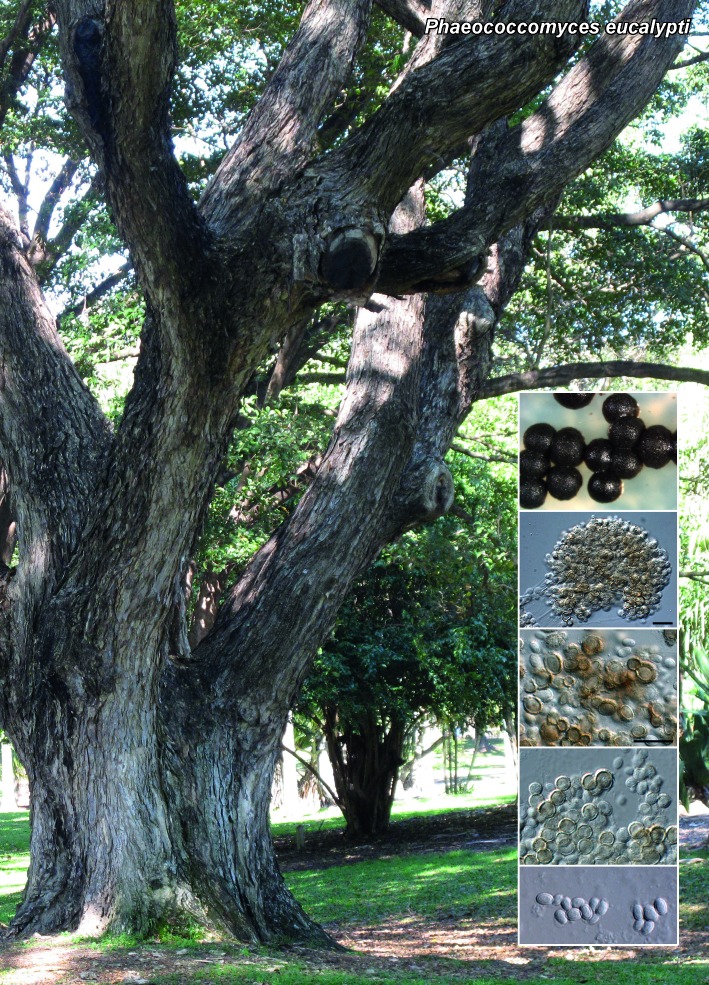
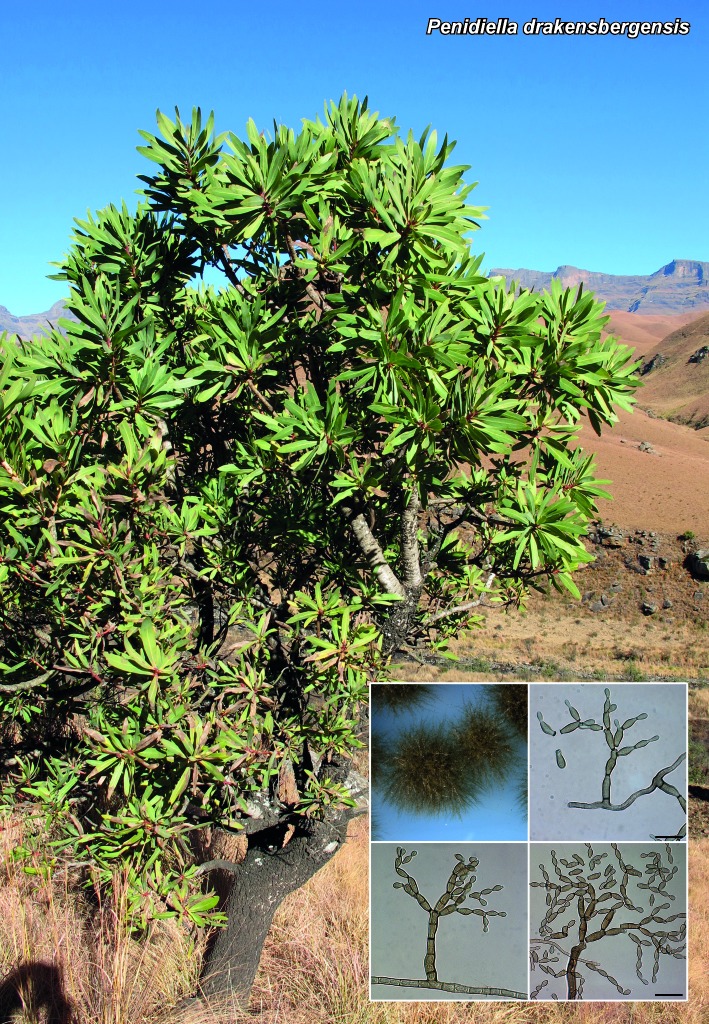
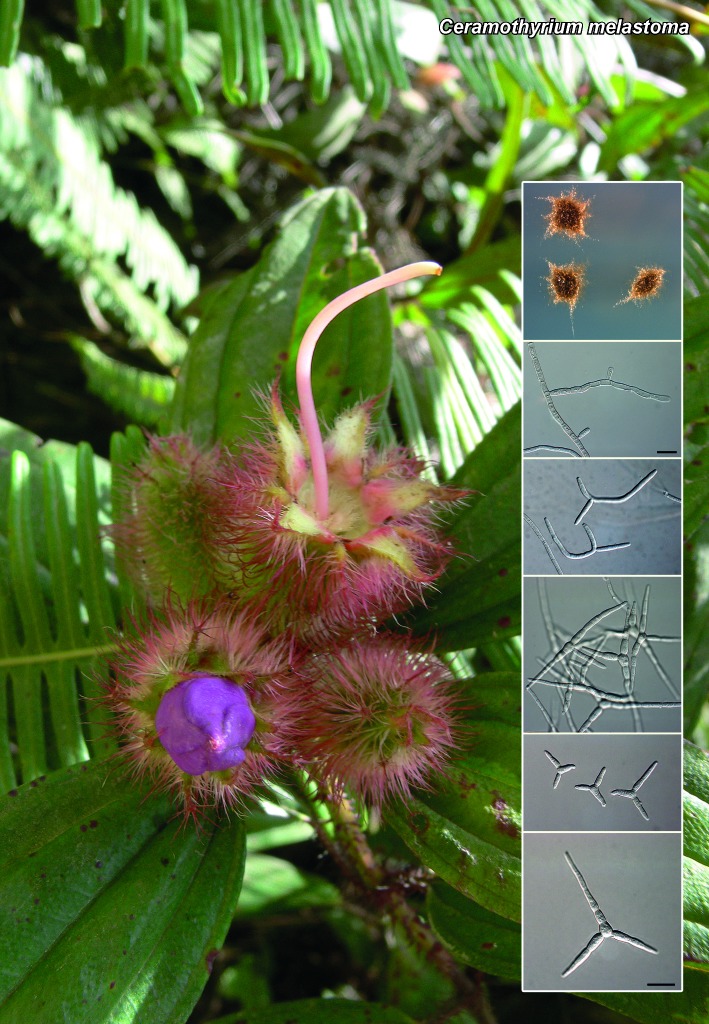
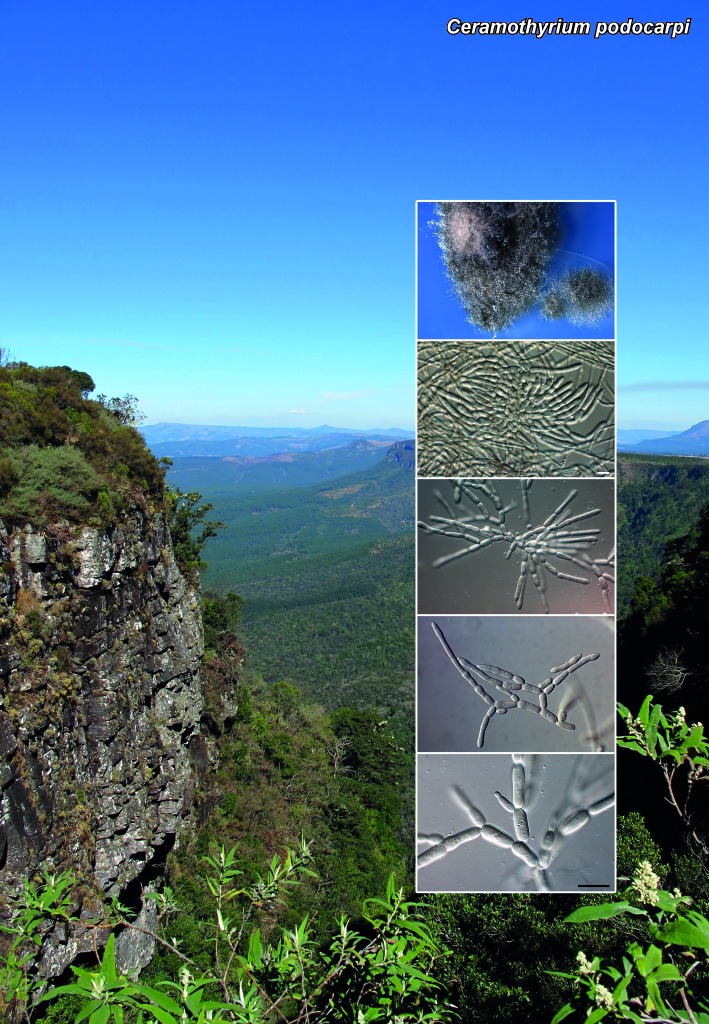
Abstract
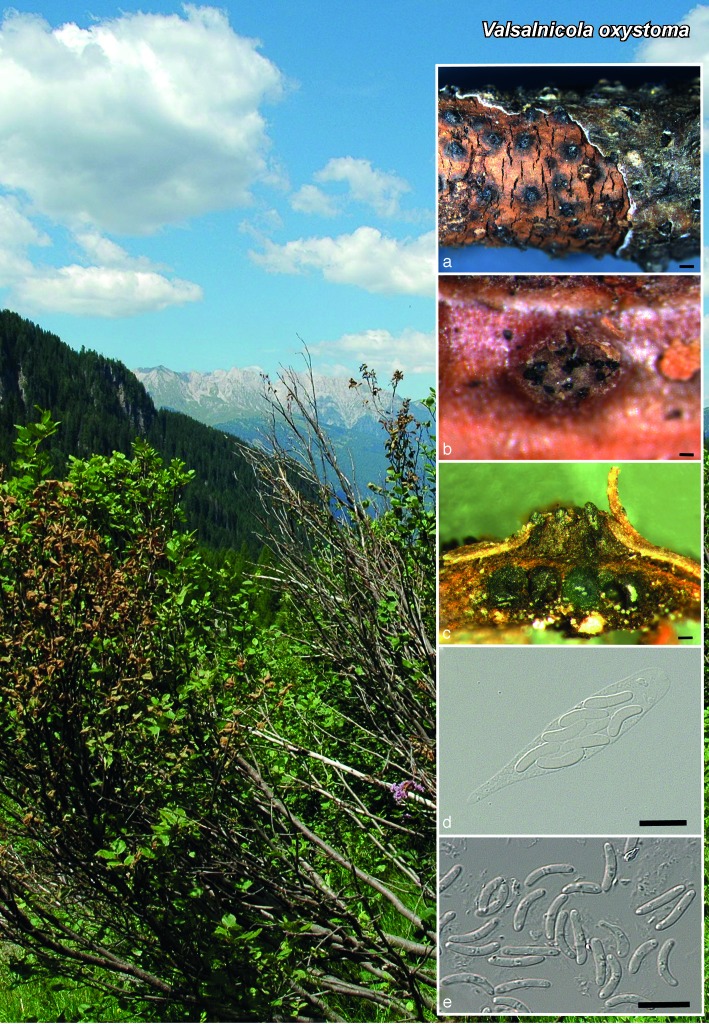
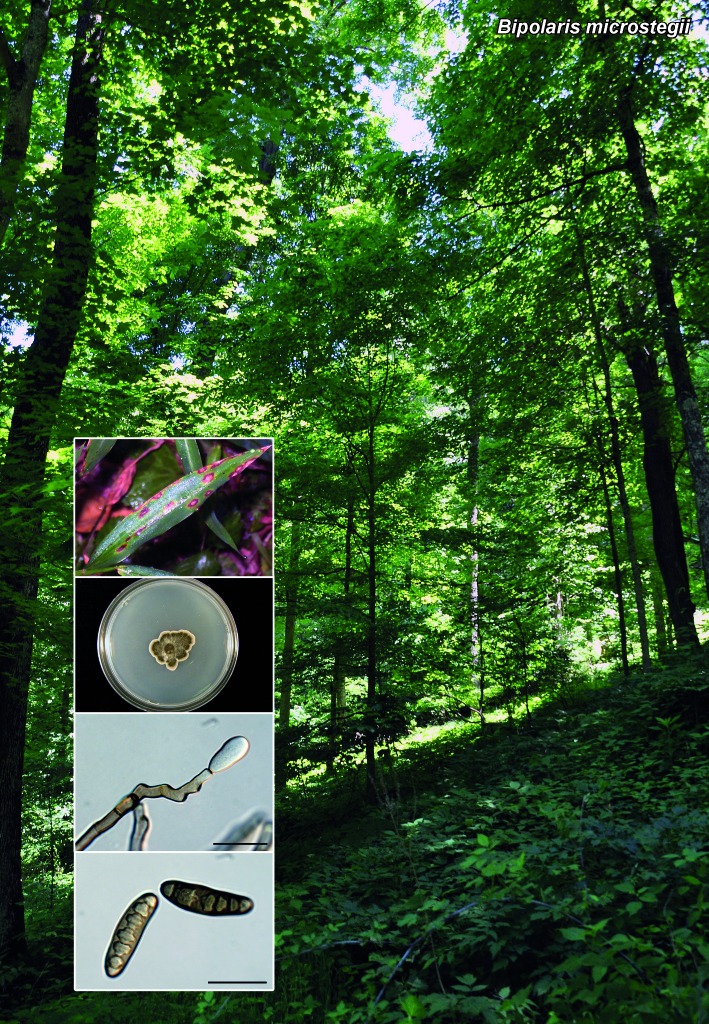
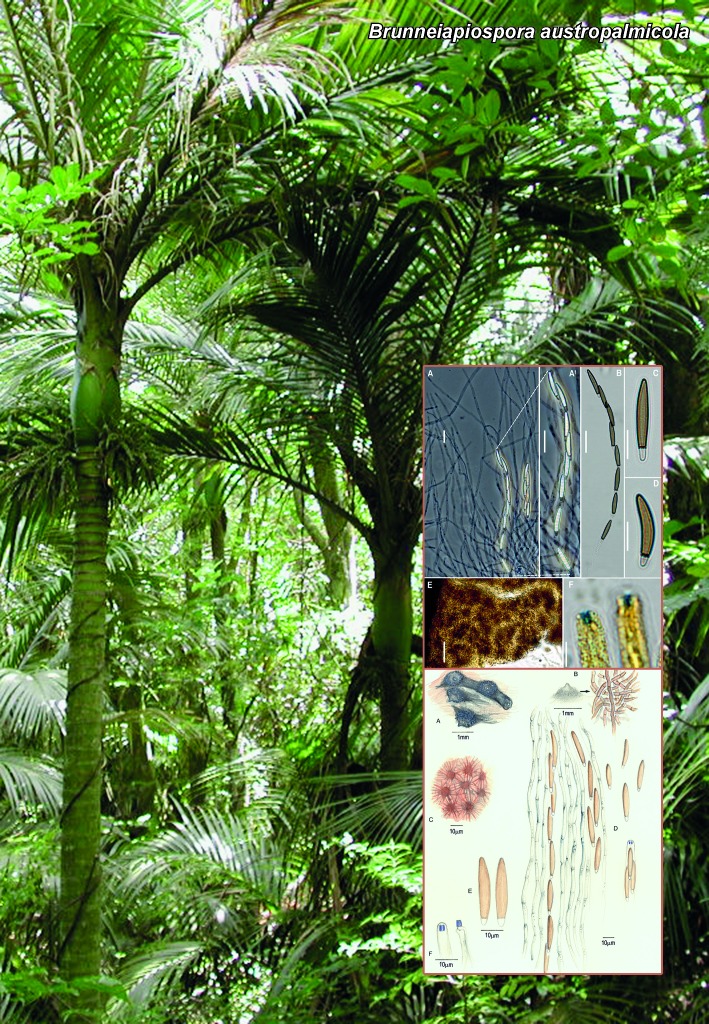
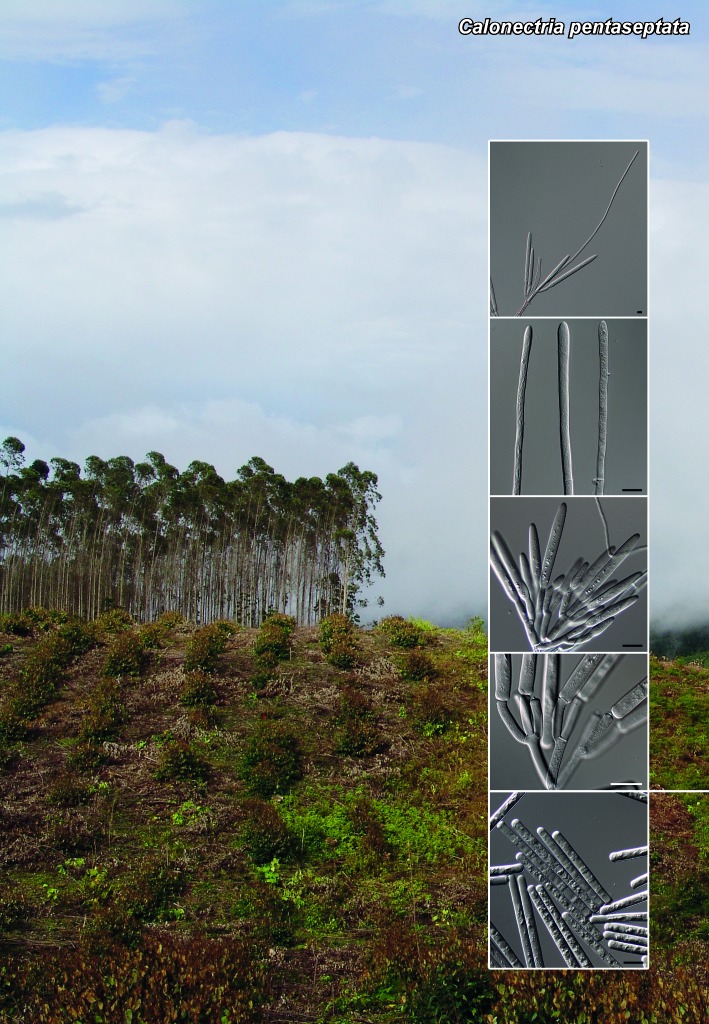
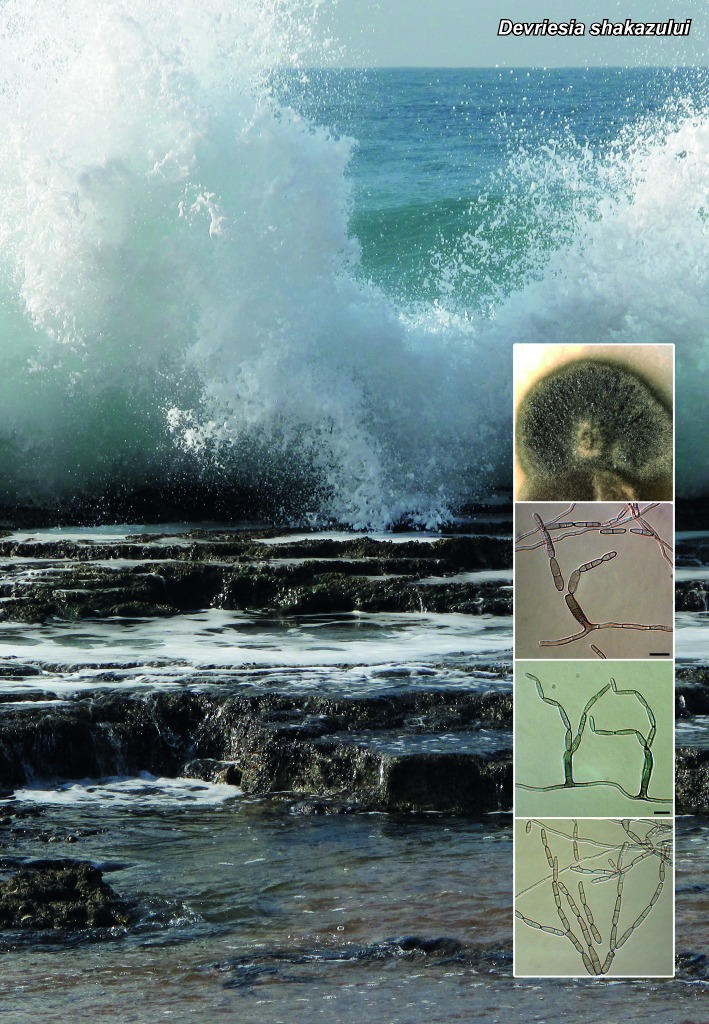
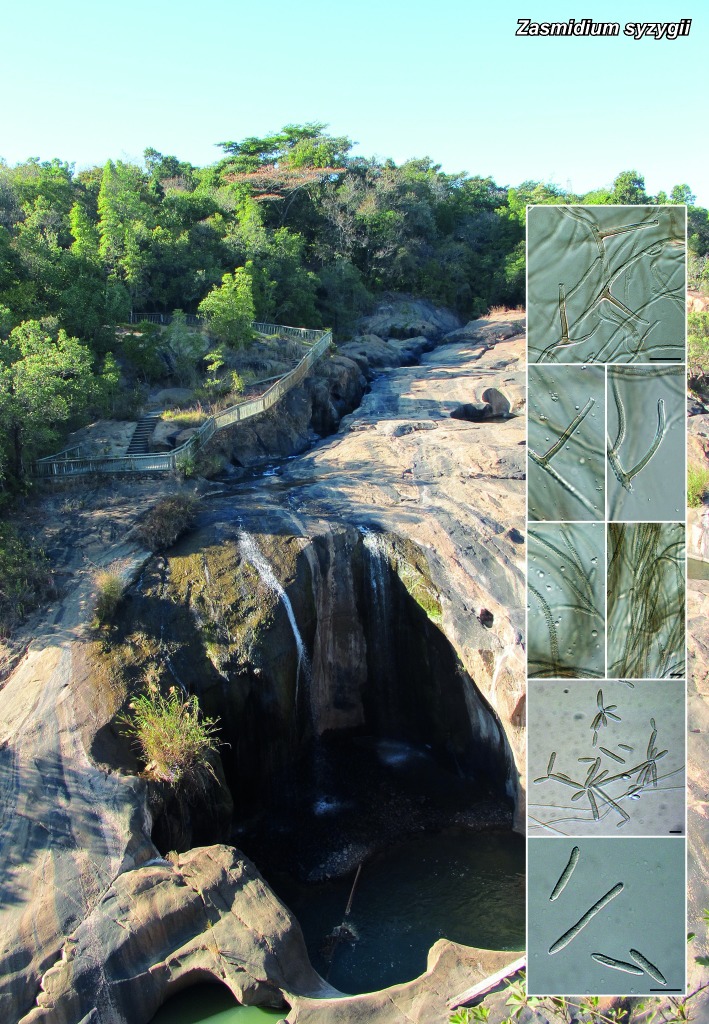
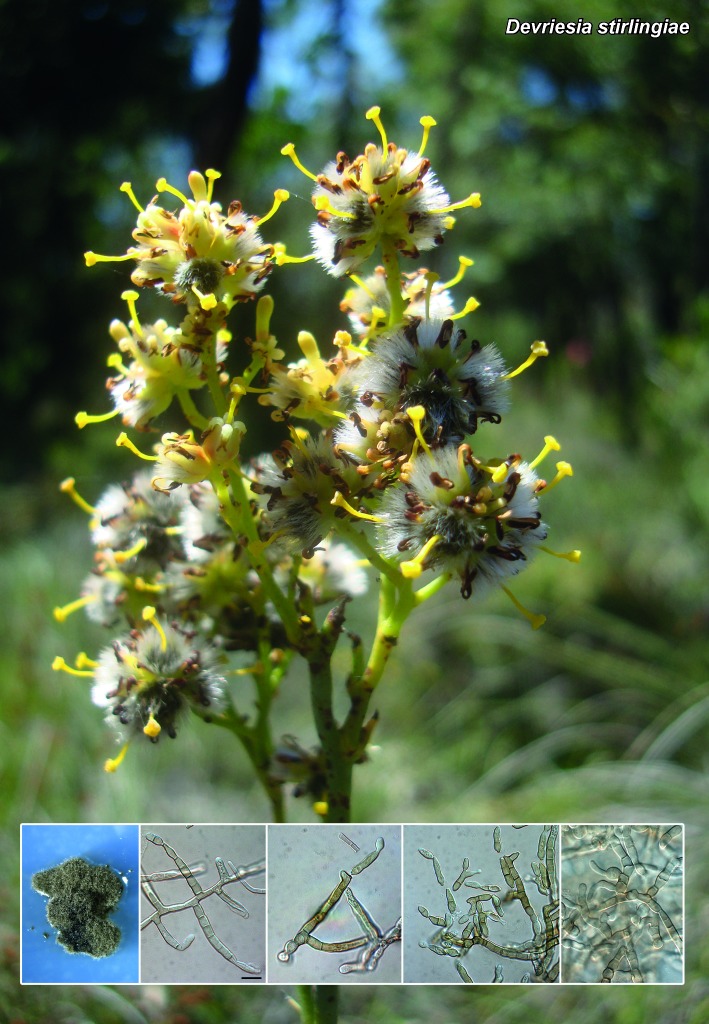
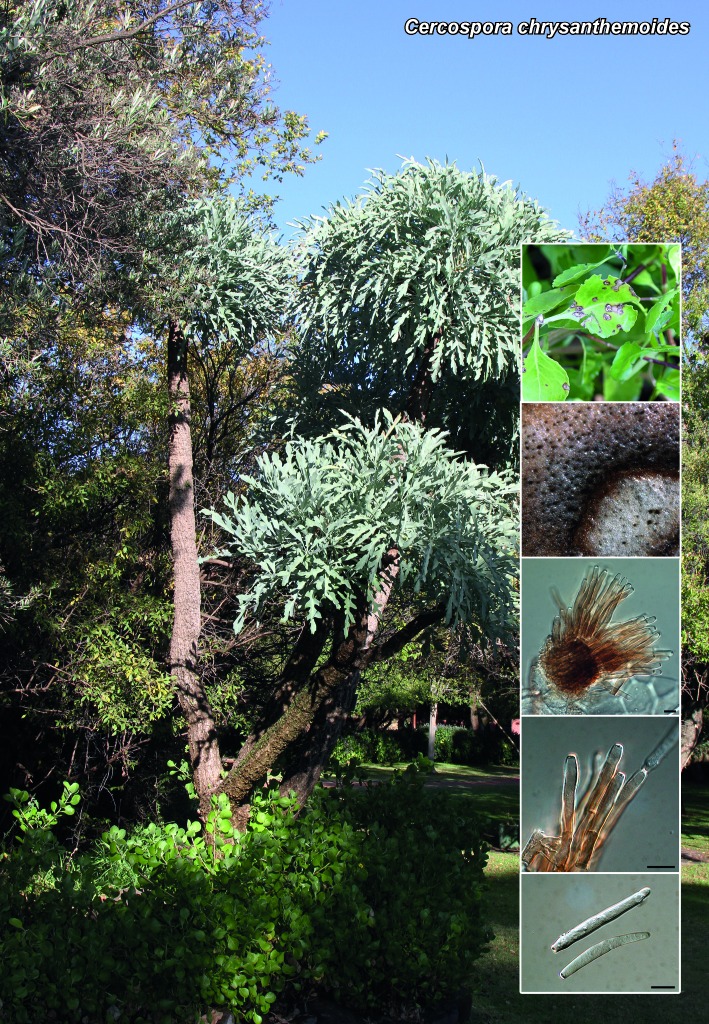
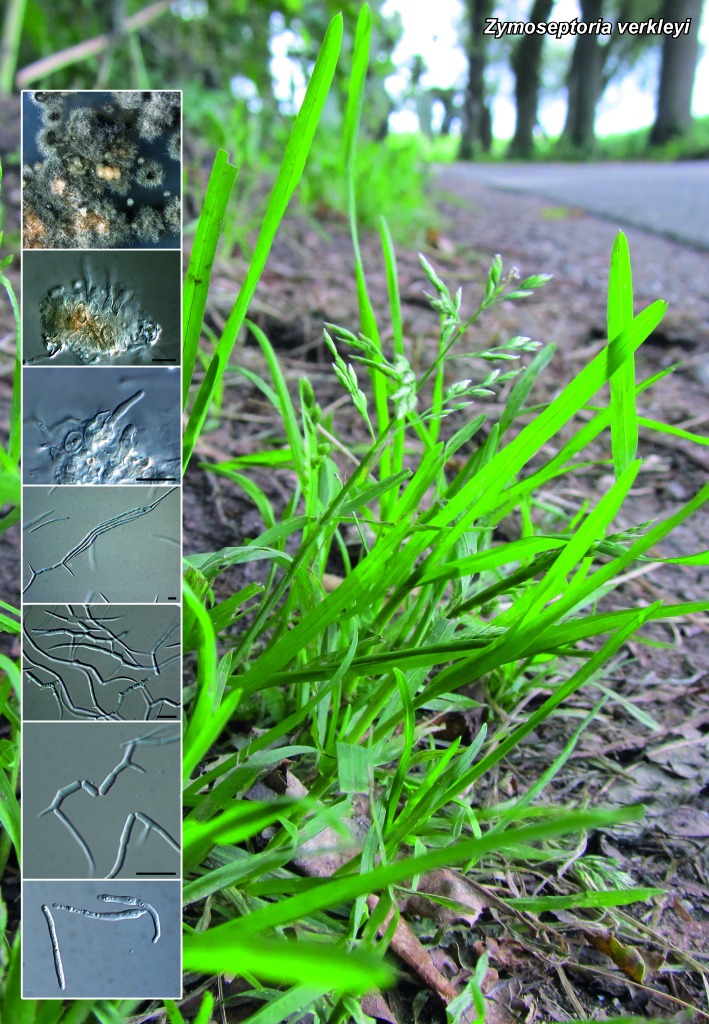
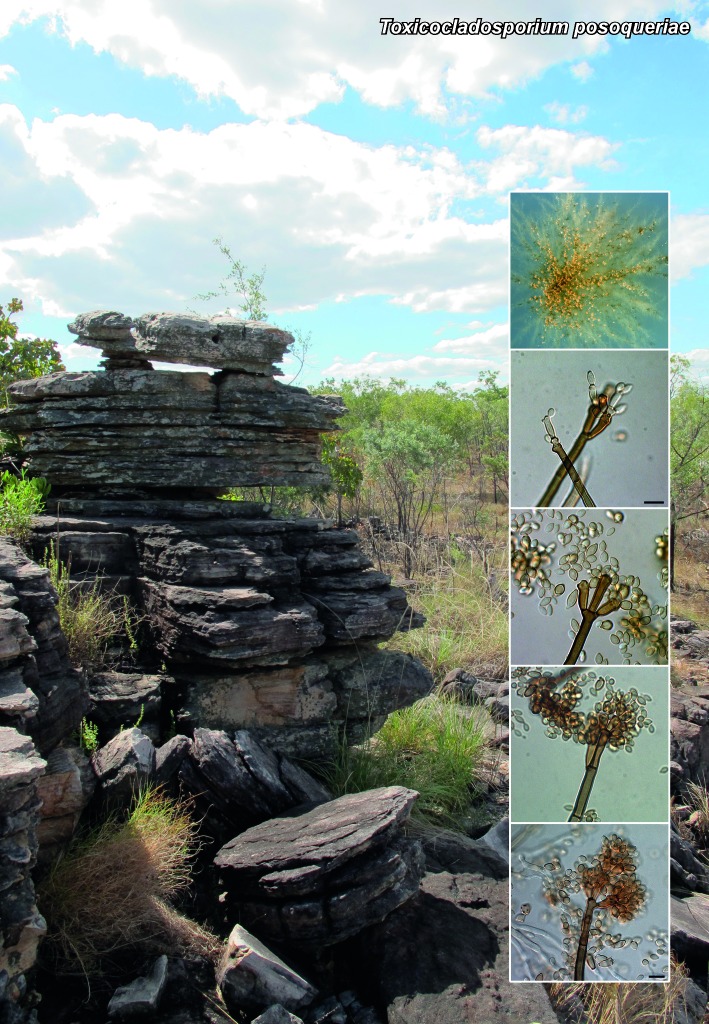
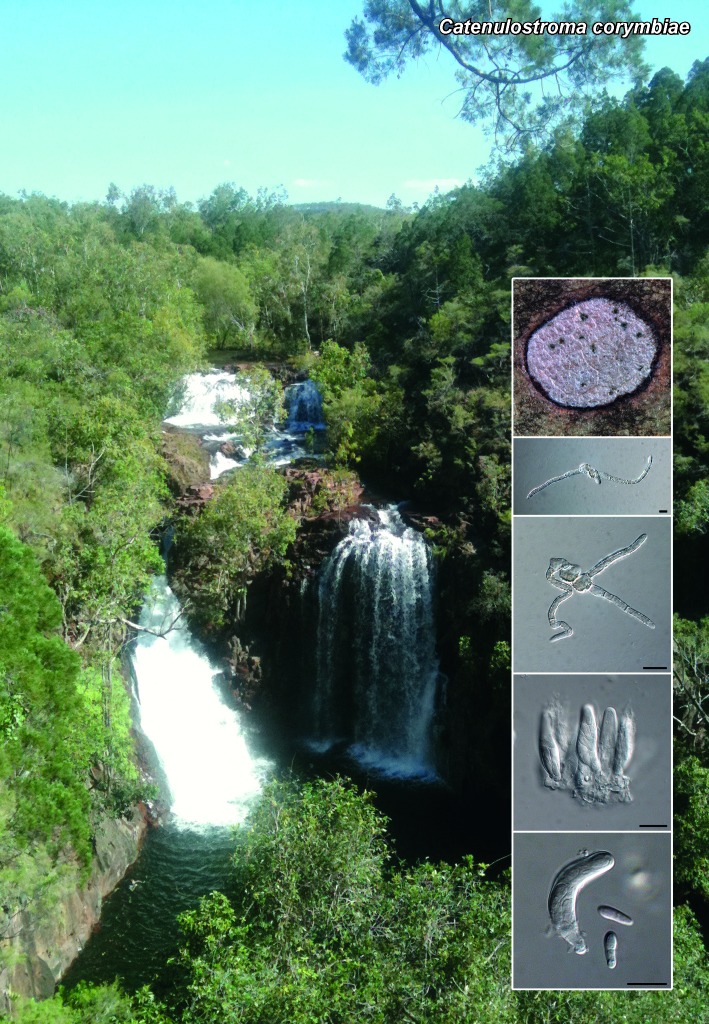
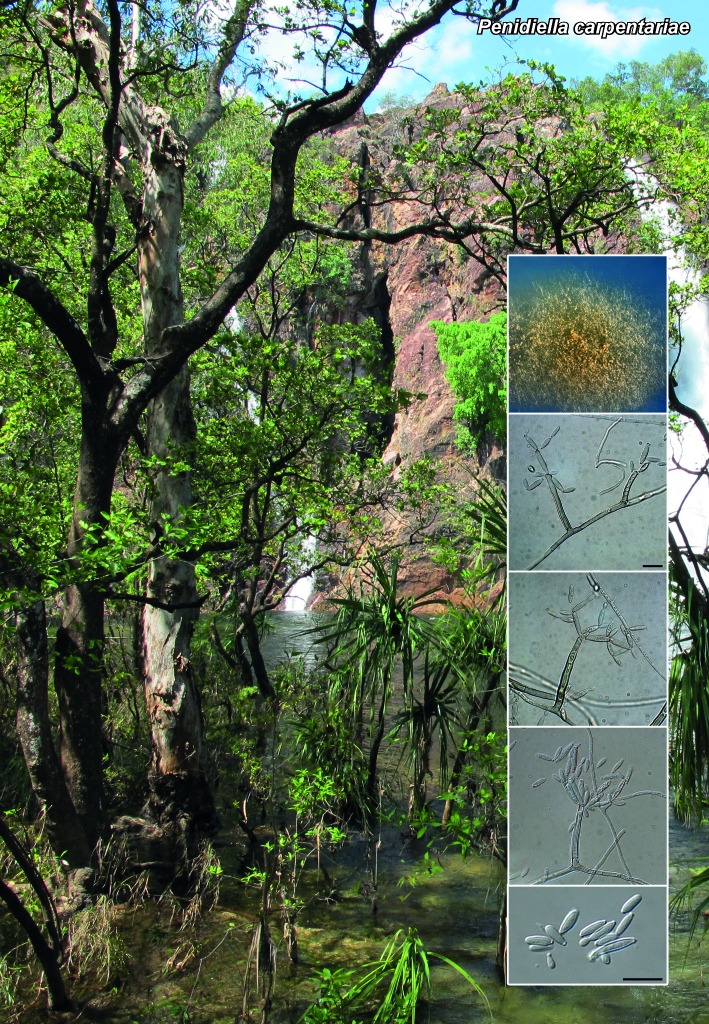
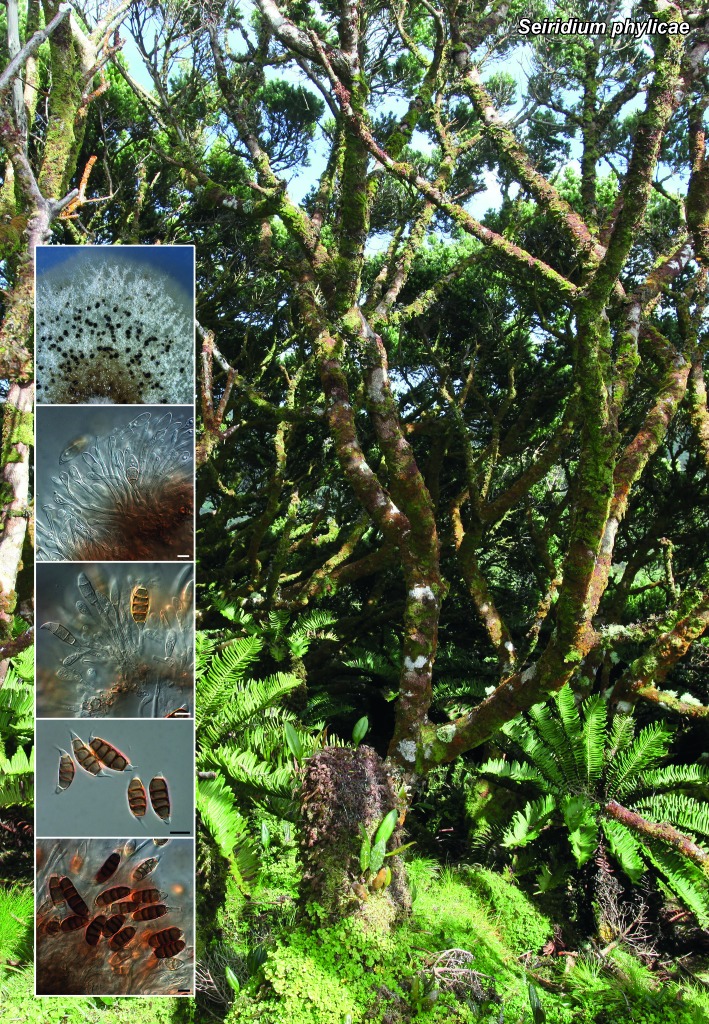
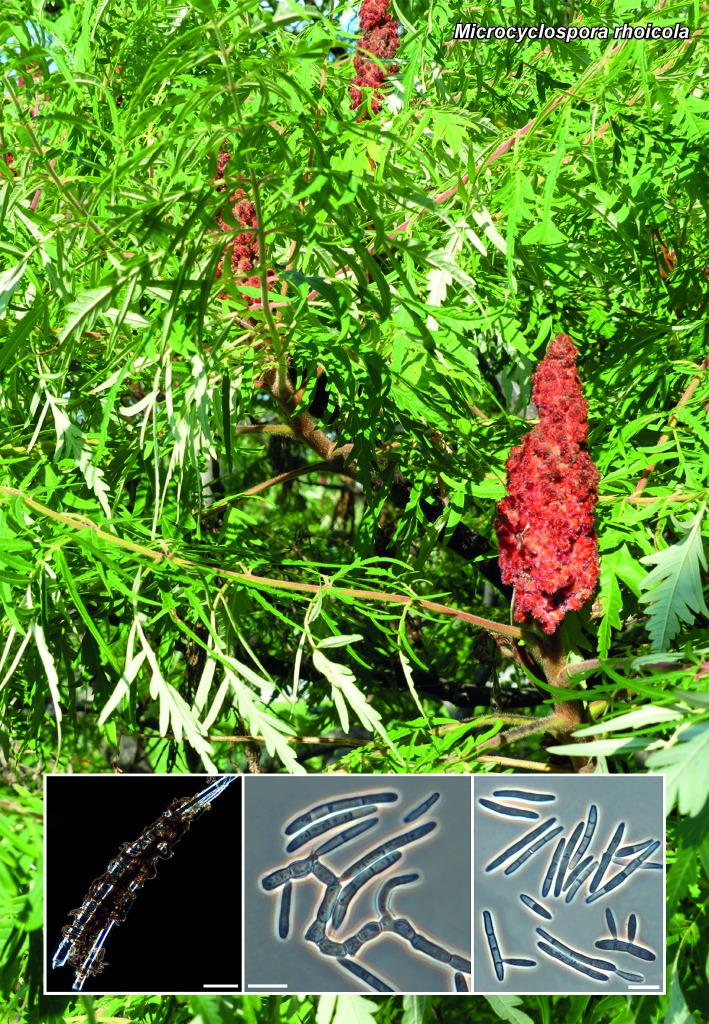
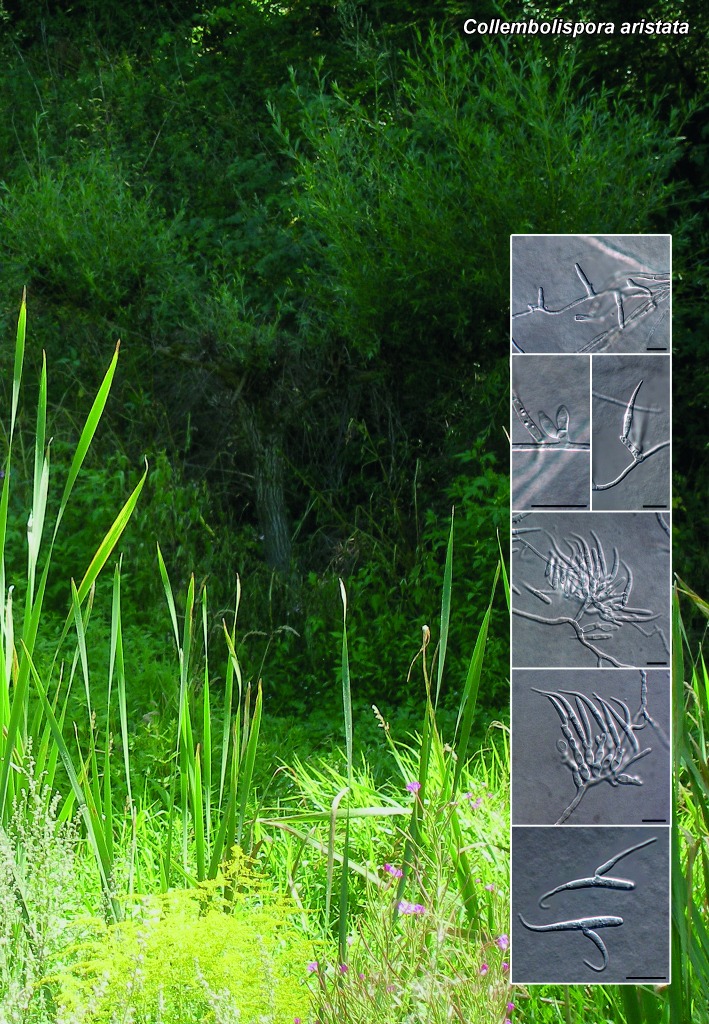
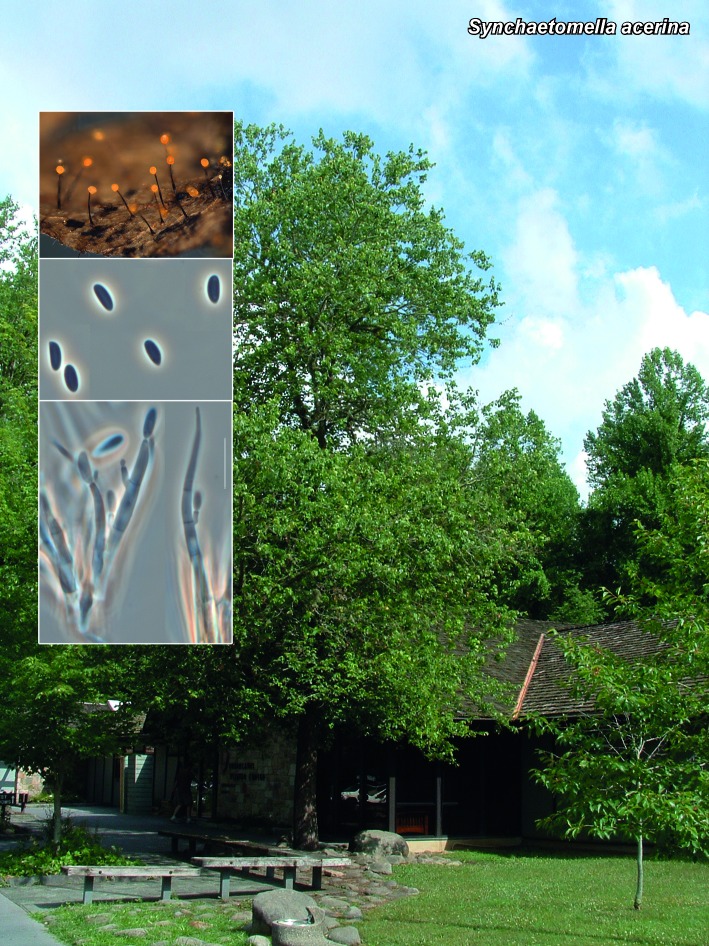
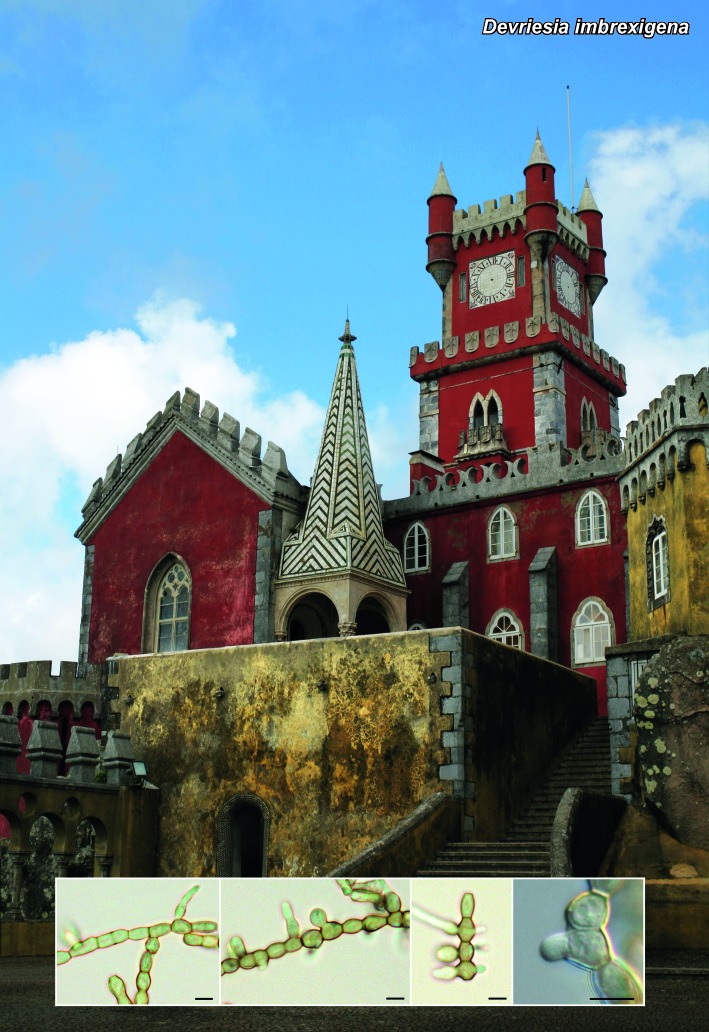
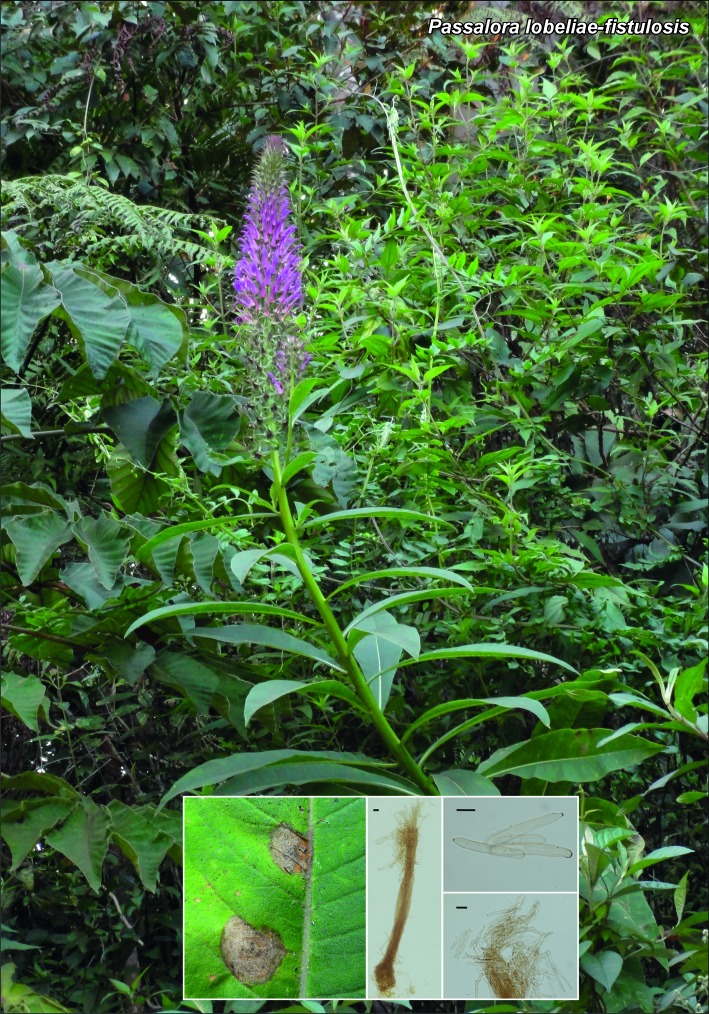
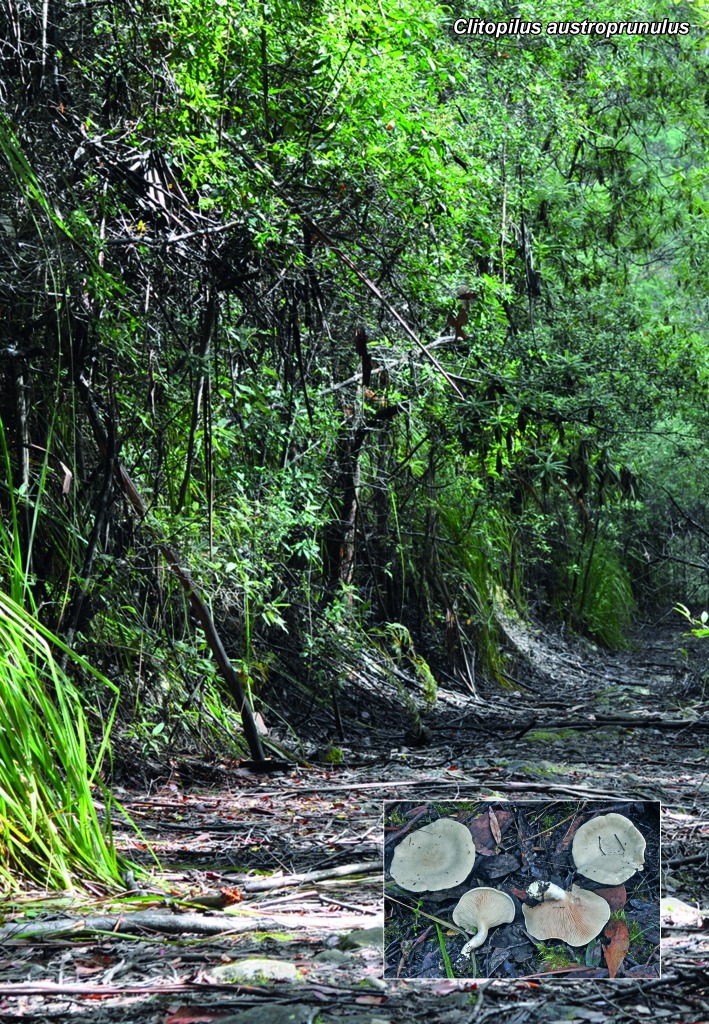
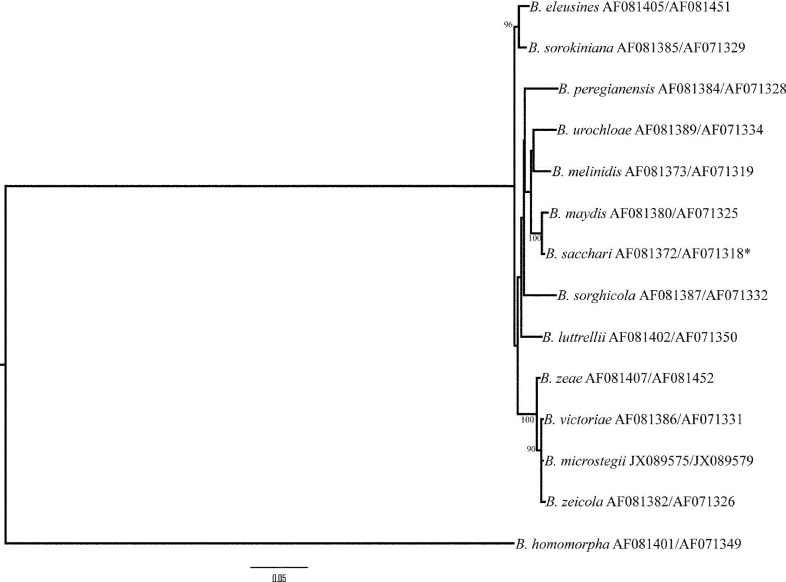
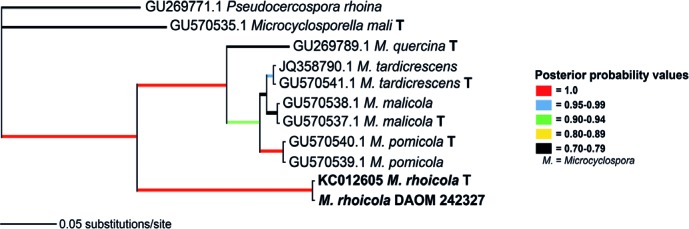
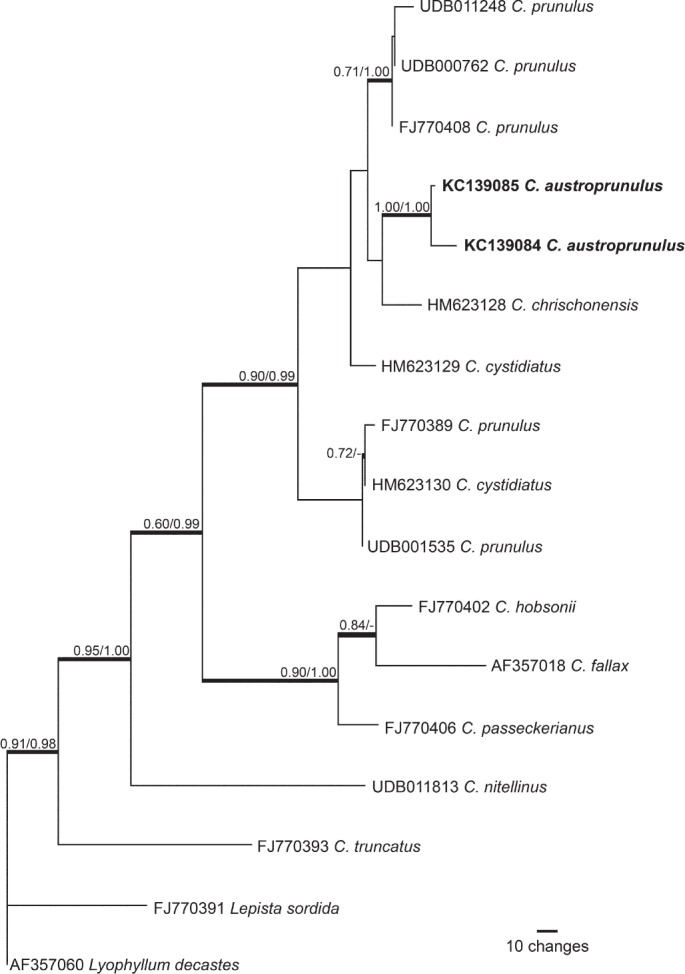
Novel species of microfungi described in the present study include the following from Australia: Catenulostroma corymbiae from Corymbia, Devriesia stirlingiae from Stirlingia, Penidiella carpentariae from Carpentaria, Phaeococcomyces eucalypti from Eucalyptus, Phialophora livistonae from Livistona, Phyllosticta aristolochiicola from Aristolochia, Clitopilus austroprunulus on sclerophyll forest litter of Eucalyptus regnans and Toxicocladosporium posoqueriae from Posoqueria. Several species are also described from South Africa, namely: Ceramothyrium podocarpi from Podocarpus, Cercospora chrysanthemoides from Chrysanthemoides, Devriesia shakazului from Aloe, Penidiella drakensbergensis from Protea, Strelitziana cliviae from Clivia and Zasmidium syzygii from Syzygium. Other species include Bipolaris microstegii from Microstegium and Synchaetomella acerina from Acer (USA), Brunneiapiospora austropalmicola from Rhopalostylis (New Zealand), Calonectria pentaseptata from Eucalyptus and Macadamia (Vietnam), Ceramothyrium melastoma from Melastoma (Indonesia), Collembolispora aristata from stream foam (Czech Republic), Devriesia imbrexigena from glazed decorative tiles (Portugal), Microcyclospora rhoicola from Rhus (Canada), Seiridium phylicae from Phylica (Tristan de Cunha, Inaccessible Island), Passalora lobeliae-fistulosis from Lobelia (Brazil) and Zymoseptoria verkleyi from Poa (The Netherlands). Valsalnicola represents a new ascomycete genus from Alnus (Austria) and Parapenidiella a new hyphomycete genus from Eucalyptus (Australia). Morphological and culture characteristics along with ITS DNA barcodes are also provided.
Keywords: ITS DNA barcodes, LSU, novel fungal species, systematics
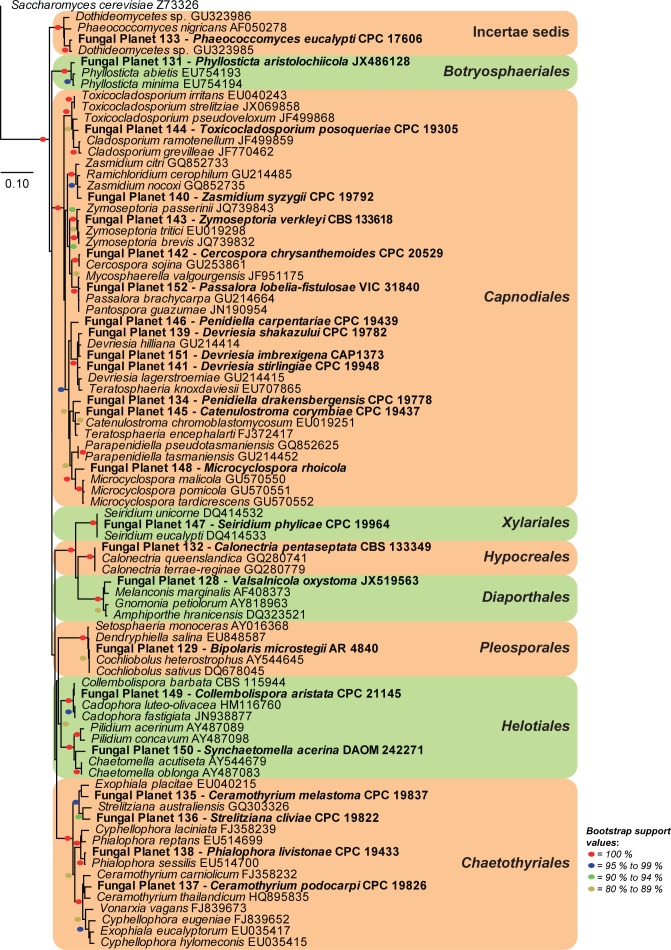
Neighbour-joining tree obtained using a distance analysis with a general time reversible (GTR) substitution model on the partial 28S nrRNA gene alignment (817 nucleotides including alignment gaps) as implemented in PAUP v. 4.0b10 (Swofford 2003). Novel species are indicated in a bold font and the orders are indicated on the right-hand side of the figure. The scale bar indicates the number of substitutions per site and the bootstrap support values (based on 1000 replicates) are shown by colour-coded dots for values > 79 % (see legend on figure). The tree was rooted to a sequence of Saccharomyces cerevisiae (GenBank Z73326.)
Acknowledgments
We thank the technical staff, A. van Iperen (cultures), M. Vermaas (photographic plates), and M. Starink-Willemse (DNA isolation, amplification and sequencing) for their invaluable assistance. Sincere thanks to Dr Barry Sneddon and Dr Patrick Brownsey for their help in confirming the host substrate (FP 130), and to Kerie McCombe and Andrew Millar for some of the photographs used. Kathie Hodge, Rebecca Bennett and D.H. DeFoe are thanked for collecting some of the specimens studied here (FP 150). The South African National Antarctic Programme is thanked for logistic support and Tristan da Cunha’s Conservation Department for permission to collect samples (FP 147). Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia, Portugal is thanked for grant SFRH/BD/46038/2008 (M. Couthinho) and PEst-OE/BIA/UI0457/2011 (A.J.L. Phillips). The contribution of L. Marvanová is part of the project MSM 0021622416 of the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports, Czech Republic.
REFERENCES
- Aa HA van der, Vanev S. 2002. A revision of the species described in Phyllosticta. Centraalbureau voor Schimmelcultures, Utrecht, The Netherlands [Google Scholar]
- Arzanlou M, Bakhshi M. 2011. Microcyclospora rumicis, a new species on Rumex crispus from Iran. Mycotaxon 118: 181–186 [Google Scholar]
- Arzanlou M, Crous PW. 2006. Strelitziana africana. Fungal Planet No. 8. Centraalbureau voor Schimmelcultures, Utrecht, The Netherlands [Google Scholar]
- Bensch K, Braun U, Groenewald JZ, Crous PW. 2012. The genus Cladosporium. Studies in Mycology 72: 1–401 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berbee ML, Pirseyedi M, Hubbard S. 1999. Cochliobolus phylogenetics and the origin of known, highly virulent pathogens, inferred from ITS and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase sequences. Mycologia 91: 964–977 [Google Scholar]
- Braun U. 1995. A monograph of Cercosporella, Ramularia and allied genera (Phytopathogenic Hyphomycetes). IHW Verlag, München, Germany [Google Scholar]
- Cannon PF, Hawksworth DL, Sherwood-Pike MA. 1985. The British Ascomycotina. An annotated checklist. Commonwealth Mycological Institute, Kew, Surrey, England [Google Scholar]
- Cheewangkoon R, Groenewald JZ, Summerell BA, Hyde KD, To-anun C, Crous PW. 2009. Myrtaceae, a cache of fungal biodiversity. Persoonia 23: 55–85 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomnunti P, Ko Ko TW, Chukeatirote E, Hyde KD, Cai L, et al. 2012. Phylogeny of the Chaetothyriaceae in northern Thailand including three new species. Mycologia 103: 382–395 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Co-David D, Langeveld D, Noordeloos M. 2009. Molecular phylogeny and spore evolution of Entolomataceae. Persoonia 23: 147–176 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constantinescu O, Holm K, Holm L. 1989. Teleomorph-anamorph connections in Ascomycetes. 1–3. Stanhughesia (Hyphomycetes) new genus, the anamorph of Ceramothyrium. Studies in Mycology 31: 69–84 [Google Scholar]
- Coutinho ML, Miller AZ, Gutierrez-Patricio S, Hernandez-Marine M, Gomez-Bolea A, et al. 2012. Microbial communities on deteriorated artistic tiles from Pena National Palace (Sintra, Portugal). International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation. doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2012.05.028. [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW. 1999. Species of Mycosphaerella and related anamorphs occurring on Myrtaceae (excluding Eucalyptus). Mycological Research 103: 607–621 [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Braun U. 2003. Mycosphaerella and its anamorphs. 1. Names published in Cercospora and Passalora. CBS Biodiversity Series 1: 1–571. Utrecht, The Netherlands [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Braun U, Groenewald JZ. 2007. Mycosphaerella is polyphyletic. Studies in Mycology 58: 1–32 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Braun U, Hunter GC, Wingfield MJ, Verkley GJM, et al. In press. Phylogenetic lineages in Pseudocercospora. Studies in Mycology 75: 37–114 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Groenewald JZ. 2011. Why everlastings don’t last. Persoonia 26: 70–84 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Groenewald JZ, Shivas RG. 2010a. Devriesia fraseriae. Fungal Planet 65. Persoonia 25: 150–151 [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Groenewald JZ, Shivas RG. 2010b. Strelitziana eucalypti. Fungal Planet 62. Persoonia 25: 144–145 [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Groenewald JZ, Shivas RG, Edwards J, Seifert KA, et al. 2011. Fungal Planet description sheets: 69–91. Persoonia 26: 108–156 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Schoch CL, Hyde KD, Wood AR, Gueidan C, et al. 2009a. Phylogenetic lineages in the Capnodiales. Studies in Mycology 64: 17–47 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Summerell BA, Carnegie AJ, Wingfield MJ, Groenewald JZ. 2009b. Novel species of Mycosphaerellaceae and Teratosphaeriaceae. Persoonia 23: 119–146 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Summerell BA, Carnegie AJ, Wingfield MJ, Hunter GC, et al. 2009c. Unravelling Mycosphaerella: do you believe in genera? Persoonia 23: 99–118 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Summerell BA, Shivas RG, Burgess TI, Decock CA, et al. 2012. Fungal Planet description sheets: 107–127. Persoonia 28: 138–182 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Wingfield MJ, Groenewald JZ. 2009d. Niche sharing reflects a poorly understood biodiversity phenomenon. Persoonia 22: 83–94 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crous PW, Wood AR, Okada G, Groenewald JZ. 2008. Foliicolous microfungi occurring on Encephalartos. Persoonia 21: 135–146 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decock C, Delgado Rodriguez G, Seifert KA. 2005. Phylogeny of Synchaetomella lunatospora, a new genus and species of synnematous fungi from Southeast Asia. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 88: 231–240 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis MB. 1971. Dematiaceous hyphomycetes. CAB International, Kew, UK [Google Scholar]
- Farr DF, Bills GF, Chamuris GP, Rossman AY. 1989. Fungi on plants and plant products in the United States. APS Press, USA [Google Scholar]
- Fernando AA, Currah RS. 1995. Leptodontidium orchidicola (Mycelium radicis atrovirens complex): Aspects of its conidiogenesis and ecology. Mycotaxon 54: 287–294 [Google Scholar]
- Flory SL, Kleczewski N, Clay K. 2011. Ecological consequences of pathogen accumulation on an invasive grass. Ecosphere 2, 120: 1–12 [Google Scholar]
- Frank J, Crous PW, Groenewald JZ, Oertel B, Hyde KD, et al. 2010. Microcyclospora and Microcyclosporella: novel genera accommodating epiphytic fungi causing sooty blotch on apple. Persoonia 24: 93–105 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glienke C, Pereira OL, Stringari D, Fabris J, Kava-Cordeiro V, et al. 2011. Endophytic and pathogenic Phyllosticta species, with reference to those associated with Citrus Black Spot. Persoonia 26: 47–56 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groenewald JZ, Nakashima C, Nishikawa J,, Shin H-D, Park JH, et al. In press. Species concepts in Cercospora: spotting the weeds among the roses. Studies in Mycology 75: 115–170 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley AJ,, Mattos-Shipley K, Collins CM, Kilaru S, Foster GD, Bailey AM. 2009. Investigating pleuromutilin-producing Clitopilus species and related basidiomycetes. FEMS Microbiology Letters 297: 24–30 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausknecht A, Noordeloos ME. 1998. Neue oder seltene arten der Entolomataceae (Agaricales) aus Mittel- und Südeuropa. Österreichische Zeitschrift für Pilzkunde 8: 199–221 [Google Scholar]
- Hoog GS de. 1977. Rhinocladiella and allied genera. Studies in Mycology 15: 1–140 [Google Scholar]
- Hoog GS de, Weenink XO, Gerrits van den Ende AHG. 1999. Taxonomy of the Phialophora verrucosa complex with the description of two new species. Studies in Mycology 43: 107–121 [Google Scholar]
- Hyde KD, Frölich J, Taylor JE. 1998. Fungi from palms XXXVI. Sydowia 50: 21–79 [Google Scholar]
- Kang JC, Crous PW, Old KM, Dudzinski MJ. 2001. Non-conspecificity of Cylindrocladium quinqueseptatum and Calonectria quinqueseptata based on beta-tubulin gene phylogeny and morphology. Canadian Journal of Botany 79: 1241–1247 [Google Scholar]
- Kang JC, Hyde KD, Kong RYC. 1999. Studies on the Amphisphaeriales 1. The Clypeosphaeriaceae. Mycoscience 40: 151–164 [Google Scholar]
- Kang JC, Kong RYC, Hyde KD. 1998. Studies on the Amphisphaeriales 1. Amphisphaeriaceae (sensu stricto) and its phylogenetic relationships inferred from 5.8SrDNA and ITS2 sequences. Fungal Diversity 1: 147–157 [Google Scholar]
- Kleczewski NM, Flory SL. 2010. Leaf blight disease of the invasive grass Microstegium vimineum caused by a Bipolaris sp. Plant Disease 94: 807–811 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleczewski NM, Flory SL, Clay K. 2012. Variation in pathogenicity and host range of Bipolaris sp. causing leaf blight disease on the invasive grass Microstegium vimineum. Weed Science 60: 486–493 [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi T. 2007. Index of fungi inhabiting woody plants in Japan. Host, distribution and literature. Zenkoku-Noson-Kyoiku Kyokai Publishing Co., Ltd., Japan [Google Scholar]
- Kornerup A, Wanscher JH. 1978. Methuen handbook of colour. Eyre Methuen Ltd., UK [Google Scholar]
- Lombard L, Crous PW, Wingfield BD, Wingfield MJ. 2010a. Species concepts in Calonectria (Cylindrocladium). Studies in Mycology 66: 1–14 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombard L, Crous PW, Wingfield BD, Wingfield MJ. 2010b. Phylogeny and systematics of the genus Calonectria. Studies in Mycology 66: 31–69 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombard L, Zhou XD, Crous PW, Wingfield BD, Wingfield MJ. 2010c. Calonectria species associated with cutting rot of Eucalyptus. Persoonia 24: 1–11 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manamgoda DS, Cai L, McKenzie EHC, Crous PW, Madrid H, et al. 2012. A phylogenetic and taxonomic re-evaluation of the Bipolaris – Cochliobolus – Curvularia complex. Fungal Diversity 56: 131–144 [Google Scholar]
- Marvanová L, Pascoal C, Cássio F. 2003. New and rare hyphomycetes from streams of Northwest Portugal. Part I. Cryptogamie Mycologie 24: 339–358 [Google Scholar]
- Noordeloos ME, Gates GM. 2012. The Entolomataceae of Tasmania. Fungal Diversity Research Series, vol. 22. [Google Scholar]
- Overholts L. 1943. Mycological notes for 1939–40. Mycologia 35: 243–254 [Google Scholar]
- Park D. 1972. On the ecology of heterotrophic micro-organisms in fresh-water. Transactions of the British Mycological Society 58: 291–299 [Google Scholar]
- Park RF, Keane PJ, Wingfield MJ, Crous PW. 2000. Fungal diseases of eucalypt foliage. In: Keane PJ, Kile GA, Podger FD, Brown BN. (eds), Diseases and pathogens of eucalypts: 153–239. CSIRO publishing, Australia [Google Scholar]
- Pereira JM, Barreto RW, Ellison AC, Maffia LA. 2003. Corynespora casiicola f. sp. lantanae: a potential biocontrol agent from Brazil for Lantana camara. Biological Control 26: 21–31 [Google Scholar]
- Pisetta M, Montecchio L, Longa CMO, Salvadori C, Zottele F, Maresi G. 2012. Green alder decline in the Italian Alps. Forest Ecology and Management 281: 75–83 [Google Scholar]
- Quaedvlieg W, Kema GHJ, Groenewald JZ, Verkley GJM, Seifbarghi S, et al. 2011. Zymoseptoria gen. nov.: a new genus to accommodate Septoria-like species occurring on graminicolous hosts. Persoonia 26: 57–69 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayner RW. 1970. A mycological colour chart. Commonwealth Mycological Institute, Kew, Surrey, England [Google Scholar]
- Roldán A, Puig MA. 1992. Hifomycetos acuáticos en la cuenca del río Esva (Asturias, norte de Espana). Anales del Real Jardín Botánico de Madrid 17: 3–11 [Google Scholar]
- Ronquist F, Teslenko M, Mark P, Ayres D, Darling A, Hohna S, Larget B, Liu L, Suchard M, Huelsenbeck J. 2012. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Systematic Biology 61: 539–542 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossman AY, Aime MC, Farr DF, Castlebury LA, Peterson KR, Leahy R. 2004. The coelomycetous genera Chaetomella and Pilidium represent a newly discovered lineage of inoperculate discomycetes. Mycological Progress 4: 275–290 [Google Scholar]
- Saccardo PA. 1882. Sylloge fungorum omnium hucusque cognitorum I. Patavii, Italy [Google Scholar]
- Seifert KA. 1985. A monograph of Stilbella and some allied hyphomycetes. Studies in Mycology 27: 1–235 [Google Scholar]
- Seifert KA, Nickerson NL, Corlett M, Jackson ED, Lois-Seize G, Davies RJ. 2004. Devriesia, a new hyphomycete genus to accommodate heat-resistant, cladosporium-like fungi. Canadian Journal of Botany 82: 914–926 [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu K, Tanaka C, Peng Y-L, Tsuda M. 1998. Phylogeny of Bipolaris inferred from nucleotide sequences of Brn1, a reductase gene involved in melanin biosynthesis. Journal of General and Applied Microbiology 44: 251–258 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shivas RG, Alcorn JL. 1996. A checklist of plant pathogenic and other microfungi in the rainforests of the wet tropics of northern Queensland. Australasian Plant Pathology 25: 158–173 [Google Scholar]
- Sivanesan A. 1987. Graminicolous species of Bipolaris, Curvularia, Drechslera, Exserohilum and their teleomorphs. Mycological Papers 158: 1–261 [Google Scholar]
- Sprague R. 1950. Diseases of cereals and grasses in North America. Ronald Press Co., New York, USA [Google Scholar]
- Stukenbrock EH, Quaedvlieg W, Javan-Nikhah M, Zala M, Crous PW, McDonald BA. 2012. Zymoseptoria ardabiliae and Z. pseudotritici, two progenitor species of the septoria tritici leaf blotch fungus Z. tritici (synonym: Mycosphaerella graminicola). Mycologia 104: 1397–1407 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton BC. 1980. The Coelomycetes. Fungi imperfecti with pycnidia, acervuli and stromata. Commonwealth Mycological Institute, Kew, Surrey, England [Google Scholar]
- Swofford DL. 2003. PAUP* 4.0b10. Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (*and other methods). Version 4. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA, USA [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson PB. 2006. The uniqueness of palms. Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society 151: 5–14 [Google Scholar]
- Vizzini A, Musumeci E, Ercole E, Contu M. 2011. Clitopilus chrischonensis sp. nov. (Agaricales, Entolomataceae), a striking new fungal species from Switzerland. Nova Hedwigia 92: 425–434 [Google Scholar]
- Yang ZL. 2007. Clitopilus amygdaliformis, a new species from tropical China. Mycotaxon 100: 241–246 [Google Scholar]
- Zhang R, Yang HL, Sun GY, Li HY, Zhuang JL, Zhai XR, Gleason ML. 2009. Strelitziana mali, a new species causing sooty blotch on apple fruit. Mycotaxon 110: 477–485 [Google Scholar]
- Zwickl D. 2006. Genetic algorithm approaches for the phylogenetic analysis of large biological sequence datasets under the maximum likelihood criterion. PhD thesis, The University of Texas at Austin. [Google Scholar]