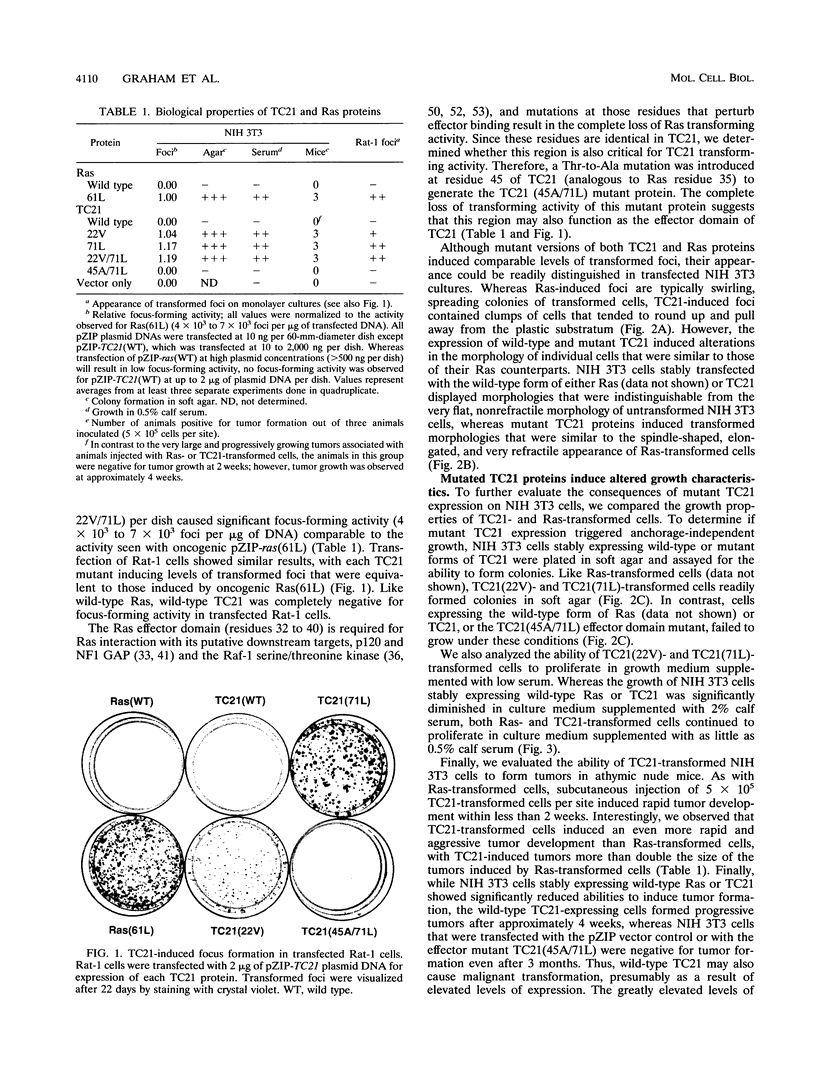
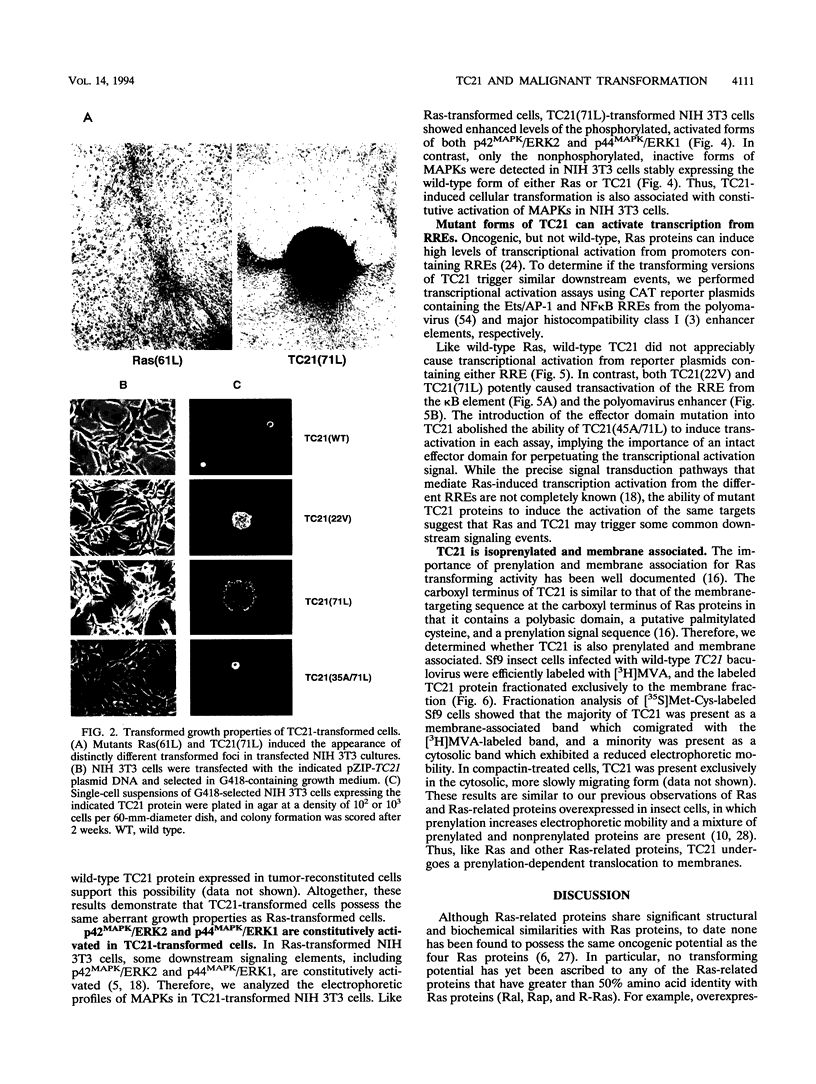
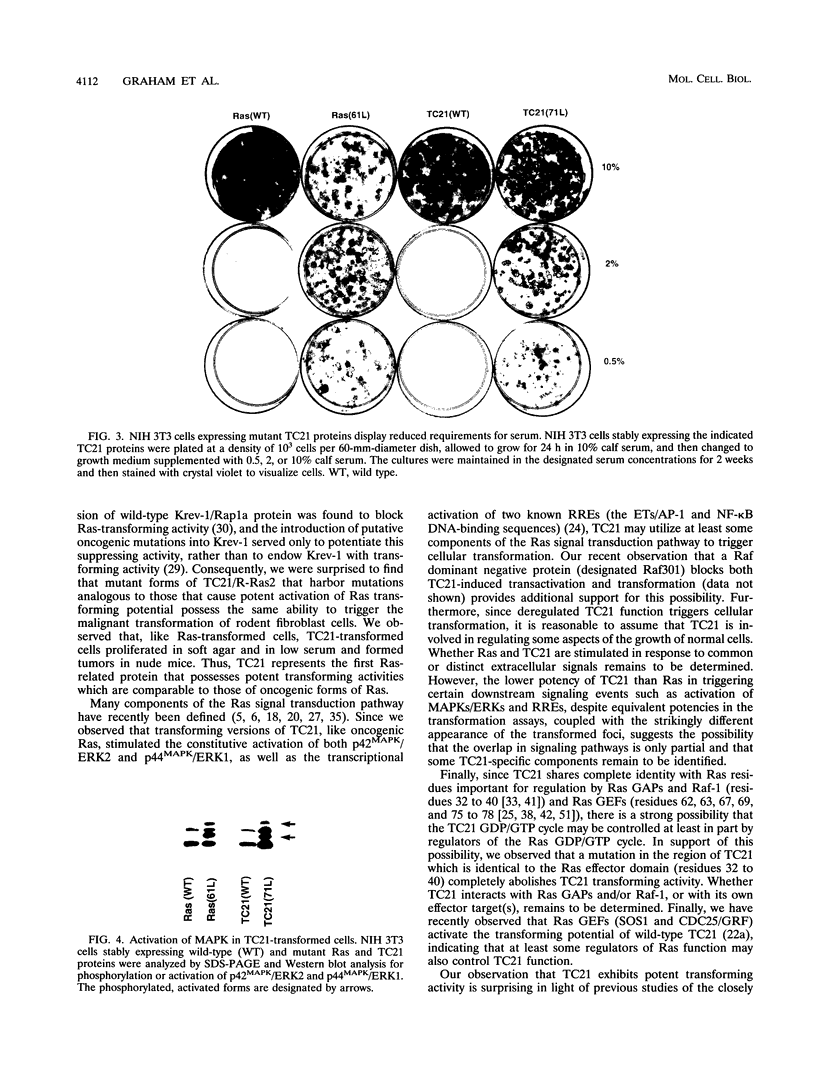
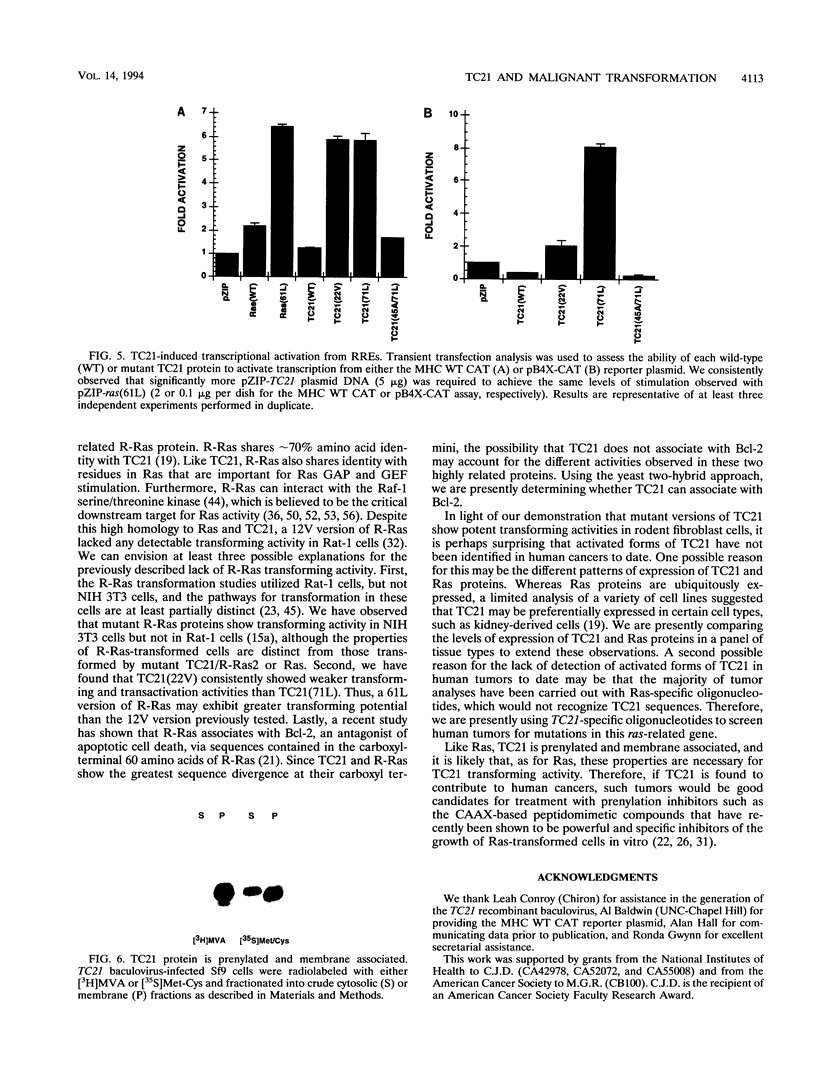
Abstract
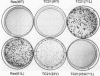
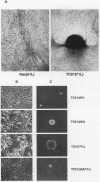
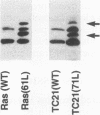
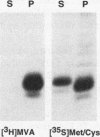
Although the human Ras proteins are members of a large superfamily of Ras-related proteins, to date, only the proteins encoded by the three mammalian ras genes have been found to possess oncogenic potential. Among the known Ras-related proteins, TC21/R-Ras2 exhibits the most significant amino acid identity (55%) to Ras proteins. We have generated mutant forms of TC21 that possess amino acid substitutions analogous to those that activate Ras oncogenic potential [designated TC21(22V) and TC21(71L)] and compared the biological properties of TC21 with those of Ras proteins in NIH 3T3 and Rat-1 transformation assays. Whereas wild-type TC21 did not show any transforming potential in vitro, both TC21(22V) and TC21(71L) displayed surprisingly potent transforming activities that were comparable to the strong transforming activity of oncogenic Ras proteins. Like Ras-transformed cells, NIH 3T3 cells expressing mutant TC21 proteins formed foci of morphologically transformed cells in monolayer cultures, proliferated in low serum, formed colonies in soft agar, and developed progressive tumors in nude mice. Thus, TC21 is the first Ras-related protein to exhibit potent transforming activity equivalent to that of Ras. Furthermore, mutant TC21 proteins also stimulated constitutive activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases as well as transcriptional activation from Ras-responsive promoter elements (Ets/AP-1 and NF-kappa B). We conclude that aberrant TC21 function may trigger cellular transformation via a signal transduction pathway similar to that of oncogenic Ras and suggest that deregulated TC21 activity may contribute significantly to human oncogenesis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avraham H., Weinberg R. A. Characterization and expression of the human rhoH12 gene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2058–2066. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbacid M. ras genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:779–827. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beg A. A., Ruben S. M., Scheinman R. I., Haskill S., Rosen C. A., Baldwin A. S., Jr I kappa B interacts with the nuclear localization sequences of the subunits of NF-kappa B: a mechanism for cytoplasmic retention. Genes Dev. 1992 Oct;6(10):1899–1913. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.10.1899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belhumeur P., Lee A., Tam R., DiPaolo T., Fortin N., Clark M. W. GSP1 and GSP2, genetic suppressors of the prp20-1 mutant in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: GTP-binding proteins involved in the maintenance of nuclear organization. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2152–2161. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J. Signal transduction via the MAP kinases: proceed at your own RSK. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):5889–5892. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokoch G. M., Der C. J. Emerging concepts in the Ras superfamily of GTP-binding proteins. FASEB J. 1993 Jun;7(9):750–759. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.9.8330683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollag G., McCormick F. GTPase activating proteins. Semin Cancer Biol. 1992 Aug;3(4):199–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos J. L. ras oncogenes in human cancer: a review. Cancer Res. 1989 Sep 1;49(17):4682–4689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: conserved structure and molecular mechanism. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):117–127. doi: 10.1038/349117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buss J. E., Quilliam L. A., Kato K., Casey P. J., Solski P. A., Wong G., Clark R., McCormick F., Bokoch G. M., Der C. J. The COOH-terminal domain of the Rap1A (Krev-1) protein is isoprenylated and supports transformation by an H-Ras:Rap1A chimeric protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1523–1530. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buss J. E., Solski P. A., Schaeffer J. P., MacDonald M. J., Der C. J. Activation of the cellular proto-oncogene product p21Ras by addition of a myristylation signal. Science. 1989 Mar 24;243(4898):1600–1603. doi: 10.1126/science.2648572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cepko C. L., Roberts B. E., Mulligan R. C. Construction and applications of a highly transmissible murine retrovirus shuttle vector. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1053–1062. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90440-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark G. J., Quilliam L. A., Hisaka M. M., Der C. J. Differential antagonism of Ras biological activity by catalytic and Src homology domains of Ras GTPase activation protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):4887–4891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.4887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook S. J., Rubinfeld B., Albert I., McCormick F. RapV12 antagonizes Ras-dependent activation of ERK1 and ERK2 by LPA and EGF in Rat-1 fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1993 Sep;12(9):3475–3485. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06022.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox A. D., Der C. J. Biological assays for cellular transformation. Methods Enzymol. 1994;238:277–294. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(94)38026-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox A. D., Der C. J. Protein prenylation: more than just glue? Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;4(6):1008–1016. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90133-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. J. The mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathway. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 15;268(20):14553–14556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drivas G. T., Shih A., Coutavas E., Rush M. G., D'Eustachio P. Characterization of four novel ras-like genes expressed in a human teratocarcinoma cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1793–1798. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feig L. A. The many roads that lead to Ras. Science. 1993 May 7;260(5109):767–768. doi: 10.1126/science.8484117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Sarabia M. J., Bischoff J. R. Bcl-2 associates with the ras-related protein R-ras p23. Nature. 1993 Nov 18;366(6452):274–275. doi: 10.1038/366274a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia A. M., Rowell C., Ackermann K., Kowalczyk J. J., Lewis M. D. Peptidomimetic inhibitors of Ras farnesylation and function in whole cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 5;268(25):18415–18418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S. K., Gallego C., Lowndes J. M., Pleiman C. M., Sable C., Eisfelder B. J., Johnson G. L. Analysis of the fibroblast transformation potential of GTPase-deficient gip2 oncogenes. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):190–197. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser C. A., Der C. J., Cox A. D. Transcriptional activation analysis of oncogene function. Methods Enzymol. 1994;238:271–276. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(94)38025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe L. R., Marshall C. J. Identification of amino acids in p21ras involved in exchange factor interaction. Oncogene. 1993 Sep;8(9):2583–2590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James G. L., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S., Rawson T. E., Somers T. C., McDowell R. S., Crowley C. W., Lucas B. K., Levinson A. D., Marsters J. C., Jr Benzodiazepine peptidomimetics: potent inhibitors of Ras farnesylation in animal cells. Science. 1993 Jun 25;260(5116):1937–1942. doi: 10.1126/science.8316834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khosravi-Far R., Der C. J. The Ras signal transduction pathway. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1994 Mar;13(1):67–89. doi: 10.1007/BF00690419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khosravi-Far R., Lutz R. J., Cox A. D., Conroy L., Bourne J. R., Sinensky M., Balch W. E., Buss J. E., Der C. J. Isoprenoid modification of rab proteins terminating in CC or CXC motifs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6264–6268. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitayama H., Matsuzaki T., Ikawa Y., Noda M. Genetic analysis of the Kirsten-ras-revertant 1 gene: potentiation of its tumor suppressor activity by specific point mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4284–4288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitayama H., Sugimoto Y., Matsuzaki T., Ikawa Y., Noda M. A ras-related gene with transformation suppressor activity. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):77–84. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90985-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl N. E., Mosser S. D., deSolms S. J., Giuliani E. A., Pompliano D. L., Graham S. L., Smith R. L., Scolnick E. M., Oliff A., Gibbs J. B. Selective inhibition of ras-dependent transformation by a farnesyltransferase inhibitor. Science. 1993 Jun 25;260(5116):1934–1937. doi: 10.1126/science.8316833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe D. G., Goeddel D. V. Heterologous expression and characterization of the human R-ras gene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2845–2856. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall M. S. The effector interactions of p21ras. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Jul;18(7):250–254. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90175-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto T., Beach D. Premature initiation of mitosis in yeast lacking RCC1 or an interacting GTPase. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):347–360. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90624-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick F. Signal transduction. How receptors turn Ras on. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):15–16. doi: 10.1038/363015a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moodie S. A., Willumsen B. M., Weber M. J., Wolfman A. Complexes of Ras.GTP with Raf-1 and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase. Science. 1993 Jun 11;260(5114):1658–1661. doi: 10.1126/science.8503013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. S., Blobel G. The GTP-binding protein Ran/TC4 is required for protein import into the nucleus. Nature. 1993 Oct 14;365(6447):661–663. doi: 10.1038/365661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosteller R. D., Han J., Broek D. Identification of residues of the H-ras protein critical for functional interaction with guanine nucleotide exchange factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;14(2):1104–1112. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.2.1104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick P., Brennwald P. Friends and family: the role of the Rab GTPases in vesicular traffic. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):597–601. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90478-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perona R., Esteve P., Jiménez B., Ballestero R. P., Ramón y Cajal S., Lacal J. C. Tumorigenic activity of rho genes from Aplysia californica. Oncogene. 1993 May;8(5):1285–1292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polakis P., McCormick F. Structural requirements for the interaction of p21ras with GAP, exchange factors, and its biological effector target. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9157–9160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quilliam L. A., Kato K., Rabun K. M., Hisaka M. M., Huff S. Y., Campbell-Burk S., Der C. J. Identification of residues critical for Ras(17N) growth-inhibitory phenotype and for Ras interaction with guanine nucleotide exchange factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;14(2):1113–1121. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.2.1113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren M., Drivas G., D'Eustachio P., Rush M. G. Ran/TC4: a small nuclear GTP-binding protein that regulates DNA synthesis. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;120(2):313–323. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.2.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rey I., Taylor-Harris P., van Erp H., Hall A. R-ras interacts with rasGAP, neurofibromin and c-raf but does not regulate cell growth or differentiation. Oncogene. 1994 Mar;9(3):685–692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricketts M. H., Levinson A. D. High-level expression of c-H-ras1 fails to fully transform rat-1 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1460–1468. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley A. J., Hall A. The small GTP-binding protein rho regulates the assembly of focal adhesions and actin stress fibers in response to growth factors. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):389–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90163-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley A. J., Paterson H. F., Johnston C. L., Diekmann D., Hall A. The small GTP-binding protein rac regulates growth factor-induced membrane ruffling. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):401–410. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90164-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Self A. J., Paterson H. F., Hall A. Different structural organization of Ras and Rho effector domains. Oncogene. 1993 Mar;8(3):655–661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valencia A., Chardin P., Wittinghofer A., Sander C. The ras protein family: evolutionary tree and role of conserved amino acids. Biochemistry. 1991 May 14;30(19):4637–4648. doi: 10.1021/bi00233a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Aelst L., Barr M., Marcus S., Polverino A., Wigler M. Complex formation between RAS and RAF and other protein kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6213–6217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verrotti A. C., Créchet J. B., Di Blasi F., Seidita G., Mirisola M. G., Kavounis C., Nastopoulos V., Burderi E., De Vendittis E., Parmeggiani A. RAS residues that are distant from the GDP binding site play a critical role in dissociation factor-stimulated release of GDP. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):2855–2862. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05353.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vojtek A. B., Hollenberg S. M., Cooper J. A. Mammalian Ras interacts directly with the serine/threonine kinase Raf. Cell. 1993 Jul 16;74(1):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90307-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warne P. H., Viciana P. R., Downward J. Direct interaction of Ras and the amino-terminal region of Raf-1 in vitro. Nature. 1993 Jul 22;364(6435):352–355. doi: 10.1038/364352a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk C., Flores P., Gutman A., Wasylyk B. PEA3 is a nuclear target for transcription activation by non-nuclear oncogenes. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3371–3378. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08500.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. F., Settleman J., Kyriakis J. M., Takeuchi-Suzuki E., Elledge S. J., Marshall M. S., Bruder J. T., Rapp U. R., Avruch J. Normal and oncogenic p21ras proteins bind to the amino-terminal regulatory domain of c-Raf-1. Nature. 1993 Jul 22;364(6435):308–313. doi: 10.1038/364308a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]