Abstract
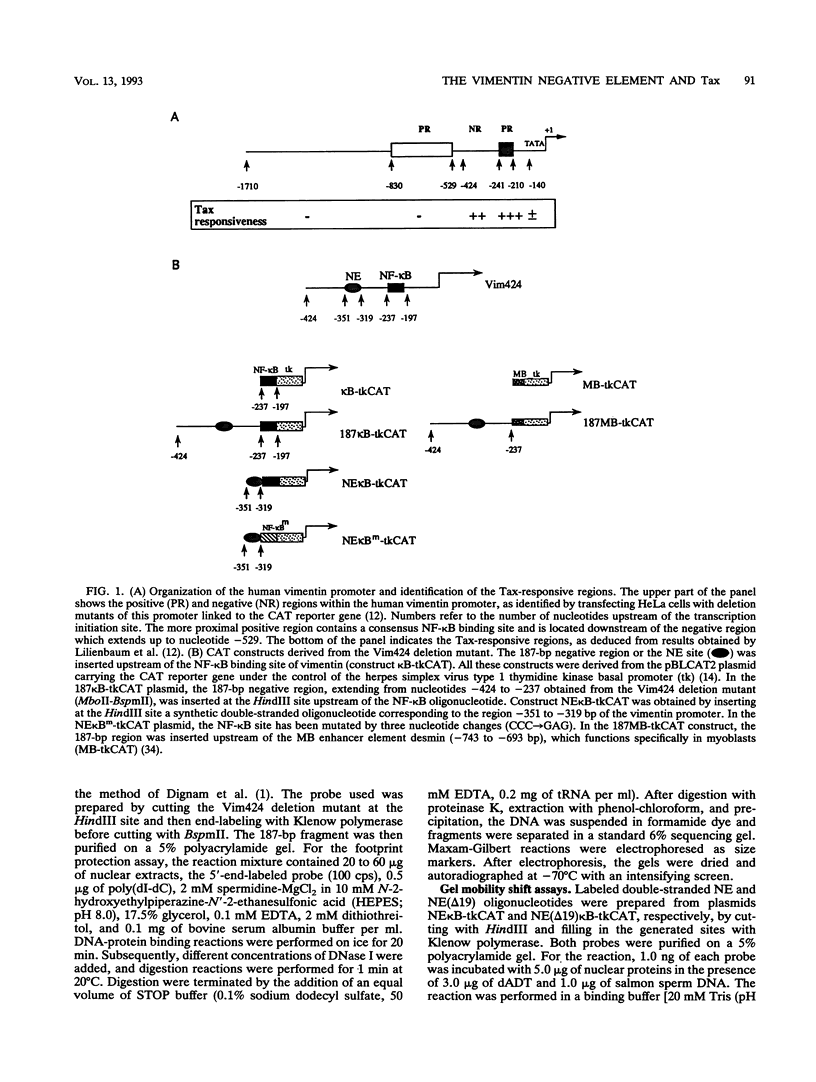
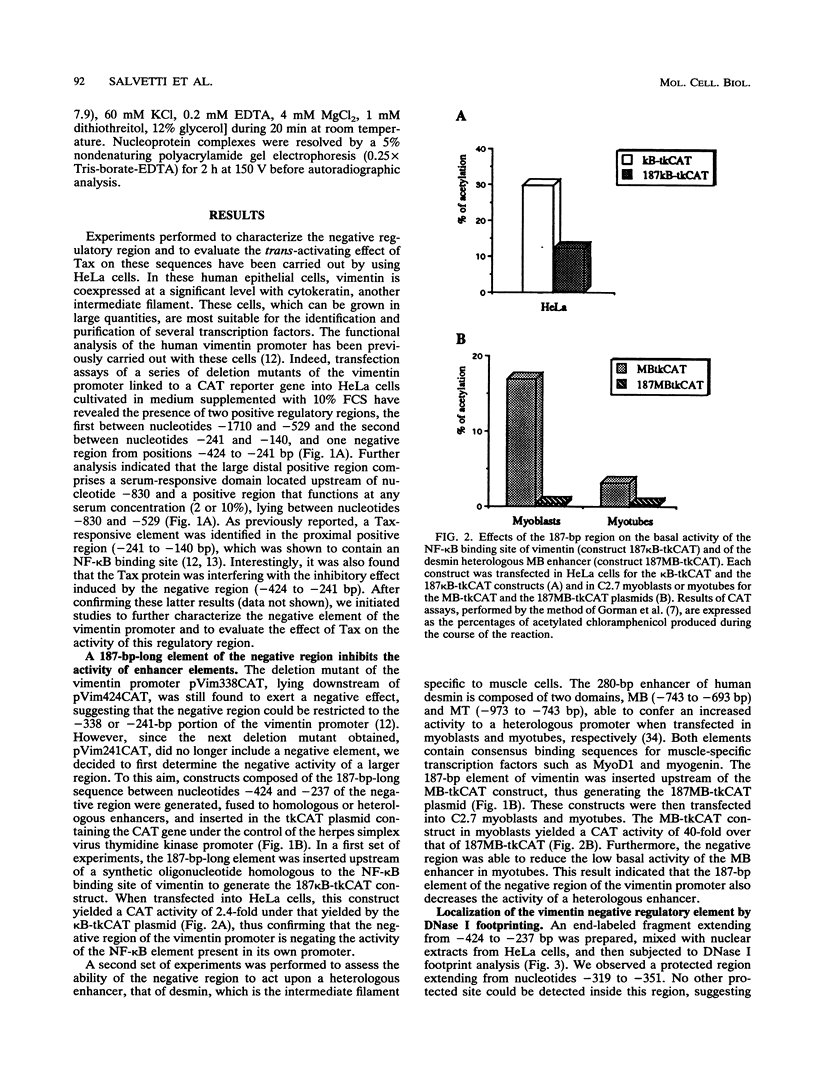
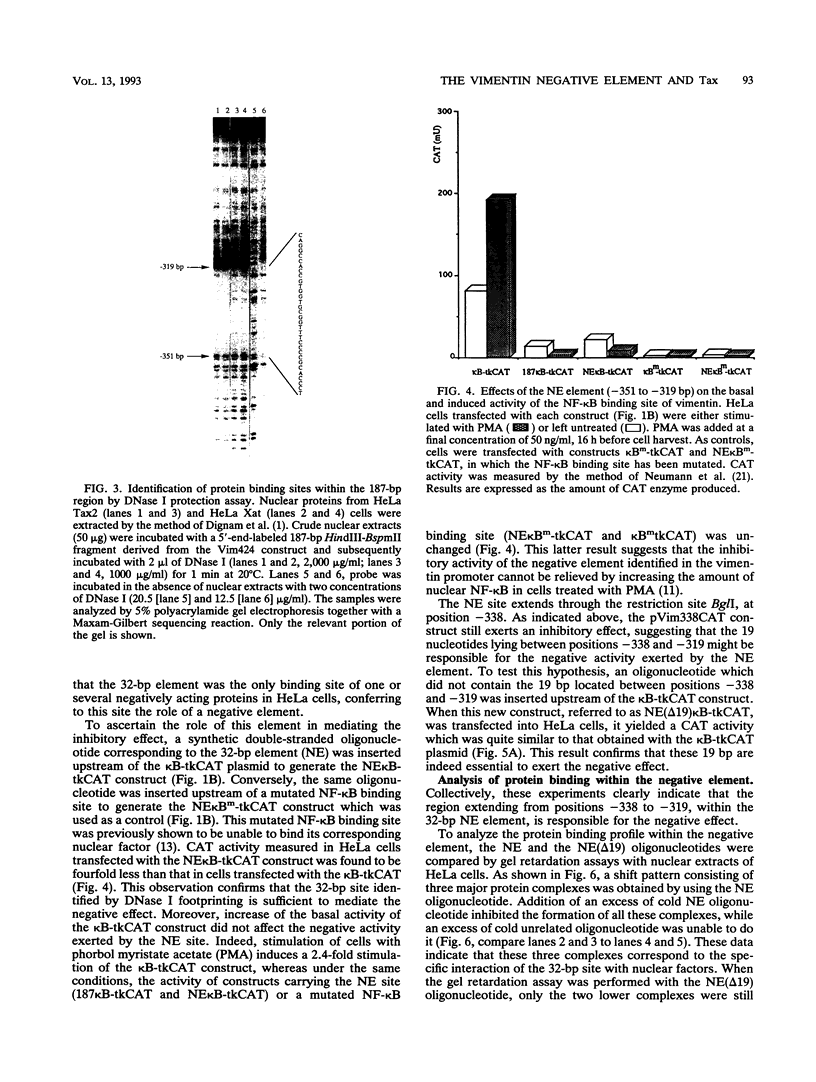
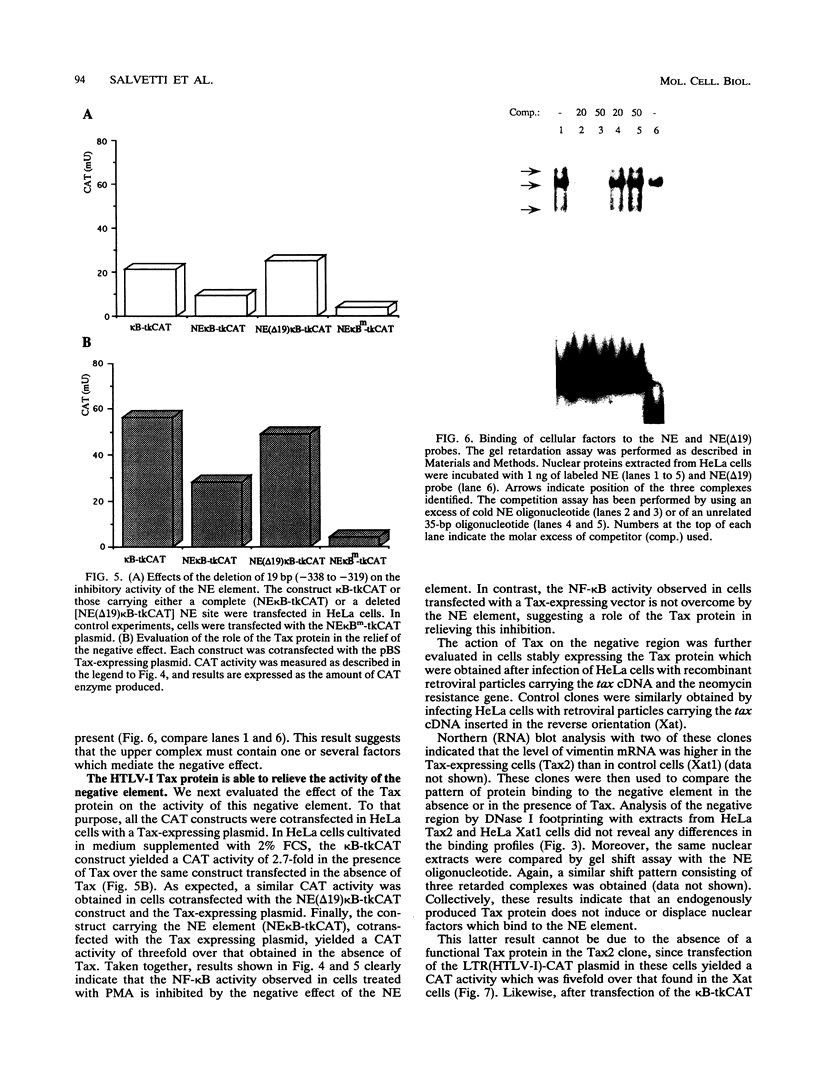
The vimentin gene is a member of the intermediate filament multigene family and encodes a protein expressed, in vivo, in all mesenchymal derivatives and, in vitro, in cell types of various origin. We have previously demonstrated that the expression of this growth-regulated gene could be trans activated by the 40-kDa Tax protein of HTLV-I (human T-cell leukemia virus type I) and that responsiveness to this viral protein was mediated by the presence of an NF-kappa B binding site located between -241 and -210 bp upstream of the mRNA cap site (A. Lilienbaum, M. Duc Dodon, C. Alexandre, L. Gazzolo, and D. Paulin, J. Virol. 64:256-263, 1990). These previous assays, performed with deletion mutants of the vimentin promoter linked to the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene, also revealed the presence of an upstream negative region between -529 and -241 bp. Interestingly, the inhibitory activity exerted by this negative region was overcome after cotransfection of a Tax-expressing plasmid. In this study, we further characterize the vimentin negative element and define the effect of the Tax protein on the inhibitory activity of this element. We first demonstrate that a 187-bp domain (-424 to -237 bp) behaves as a negative region when placed upstream either of the NF-kappa B binding site of vimentin or of a heterologous enhancer such as that present in the desmin gene promoter. The negative effect can be further assigned to a 32-bp element which is indeed shown to repress the basal or induced activity of the NF-kappa B binding site.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF

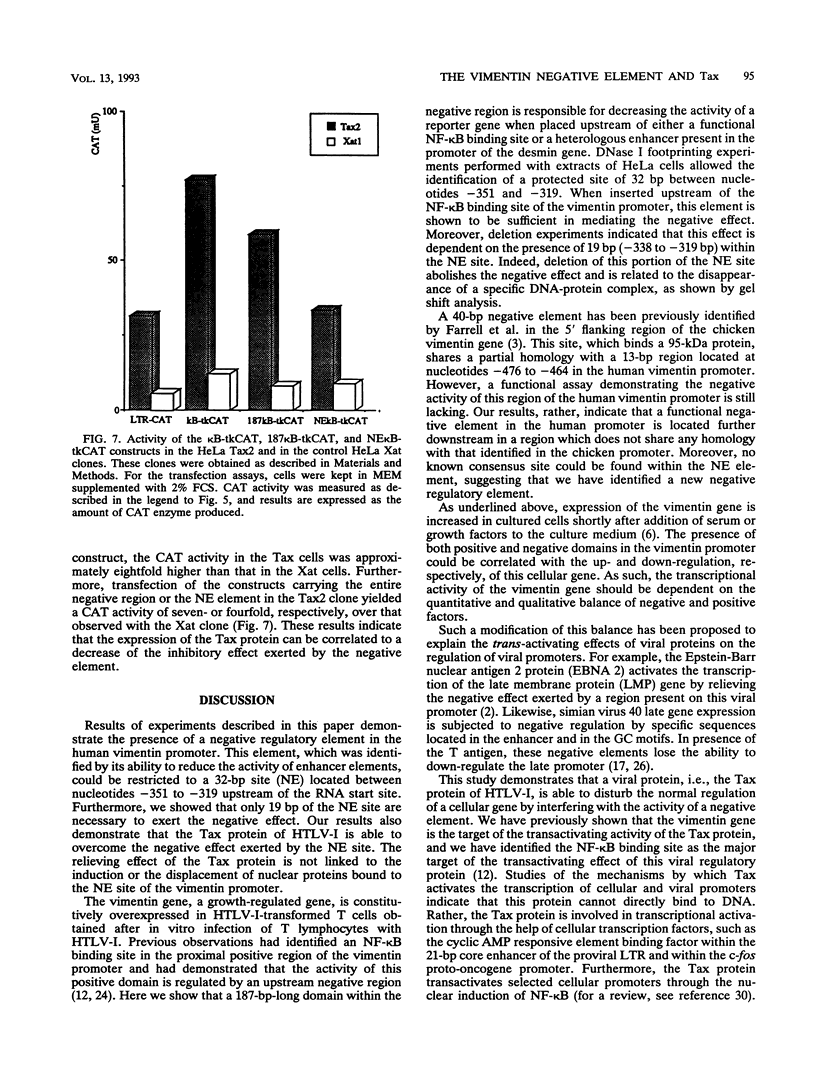


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell F. X., Sax C. M., Zehner Z. E. A negative element involved in vimentin gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2349–2358. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii M., Sassone-Corsi P., Verma I. M. c-fos promoter trans-activation by the tax1 protein of human T-cell leukemia virus type I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8526–8530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa J., Seiki M., Sato M., Yoshida M. A transcriptional enhancer sequence of HTLV-I is responsible for trans-activation mediated by p40 chi HTLV-I. EMBO J. 1986 Apr;5(4):713–718. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04272.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fåhraeus R., Jansson A., Ricksten A., Sjöblom A., Rymo L. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded nuclear antigen 2 activates the viral latent membrane protein promoter by modulating the activity of a negative regulatory element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7390–7394. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson C. W., Rittling S. R., Hirschhorn R. R., Kaczmarek L., Calabretta B., Stiles C. D., Baserga R. Cell cycle dependent genes inducible by different mitogens in cells from different species. Mol Cell Biochem. 1986 Jun;71(1):61–69. doi: 10.1007/BF00219329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbst R. S., Boczko E. M., Darnell J. E., Jr, Babiss L. E. The mouse albumin enhancer contains a negative regulatory element that interacts with a novel DNA-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):3896–3905. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.3896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaczmarek L., Calabretta B., Baserga R. Expression of cell-cycle-dependent genes in phytohemagglutinin-stimulated human lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5375–5379. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. J., Kehrl J. H., Burton J., Tendler C. L., Jeang K. T., Danielpour D., Thevenin C., Kim K. Y., Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B. Transactivation of the transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-beta 1) gene by human T lymphotropic virus type 1 tax: a potential mechanism for the increased production of TGF-beta 1 in adult T cell leukemia. J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):121–129. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M. J., Baltimore D. NF-kappa B: a pleiotropic mediator of inducible and tissue-specific gene control. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):227–229. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90833-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Z. L., Paulin D. High level desmin expression depends on a muscle-specific enhancer. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6562–6570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilienbaum A., Duc Dodon M., Alexandre C., Gazzolo L., Paulin D. Effect of human T-cell leukemia virus type I tax protein on activation of the human vimentin gene. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):256–263. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.256-263.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz D., Goff S., Bank A. Construction and use of a safe and efficient amphotropic packaging cell line. Virology. 1988 Dec;167(2):400–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marriott S. J., Lindholm P. F., Brown K. M., Gitlin S. D., Duvall J. F., Radonovich M. F., Brady J. N. A 36-kilodalton cellular transcription factor mediates an indirect interaction of human T-cell leukemia/lymphoma virus type I TAX1 with a responsive element in the viral long terminal repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4192–4201. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May E., Omilli F., Borde J., Scieller P. Simian virus 40 T antigen activates the late promoter by modulating the activity of negative regulatory elements. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3347–3354. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3347-3354.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Rosman G. J. Improved retroviral vectors for gene transfer and expression. Biotechniques. 1989 Oct;7(9):980-2, 984-6, 989-90. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyatake S., Seiki M., Yoshida M., Arai K. T-cell activation signals and human T-cell leukemia virus type I-encoded p40x protein activate the mouse granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor gene through a common DNA element. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5581–5587. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinset C., Montarras D., Chenevert J., Minty A., Barton P., Laurent C., Gros F. Control of myogenesis in the mouse myogenic C2 cell line by medium composition and by insulin: characterization of permissive and inducible C2 myoblasts. Differentiation. 1988 Jun;38(1):28–34. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1988.tb00588.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poiesz B. J., Ruscetti F. W., Gazdar A. F., Bunn P. A., Minna J. D., Gallo R. C. Detection and isolation of type C retrovirus particles from fresh and cultured lymphocytes of a patient with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7415–7419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittling S. R., Baserga R. Functional analysis and growth factor regulation of the human vimentin promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):3908–3915. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.3908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scieller P., Omilli F., Borde J., May E. Characterization of SV40 enhancer motifs involved in positive and negative regulation of the constitutive late promoter activity; effect of T-antigen. Virology. 1991 Apr;181(2):783–786. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90918-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiki M., Inoue J., Takeda T., Hikikoshi A., Sato M., Yoshida M. The p40x of human T-cell leukemia virus type I is a trans-acting activator of viral gene transcription. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1985 Dec;76(12):1127–1131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiki M., Inoue J., Takeda T., Yoshida M. Direct evidence that p40x of human T-cell leukemia virus type I is a trans-acting transcriptional activator. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):561–565. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04247.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen R. A., Goswami S. K., Mascareno E., Kumar A., Siddiqui M. A. Tissue-specific transcription of the cardiac myosin light-chain 2 gene is regulated by an upstream repressor element. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1676–1685. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siekevitz M., Feinberg M. B., Holbrook N., Wong-Staal F., Greene W. C. Activation of interleukin 2 and interleukin 2 receptor (Tac) promoter expression by the trans-activator (tat) gene product of human T-cell leukemia virus, type I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5389–5393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. R., Greene W. C. Molecular biology of the type I human T-cell leukemia virus (HTLV-I) and adult T-cell leukemia. J Clin Invest. 1991 Mar;87(3):761–766. doi: 10.1172/JCI115078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodroski J. G., Rosen C. A., Haseltine W. A. Trans-acting transcriptional activation of the long terminal repeat of human T lymphotropic viruses in infected cells. Science. 1984 Jul 27;225(4660):381–385. doi: 10.1126/science.6330891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittemore L. A., Maniatis T. Postinduction repression of the beta-interferon gene is mediated through two positive regulatory domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):7799–7803. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.7799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida M., Miyoshi I., Hinuma Y. Isolation and characterization of retrovirus from cell lines of human adult T-cell leukemia and its implication in the disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):2031–2035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.2031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




