Abstract
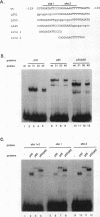
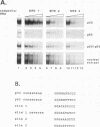
Transcription of the gene encoding the endothelial cell-leukocyte adhesion molecule (ELAM-1; E-selectin) is induced in response to various cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin-1. A DNase I-hypersensitive site in the 5' proximal promoter region of the E-selectin gene is observed in human umbilical vein endothelial cells only following TNF-alpha treatment, suggesting the presence of a TNF-alpha-inducible element close to the transcriptional start site. Transient transfection studies in endothelial cells demonstrated that 170 bp of upstream sequences is sufficient to confer TNF-alpha inducibility. Systematic site-directed mutagenesis of this region revealed two regulatory elements (-129 to -110 and -99 to -80) that are essential for maximal promoter activity following cytokine treatment. Protein binding studies with crude nuclear extracts and recombinant proteins revealed that the two elements correspond to three NF-kappa B binding sites (site 1, -126; site 2, 116; and site 3, -94). All three sites can be bound by NF-kappa B when used as independent oligonucleotides in mobility shift assays. However, within the context of a larger promoter fragment, sites 2 and 3 are preferentially occupied over site 1. These data are consistent with results obtained in transfection studies demonstrating that mutations in sites 2 and 3 are more detrimental than mutations within site 1. Hence, inducibility of the E-selectin gene requires the interaction of NF-kappa B proteins bound to multiple regulatory elements.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baeuerle P. A., Henkel T. Function and activation of NF-kappa B in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:141–179. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.12.040194.001041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker-André M., Hooft van Huijsduijnen R., Losberger C., Whelan J., Delamarter J. F. Murine endothelial leukocyte-adhesion molecule 1 is a close structural and functional homologue of the human protein. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Jun 1;206(2):401–411. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16940.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beg A. A., Baldwin A. S., Jr The I kappa B proteins: multifunctional regulators of Rel/NF-kappa B transcription factors. Genes Dev. 1993 Nov;7(11):2064–2070. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.11.2064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beg A. A., Finco T. S., Nantermet P. V., Baldwin A. S., Jr Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 lead to phosphorylation and loss of I kappa B alpha: a mechanism for NF-kappa B activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3301–3310. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P., Stengelin S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Seed B. Endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule 1: an inducible receptor for neutrophils related to complement regulatory proteins and lectins. Science. 1989 Mar 3;243(4895):1160–1165. doi: 10.1126/science.2466335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank V., Kourilsky P., Israël A. NF-kappa B and related proteins: Rel/dorsal homologies meet ankyrin-like repeats. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Apr;17(4):135–140. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90321-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher E. C. Leukocyte-endothelial cell recognition: three (or more) steps to specificity and diversity. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1033–1036. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90279-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins T., Williams A., Johnston G. I., Kim J., Eddy R., Shows T., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Bevilacqua M. P. Structure and chromosomal location of the gene for endothelial-leukocyte adhesion molecule 1. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2466–2473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotran R. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Bevilacqua M. P., Mendrick D. L., Pober J. S. Induction and detection of a human endothelial activation antigen in vivo. J Exp Med. 1986 Aug 1;164(2):661–666. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.2.661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du W., Thanos D., Maniatis T. Mechanisms of transcriptional synergism between distinct virus-inducible enhancer elements. Cell. 1993 Sep 10;74(5):887–898. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90468-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C. The formation and function of DNase I hypersensitive sites in the process of gene activation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19259–19262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enver T., Brewer A. C., Patient R. K. Simian virus 40-mediated cis induction of the Xenopus beta-globin DNase I hypersensitive site. Nature. 1985 Dec 19;318(6047):680–683. doi: 10.1038/318680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghersa P., Hooft van Huijsduijnen R., Whelan J., DeLamarter J. F. Labile proteins play a dual role in the control of endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule-1 (ELAM-1) gene regulation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19226–19232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore T. D., Morin P. J. The I kappa B proteins: members of a multifunctional family. Trends Genet. 1993 Dec;9(12):427–433. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(93)90106-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grilli M., Chiu J. J., Lenardo M. J. NF-kappa B and Rel: participants in a multiform transcriptional regulatory system. Int Rev Cytol. 1993;143:1–62. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61873-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross D. S., Garrard W. T. Nuclease hypersensitive sites in chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:159–197. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai T. W., Liu F., Coukos W. J., Green M. R. Transcription factor ATF cDNA clones: an extensive family of leucine zipper proteins able to selectively form DNA-binding heterodimers. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2083–2090. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooft van Huijsduijnen R., Whelan J., Pescini R., Becker-André M., Schenk A. M., DeLamarter J. F. A T-cell enhancer cooperates with NF-kappa B to yield cytokine induction of E-selectin gene transcription in endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):22385–22391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iademarco M. F., McQuillan J. J., Rosen G. D., Dean D. C. Characterization of the promoter for vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1). J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16323–16329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karim F. D., Urness L. D., Thummel C. S., Klemsz M. J., McKercher S. R., Celada A., Van Beveren C., Maki R. A., Gunther C. V., Nye J. A. The ETS-domain: a new DNA-binding motif that recognizes a purine-rich core DNA sequence. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1451–1453. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaszubska W., Hooft van Huijsduijnen R., Ghersa P., DeRaemy-Schenk A. M., Chen B. P., Hai T., DeLamarter J. F., Whelan J. Cyclic AMP-independent ATF family members interact with NF-kappa B and function in the activation of the E-selectin promoter in response to cytokines. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;13(11):7180–7190. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.11.7180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunsch C., Ruben S. M., Rosen C. A. Selection of optimal kappa B/Rel DNA-binding motifs: interaction of both subunits of NF-kappa B with DNA is required for transcriptional activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4412–4421. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liou H. C., Baltimore D. Regulation of the NF-kappa B/rel transcription factor and I kappa B inhibitor system. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;5(3):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90014-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEver R. P. Selectins: novel receptors that mediate leukocyte adhesion during inflammation. Thromb Haemost. 1991 Mar 4;65(3):223–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery K. F., Osborn L., Hession C., Tizard R., Goff D., Vassallo C., Tarr P. I., Bomsztyk K., Lobb R., Harlan J. M. Activation of endothelial-leukocyte adhesion molecule 1 (ELAM-1) gene transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6523–6527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayanan R., Higgins K. A., Perez J. R., Coleman T. A., Rosen C. A. Evidence for differential functions of the p50 and p65 subunits of NF-kappa B with a cell adhesion model. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3802–3810. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neish A. S., Williams A. J., Palmer H. J., Whitley M. Z., Collins T. Functional analysis of the human vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 promoter. J Exp Med. 1992 Dec 1;176(6):1583–1593. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.6.1583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn L., Hession C., Tizard R., Vassallo C., Luhowskyj S., Chi-Rosso G., Lobb R. Direct expression cloning of vascular cell adhesion molecule 1, a cytokine-induced endothelial protein that binds to lymphocytes. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1203–1211. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90775-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn L., Kunkel S., Nabel G. J. Tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 1 stimulate the human immunodeficiency virus enhancer by activation of the nuclear factor kappa B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2336–2340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn L. Leukocyte adhesion to endothelium in inflammation. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):3–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90230-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins N. D., Schmid R. M., Duckett C. S., Leung K., Rice N. R., Nabel G. J. Distinct combinations of NF-kappa B subunits determine the specificity of transcriptional activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1529–1533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Lapierre L. A., Mendrick D. L., Fiers W., Rothlein R., Springer T. A. Overlapping patterns of activation of human endothelial cells by interleukin 1, tumor necrosis factor, and immune interferon. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 15;137(6):1893–1896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shu H. B., Agranoff A. B., Nabel E. G., Leung K., Duckett C. S., Neish A. S., Collins T., Nabel G. J. Differential regulation of vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 gene expression by specific NF-kappa B subunits in endothelial and epithelial cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;13(10):6283–6289. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.10.6283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. C., Brown T. A., McKnight S. L. Convergence of Ets- and notch-related structural motifs in a heteromeric DNA binding complex. Science. 1991 Aug 16;253(5021):762–768. doi: 10.1126/science.1876833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R., Maniatis T. Transcriptional activation: a complex puzzle with few easy pieces. Cell. 1994 Apr 8;77(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90227-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whelan J., Ghersa P., Hooft van Huijsduijnen R., Gray J., Chandra G., Talabot F., DeLamarter J. F. An NF kappa B-like factor is essential but not sufficient for cytokine induction of endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule 1 (ELAM-1) gene transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 25;19(10):2645–2653. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.10.2645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]