Abstract
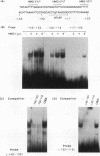
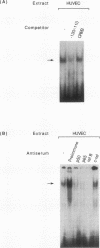
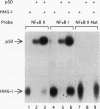
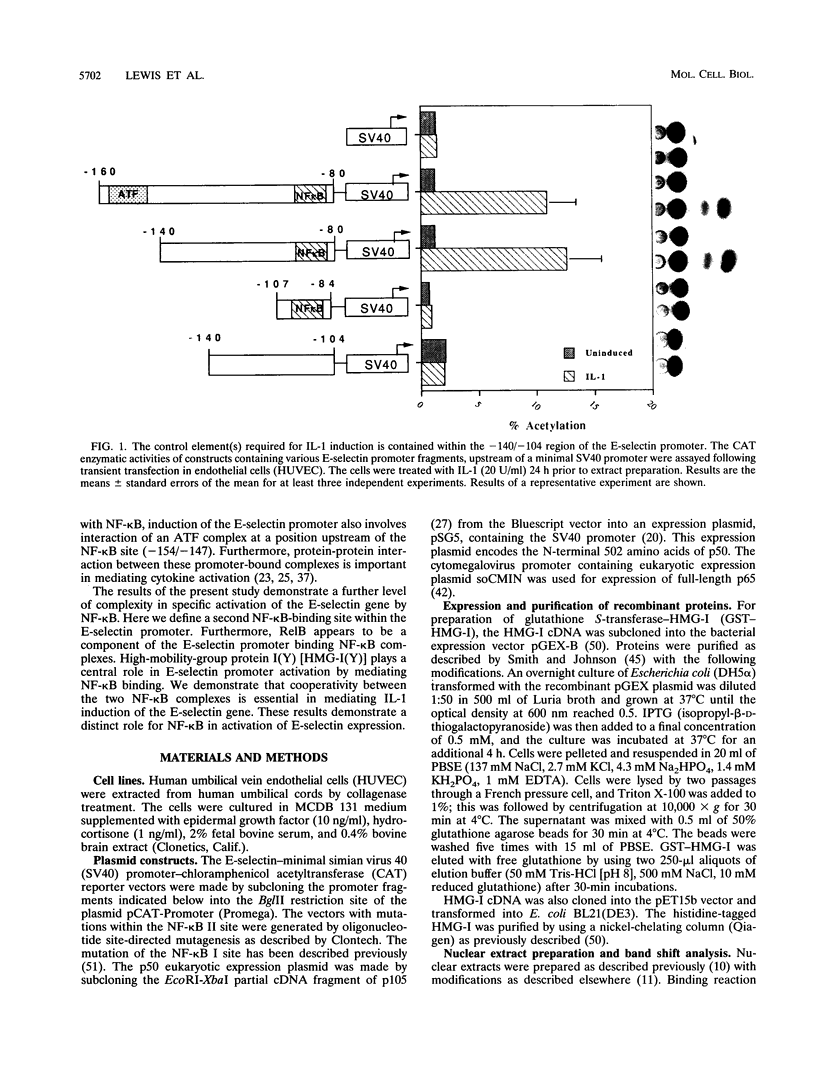
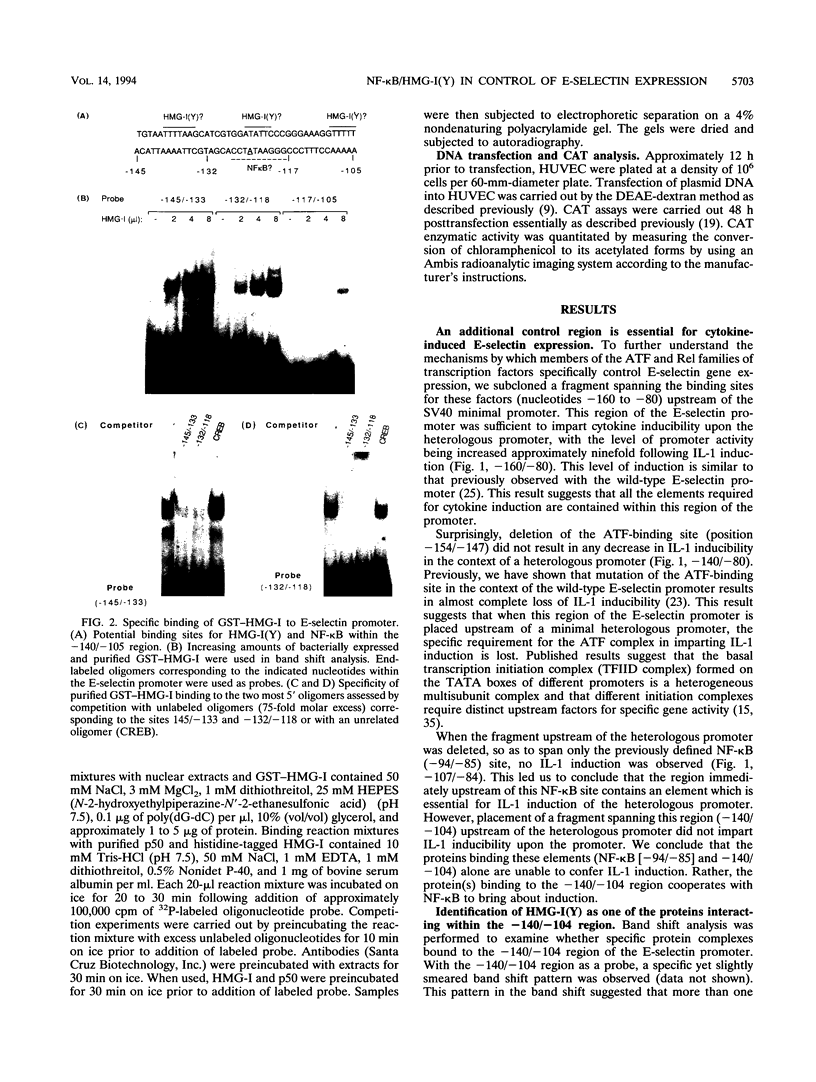
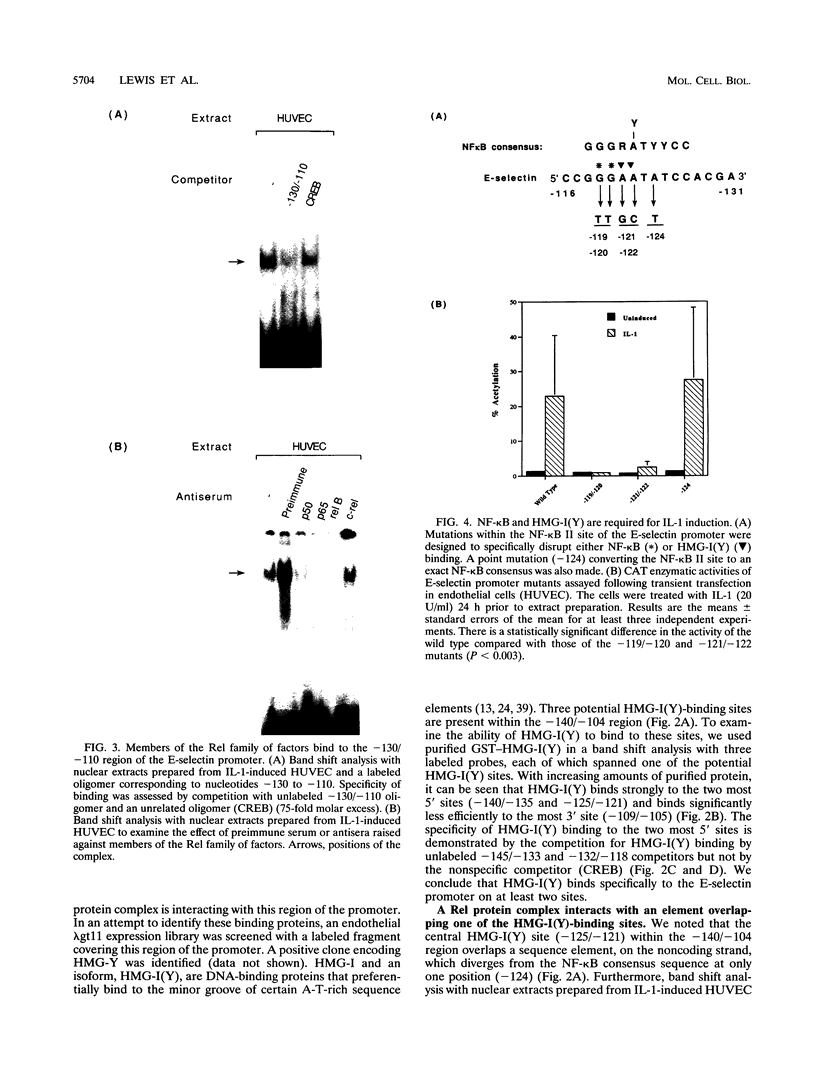
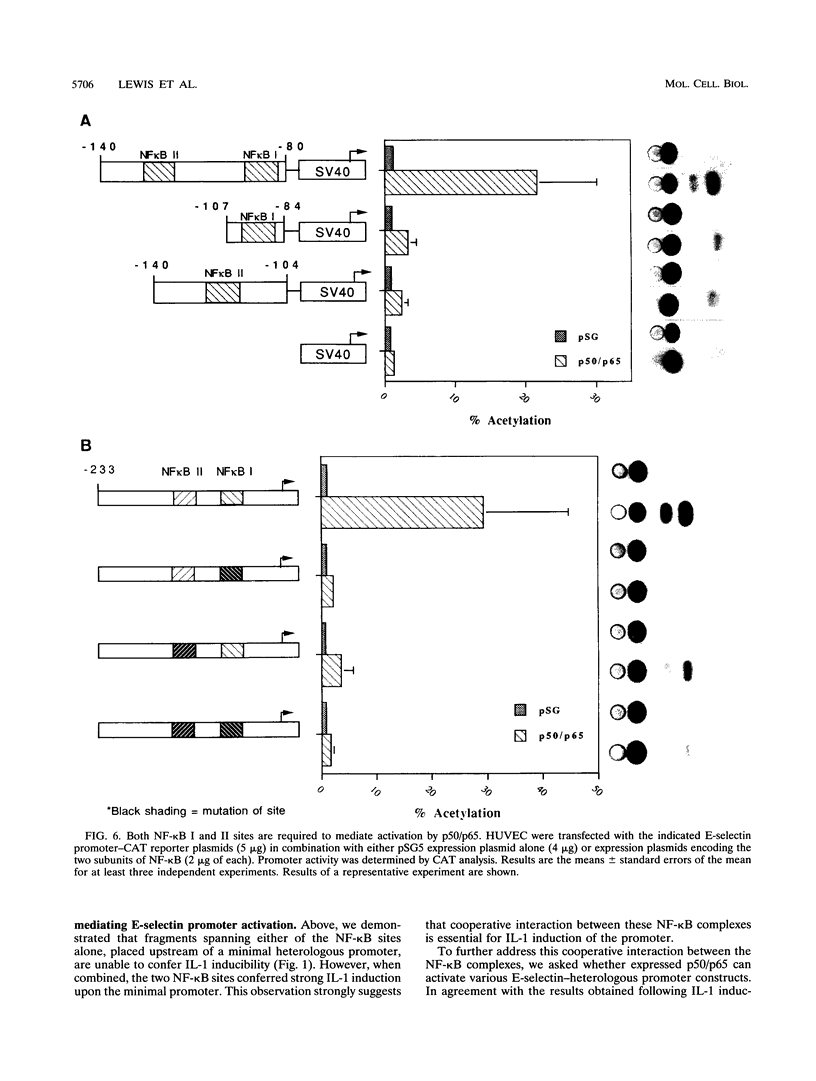
Cytokine-induced expression of the E-selectin gene requires the promoter binding and interaction of the transcription factors NF-kappa B and ATF. Here we have further analyzed the E-selectin promoter and revealed an additional region (nucleotides -140 to -105 [-140/-105]) which is essential in controlling promoter activation by cytokines. We identified high-mobility-group protein I(Y) [HMG-I(Y)] interacting specifically at two sites within this region. We noted that one of the HMG-I(Y)-binding sites overlaps a sequence element (-127/-118) diverging at only one position from the NF-kappa B consensus binding sequence. This led us to ask whether the -127/-118 element represents a second functional NF-kappa B-binding site within the E-selectin promoter. Using specific antisera, we show that p50, p65, and, interestingly, RelB are components of the complex interacting at this site. Mutational analysis of the -127/-118 NF-kappa B site indicates that both NF-kappa B and HMG-I(Y) binding at this site are essential for interleukin-1 induction of the promoter. We demonstrate that the binding affinity of the p50 subunit of NF-kappa B to both NF-kappa B sites within the E-selectin promoter is significantly enhanced by HMG-I(Y). In addition, an essential role for cooperative interaction between the two NF-kappa B complexes is shown by the requirement for both NF-kappa B sites to mediate E-selectin promoter activation by interleukin-1 and p50/p65 expression. We conclude that HMG-I(Y) mediates binding of a distinct NF-kappa B complex at two sites within the E-selectin promoter. Furthermore, a unique cooperativity between these NF-kappa B complexes is essential for induced E-selectin expression. These results suggest mechanisms by which NF-kappa B complexes are involved in specific gene activation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arima N., Molitor J. A., Smith M. R., Kim J. H., Daitoku Y., Greene W. C. Human T-cell leukemia virus type I Tax induces expression of the Rel-related family of kappa B enhancer-binding proteins: evidence for a pretranslational component of regulation. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6892–6899. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6892-6899.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. A 65-kappaD subunit of active NF-kappaB is required for inhibition of NF-kappaB by I kappaB. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1689–1698. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A. The inducible transcription activator NF-kappa B: regulation by distinct protein subunits. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Apr 16;1072(1):63–80. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(91)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betts J. C., Cheshire J. K., Akira S., Kishimoto T., Woo P. The role of NF-kappa B and NF-IL6 transactivating factors in the synergistic activation of human serum amyloid A gene expression by interleukin-1 and interleukin-6. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 5;268(34):25624–25631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P., Stengelin S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Seed B. Endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule 1: an inducible receptor for neutrophils related to complement regulatory proteins and lectins. Science. 1989 Mar 3;243(4895):1160–1165. doi: 10.1126/science.2466335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank V., Kourilsky P., Israël A. NF-kappa B and related proteins: Rel/dorsal homologies meet ankyrin-like repeats. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Apr;17(4):135–140. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90321-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher E. C. Leukocyte-endothelial cell recognition: three (or more) steps to specificity and diversity. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1033–1036. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90279-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins T., Williams A., Johnston G. I., Kim J., Eddy R., Shows T., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Bevilacqua M. P. Structure and chromosomal location of the gene for endothelial-leukocyte adhesion molecule 1. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2466–2473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. Use of eukaryotic expression technology in the functional analysis of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:684–704. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52074-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn A., Benoist C., Mathis D. New B-lymphocyte-specific enhancer-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):312–320. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du W., Thanos D., Maniatis T. Mechanisms of transcriptional synergism between distinct virus-inducible enhancer elements. Cell. 1993 Sep 10;74(5):887–898. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90468-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fashena S. J., Reeves R., Ruddle N. H. A poly(dA-dT) upstream activating sequence binds high-mobility group I protein and contributes to lymphotoxin (tumor necrosis factor-beta) gene regulation. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):894–903. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreri K., Gill G., Montminy M. The cAMP-regulated transcription factor CREB interacts with a component of the TFIID complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 15;91(4):1210–1213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.4.1210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaynor R. B., Kuwabara M. D., Wu F. K., Garcia J. A., Harrich D., Briskin M., Wall R., Sigman D. S. Repeated B motifs in the human immunodeficiency virus type I long terminal repeat enhancer region do not exhibit cooperative factor binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9406–9410. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghersa P., Hooft van Huijsduijnen R., Whelan J., DeLamarter J. F. Labile proteins play a dual role in the control of endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule-1 (ELAM-1) gene regulation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19226–19232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore T. D. NF-kappa B, KBF1, dorsal, and related matters. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):841–843. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90257-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Issemann I., Sheer E. A versatile in vivo and in vitro eukaryotic expression vector for protein engineering. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 11;16(1):369–369. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.1.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grilli M., Chiu J. J., Lenardo M. J. NF-kappa B and Rel: participants in a multiform transcriptional regulatory system. Int Rev Cytol. 1993;143:1–62. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61873-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grumont R. J., Richardson I. B., Gaff C., Gerondakis S. rel/NF-kappa B nuclear complexes that bind kB sites in the murine c-rel promoter are required for constitutive c-rel transcription in B-cells. Cell Growth Differ. 1993 Sep;4(9):731–743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooft van Huijsduijnen R., Whelan J., Pescini R., Becker-André M., Schenk A. M., DeLamarter J. F. A T-cell enhancer cooperates with NF-kappa B to yield cytokine induction of E-selectin gene transcription in endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):22385–22391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. R., Lehn D. A., Reeves R. Alternative processing of mRNAs encoding mammalian chromosomal high-mobility-group proteins HMG-I and HMG-Y. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2114–2123. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaszubska W., Hooft van Huijsduijnen R., Ghersa P., DeRaemy-Schenk A. M., Chen B. P., Hai T., DeLamarter J. F., Whelan J. Cyclic AMP-independent ATF family members interact with NF-kappa B and function in the activation of the E-selectin promoter in response to cytokines. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;13(11):7180–7190. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.11.7180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr L. D., Ransone L. J., Wamsley P., Schmitt M. J., Boyer T. G., Zhou Q., Berk A. J., Verma I. M. Association between proto-oncoprotein Rel and TATA-binding protein mediates transcriptional activation by NF-kappa B. Nature. 1993 Sep 30;365(6445):412–419. doi: 10.1038/365412a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieran M., Blank V., Logeat F., Vandekerckhove J., Lottspeich F., Le Bail O., Urban M. B., Kourilsky P., Baeuerle P. A., Israël A. The DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B is identical to factor KBF1 and homologous to the rel oncogene product. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1007–1018. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90275-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunsch C., Ruben S. M., Rosen C. A. Selection of optimal kappa B/Rel DNA-binding motifs: interaction of both subunits of NF-kappa B with DNA is required for transcriptional activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4412–4421. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasky L. A. Selectins: interpreters of cell-specific carbohydrate information during inflammation. Science. 1992 Nov 6;258(5084):964–969. doi: 10.1126/science.1439808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M. J., Baltimore D. NF-kappa B: a pleiotropic mediator of inducible and tissue-specific gene control. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):227–229. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90833-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lernbecher T., Müller U., Wirth T. Distinct NF-kappa B/Rel transcription factors are responsible for tissue-specific and inducible gene activation. Nature. 1993 Oct 21;365(6448):767–770. doi: 10.1038/365767a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liou H. C., Baltimore D. Regulation of the NF-kappa B/rel transcription factor and I kappa B inhibitor system. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;5(3):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90014-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molitor J. A., Walker W. H., Doerre S., Ballard D. W., Greene W. C. NF-kappa B: a family of inducible and differentially expressed enhancer-binding proteins in human T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):10028–10032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.10028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery K. F., Osborn L., Hession C., Tizard R., Goff D., Vassallo C., Tarr P. I., Bomsztyk K., Lobb R., Harlan J. M. Activation of endothelial-leukocyte adhesion molecule 1 (ELAM-1) gene transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6523–6527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parvin J. D., Timmers H. T., Sharp P. A. Promoter specificity of basal transcription factors. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1135–1144. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90084-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins N. D., Edwards N. L., Duckett C. S., Agranoff A. B., Schmid R. M., Nabel G. J. A cooperative interaction between NF-kappa B and Sp1 is required for HIV-1 enhancer activation. EMBO J. 1993 Sep;12(9):3551–3558. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06029.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pescini R., Kaszubska W., Whelan J., DeLamarter J. F., Hooft van Huijsduijnen R. ATF-a0, a novel variant of the ATF/CREB transcription factor family, forms a dominant transcription inhibitor in ATF-a heterodimers. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 14;269(2):1159–1165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picker L. J., Kishimoto T. K., Smith C. W., Warnock R. A., Butcher E. C. ELAM-1 is an adhesion molecule for skin-homing T cells. Nature. 1991 Feb 28;349(6312):796–799. doi: 10.1038/349796a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Diverse transcriptional functions of the multisubunit eukaryotic TFIID complex. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):679–682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves R., Elton T. S., Nissen M. S., Lehn D., Johnson K. R. Posttranscriptional gene regulation and specific binding of the nonhistone protein HMG-I by the 3' untranslated region of bovine interleukin 2 cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6531–6535. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reis L. F., Harada H., Wolchok J. D., Taniguchi T., Vilcek J. Critical role of a common transcription factor, IRF-1, in the regulation of IFN-beta and IFN-inducible genes. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):185–193. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05041.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruben S. M., Klement J. F., Coleman T. A., Maher M., Chen C. H., Rosen C. A. I-Rel: a novel rel-related protein that inhibits NF-kappa B transcriptional activity. Genes Dev. 1992 May;6(5):745–760. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.5.745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruben S. M., Narayanan R., Klement J. F., Chen C. H., Rosen C. A. Functional characterization of the NF-kappa B p65 transcriptional activator and an alternatively spliced derivative. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):444–454. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryseck R. P., Bull P., Takamiya M., Bours V., Siebenlist U., Dobrzanski P., Bravo R. RelB, a new Rel family transcription activator that can interact with p50-NF-kappa B. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):674–684. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid R. M., Perkins N. D., Duckett C. S., Andrews P. C., Nabel G. J. Cloning of an NF-kappa B subunit which stimulates HIV transcription in synergy with p65. Nature. 1991 Aug 22;352(6337):733–736. doi: 10.1038/352733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A. Adhesion receptors of the immune system. Nature. 1990 Aug 2;346(6283):425–434. doi: 10.1038/346425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein B., Baldwin A. S., Jr, Ballard D. W., Greene W. C., Angel P., Herrlich P. Cross-coupling of the NF-kappa B p65 and Fos/Jun transcription factors produces potentiated biological function. EMBO J. 1993 Oct;12(10):3879–3891. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06066.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein B., Baldwin A. S., Jr Distinct mechanisms for regulation of the interleukin-8 gene involve synergism and cooperativity between C/EBP and NF-kappa B. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;13(11):7191–7198. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.11.7191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein B., Cogswell P. C., Baldwin A. S., Jr Functional and physical associations between NF-kappa B and C/EBP family members: a Rel domain-bZIP interaction. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):3964–3974. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.3964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thanos D., Maniatis T. The high mobility group protein HMG I(Y) is required for NF-kappa B-dependent virus induction of the human IFN-beta gene. Cell. 1992 Nov 27;71(5):777–789. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90554-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whelan J., Ghersa P., Hooft van Huijsduijnen R., Gray J., Chandra G., Talabot F., DeLamarter J. F. An NF kappa B-like factor is essential but not sufficient for cytokine induction of endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule 1 (ELAM-1) gene transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 25;19(10):2645–2653. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.10.2645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]