Abstract
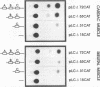
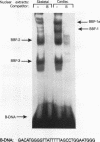
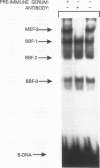
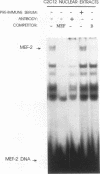
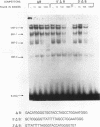
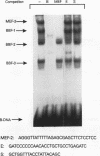
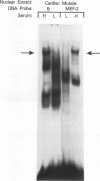
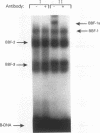
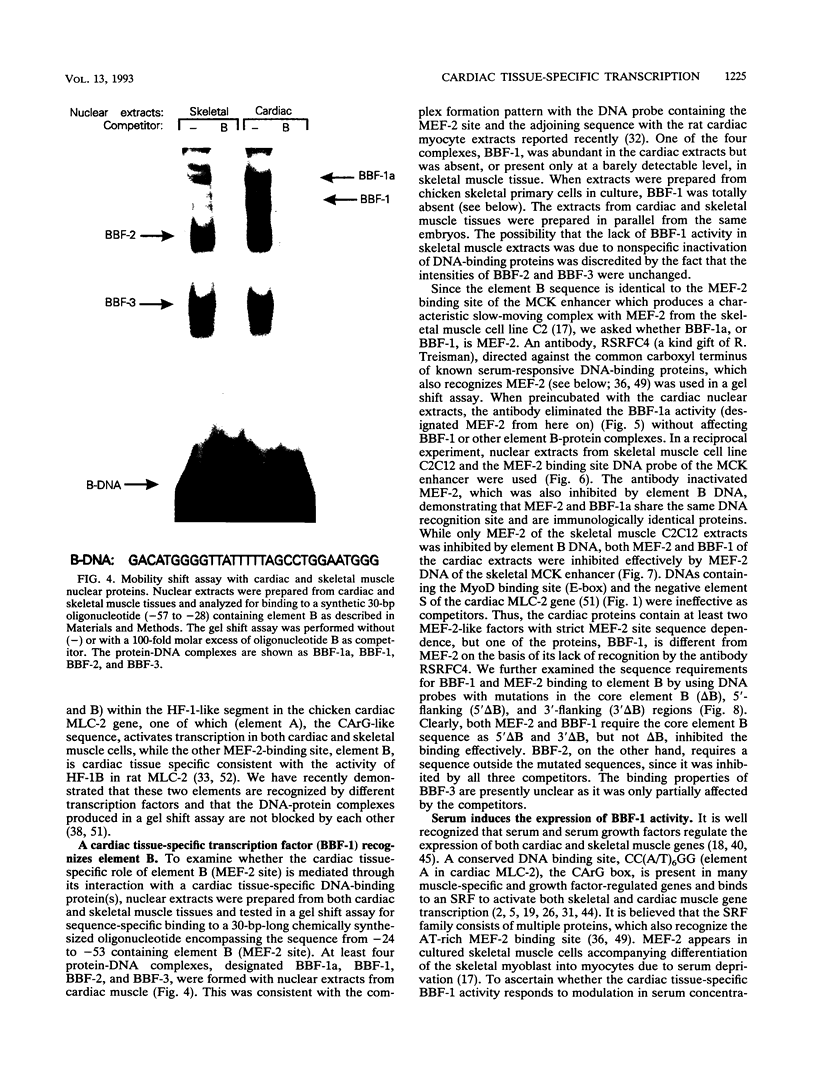
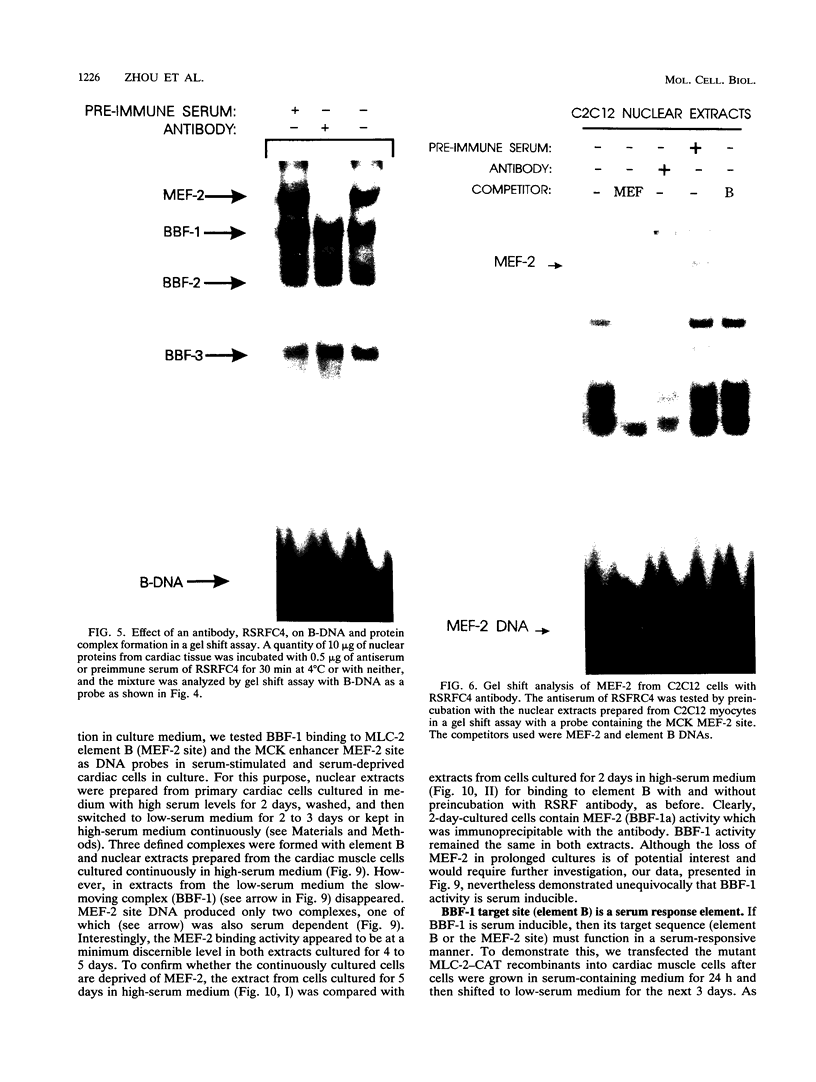
We have identified a serum-responsive, cardiac tissue-specific transcription factor, BBF-1, that recognizes an AT-rich sequence (element B), identical to the myocyte enhancer factor (MEF-2) target site, in the cardiac myosin light chain-2 (MLC-2) promoter. Deletion of the element B sequence alone from the cardiac MLC-2 promoter causes, as does that of the MEF-2 site from other promoters and the enhancer of skeletal muscle genes, a marked reduction of transcription. BBF-1 is distinguishable from cardiac MEF-2 on the basis of immunoprecipitation with an antibody which recognizes MEF-2 but not BBF-1. Unlike MEF-2, BBF-1 is present exclusively in nuclear extracts from cardiac muscle cells cultured in a medium containing a high concentration of serum. Removal of serum from culture medium abolishes BBF-1 activity selectively with a concomitant loss of the positive regulatory effect of element B on MLC-2 gene transcription, indicating that there is a correlation between the BBF-1 binding activity and the tissue-specific role of the element B (MEF-2 site) sequence. The loss of element B-mediated activation of transcription is reversed following the refeeding of cells with serum-containing medium. These data demonstrate that cardiac muscle cells contain two distinct protein factors, MEF-2 and BBF-1, which bind to the same target site but that, unlike MEF-2, BBF-1 is serum inducible and cardiac tissue specific. BBF-1 thus appears to be a crucial member of the MEF-2 family of proteins which will serve as an important tool in understanding the regulatory mechanism(s) underlying cardiogenic differentiation.
Full text
PDF

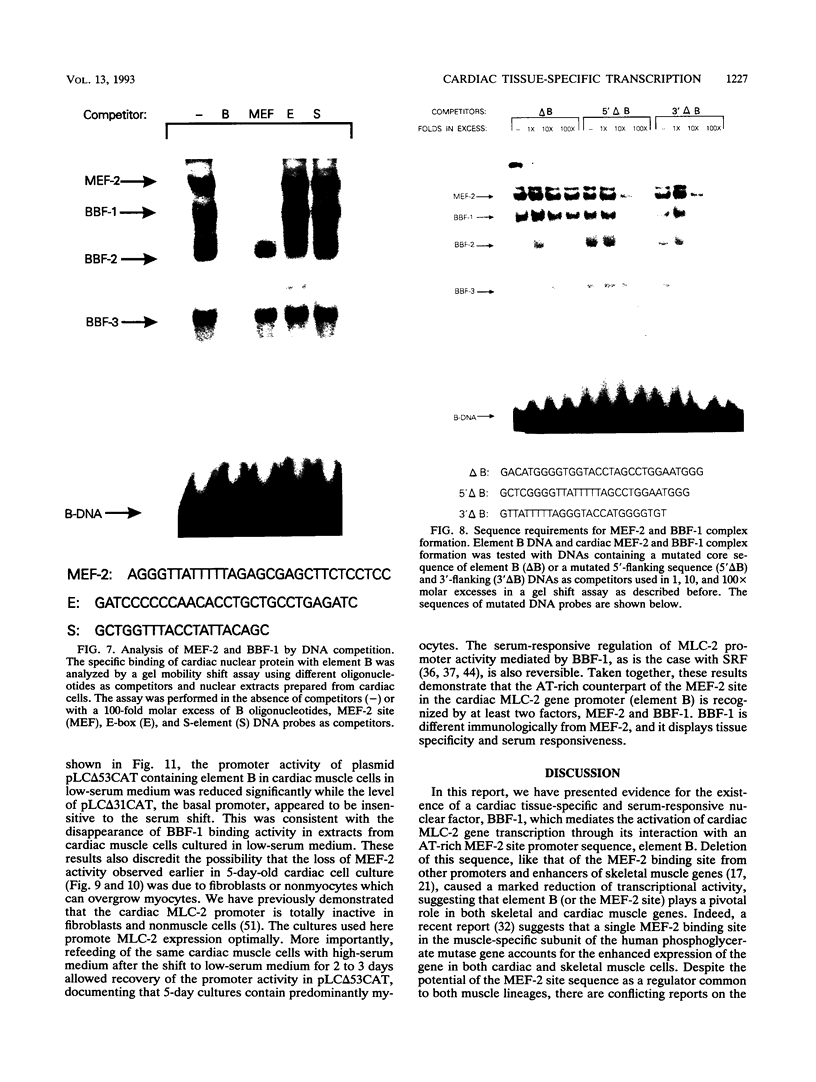
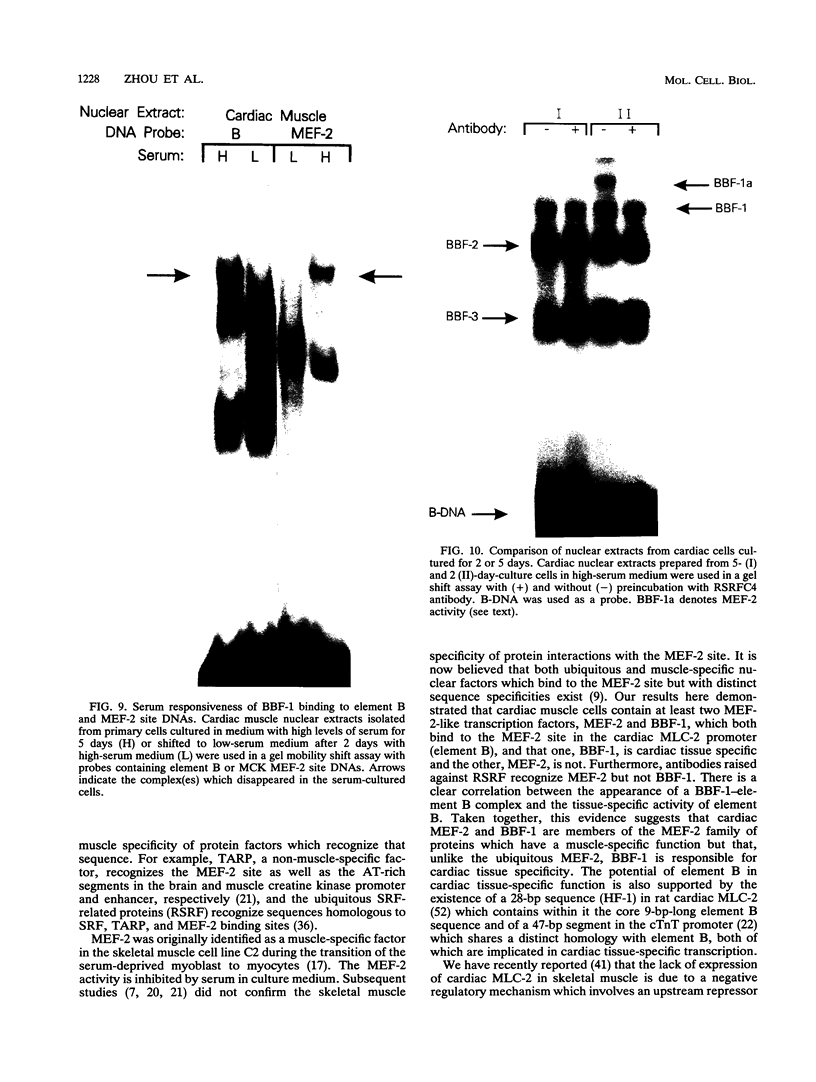
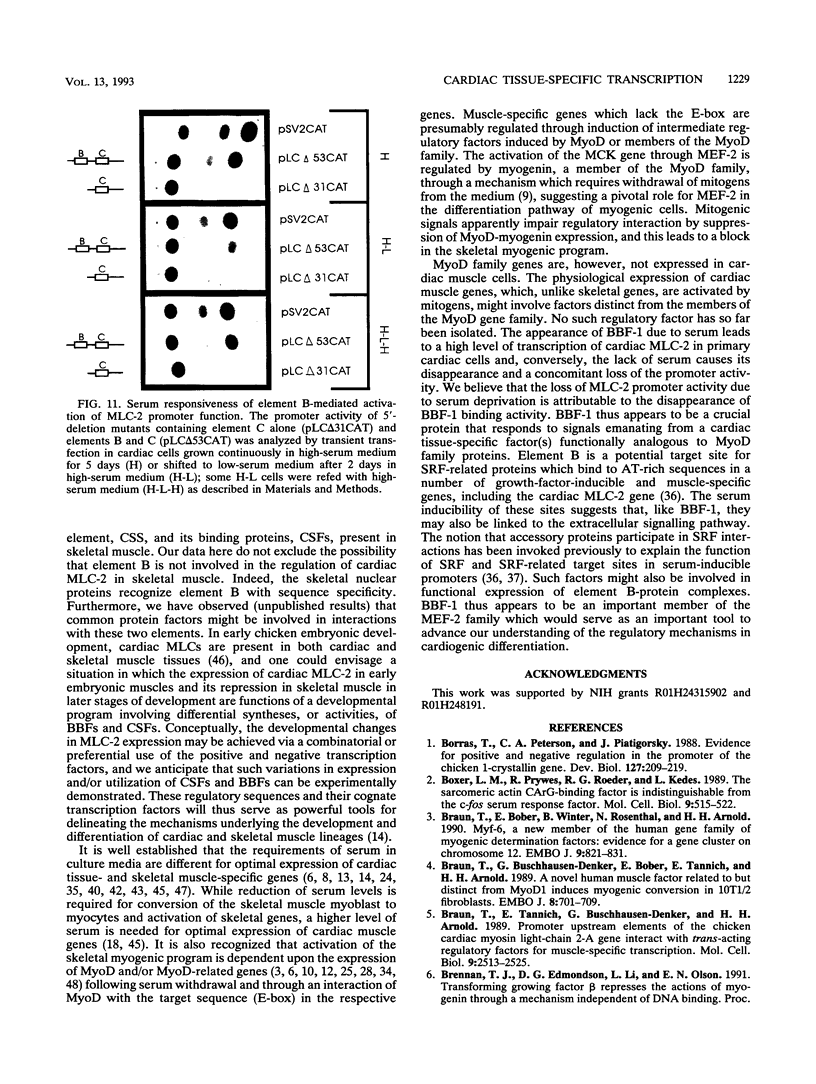


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borrás T., Peterson C. A., Piatigorsky J. Evidence for positive and negative regulation in the promoter of the chicken delta 1-crystallin gene. Dev Biol. 1988 May;127(1):209–219. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90202-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boxer L. M., Prywes R., Roeder R. G., Kedes L. The sarcomeric actin CArG-binding factor is indistinguishable from the c-fos serum response factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):515–522. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Bober E., Winter B., Rosenthal N., Arnold H. H. Myf-6, a new member of the human gene family of myogenic determination factors: evidence for a gene cluster on chromosome 12. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):821–831. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08179.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Buschhausen-Denker G., Bober E., Tannich E., Arnold H. H. A novel human muscle factor related to but distinct from MyoD1 induces myogenic conversion in 10T1/2 fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):701–709. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03429.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Tannich E., Buschhausen-Denker G., Arnold H. H. Promoter upstream elements of the chicken cardiac myosin light-chain 2-A gene interact with trans-acting regulatory factors for muscle-specific transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2513–2525. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buskin J. N., Hauschka S. D. Identification of a myocyte nuclear factor that binds to the muscle-specific enhancer of the mouse muscle creatine kinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2627–2640. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg C. H., Linkhart T. A., Olwin B. B., Hauschka S. D. Growth factor control of skeletal muscle differentiation: commitment to terminal differentiation occurs in G1 phase and is repressed by fibroblast growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;105(2):949–956. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.2.949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cserjesi P., Olson E. N. Myogenin induces the myocyte-specific enhancer binding factor MEF-2 independently of other muscle-specific gene products. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4854–4862. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Weintraub H., Lassar A. B. Expression of a single transfected cDNA converts fibroblasts to myoblasts. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):987–1000. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90585-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmondson D. G., Olson E. N. A gene with homology to the myc similarity region of MyoD1 is expressed during myogenesis and is sufficient to activate the muscle differentiation program. Genes Dev. 1989 May;3(5):628–640. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.5.628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eghbali M., Tomek R., Woods C., Bhambi B. Cardiac fibroblasts are predisposed to convert into myocyte phenotype: specific effect of transforming growth factor beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):795–799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flink I. L., Morkin E. Interaction of thyroid hormone receptors with strong and weak cis-acting elements in the human alpha-myosin heavy chain gene promoter. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):11233–11237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossett L. A., Kelvin D. J., Sternberg E. A., Olson E. N. A new myocyte-specific enhancer-binding factor that recognizes a conserved element associated with multiple muscle-specific genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5022–5033. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta M. P., Gupta M., Zak R., Sukhatme V. P. Egr-1, a serum-inducible zinc finger protein, regulates transcription of the rat cardiac alpha-myosin heavy chain gene. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):12813–12816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson T. A., Kedes L. Identification of multiple proteins that interact with functional regions of the human cardiac alpha-actin promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3269–3283. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horlick R. A., Benfield P. A. The upstream muscle-specific enhancer of the rat muscle creatine kinase gene is composed of multiple elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2396–2413. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horlick R. A., Hobson G. M., Patterson J. H., Mitchell M. T., Benfield P. A. Brain and muscle creatine kinase genes contain common TA-rich recognition protein-binding regulatory elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4826–4836. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iannello R. C., Mar J. H., Ordahl C. P. Characterization of a promoter element required for transcription in myocardial cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):3309–3316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izumo S., Mahdavi V. Thyroid hormone receptor alpha isoforms generated by alternative splicing differentially activate myosin HC gene transcription. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):539–542. doi: 10.1038/334539a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelvin D. J., Simard G., Tai H. H., Yamaguchi T. P., Connolly J. A. Growth factors, signaling pathways, and the regulation of proliferation and differentiation in BC3H1 muscle cells. I. A pertussis toxin-sensitive pathway is involved. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;108(1):159–167. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.1.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Buskin J. N., Lockshon D., Davis R. L., Apone S., Hauschka S. D., Weintraub H. MyoD is a sequence-specific DNA binding protein requiring a region of myc homology to bind to the muscle creatine kinase enhancer. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):823–831. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90935-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
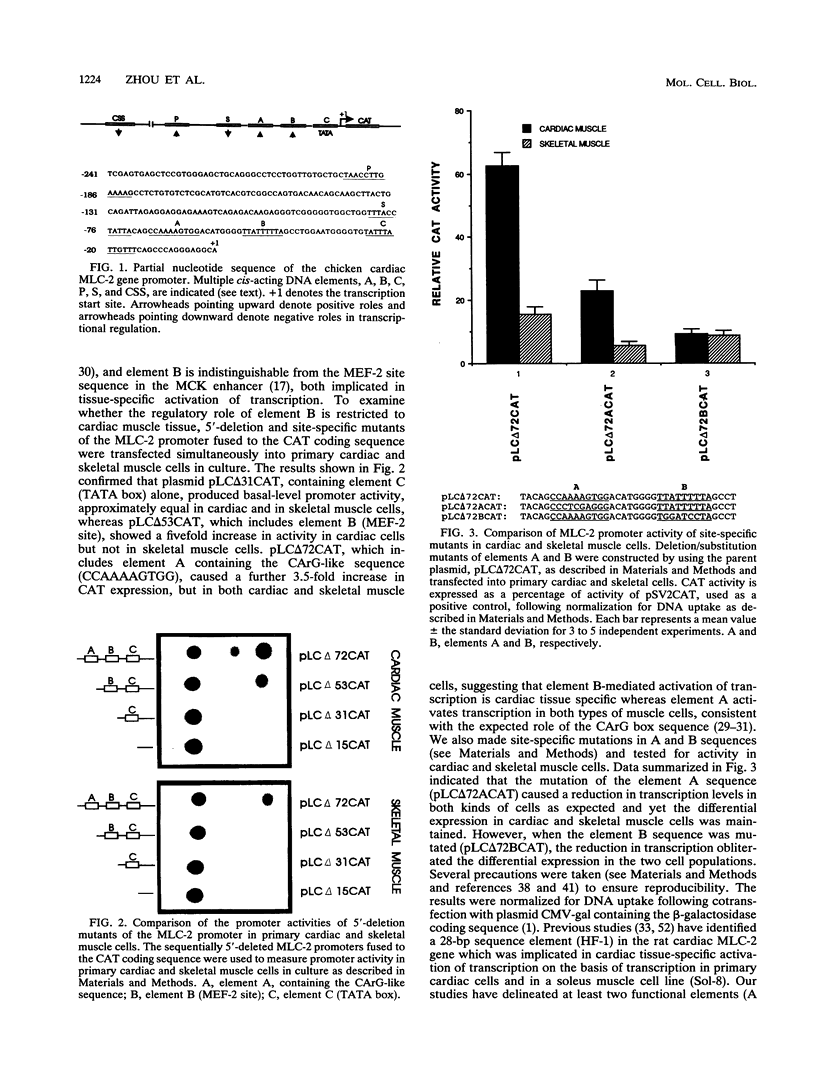
- Lee T. C., Chow K. L., Fang P., Schwartz R. J. Activation of skeletal alpha-actin gene transcription: the cooperative formation of serum response factor-binding complexes over positive cis-acting promoter serum response elements displaces a negative-acting nuclear factor enriched in replicating myoblasts and nonmyogenic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5090–5100. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lompré A. M., Nadal-Ginard B., Mahdavi V. Expression of the cardiac ventricular alpha- and beta-myosin heavy chain genes is developmentally and hormonally regulated. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6437–6446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miner J. H., Wold B. Herculin, a fourth member of the MyoD family of myogenic regulatory genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1089–1093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A., Kedes L. Upstream regions of the human cardiac actin gene that modulate its transcription in muscle cells: presence of an evolutionarily conserved repeated motif. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2125–2136. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miwa T., Kedes L. Duplicated CArG box domains have positive and mutually dependent regulatory roles in expression of the human alpha-cardiac actin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2803–2813. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muscat G. E., Gustafson T. A., Kedes L. A common factor regulates skeletal and cardiac alpha-actin gene transcription in muscle. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4120–4133. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakatsuji Y., Hidaka K., Tsujino S., Yamamoto Y., Mukai T., Yanagihara T., Kishimoto T., Sakoda S. A single MEF-2 site is a major positive regulatory element required for transcription of the muscle-specific subunit of the human phosphoglycerate mutase gene in skeletal and cardiac muscle cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4384–4390. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navankasattusas S., Zhu H., Garcia A. V., Evans S. M., Chien K. R. A ubiquitous factor (HF-1a) and a distinct muscle factor (HF-1b/MEF-2) form an E-box-independent pathway for cardiac muscle gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1469–1479. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N. MyoD family: a paradigm for development? Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1454–1461. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N., Sternberg E., Hu J. S., Spizz G., Wilcox C. Regulation of myogenic differentiation by type beta transforming growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;103(5):1799–1805. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.5.1799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock R., Treisman R. Human SRF-related proteins: DNA-binding properties and potential regulatory targets. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12A):2327–2341. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12a.2327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prywes R., Dutta A., Cromlish J. A., Roeder R. G. Phosphorylation of serum response factor, a factor that binds to the serum response element of the c-FOS enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7206–7210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qasba P., Lin E., Zhou M. D., Kumar A., Siddiqui M. A. A single transcription factor binds to two divergent sequence elements with a common function in cardiac myosin light chain-2 promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1107–1116. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal N. Muscle cell differentiation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;1(6):1094–1101. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(89)80056-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen R. A., Goswami S. K., Mascareno E., Kumar A., Siddiqui M. A. Tissue-specific transcription of the cardiac myosin light-chain 2 gene is regulated by an upstream repressor element. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1676–1685. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spizz G., Hu J. S., Olson E. N. Inhibition of myogenic differentiation by fibroblast growth factor or type beta transforming growth factor does not require persistent c-myc expression. Dev Biol. 1987 Oct;123(2):500–507. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90408-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spizz G., Roman D., Strauss A., Olson E. N. Serum and fibroblast growth factor inhibit myogenic differentiation through a mechanism dependent on protein synthesis and independent of cell proliferation. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9483–9488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Identification of a protein-binding site that mediates transcriptional response of the c-fos gene to serum factors. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):567–574. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90882-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueno H., Perryman M. B., Roberts R., Schneider M. D. Differentiation of cardiac myocytes after mitogen withdrawal exhibits three sequential states of the ventricular growth response. J Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;107(5):1911–1918. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.5.1911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uetsuki T., Nabeshima Y., Fujisawa-Sehara A., Nabeshima Y. Regulation of the chicken embryonic myosin light-chain (L23) gene: existence of a common regulatory element shared by myosin alkali light-chain genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2562–2569. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waspe L. E., Ordahl C. P., Simpson P. C. The cardiac beta-myosin heavy chain isogene is induced selectively in alpha 1-adrenergic receptor-stimulated hypertrophy of cultured rat heart myocytes. J Clin Invest. 1990 Apr;85(4):1206–1214. doi: 10.1172/JCI114554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright W. E., Sassoon D. A., Lin V. K. Myogenin, a factor regulating myogenesis, has a domain homologous to MyoD. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):607–617. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90583-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu Y. T., Breitbart R. E., Smoot L. B., Lee Y., Mahdavi V., Nadal-Ginard B. Human myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2 comprises a group of tissue-restricted MADS box transcription factors. Genes Dev. 1992 Sep;6(9):1783–1798. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.9.1783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarraga A. M., Danishefsky K., Deshpande A., Nicholson D., Mendola C., Siddiqui M. A. Characterization of 5'-flanking region of heart myosin light chain 2A gene. Structural and functional evidence for promoter activity. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 15;261(29):13852–13860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou M. D., Wu Y., Kumar A., Siddiqui M. A. Mechanism of tissue-specific transcription: interplay between positive and negative regulatory factors. Gene Expr. 1992;2(2):127–138. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu H., Garcia A. V., Ross R. S., Evans S. M., Chien K. R. A conserved 28-base-pair element (HF-1) in the rat cardiac myosin light-chain-2 gene confers cardiac-specific and alpha-adrenergic-inducible expression in cultured neonatal rat myocardial cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2273–2281. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]