Abstract
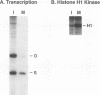
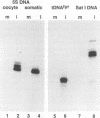
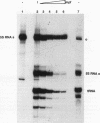
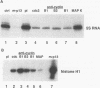
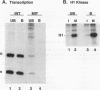
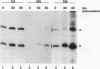
Transcription of 5S rRNA and tRNA genes by RNA polymerase III (pol III) in cytosolic extracts of unfertilized Xenopus eggs and in a reconstituted system derived from Xenopus oocytes is repressed by the action of one or more mitotic protein kinases. Repression is due to the phosphorylation of a component of the pol III transcription apparatus. We find that the maturation/mitosis-promoting factor kinase (MPF, p34cdc2-cyclin B) can directly mediate this repression in vitro. Affinity-purified MPF and immune complexes formed with antibodies to the protein subunits of MPF (p34cdc2 and cyclin B) retain both histone H1 kinase activity and the capacity to repress transcription in the reconstituted transcription system. Transcription complexes of oocyte-type 5S RNA genes and tRNA genes are quantitatively more sensitive to MPF repression than the corresponding transcription complexes of the somatic-type 5S RNA gene. The differential transcription of oocyte- and somatic-type genes observed during early Xenopus embryogenesis has been reproduced with the reconstituted transcription system and affinity-purified MPF. This differential transcription may be due to the instability of transcription complexes on the oocyte-type genes and the heightened sensitivity of soluble transcription factors to inactivation by mitotic phosphorylation. Our results suggest that MPF may play a role in vivo in the establishment of the embryonic pattern of pol III gene expression.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almouzni G., Méchali M., Wolffe A. P. Competition between transcription complex assembly and chromatin assembly on replicating DNA. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):573–582. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08145.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almouzni G., Méchali M., Wolffe A. P. Transcription complex disruption caused by a transition in chromatin structure. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):655–665. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews M. T., Brown D. D. Transient activation of oocyte 5S RNA genes in Xenopus embryos by raising the level of the trans-acting factor TFIIIA. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):445–453. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90640-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. Nucleotide sequences in Xenopus 5S DNA required for transcription termination. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90522-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Wormington W. M., Brown D. D. Stable transcription complexes of Xenopus 5S RNA genes: a means to maintain the differentiated state. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):413–421. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90359-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. D., Schlissel M. S. A positive transcription factor controls the differential expression of two 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):759–767. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90272-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarkson S. G., Birnstiel M. L., Serra V. Reiterated transfer RNA genes of Xenopus laevis. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 15;79(2):391–410. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darby M. K., Andrews M. T., Brown D. D. Transcription complexes that program Xenopus 5S RNA genes are stable in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5516–5520. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Luca F., Westendorf J., Brizuela L., Ruderman J., Beach D. Cdc2 protein kinase is complexed with both cyclin A and B: evidence for proteolytic inactivation of MPF. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):829–838. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90687-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Brizuela L., Beach D., Newport J. The Xenopus cdc2 protein is a component of MPF, a cytoplasmic regulator of mitosis. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):423–431. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90205-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Newport J. W. Mitosis-inducing factors are present in a latent form during interphase in the Xenopus embryo. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;106(6):2047–2056. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.6.2047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang F., Newport J. W. Evidence that the G1-S and G2-M transitions are controlled by different cdc2 proteins in higher eukaryotes. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):731–742. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90117-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Norbury C., Lohka M., Nurse P., Maller J. Purified maturation-promoting factor contains the product of a Xenopus homolog of the fission yeast cell cycle control gene cdc2+. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):433–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90206-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiduschek E. P., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Transcription by RNA polymerase III. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:873–914. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesfeld J. M., Wolf V. J., Dang T., Forbes D. J., Hartl P. Mitotic repression of RNA polymerase III transcription in vitro mediated by phosphorylation of a TFIIIB component. Science. 1994 Jan 7;263(5143):81–84. doi: 10.1126/science.8272869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesfeld J., Bloomer L. S. Assembly of transcriptionally active 5S RNA gene chromatin in vitro. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):781–791. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90057-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartl P., Gottesfeld J., Forbes D. J. Mitotic repression of transcription in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;120(3):613–624. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.3.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes J., Tullius T. D., Wolffe A. P. A protein-protein interaction is essential for stable complex formation on a 5 S RNA gene. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6009–6012. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessus C., Beach D. Oscillation of MPF is accompanied by periodic association between cdc25 and cdc2-cyclin B. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):323–332. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90473-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Braun B. R., Nguyen L. H., Geiduschek E. P. S. cerevisiae TFIIIB is the transcription initiation factor proper of RNA polymerase III, while TFIIIA and TFIIIC are assembly factors. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):235–245. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90739-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Joazeiro C. A., Pisano M., Geiduschek E. P., Colbert T., Hahn S., Blanco J. A. The role of the TATA-binding protein in the assembly and function of the multisubunit yeast RNA polymerase III transcription factor, TFIIIB. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):1055–1064. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90399-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller H. J., Romaniuk P. J., Gottesfeld J. M. Interaction of Xenopus TFIIIC with the TFIIIA.5 S RNA gene complex. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):18190–18198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller H. J., You Q. M., Romaniuk P. J., Gottesfeld J. M. Additional intragenic promoter elements of the Xenopus 5S RNA genes upstream from the TFIIIA-binding site. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5166–5176. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn L. J., Gurdon J. B. The reactivation of developmentally inert 5S genes in somatic nuclei injected into Xenopus oocytes. Nature. 1981 Feb 5;289(5797):461–465. doi: 10.1038/289461a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam B. S., Carroll D. Tandemly repeated DNA sequences from Xenopus laevis. I. Studies on sequence organization and variation in satellite 1 DNA (741 base-pair repeat). J Mol Biol. 1983 Apr 25;165(4):567–585. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80267-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobo S. M., Tanaka M., Sullivan M. L., Hernandez N. A TBP complex essential for transcription from TATA-less but not TATA-containing RNA polymerase III promoters is part of the TFIIIB fraction. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):1029–1040. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90397-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohka M. J., Hayes M. K., Maller J. L. Purification of maturation-promoting factor, an intracellular regulator of early mitotic events. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3009–3013. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConkey G. A., Bogenhagen D. F. TFIIIA binds with equal affinity to somatic and major oocyte 5S RNA genes. Genes Dev. 1988 Feb;2(2):205–214. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.2.205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millstein L., Eversole-Cire P., Blanco J., Gottesfeld J. M. Differential transcription of Xenopus oocyte and somatic-type 5 S genes in a Xenopus oocyte extract. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 15;262(35):17100–17110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Solomon M. J., Kirschner M. W. The role of cyclin synthesis and degradation in the control of maturation promoting factor activity. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):280–286. doi: 10.1038/339280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newport J. W., Kirschner M. W. Regulation of the cell cycle during early Xenopus development. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):731–742. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90409-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer J. M., Folk W. R. Unraveling the complexities of transcription by RNA polymerase III. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Aug;15(8):300–304. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck L. J., Millstein L., Eversole-Cire P., Gottesfeld J. M., Varshavsky A. Transcriptionally inactive oocyte-type 5S RNA genes of Xenopus laevis are complexed with TFIIIA in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3503–3510. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson R. C., Doering J. L., Brown D. D. Characterization of two xenopus somatic 5S DNAs and one minor oocyte-specific 5S DNA. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):131–141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90241-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds W. F. Effect of sequence differences between somatic and oocyte 5S RNA genes on transcriptional efficiency in an oocyte S150 extract. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):5056–5058. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.5056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romaniuk P. J. The role of highly conserved single-stranded nucleotides of Xenopus 5S RNA in the binding of transcription factor IIIA. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 7;28(3):1388–1395. doi: 10.1021/bi00429a067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlissel M. S., Brown D. D. The transcriptional regulation of Xenopus 5s RNA genes in chromatin: the roles of active stable transcription complexes and histone H1. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):903–913. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90425-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall J., Matsui T., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors are required for the accurate transcription of purified genes by RNA polymerase III. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11986–11991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidel C. W., Peck L. J. Kinetic control of 5 S RNA gene transcription. J Mol Biol. 1992 Oct 20;227(4):1009–1018. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90517-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya E. K., Boulton T. G., Cobb M. H., Ruderman J. V. Activation of p42 MAP kinase and the release of oocytes from cell cycle arrest. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):3963–3975. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05490.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smythe C., Newport J. W. Coupling of mitosis to the completion of S phase in Xenopus occurs via modulation of the tyrosine kinase that phosphorylates p34cdc2. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):787–797. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90153-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smythe C., Newport J. W. Systems for the study of nuclear assembly, DNA replication, and nuclear breakdown in Xenopus laevis egg extracts. Methods Cell Biol. 1991;35:449–468. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60583-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Glotzer M., Lee T. H., Philippe M., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin activation of p34cdc2. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):1013–1024. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90504-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutz F., Gouilloud E., Clarkson S. G. Oocyte and somatic tyrosine tRNA genes in Xenopus laevis. Genes Dev. 1989 Aug;3(8):1190–1198. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.8.1190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taggart A. K., Fisher T. S., Pugh B. F. The TATA-binding protein and associated factors are components of pol III transcription factor TFIIIB. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):1015–1028. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90396-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakefield L., Gurdon J. B. Cytoplasmic regulation of 5S RNA genes in nuclear-transplant embryos. EMBO J. 1983;2(9):1613–1619. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01632.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. J., Jackson S. P. Mechanism of TATA-binding protein recruitment to a TATA-less class III promoter. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):1041–1053. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90398-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P., Brown D. D. Developmental regulation of two 5S ribosomal RNA genes. Science. 1988 Sep 23;241(4873):1626–1632. doi: 10.1126/science.241.4873.1626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P., Brown D. D. Differential 5S RNA gene expression in vitro. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):733–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90096-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P. Dominant and specific repression of Xenopus oocyte 5S RNA genes and satellite I DNA by histone H1. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):527–537. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03407.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P. RNA polymerase III transcription. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;3(3):461–466. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P. Replication timing and Xenopus 5S RNA gene transcription in vitro. Dev Biol. 1993 May;157(1):224–231. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1993.1126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P. Transcription fraction TFIIIC can regulate differential Xenopus 5S RNA gene transcription in vitro. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):1071–1079. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02915.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wormington W. M., Brown D. D. Onset of 5 S RNA gene regulation during Xenopus embryogenesis. Dev Biol. 1983 Sep;99(1):248–257. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90273-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]