Abstract
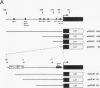
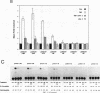
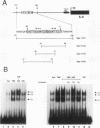
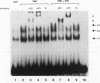
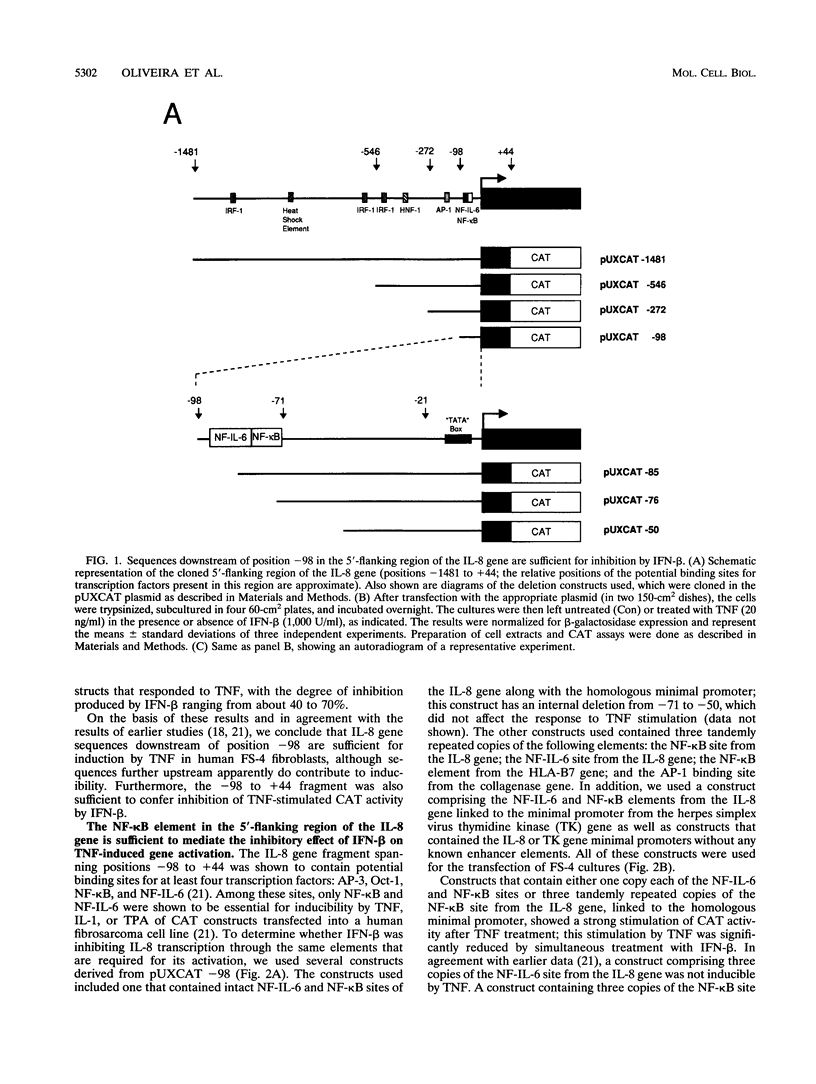
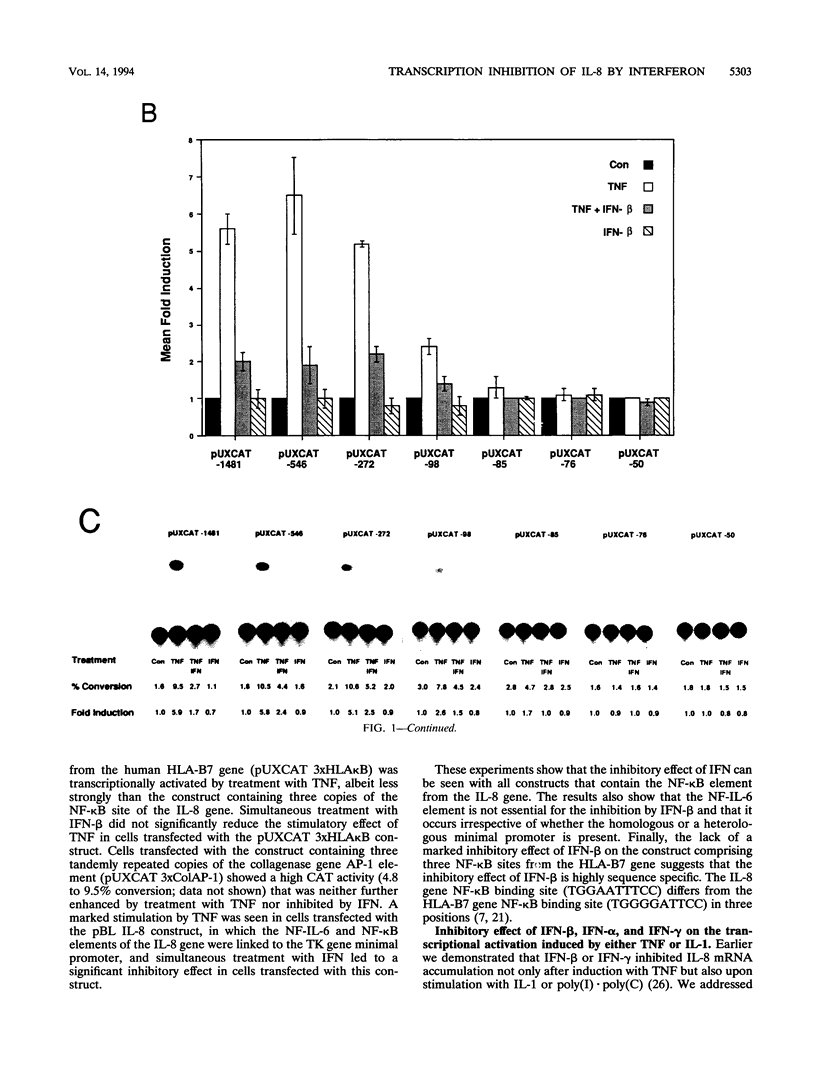
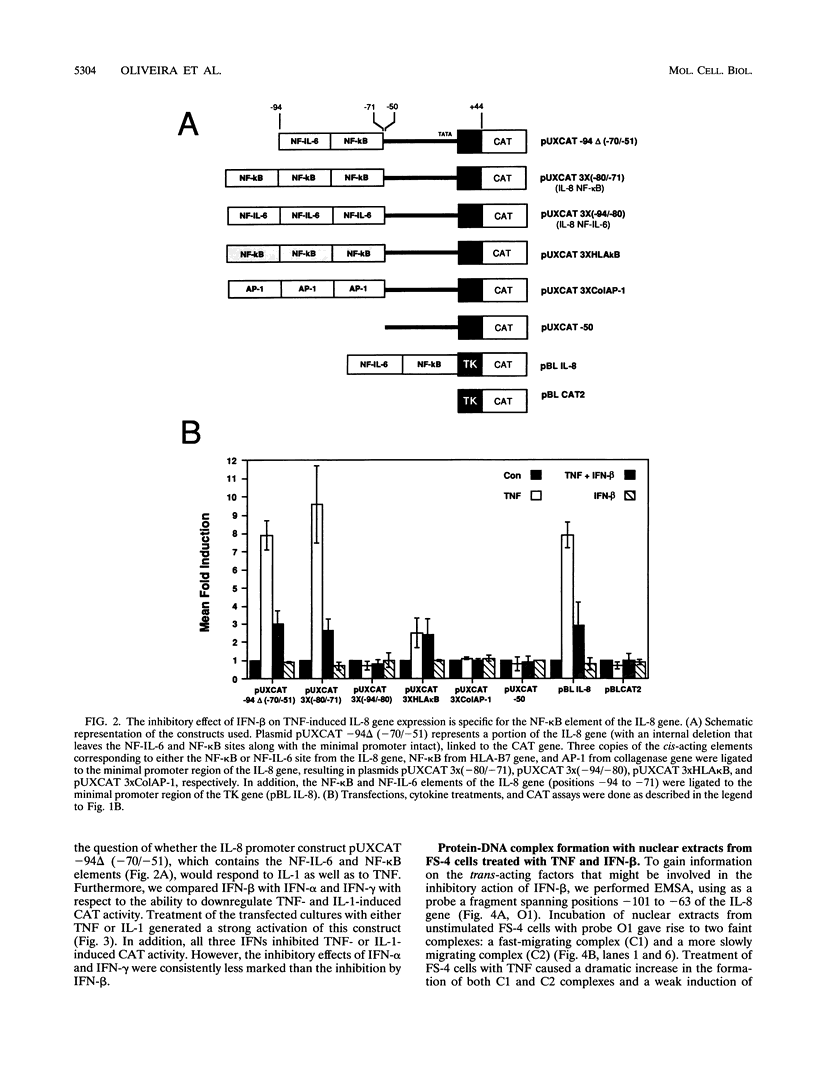
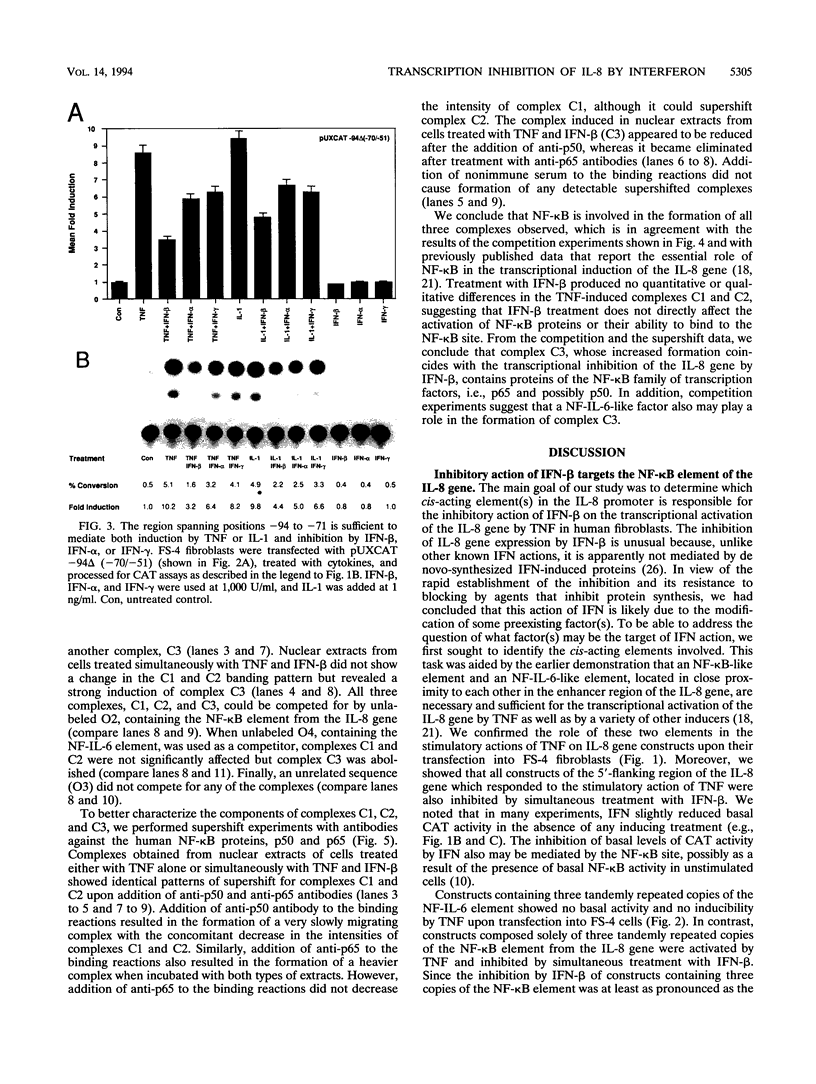
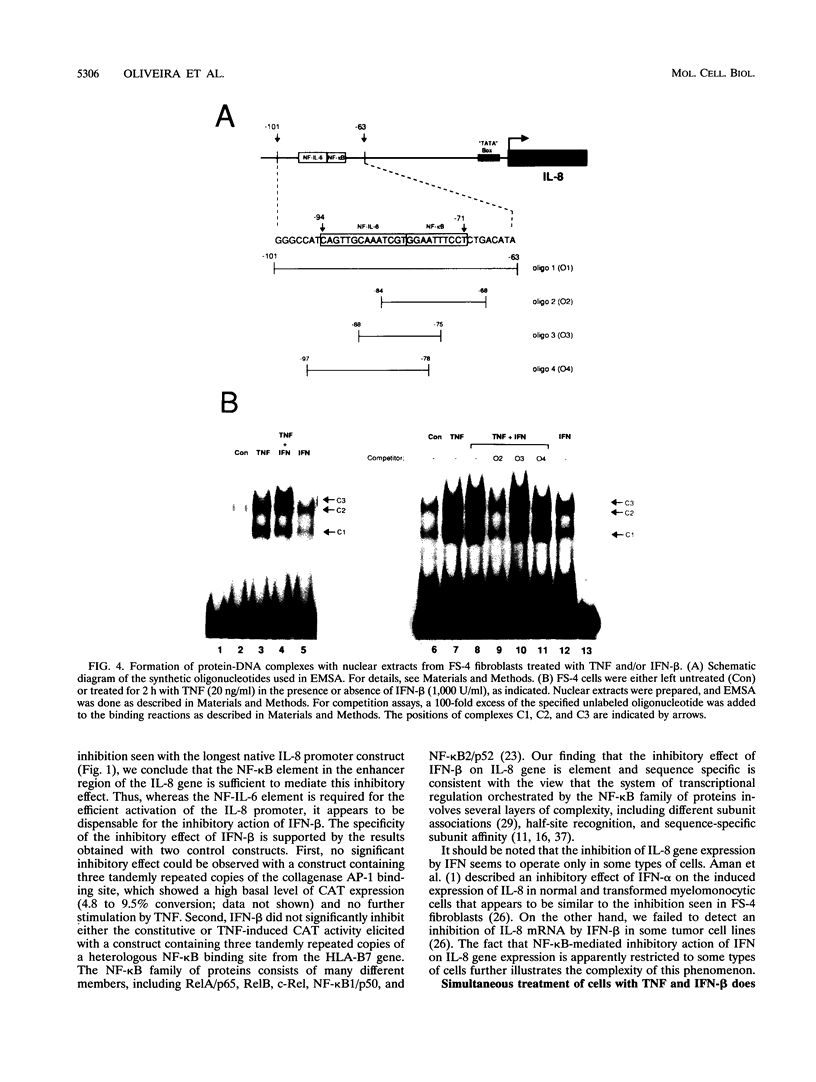
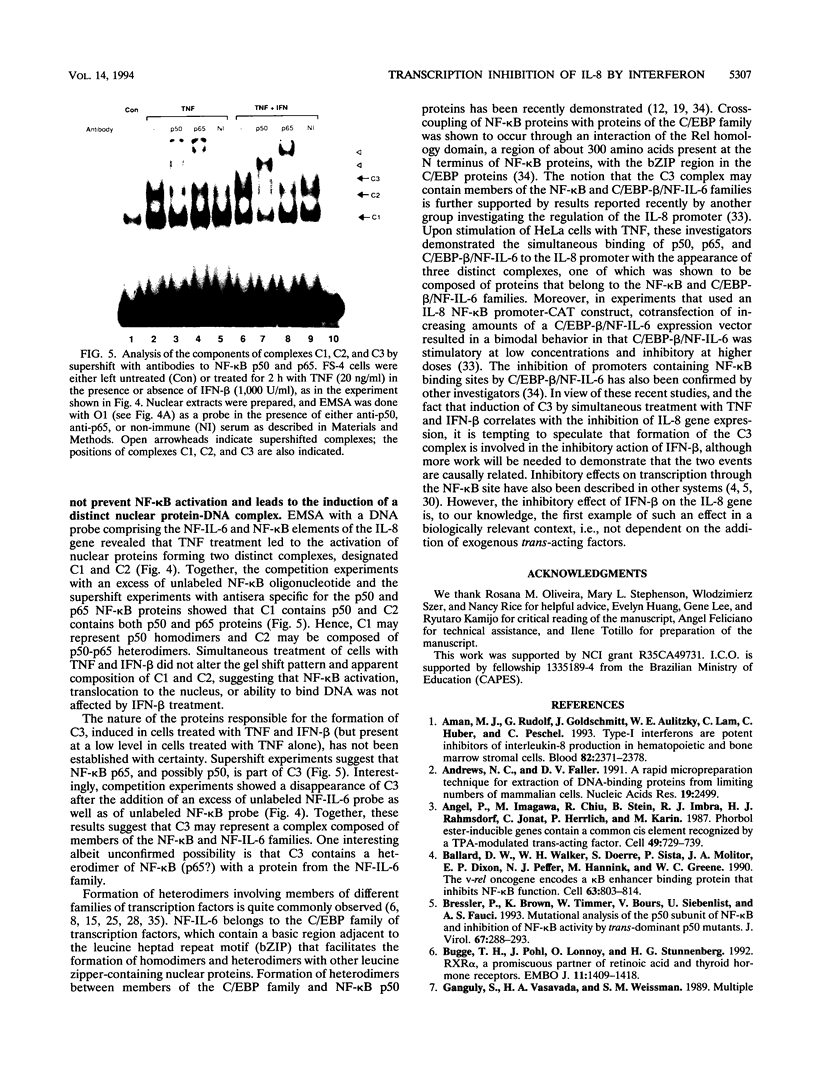
The cytokine interleukin-8 (IL-8) is an important mediator of neutrophil, lymphocyte, and basophil chemotaxis and activation. Earlier we demonstrated that beta interferon (IFN-beta) can inhibit tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-induced IL-8 gene expression at the transcriptional level, apparently by a novel mechanism. To define the cis-acting elements and trans-acting factors involved in this inhibition, DNA constructs containing portions of the 5'-flanking region of the IL-8 gene were linked to the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) reporter gene and transfected into human diploid FS-4 fibroblasts. The region spanning positions -98 to +44 was sufficient to confer both inducibility by TNF and inhibition by simultaneous treatment with IFN-beta. Inhibition of TNF- or IL-1-induced CAT activity by IFN-beta or IFN-alpha was also observed when a DNA fragment containing only the NF-IL-6 and NF-kappa B sites (positions -94 to -70) was placed upstream of the homologous or a heterologous minimal promoter. A construct containing three copies of the NF-kappa B element in front of the CAT gene also was inducible by TNF, and this stimulatory effect too was inhibited by IFN-beta, indicating that the NF-kappa B element is sufficient to confer inhibition by IFN-beta. This inhibitory effect was specific for the NF-kappa B site of the IL-8 gene since it was less marked with constructs containing three copies of the NF-kappa B site from the HLA-B7 gene. Gel shift assays with a probe containing the NF-kappa B and NF-IL-6 binding sites of the IL-8 gene (positions -101 to -63) showed that IFN-beta treatment did not block the activation of NF-kappa B proteins or their ability to bind to the NF-kappa B site. However, nuclear extracts from cells treated with TNF in the presence of IFN-beta gave rise to an additional band that appears to contain protein components from the NF-kappa B and NF-IL-6 families. NF-kappa B site-mediated suppression of IL-8 gene expression by IFN-beta represents a hitherto unknown mechanism and target of IFN action.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aman M. J., Rudolf G., Goldschmitt J., Aulitzky W. E., Lam C., Huber C., Peschel C. Type-I interferons are potent inhibitors of interleukin-8 production in hematopoietic and bone marrow stromal cells. Blood. 1993 Oct 15;82(8):2371–2378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews N. C., Faller D. V. A rapid micropreparation technique for extraction of DNA-binding proteins from limiting numbers of mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 11;19(9):2499–2499. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.9.2499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard D. W., Walker W. H., Doerre S., Sista P., Molitor J. A., Dixon E. P., Peffer N. J., Hannink M., Greene W. C. The v-rel oncogene encodes a kappa B enhancer binding protein that inhibits NF-kappa B function. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):803–814. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90146-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bressler P., Brown K., Timmer W., Bours V., Siebenlist U., Fauci A. S. Mutational analysis of the p50 subunit of NF-kappa B and inhibition of NF-kappa B activity by trans-dominant p50 mutants. J Virol. 1993 Jan;67(1):288–293. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.1.288-293.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bugge T. H., Pohl J., Lonnoy O., Stunnenberg H. G. RXR alpha, a promiscuous partner of retinoic acid and thyroid hormone receptors. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1409–1418. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05186.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonat C., Rahmsdorf H. J., Park K. K., Cato A. C., Gebel S., Ponta H., Herrlich P. Antitumor promotion and antiinflammation: down-modulation of AP-1 (Fos/Jun) activity by glucocorticoid hormone. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1189–1204. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90395-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A. E., Polverini P. J., Kunkel S. L., Harlow L. A., DiPietro L. A., Elner V. M., Elner S. G., Strieter R. M. Interleukin-8 as a macrophage-derived mediator of angiogenesis. Science. 1992 Dec 11;258(5089):1798–1801. doi: 10.1126/science.1281554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunsch C., Rosen C. A. NF-kappa B subunit-specific regulation of the interleukin-8 promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;13(10):6137–6146. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.10.6137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunsch C., Ruben S. M., Rosen C. A. Selection of optimal kappa B/Rel DNA-binding motifs: interaction of both subunits of NF-kappa B with DNA is required for transcriptional activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4412–4421. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeClair K. P., Blanar M. A., Sharp P. A. The p50 subunit of NF-kappa B associates with the NF-IL6 transcription factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):8145–8149. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. H., Lee G. W., Ziff E. B., Vilcek J. Isolation and characterization of eight tumor necrosis factor-induced gene sequences from human fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):1982–1988. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez G., Schaufele F., Webb P., Holloway J. M., Baxter J. D., Kushner P. J. Positive and negative modulation of Jun action by thyroid hormone receptor at a unique AP1 site. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 May;13(5):3042–3049. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.5.3042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenthal J. W., Ballard D. W., Böhnlein E., Greene W. C. Tumor necrosis factor alpha induces proteins that bind specifically to kappa B-like enhancer elements and regulate interleukin 2 receptor alpha-chain gene expression in primary human T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2331–2335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahé Y., Mukaida N., Kuno K., Akiyama M., Ikeda N., Matsushima K., Murakami S. Hepatitis B virus X protein transactivates human interleukin-8 gene through acting on nuclear factor kB and CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-like cis-elements. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 25;266(21):13759–13763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsusaka T., Fujikawa K., Nishio Y., Mukaida N., Matsushima K., Kishimoto T., Akira S. Transcription factors NF-IL6 and NF-kappa B synergistically activate transcription of the inflammatory cytokines, interleukin 6 and interleukin 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):10193–10197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.10193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukaida N., Gussella G. L., Kasahara T., Ko Y., Zachariae C. O., Kawai T., Matsushima K. Molecular analysis of the inhibition of interleukin-8 production by dexamethasone in a human fibrosarcoma cell line. Immunology. 1992 Apr;75(4):674–679. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukaida N., Mahe Y., Matsushima K. Cooperative interaction of nuclear factor-kappa B- and cis-regulatory enhancer binding protein-like factor binding elements in activating the interleukin-8 gene by pro-inflammatory cytokines. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):21128–21133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukaida N., Shiroo M., Matsushima K. Genomic structure of the human monocyte-derived neutrophil chemotactic factor IL-8. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 15;143(4):1366–1371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G. J., Verma I. M. Proposed NF-kappa B/I kappa B family nomenclature. Genes Dev. 1993 Nov;7(11):2063–2063. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.11.2063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickoloff B. J., Karabin G. D., Barker J. N., Griffiths C. E., Sarma V., Mitra R. S., Elder J. T., Kunkel S. L., Dixit V. M. Cellular localization of interleukin-8 and its inducer, tumor necrosis factor-alpha in psoriasis. Am J Pathol. 1991 Jan;138(1):129–140. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishio Y., Isshiki H., Kishimoto T., Akira S. A nuclear factor for interleukin-6 expression (NF-IL6) and the glucocorticoid receptor synergistically activate transcription of the rat alpha 1-acid glycoprotein gene via direct protein-protein interaction. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1854–1862. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira I. C., Sciavolino P. J., Lee T. H., Vilcek J. Downregulation of interleukin 8 gene expression in human fibroblasts: unique mechanism of transcriptional inhibition by interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9049–9053. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim J. J., Zachariae C. O., Mukaida N., Matsushima K. Properties of the novel proinflammatory supergene "intercrine" cytokine family. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:617–648. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.003153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulweber B., Sandhofer F., Levy-Wilson B. The mechanism by which the human apolipoprotein B gene reducer operates involves blocking of transcriptional activation by hepatocyte nuclear factor 3. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1534–1546. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins N. D., Schmid R. M., Duckett C. S., Leung K., Rice N. R., Nabel G. J. Distinct combinations of NF-kappa B subunits determine the specificity of transcriptional activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1529–1533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruben S. M., Klement J. F., Coleman T. A., Maher M., Chen C. H., Rosen C. A. I-Rel: a novel rel-related protein that inhibits NF-kappa B transcriptional activity. Genes Dev. 1992 May;6(5):745–760. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.5.745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein B., Baldwin A. S., Jr Distinct mechanisms for regulation of the interleukin-8 gene involve synergism and cooperativity between C/EBP and NF-kappa B. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;13(11):7191–7198. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.11.7191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein B., Cogswell P. C., Baldwin A. S., Jr Functional and physical associations between NF-kappa B and C/EBP family members: a Rel domain-bZIP interaction. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):3964–3974. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.3964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallejo M., Ron D., Miller C. P., Habener J. F. C/ATF, a member of the activating transcription factor family of DNA-binding proteins, dimerizes with CAAT/enhancer-binding proteins and directs their binding to cAMP response elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4679–4683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabel U., Schreck R., Baeuerle P. A. DNA binding of purified transcription factor NF-kappa B. Affinity, specificity, Zn2+ dependence, and differential half-site recognition. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):252–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]