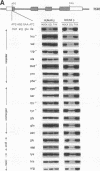
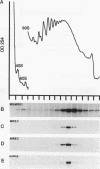
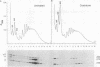
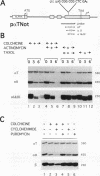
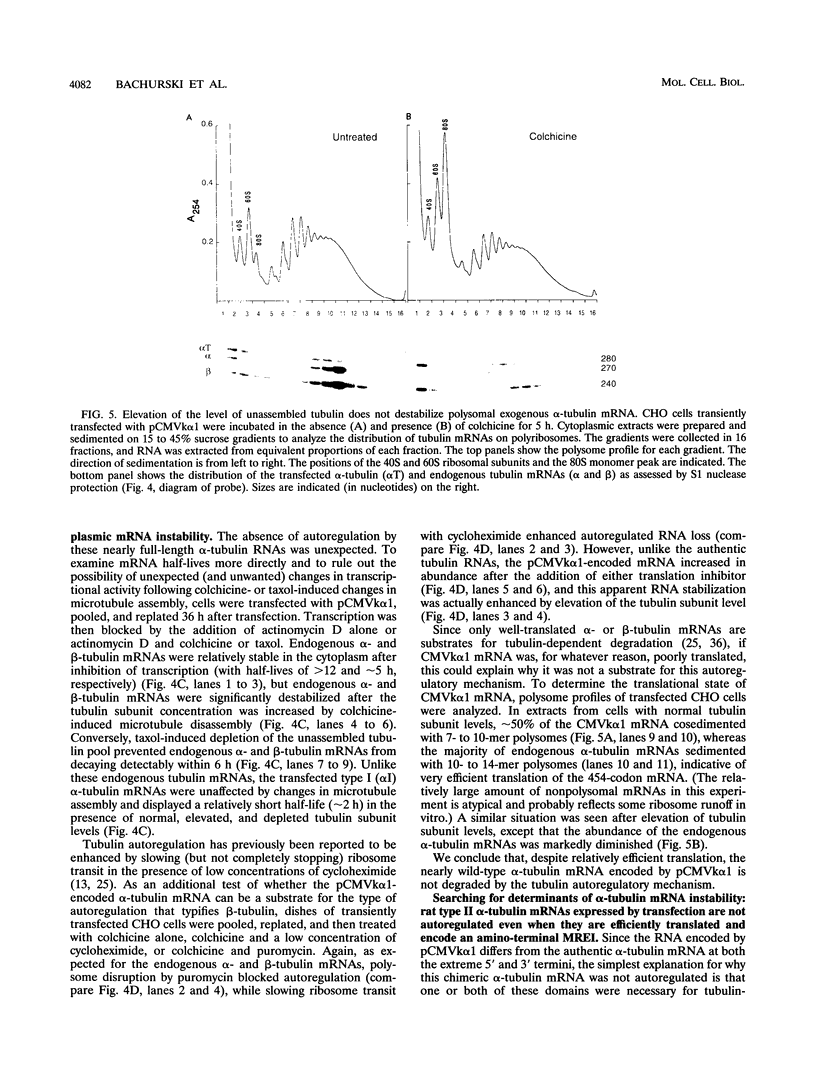
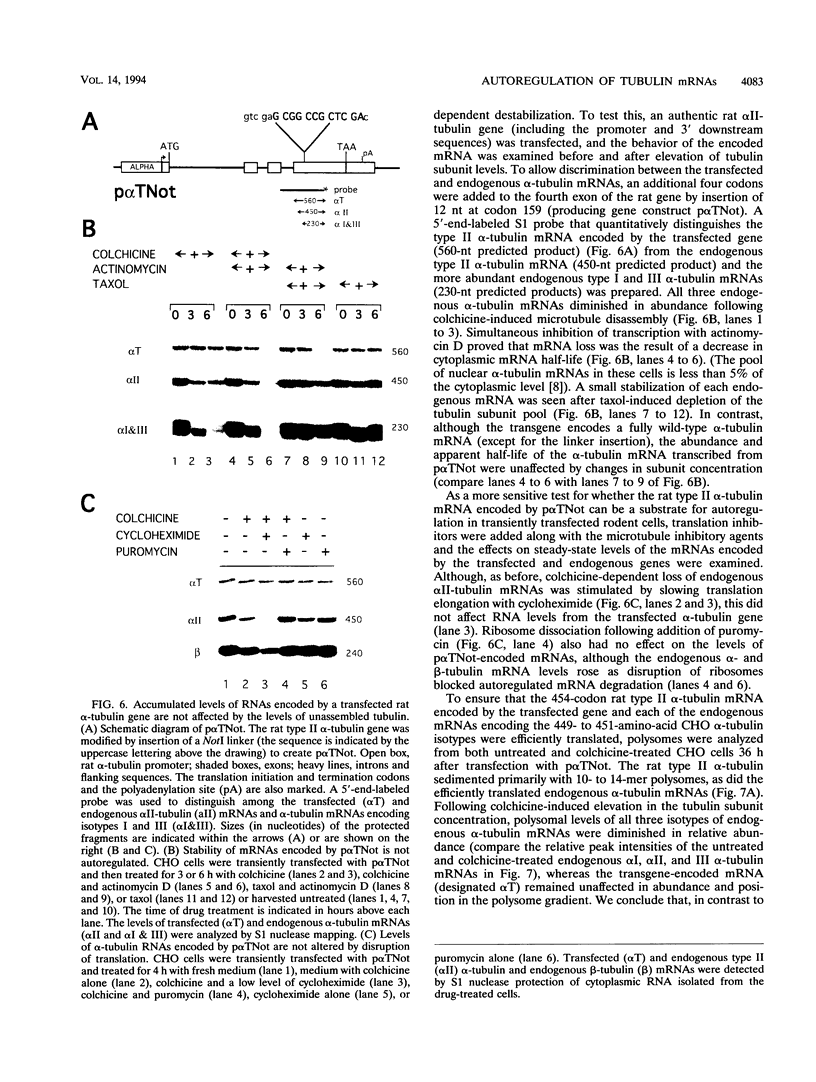
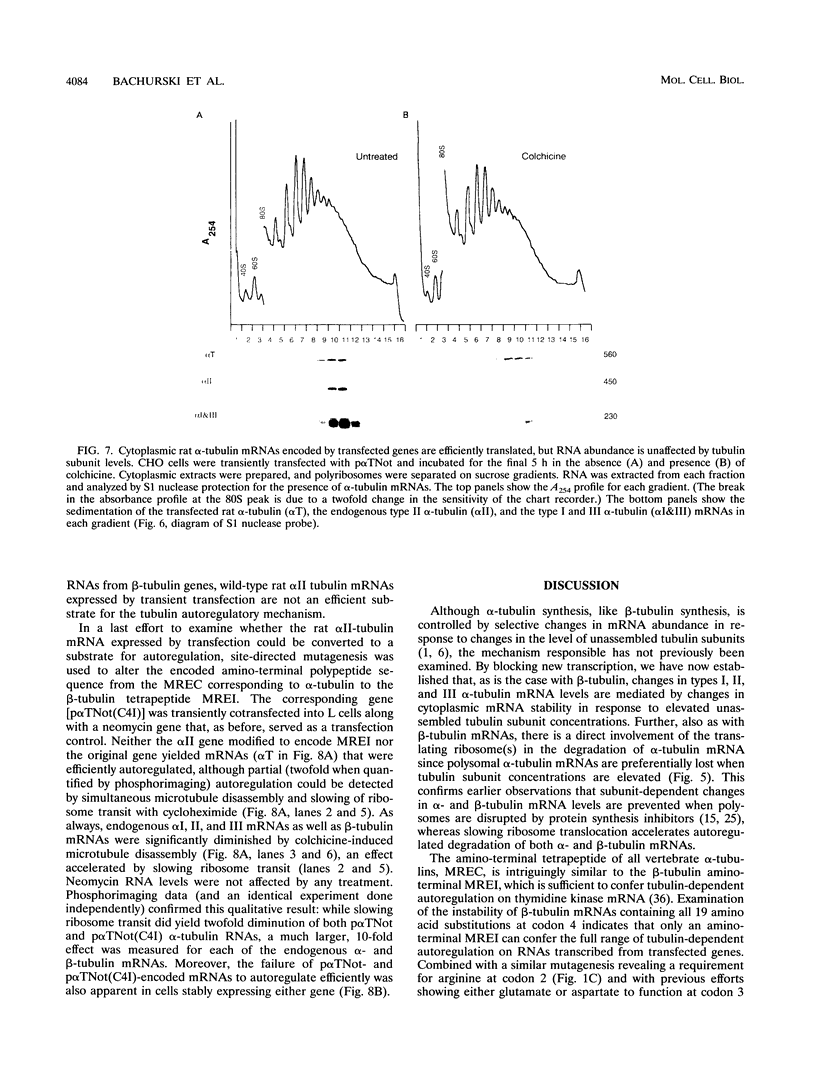
Abstract
The steady-state level of alpha- and beta-tubulin synthesis is autoregulated by a posttranscriptional mechanism that selectively alters alpha- and beta-tubulin mRNA levels in response to changes in the unassembled tubulin subunit concentration. For beta-tubulin mRNAs, previous efforts have shown that this is the result of a selective mRNA degradation mechanism which involves cotranslational recognition of the nascent amino-terminal beta-tubulin tetrapeptide as it emerges from the ribosome. Site-directed mutagenesis is now used to determine that the minimal sequence requirement for conferring the full range of beta-tubulin autoregulation is the amino-terminal tetrapeptide MR(E/D)I. Although tubulin-dependent changes in alpha-tubulin mRNA levels are shown to result from changes in cytoplasmic mRNA stability, transfection of wild-type and mutated alpha-tubulin genes reveals that alpha- and beta-tubulin mRNA degradation is not mediated through a common pathway. Not only does the amino-terminal alpha-tubulin tetrapeptide MREC fail to confer regulated mRNA degradation, neither wild-type alpha-tubulin transgenes nor an alpha-tubulin gene mutated to encode an amino-terminal MREI yields mRNAs that are autoregulated. Further, although slowing ribosome transit accelerates the autoregulated degradation of endogenous alpha- and beta-tubulin mRNAs, degradation of alpha-tubulin transgene mRNAs is not enhanced, and in one case, the mRNA is actually stabilized. We conclude that, despite similarities, alpha- and beta-tubulin mRNA destabilization pathways utilize divergent determinants to link RNA instability to tubulin subunit concentrations.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ben-Ze'ev A., Farmer S. R., Penman S. Mechanisms of regulating tubulin synthesis in cultured mammalian cells. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):319–325. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90157-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caron J. M., Jones A. L., Rall L. B., Kirschner M. W. Autoregulation of tubulin synthesis in enucleated cells. Nature. 1985 Oct 17;317(6038):648–651. doi: 10.1038/317648a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W. Autoregulated control of tubulin synthesis in animal cells. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;1(1):10–14. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(89)80030-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Havercroft J. C. Is apparent autoregulatory control of tubulin synthesis nontranscriptionally regulated? J Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;97(3):919–924. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.3.919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Lopata M. A., Sherline P., Kirschner M. W. Unpolymerized tubulin modulates the level of tubulin mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):537–546. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90072-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Pittenger M. F., Feramisco J. R. Elevation of tubulin levels by microinjection suppresses new tubulin synthesis. Nature. 1983 Oct 20;305(5936):738–740. doi: 10.1038/305738a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulson R. M., Cleveland D. W. Ferritin synthesis is controlled by iron-dependent translational derepression and by changes in synthesis/transport of nuclear ferritin RNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 15;90(16):7613–7617. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.16.7613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan N. J., Dobner P. R., Fuchs E. V., Cleveland D. W. Expression of human alpha-tubulin genes: interspecies conservation of 3' untranslated regions. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Oct;3(10):1738–1745. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.10.1738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker C. J., Parker R. A turnover pathway for both stable and unstable mRNAs in yeast: evidence for a requirement for deadenylation. Genes Dev. 1993 Aug;7(8):1632–1643. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.8.1632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott E. M., Henderson G., Sarangi F., Ling V. Complete sequence of three alpha-tubulin cDNAs in Chinese hamster ovary cells: each encodes a distinct alpha-tubulin isoprotein. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;6(3):906–913. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.3.906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favaloro J., Treisman R., Kamen R. Transcription maps of polyoma virus-specific RNA: analysis by two-dimensional nuclease S1 gel mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):718–749. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay D. A., Sisodia S. S., Cleveland D. W. Autoregulatory control of beta-tubulin mRNA stability is linked to translation elongation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5763–5767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay D. A., Yen T. J., Lau J. T., Cleveland D. W. Sequences that confer beta-tubulin autoregulation through modulated mRNA stability reside within exon 1 of a beta-tubulin mRNA. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):671–679. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90325-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gong Z. Y., Brandhorst B. P. Stabilization of tubulin mRNA by inhibition of protein synthesis in sea urchin embryos. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3518–3525. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves R. A., Pandey N. B., Chodchoy N., Marzluff W. F. Translation is required for regulation of histone mRNA degradation. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):615–626. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90240-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kislauskis E. H., Singer R. H. Determinants of mRNA localization. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;4(6):975–978. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90128-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence J. B., Singer R. H., Marselle L. M. Highly localized tracks of specific transcripts within interphase nuclei visualized by in situ hybridization. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):493–502. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90924-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. G., Lewis S. A., Wilde C. D., Cowan N. J. Evolutionary history of a multigene family: an expressed human beta-tubulin gene and three processed pseudogenes. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90429-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemischka I. R., Farmer S., Racaniello V. R., Sharp P. A. Nucleotide sequence and evolution of a mammalian alpha-tubulin messenger RNA. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 5;151(1):101–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90223-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemischka I., Sharp P. A. The sequences of an expressed rat alpha-tubulin gene and a pseudogene with an inserted repetitive element. Nature. 1982 Nov 25;300(5890):330–335. doi: 10.1038/300330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopata M. A., Cleveland D. W., Sollner-Webb B. High level transient expression of a chloramphenicol acetyl transferase gene by DEAE-dextran mediated DNA transfection coupled with a dimethyl sulfoxide or glycerol shock treatment. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5707–5717. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maquat L. E. Nuclear mRNA export. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;3(6):1004–1012. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90121-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pachter J. S., Yen T. J., Cleveland D. W. Autoregulation of tubulin expression is achieved through specific degradation of polysomal tubulin mRNAs. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90155-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittenger M. F., Cleveland D. W. Retention of autoregulatory control of tubulin synthesis in cytoplasts: demonstration of a cytoplasmic mechanism that regulates the level of tubulin expression. J Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;101(5 Pt 1):1941–1952. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.5.1941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savant-Bhonsale S., Cleveland D. W. Evidence for instability of mRNAs containing AUUUA motifs mediated through translation-dependent assembly of a > 20S degradation complex. Genes Dev. 1992 Oct;6(10):1927–1939. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.10.1927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada T., Cabral F. Expression and function of beta-tubulin isotypes in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):3013–3020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sisodia S. S., Gay D. A., Cleveland D. W. In vivo discrimination among beta-tubulin isotypes: selective degradation of a type IV beta-tubulin isotype following overexpression in cultured animal cells. New Biol. 1990 Jan;2(1):66–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan K. F., Cleveland D. W. Identification of conserved isotype-defining variable region sequences for four vertebrate beta tubulin polypeptide classes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4327–4331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan K. F. Structure and utilization of tubulin isotypes. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:687–716. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.003351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theodorakis N. G., Cleveland D. W. Physical evidence for cotranslational regulation of beta-tubulin mRNA degradation. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):791–799. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. C., Cleveland D. W. Characterization of dominant and recessive assembly-defective mutations in mouse neurofilament NF-M. J Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;111(5 Pt 1):1987–2003. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.5.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen T. J., Gay D. A., Pachter J. S., Cleveland D. W. Autoregulated changes in stability of polyribosome-bound beta-tubulin mRNAs are specified by the first 13 translated nucleotides. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1224–1235. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen T. J., Machlin P. S., Cleveland D. W. Autoregulated instability of beta-tubulin mRNAs by recognition of the nascent amino terminus of beta-tubulin. Nature. 1988 Aug 18;334(6183):580–585. doi: 10.1038/334580a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]