Abstract
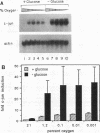
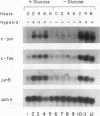
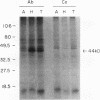
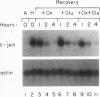
Hypoxic stress in tumor cells has been implicated in malignant progression and in the development of therapeutic resistance. We have investigated the effects of acute hypoxic exposure on regulation of the proto-oncogene c-jun in SiHa cells, a human squamous carcinoma cell line. Hypoxic exposure produced increased levels of c-jun mRNA resulting from both message stabilization and transcriptional activation. A superinduction of c-jun message resulted during simultaneous oxygen and glucose deprivation, with several characteristics of an induction mediated by oxidative-stress pathways. This superinduction was blocked by preincubation of cells with the glutathione precursor N-acetyl cysteine or with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate, which indicates redox control of c-jun expression and probable involvement of protein kinase C. By gel retardation assay, no increase in AP-1 DNA binding activity was found to be concomitant with the transcriptional activation of c-jun. A lack of increased DNA binding was observed for the consensus AP-1 sequence and for the two AP-1 sequence variants found within the c-Jun promoter. Additionally, hypoxic and low-glucose stress produced no activation of stably transfected AP-1 reporter sequences. Taken together, these results indicate that the transcriptional activation of c-jun during hypoxic and low-glucose stress involves redox control and is unlikely to be mediated by AP-1 recognition elements within the c-jun promoter.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abate C., Luk D., Curran T. A ubiquitous nuclear protein stimulates the DNA-binding activity of fos and jun indirectly. Cell Growth Differ. 1990 Oct;1(10):455–462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abate C., Patel L., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Curran T. Redox regulation of fos and jun DNA-binding activity in vitro. Science. 1990 Sep 7;249(4973):1157–1161. doi: 10.1126/science.2118682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alam J., Den Z. Distal AP-1 binding sites mediate basal level enhancement and TPA induction of the mouse heme oxygenase-1 gene. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 25;267(30):21894–21900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson G. R., Stoler D. L., Scarcello L. A. Normal fibroblasts responding to anoxia exhibit features of the malignant phenotype. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14885–14892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson G. R., Stoler D. L., Scarcello L. A. Retrotransposon-like VL30 elements are efficiently induced in anoxic rat fibroblasts. J Mol Biol. 1989 Feb 20;205(4):765–769. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90320-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews N. C., Faller D. V. A rapid micropreparation technique for extraction of DNA-binding proteins from limiting numbers of mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 11;19(9):2499–2499. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.9.2499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Hattori K., Smeal T., Karin M. The jun proto-oncogene is positively autoregulated by its product, Jun/AP-1. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):875–885. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90143-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker S. J., Kerppola T. K., Luk D., Vandenberg M. T., Marshak D. R., Curran T., Abate C. Jun is phosphorylated by several protein kinases at the same sites that are modified in serum-stimulated fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4694–4705. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barber J. R., Verma I. M. Modification of fos proteins: phosphorylation of c-fos, but not v-fos, is stimulated by 12-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate and serum. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2201–2211. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binétruy B., Smeal T., Karin M. Ha-Ras augments c-Jun activity and stimulates phosphorylation of its activation domain. Nature. 1991 May 9;351(6322):122–127. doi: 10.1038/351122a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohmann D., Bos T. J., Admon A., Nishimura T., Vogt P. K., Tjian R. Human proto-oncogene c-jun encodes a DNA binding protein with structural and functional properties of transcription factor AP-1. Science. 1987 Dec 4;238(4832):1386–1392. doi: 10.1126/science.2825349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossy-Wetzel E., Bravo R., Hanahan D. Transcription factors junB and c-jun are selectively up-regulated and functionally implicated in fibrosarcoma development. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12A):2340–2351. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12a.2340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., Smeal T., Defize L. H., Angel P., Woodgett J. R., Karin M., Hunter T. Activation of protein kinase C decreases phosphorylation of c-Jun at sites that negatively regulate its DNA-binding activity. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):573–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90241-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. A., O'Hara M., Angel P., Chojkier M., Karin M. Prolonged activation of jun and collagenase genes by tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Nature. 1989 Feb 16;337(6208):661–663. doi: 10.1038/337661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devary Y., Gottlieb R. A., Lau L. F., Karin M. Rapid and preferential activation of the c-jun gene during the mammalian UV response. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2804–2811. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devary Y., Gottlieb R. A., Smeal T., Karin M. The mammalian ultraviolet response is triggered by activation of Src tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1992 Dec 24;71(7):1081–1091. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80058-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards D. R., Mahadevan L. C. Protein synthesis inhibitors differentially superinduce c-fos and c-jun by three distinct mechanisms: lack of evidence for labile repressors. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2415–2424. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05306.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin C. C., Sanchez V., Wagner F., Woodgett J. R., Kraft A. S. Phorbol ester-induced amino-terminal phosphorylation of human JUN but not JUNB regulates transcriptional activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):7247–7251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.7247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentz R., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Abate C., Curran T. Parallel association of Fos and Jun leucine zippers juxtaposes DNA binding domains. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1695–1699. doi: 10.1126/science.2494702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giaccia A. J., Auger E. A., Koong A., Terris D. J., Minchinton A. I., Hahn G. M., Brown J. M. Activation of the heat shock transcription factor by hypoxia in normal and tumor cell lines in vivo and in vitro. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1992;23(4):891–897. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(92)90667-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai T., Curran T. Cross-family dimerization of transcription factors Fos/Jun and ATF/CREB alters DNA binding specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3720–3724. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heacock C. S., Sutherland R. M. Enhanced synthesis of stress proteins caused by hypoxia and relation to altered cell growth and metabolism. Br J Cancer. 1990 Aug;62(2):217–225. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1990.264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heacock C. S., Sutherland R. M. Induction characteristics of oxygen regulated proteins. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1986 Aug;12(8):1287–1290. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(86)90155-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa U., Kishimoto A., Nishizuka Y. The protein kinase C family: heterogeneity and its implications. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:31–44. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.000335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laderoute K. R., Grant T. D., Murphy B. J., Sutherland R. M. Enhanced epidermal growth factor receptor synthesis in human squamous carcinoma cells exposed to low levels of oxygen. Int J Cancer. 1992 Sep 30;52(3):428–432. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910520317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamph W. W., Wamsley P., Sassone-Corsi P., Verma I. M. Induction of proto-oncogene JUN/AP-1 by serum and TPA. Nature. 1988 Aug 18;334(6183):629–631. doi: 10.1038/334629a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. M., Lin C., Curran T. Activation of the transforming potential of the human fos proto-oncogene requires message stabilization and results in increased amounts of partially modified fos protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5521–5527. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin A., Frost J., Deng T., Smeal T., al-Alawi N., Kikkawa U., Hunter T., Brenner D., Karin M. Casein kinase II is a negative regulator of c-Jun DNA binding and AP-1 activity. Cell. 1992 Sep 4;70(5):777–789. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90311-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowry C. V., Lieber R. H. Negative regulation of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae ANB1 gene by heme, as mediated by the ROX1 gene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4145–4148. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maines M. D. Heme oxygenase: function, multiplicity, regulatory mechanisms, and clinical applications. FASEB J. 1988 Jul;2(10):2557–2568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maki Y., Bos T. J., Davis C., Starbuck M., Vogt P. K. Avian sarcoma virus 17 carries the jun oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2848–2852. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehta K. D., Leung D., Lefebvre L., Smith M. The ANB1 locus of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes the protein synthesis initiation factor eIF-4D. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8802–8807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister A. Glutathione deficiency produced by inhibition of its synthesis, and its reversal; applications in research and therapy. Pharmacol Ther. 1991;51(2):155–194. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(91)90076-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer M., Schreck R., Baeuerle P. A. H2O2 and antioxidants have opposite effects on activation of NF-kappa B and AP-1 in intact cells: AP-1 as secondary antioxidant-responsive factor. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):2005–2015. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05850.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy B. J., Laderoute K. R., Short S. M., Sutherland R. M. The identification of heme oxygenase as a major hypoxic stress protein in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Br J Cancer. 1991 Jul;64(1):69–73. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1991.241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Conner J. L., Wade M. F. Determination of coexisting nuclear transcription rates and cytoplasmic mRNA levels for gonadotropin subunit genes in rat anterior pituitary. Biotechniques. 1992 Feb;12(2):238–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plate K. H., Breier G., Weich H. A., Risau W. Vascular endothelial growth factor is a potential tumour angiogenesis factor in human gliomas in vivo. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):845–848. doi: 10.1038/359845a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price B. D., Calderwood S. K. Gadd45 and Gadd153 messenger RNA levels are increased during hypoxia and after exposure of cells to agents which elevate the levels of the glucose-regulated proteins. Cancer Res. 1992 Jul 1;52(13):3814–3817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulverer B. J., Kyriakis J. M., Avruch J., Nikolakaki E., Woodgett J. R. Phosphorylation of c-jun mediated by MAP kinases. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):670–674. doi: 10.1038/353670a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quantin B., Breathnach R. Epidermal growth factor stimulates transcription of the c-jun proto-oncogene in rat fibroblasts. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):538–539. doi: 10.1038/334538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice G. C., Hoy C., Schimke R. T. Transient hypoxia enhances the frequency of dihydrofolate reductase gene amplification in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5978–5982. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice G. C., Ling V., Schimke R. T. Frequencies of independent and simultaneous selection of Chinese hamster cells for methotrexate and doxorubicin (adriamycin) resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9261–9264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roll D. E., Murphy B. J., Laderoute K. R., Sutherland R. M., Smith H. C. Oxygen regulated 80 kDa protein and glucose regulated 78kDa protein are identical. Mol Cell Biochem. 1991 May 15;103(2):141–148. doi: 10.1007/BF00227480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakata K., Kwok T. T., Murphy B. J., Laderoute K. R., Gordon G. R., Sutherland R. M. Hypoxia-induced drug resistance: comparison to P-glycoprotein-associated drug resistance. Br J Cancer. 1991 Nov;64(5):809–814. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1991.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönthal A., Srinivas S., Eckhart W. Induction of c-jun protooncogene expression and transcription factor AP-1 activity by the polyoma virus middle-sized tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):4972–4976. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.4972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schütte J., Minna J. D., Birrer M. J. Deregulated expression of human c-jun transforms primary rat embryo cells in cooperation with an activated c-Ha-ras gene and transforms rat-1a cells as a single gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2257–2261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sciandra J. J., Subjeck J. R., Hughes C. S. Induction of glucose-regulated proteins during anaerobic exposure and of heat-shock proteins after reoxygenation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4843–4847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto E., Mitchell P. J., Yen T. S. Transactivation by the hepatitis B virus X protein depends on AP-2 and other transcription factors. Nature. 1990 Mar 1;344(6261):72–74. doi: 10.1038/344072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shweiki D., Itin A., Soffer D., Keshet E. Vascular endothelial growth factor induced by hypoxia may mediate hypoxia-initiated angiogenesis. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):843–845. doi: 10.1038/359843a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeal T., Binetruy B., Mercola D., Grover-Bardwick A., Heidecker G., Rapp U. R., Karin M. Oncoprotein-mediated signalling cascade stimulates c-Jun activity by phosphorylation of serines 63 and 73. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;12(8):3507–3513. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.8.3507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein B., Angel P., van Dam H., Ponta H., Herrlich P., van der Eb A., Rahmsdorf H. J. Ultraviolet-radiation induced c-jun gene transcription: two AP-1 like binding sites mediate the response. Photochem Photobiol. 1992 Mar;55(3):409–415. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1992.tb04255.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoler D. L., Anderson G. R., Russo C. A., Spina A. M., Beerman T. A. Anoxia-inducible endonuclease activity as a potential basis of the genomic instability of cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1992 Aug 15;52(16):4372–4378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R., Tjian R. Leucine repeats and an adjacent DNA binding domain mediate the formation of functional cFos-cJun heterodimers. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1689–1694. doi: 10.1126/science.2494701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt P. K., Bos T. J. jun: oncogene and transcription factor. Adv Cancer Res. 1990;55:1–35. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60466-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xanthoudakis S., Curran T. Identification and characterization of Ref-1, a nuclear protein that facilitates AP-1 DNA-binding activity. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):653–665. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05097.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xanthoudakis S., Miao G., Wang F., Pan Y. C., Curran T. Redox activation of Fos-Jun DNA binding activity is mediated by a DNA repair enzyme. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3323–3335. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05411.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida T., Biro P., Cohen T., Müller R. M., Shibahara S. Human heme oxygenase cDNA and induction of its mRNA by hemin. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Feb 1;171(3):457–461. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13811.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. D., Marshall R. S., Hill R. P. Hypoxia induces DNA overreplication and enhances metastatic potential of murine tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9533–9537. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dam H., Duyndam M., Rottier R., Bosch A., de Vries-Smits L., Herrlich P., Zantema A., Angel P., van der Eb A. J. Heterodimer formation of cJun and ATF-2 is responsible for induction of c-jun by the 243 amino acid adenovirus E1A protein. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):479–487. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05680.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]