Abstract
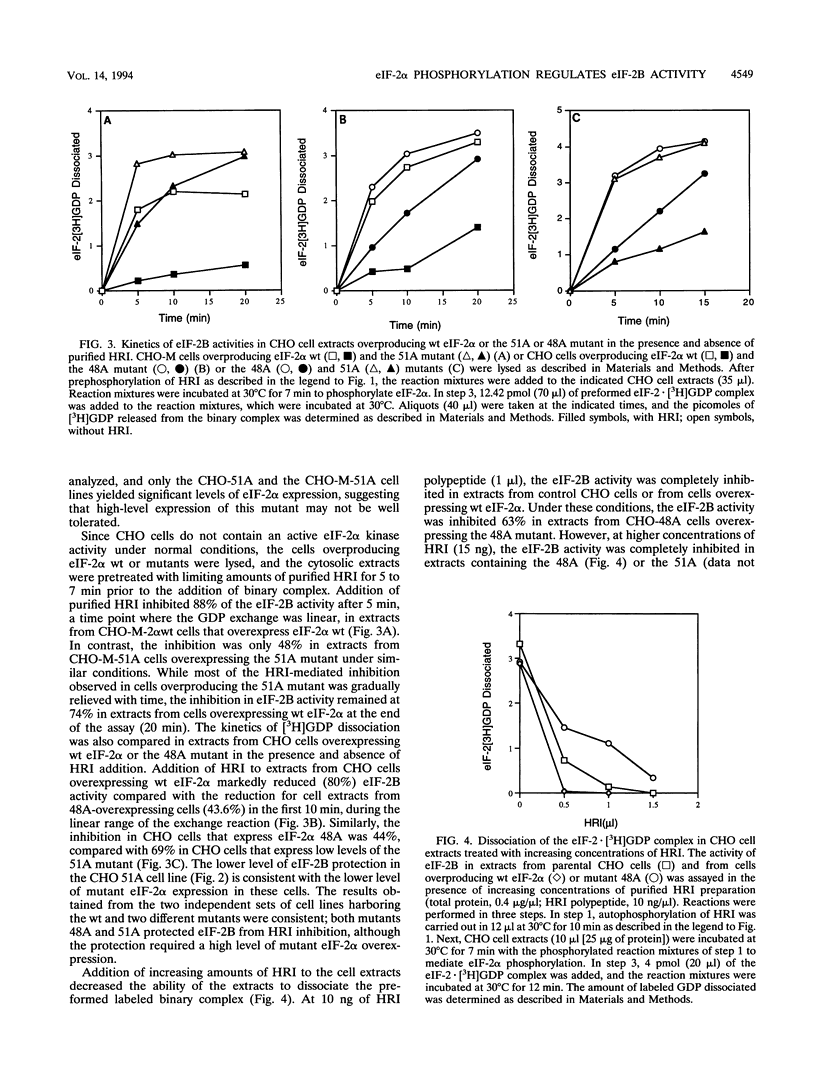
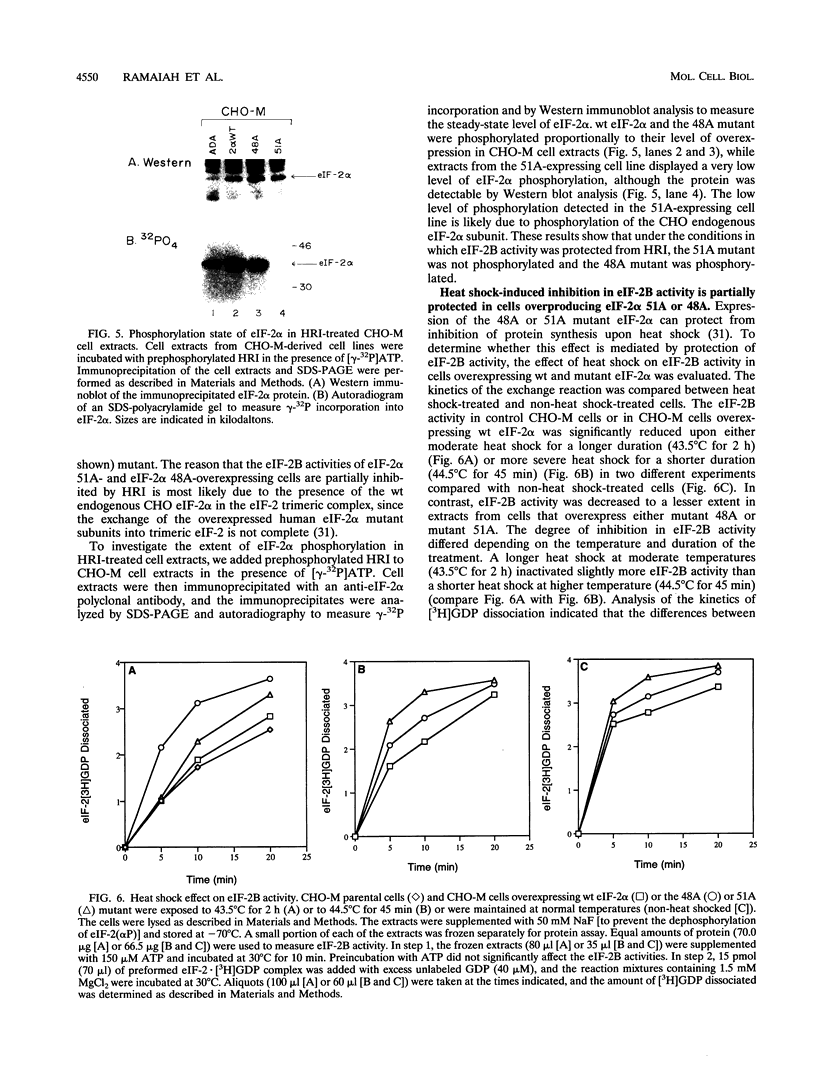
The inhibition of protein synthesis that occurs upon phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 (eIF-2 alpha) at serine 51 correlates with reduced guanine nucleotide exchange activity of eIF-2B in vivo and inhibition of eIF-2B activity in vitro, although it is not known if phosphorylation is the cause of the reduced eIF-2B activity in vivo. To characterize the importance of eIF-2 alpha phosphorylation in the regulation of eIF-2B activity, we studied the overexpression of mutant eIF-2 alpha subunits in which serine 48 or 51 was replaced by an alanine (48A or 51A mutant). Previous studies demonstrated that the 51A mutant was resistant to phosphorylation, whereas the 48A mutant was a substrate for phosphorylation. Additionally, expression of either mutant partially protected Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells from the inhibition of protein synthesis in response to heat shock treatment (P. Murtha-Riel, M. V. Davies, J. B. Scherer, S. Y. Choi, J. W. B. Hershey, and R. J. Kaufman, J. Biol. Chem. 268:12946-12951, 1993). In this study, we show that eIF-2B activity was inhibited in parental CHO cell extracts upon addition of purified reticulocyte heme-regulated inhibitor (HRI), an eIF-2 alpha kinase that phosphorylates Ser-51. Preincubation with purified HRI also reduced the eIF-2B activity in extracts from cells overexpressing wild-type eIF-2 alpha. In contrast, the eIF-2B activity was not readily inhibited in extracts from cells overexpressing either the eIF-2 alpha 48A or 51A mutant. In addition, eIF-2B activity was decreased in extracts prepared from heat-shocked cells overexpressing wild-type eIF-2 alpha, whereas the decrease in eIF-2B activity was less in heat-shocked cells overexpressing either mutant 48A or mutant 51A. While the phosphorylation at serine 51 in eIF-2 alpha impairs the eIF-2B activity, we propose that serine 48 acts to maintain a high affinity between phosphorylated eIF-2 alpha and eIF-2B, thereby inactivating eIF-2B activity. These findings support the hypothesis that phosphorylation of eIF-2 alpha inhibits protein synthesis directly through reducing eIF-2B activity and emphasize the importance of both serine 48 and serine 51 in the interaction with eIF-2B and regulation of eIF-2B activity.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amesz H., Goumans H., Haubrich-Morree T., Voorma H. O., Benne R. Purification and characterization of a protein factor that reverses the inhibition of protein synthesis by the heme-regulated translational inhibitor in rabbit reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Aug 1;98(2):513–520. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13212.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews N. C., Levin D., Baltimore D. Poliovirus replicase stimulation by terminal uridylyl transferase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7628–7635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. J., Yang J. M., Petryshyn R., Kosower N., London I. M. Disulfide bond formation in the regulation of eIF-2 alpha kinase by heme. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 5;264(16):9559–9564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi S. Y., Scherer B. J., Schnier J., Davies M. V., Kaufman R. J., Hershey J. W. Stimulation of protein synthesis in COS cells transfected with variants of the alpha-subunit of initiation factor eIF-2. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):286–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemens M. J., Pain V. M., Wong S. T., Henshaw E. C. Phosphorylation inhibits guanine nucleotide exchange on eukaryotic initiation factor 2. Nature. 1982 Mar 4;296(5852):93–95. doi: 10.1038/296093a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colthurst D. R., Campbell D. G., Proud C. G. Structure and regulation of eukaryotic initiation factor eIF-2. Sequence of the site in the alpha subunit phosphorylated by the haem-controlled repressor and by the double-stranded RNA-activated inhibitor. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jul 15;166(2):357–363. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13523.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies M. V., Furtado M., Hershey J. W., Thimmappaya B., Kaufman R. J. Complementation of adenovirus virus-associated RNA I gene deletion by expression of a mutant eukaryotic translation initiation factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9163–9167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Benedetti A., Baglioni C. Activation of hemin-regulated initiation factor-2 kinase in heat-shocked HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):338–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dever T. E., Chen J. J., Barber G. N., Cigan A. M., Feng L., Donahue T. F., London I. M., Katze M. G., Hinnebusch A. G. Mammalian eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha kinases functionally substitute for GCN2 protein kinase in the GCN4 translational control mechanism of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4616–4620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dever T. E., Feng L., Wek R. C., Cigan A. M., Donahue T. F., Hinnebusch A. G. Phosphorylation of initiation factor 2 alpha by protein kinase GCN2 mediates gene-specific translational control of GCN4 in yeast. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):585–596. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90193-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dholakia J. N., Wahba A. J. Phosphorylation of the guanine nucleotide exchange factor from rabbit reticulocytes regulates its activity in polypeptide chain initiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):51–54. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan R. F., Hershey J. W. Protein synthesis and protein phosphorylation during heat stress, recovery, and adaptation. J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;109(4 Pt 1):1467–1481. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.4.1467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan R., Hershey J. W. Heat shock-induced translational alterations in HeLa cells. Initiation factor modifications and the inhibition of translation. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):11882–11889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershey J. W. Translational control in mammalian cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:717–755. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.003441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kan B., London I. M., Levin D. H. Role of reversing factor in the inhibition of protein synthesis initiation by oxidized glutathione. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15652–15656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Davies M. V., Pathak V. K., Hershey J. W. The phosphorylation state of eucaryotic initiation factor 2 alters translational efficiency of specific mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):946–958. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Davies M. V., Wasley L. C., Michnick D. Improved vectors for stable expression of foreign genes in mammalian cells by use of the untranslated leader sequence from EMC virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 25;19(16):4485–4490. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.16.4485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J. Selection and coamplification of heterologous genes in mammalian cells. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:537–566. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85044-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimball S. R., Jefferson L. S. Mechanism of the inhibition of protein synthesis by vasopressin in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):16794–16798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konieczny A., Safer B. Purification of the eukaryotic initiation factor 2-eukaryotic initiation factor 2B complex and characterization of its guanine nucleotide exchange activity during protein synthesis initiation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3402–3408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leroux A., London I. M. Regulation of protein synthesis by phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha in intact reticulocytes and reticulocyte lysates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2147–2151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariano T. M., Siekierka J. Inhibition of HeLa cell protein synthesis under heat shock conditions in the absence of initiation factor eIF-2 alpha phosphorylation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jul 31;138(2):519–525. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80527-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matts R. L., Levin D. H., London I. M. Effect of phosphorylation of the alpha-subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 on the function of reversing factor in the initiation of protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2559–2563. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matts R. L., London I. M. The regulation of initiation of protein synthesis by phosphorylation of eIF-2(alpha) and the role of reversing factor in the recycling of eIF-2. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):6708–6711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matts R. L., Thomas N. S., Hurst R., London I. M. Correlation between the distribution of the reversing factor and eukaryotic initiation factor 2 in heme-deficient or double-stranded RNA-inhibited reticulocyte lysates. FEBS Lett. 1988 Aug 15;236(1):179–184. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80310-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrick W. C. Mechanism and regulation of eukaryotic protein synthesis. Microbiol Rev. 1992 Jun;56(2):291–315. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.2.291-315.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meurs E., Chong K., Galabru J., Thomas N. S., Kerr I. M., Williams B. R., Hovanessian A. G. Molecular cloning and characterization of the human double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase induced by interferon. Cell. 1990 Jul 27;62(2):379–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90374-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murtha-Riel P., Davies M. V., Scherer B. J., Choi S. Y., Hershey J. W., Kaufman R. J. Expression of a phosphorylation-resistant eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha-subunit mitigates heat shock inhibition of protein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 15;268(17):12946–12951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panniers R., Henshaw E. C. A GDP/GTP exchange factor essential for eukaryotic initiation factor 2 cycling in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells and its regulation by eukaryotic initiation factor 2 phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):7928–7934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pathak V. K., Schindler D., Hershey J. W. Generation of a mutant form of protein synthesis initiation factor eIF-2 lacking the site of phosphorylation by eIF-2 kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):993–995. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prostko C. R., Brostrom M. A., Malara E. M., Brostrom C. O. Phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor (eIF) 2 alpha and inhibition of eIF-2B in GH3 pituitary cells by perturbants of early protein processing that induce GRP78. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):16751–16754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowlands A. G., Montine K. S., Henshaw E. C., Panniers R. Physiological stresses inhibit guanine-nucleotide-exchange factor in Ehrlich cells. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jul 15;175(1):93–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14170.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowlands A. G., Panniers R., Henshaw E. C. The catalytic mechanism of guanine nucleotide exchange factor action and competitive inhibition by phosphorylated eukaryotic initiation factor 2. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5526–5533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safer B. 2B or not 2B: regulation of the catalytic utilization of eIF-2. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):7–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90326-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel C. E. The eIF-2 alpha protein kinases, regulators of translation in eukaryotes from yeasts to humans. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 15;268(11):7603–7606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scorsone K. A., Panniers R., Rowlands A. G., Henshaw E. C. Phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 during physiological stresses which affect protein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14538–14543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siekierka J., Mitsui K. I., Ochoa S. Mode of action of the heme-controlled translational inhibitor: relationship of eukaryotic initiation factor 2-stimulating protein to translation restoring factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):220–223. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas N. S., Matts R. L., Petryshyn R., London I. M. Distribution of reversing factor in reticulocyte lysates during active protein synthesis and on inhibition by heme deprivation or double-stranded RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6998–7002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urlaub G., Chasin L. A. Isolation of Chinese hamster cell mutants deficient in dihydrofolate reductase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4216–4220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez de Aldana C. R., Dever T. E., Hinnebusch A. G. Mutations in the alpha subunit of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 (eIF-2 alpha) that overcome the inhibitory effect of eIF-2 alpha phosphorylation on translation initiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 1;90(15):7215–7219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.7215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh G. I., Proud C. G. Regulation of protein synthesis in Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts. Rapid activation of the guanine-nucleotide-exchange factor by insulin and growth factors. Biochem J. 1992 May 15;284(Pt 1):19–23. doi: 10.1042/bj2840019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wettenhall R. E., Kudlicki W., Kramer G., Hardesty B. The NH2-terminal sequence of the alpha and gamma subunits of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 and the phosphorylation site for the heme-regulated eIF-2 alpha kinase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12444–12447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]