Abstract
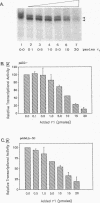
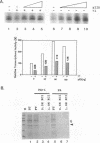
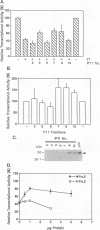
We have used a yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) cell free transcription system to study protein-protein interactions involving the tau 1 transactivation domain of the human glucocorticoid receptor that are important for transcriptional transactivation by the receptor. Purified tau 1 specifically inhibited transcription from a basal promoter derived from the CYC1 gene and from the adenovirus 2 major late core promoter in a concentration-dependent manner. This inhibition or squelching was correlated with the transactivation activity of tau 1. Recombinant yeast TATA-binding protein (yTFIID), although active in vitro, did not specifically reverse the inhibitory effect of tau 1. In addition, no specific interaction between tau 1 and yTFIID could be shown in vitro by affinity chromatography. Taken together, these results indicate that the tau 1 transactivation domain of the human glucocorticoid receptor interacts directly with the general transcriptional apparatus through some target protein(s) that is distinct from the TATA-binding factor. Furthermore, this assay can be used to identify interacting factors, since after phosphocellulose chromatography of a whole-cell yeast extract, a fraction that contained an activity which selectively counteracted the squelching effect of tau 1 was found.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger S. L., Cress W. D., Cress A., Triezenberg S. J., Guarente L. Selective inhibition of activated but not basal transcription by the acidic activation domain of VP16: evidence for transcriptional adaptors. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1199–1208. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90684-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkenstam A., Vivanco Ruiz M. M., Barettino D., Horikoshi M., Stunnenberg H. G. Cooperativity in transactivation between retinoic acid receptor and TFIID requires an activity analogous to E1A. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):401–412. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90443-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
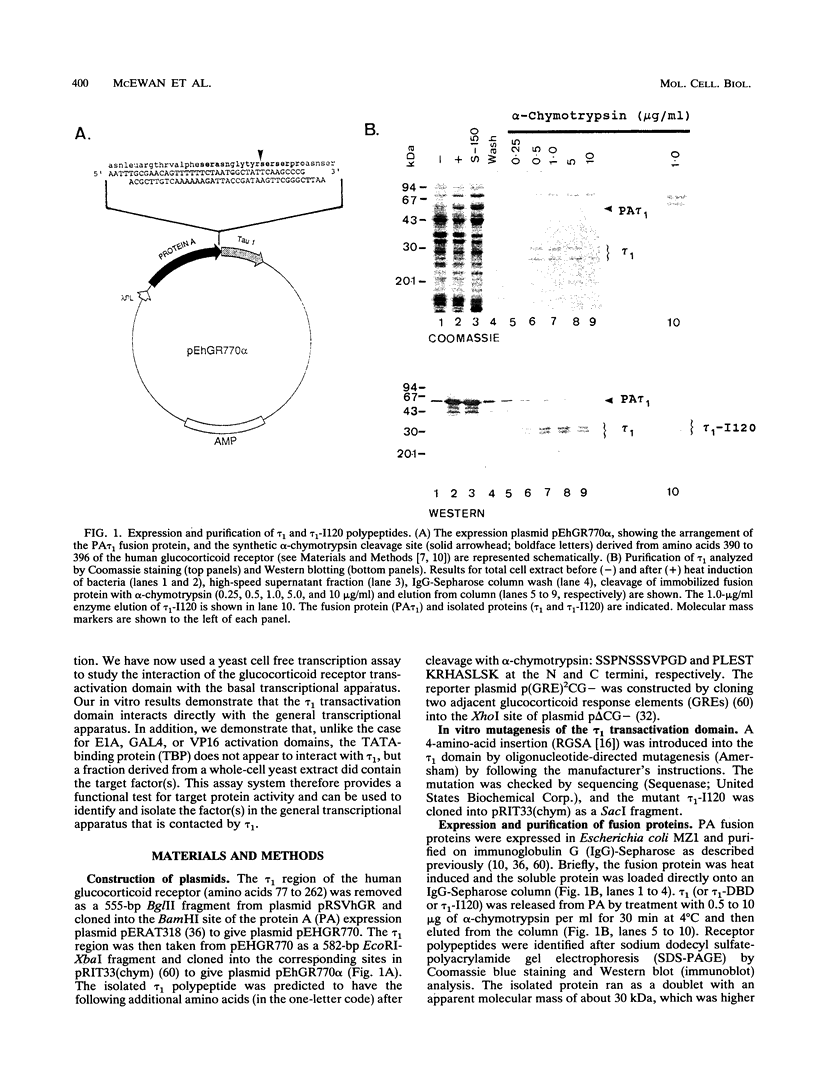
- Bodwell J. E., Ortí E., Coull J. M., Pappin D. J., Smith L. I., Swift F. Identification of phosphorylated sites in the mouse glucocorticoid receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7549–7555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski S., Hahn S., Guarente L., Sharp P. A. Five intermediate complexes in transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):549–561. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90578-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski S., Hahn S., Sharp P. A., Guarente L. Function of a yeast TATA element-binding protein in a mammalian transcription system. Nature. 1988 Jul 7;334(6177):37–42. doi: 10.1038/334037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlstedt-Duke J., Strömstedt P. E., Wrange O., Bergman T., Gustafsson J. A., Jörnvall H. Domain structure of the glucocorticoid receptor protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4437–4440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavallini B., Huet J., Plassat J. L., Sentenac A., Egly J. M., Chambon P. A yeast activity can substitute for the HeLa cell TATA box factor. Nature. 1988 Jul 7;334(6177):77–80. doi: 10.1038/334077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordingley M. G., Riegel A. T., Hager G. L. Steroid-dependent interaction of transcription factors with the inducible promoter of mouse mammary tumor virus in vivo. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90429-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlman K., Strömstedt P. E., Rae C., Jörnvall H., Flock J. I., Carlstedt-Duke J., Gustafsson J. A. High level expression in Escherichia coli of the DNA-binding domain of the glucocorticoid receptor in a functional form utilizing domain-specific cleavage of a fusion protein. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):804–809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynlacht B. D., Hoey T., Tjian R. Isolation of coactivators associated with the TATA-binding protein that mediate transcriptional activation. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):563–576. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90019-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan P. M., Kelleher R. J., 3rd, Sayre M. H., Tschochner H., Kornberg R. D. A mediator required for activation of RNA polymerase II transcription in vitro. Nature. 1991 Apr 4;350(6317):436–438. doi: 10.1038/350436a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores O., Lu H., Reinberg D. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Identification and characterization of factor IIH. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2786–2793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman L. P., Yoshinaga S. K., Vanderbilt J. N., Yamamoto K. R. In vitro transcription enhancement by purified derivatives of the glucocorticoid receptor. Science. 1989 Jul 21;245(4915):298–301. doi: 10.1126/science.2473529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguère V., Hollenberg S. M., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Functional domains of the human glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):645–652. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90339-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Chambon P. Nuclear receptors enhance our understanding of transcription regulation. Trends Genet. 1988 Nov;4(11):309–314. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90108-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn S., Buratowski S., Sharp P. A., Guarente L. Identification of a yeast protein homologous in function to the mammalian general transcription factor, TFIIA. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3379–3382. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08501.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeck W., Groner B. Hormone-dependent phosphorylation of the glucocorticoid receptor occurs mainly in the amino-terminal transactivation domain. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5403–5408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg S. M., Evans R. M. Multiple and cooperative trans-activation domains of the human glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):899–906. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90145-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg S. M., Giguere V., Segui P., Evans R. M. Colocalization of DNA-binding and transcriptional activation functions in the human glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90753-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi M., Carey M. F., Kakidani H., Roeder R. G. Mechanism of action of a yeast activator: direct effect of GAL4 derivatives on mammalian TFIID-promoter interactions. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):665–669. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi N., Maguire K., Kralli A., Maldonado E., Reinberg D., Weinmann R. Direct interaction between adenovirus E1A protein and the TATA box binding transcription factor IID. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5124–5128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingles C. J., Shales M., Cress W. D., Triezenberg S. J., Greenblatt J. Reduced binding of TFIID to transcriptionally compromised mutants of VP16. Nature. 1991 Jun 13;351(6327):588–590. doi: 10.1038/351588a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakidani H., Ptashne M. GAL4 activates gene expression in mammalian cells. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):161–167. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90504-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelleher R. J., 3rd, Flanagan P. M., Kornberg R. D. A novel mediator between activator proteins and the RNA polymerase II transcription apparatus. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1209–1215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90685-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. S., Kao C. C., Bryant G. O., Liu X., Berk A. J. Adenovirus E1A activation domain binds the basic repeat in the TATA box transcription factor. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):365–376. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90188-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman P. M., Schmidt M. C., Kao C. C., Berk A. J. Two distinct domains in the yeast transcription factor IID and evidence for a TATA box-induced conformational change. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):63–74. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. S., Green M. R. Mechanism of action of an acidic transcriptional activator in vitro. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):971–981. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90321-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. S., Ha I., Maldonado E., Reinberg D., Green M. R. Binding of general transcription factor TFIIB to an acidic activating region. Nature. 1991 Oct 10;353(6344):569–571. doi: 10.1038/353569a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lue N. F., Flanagan P. M., Kelleher R. J., 3rd, Edwards A. M., Kornberg R. D. RNA polymerase II transcription in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:545–550. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94041-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lue N. F., Flanagan P. M., Sugimoto K., Kornberg R. D. Initiation by yeast RNA polymerase II at the adenoviral major late promoter in vitro. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):661–664. doi: 10.1126/science.2510298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin K. J., Lillie J. W., Green M. R. Evidence for interaction of different eukaryotic transcriptional activators with distinct cellular targets. Nature. 1990 Jul 12;346(6280):147–152. doi: 10.1038/346147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger D., White J. H., Chambon P. The human oestrogen receptor functions in yeast. Nature. 1988 Jul 7;334(6177):31–36. doi: 10.1038/334031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson B., Abrahmsén L., Uhlén M. Immobilization and purification of enzymes with staphylococcal protein A gene fusion vectors. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):1075–1080. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03741.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olesen J., Hahn S., Guarente L. Yeast HAP2 and HAP3 activators both bind to the CYC1 upstream activation site, UAS2, in an interdependent manner. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):953–961. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90582-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C. L., Herskowitz I. Characterization of the yeast SWI1, SWI2, and SWI3 genes, which encode a global activator of transcription. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):573–583. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90192-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M. G., Tanese N., Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Functional domains and upstream activation properties of cloned human TATA binding protein. Science. 1990 Jun 29;248(4963):1625–1630. doi: 10.1126/science.2363050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M., Gann A. A. Activators and targets. Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):329–331. doi: 10.1038/346329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Diverse transcriptional functions of the multisubunit eukaryotic TFIID complex. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):679–682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Mechanism of transcriptional activation by Sp1: evidence for coactivators. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1187–1197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90683-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinberg D., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription in mammalian RNA polymerase II. Functional analysis of initiation factors IIA and IID and identification of a new factor operating at sequences downstream of the initiation site. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3322–3330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigaud G., Roux J., Pictet R., Grange T. In vivo footprinting of rat TAT gene: dynamic interplay between the glucocorticoid receptor and a liver-specific factor. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):977–986. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90370-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltzman A. G., Weinmann R. Promoter specificity and modulation of RNA polymerase II transcription. FASEB J. 1989 Apr;3(6):1723–1733. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.6.2649403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by human RNA polymerase II: analysis by a rapid and quantitative in vitro assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4394–4398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Interaction of a gene-specific transcription factor with the adenovirus major late promoter upstream of the TATA box region. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Sentenac A. RNA polymerase B (II) and general transcription factors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:711–754. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.003431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schena M., Yamamoto K. R. Mammalian glucocorticoid receptor derivatives enhance transcription in yeast. Science. 1988 Aug 19;241(4868):965–967. doi: 10.1126/science.3043665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer K. F., Ingles C. J., Greenblatt J. Direct and selective binding of an acidic transcriptional activation domain to the TATA-box factor TFIID. Nature. 1990 Jun 28;345(6278):783–786. doi: 10.1038/345783a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamkun J. W., Deuring R., Scott M. P., Kissinger M., Pattatucci A. M., Kaufman T. C., Kennison J. A. brahma: a regulator of Drosophila homeotic genes structurally related to the yeast transcriptional activator SNF2/SWI2. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):561–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90191-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanese N., Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Coactivators for a proline-rich activator purified from the multisubunit human TFIID complex. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12A):2212–2224. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12a.2212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tasset D., Tora L., Fromental C., Scheer E., Chambon P. Distinct classes of transcriptional activating domains function by different mechanisms. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1177–1187. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90394-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tora L., White J., Brou C., Tasset D., Webster N., Scheer E., Chambon P. The human estrogen receptor has two independent nonacidic transcriptional activation functions. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90031-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. Y., Srinivasan G., Allan G. F., Thompson E. B., O'Malley B. W., Tsai M. J. Recombinant human glucocorticoid receptor induces transcription of hormone response genes in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):17055–17061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster N., Jin J. R., Green S., Hollis M., Chambon P. The yeast UASG is a transcriptional enhancer in human HeLa cells in the presence of the GAL4 trans-activator. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):169–178. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90505-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieland S., Döbbeling U., Rusconi S. Interference and synergism of glucocorticoid receptor and octamer factors. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2513–2521. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07791.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright A. P., Carlstedt-Duke J., Gustafsson J. A. Ligand-specific transactivation of gene expression by a derivative of the human glucocorticoid receptor expressed in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):14763–14769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright A. P., Gustafsson J. A. Mechanism of synergistic transcriptional transactivation by the human glucocorticoid receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8283–8287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright A. P., McEwan I. J., Dahlman-Wright K., Gustafsson J. A. High level expression of the major transactivation domain of the human glucocorticoid receptor in yeast cells inhibits endogenous gene expression and cell growth. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Oct;5(10):1366–1372. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-10-1366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]