot F., Szapary D., Schmidt A., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Point mutation at the ATP binding site of EGF receptor abolishes protein-tyrosine kinase activity and alters cellular routing. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):199–209. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90147-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins C. R., Gibson A., Shipman M., Miller K. Movement of internalized ligand-receptor complexes along a continuous endosomal reticulum. Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):335–339. doi: 10.1038/346335a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins C. R. Intracellular routing of transferrin and transferrin receptors in epidermoid carcinoma A431 cells. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):321–330. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90235-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K. S., Wallner B. P., Mattaliano R. J., Tizard R., Burne C., Frey A., Hession C., McGray P., Sinclair L. K., Chow E. P. Two human 35 kd inhibitors of phospholipase A2 are related to substrates of pp60v-src and of the epidermal growth factor receptor/kinase. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):191–199. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90736-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. F., Pickett S. C., Barker D. L. Autoradiography using storage phosphor technology. Electrophoresis. 1990 May;11(5):355–360. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150110503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krajcsi P., Tollefson A. E., Anderson C. W., Stewart A. R., Carlin C. R., Wold W. S. The E3-10.4K protein of adenovirus is an integral membrane protein that is partially cleaved between Ala22 and Ala23 and has a Ccyt orientation. Virology. 1992 Mar;187(1):131–144. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90302-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuivinen E., Hoffman B. L., Hoffman P. A., Carlin C. R. Structurally related class I and class II receptor protein tyrosine kinases are down-regulated by the same E3 protein coded for by human group C adenoviruses. J Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;120(5):1271–1279. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.5.1271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kull F. C., Jr, Jacobs S., Su Y. F., Svoboda M. E., Van Wyk J. J., Cuatrecasas P. Monoclonal antibodies to receptors for insulin and somatomedin-C. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6561–6566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai W. H., Cameron P. H., Wada I., Doherty J. J., 2nd, Kay D. G., Posner B. I., Bergeron J. J. Ligand-mediated internalization, recycling, and downregulation of the epidermal growth factor receptor in vivo. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2741–2749. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maratos-Flier E., Kao C. Y., Verdin E. M., King G. L. Receptor-mediated vectorial transcytosis of epidermal growth factor by Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. J Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;105(4):1595–1601. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.4.1595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall S., Green A., Olefsky J. M. Evidence for recycling of insulin receptors in isolated rat adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11464–11470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin P., Vass W. C., Schiller J. T., Lowy D. R., Velu T. J. The bovine papillomavirus E5 transforming protein can stimulate the transforming activity of EGF and CSF-1 receptors. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):21–32. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90866-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masui H., Castro L., Mendelsohn J. Consumption of EGF by A431 cells: evidence for receptor recycling. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;120(1):85–93. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellman I., Fuchs R., Helenius A. Acidification of the endocytic and exocytic pathways. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:663–700. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K., Beardmore J., Kanety H., Schlessinger J., Hopkins C. R. Localization of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor within the endosome of EGF-stimulated epidermoid carcinoma (A431) cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;102(2):500–509. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.2.500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse B. M., Robinson M. S. Clathrin, adaptors, and sorting. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:151–171. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.001055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petti L., Nilson L. A., DiMaio D. Activation of the platelet-derived growth factor receptor by the bovine papillomavirus E5 transforming protein. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):845–855. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08017.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Boulan E., Nelson W. J. Morphogenesis of the polarized epithelial cell phenotype. Science. 1989 Aug 18;245(4919):718–725. doi: 10.1126/science.2672330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slot J. W., Geuze H. J. A new method of preparing gold probes for multiple-labeling cytochemistry. Eur J Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;38(1):87–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoorvogel W., Geuze H. J., Griffith J. M., Schwartz A. L., Strous G. J. Relations between the intracellular pathways of the receptors for transferrin, asialoglycoprotein, and mannose 6-phosphate in human hepatoma cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;108(6):2137–2148. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.6.2137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takishima K., Griswold-Prenner I., Ingebritsen T., Rosner M. R. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor T669 peptide kinase from 3T3-L1 cells is an EGF-stimulated "MAP" kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2520–2524. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley H. S., Herbst J. J., Walsh B. J., Lauffenburger D. A., Rosenfeld M. G., Gill G. N. The role of tyrosine kinase activity in endocytosis, compartmentation, and down-regulation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):11083–11094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- den Hartigh J. C., van Bergen en Henegouwen P. M., Verkleij A. J., Boonstra J. The EGF receptor is an actin-binding protein. J Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;119(2):349–355. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.2.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]