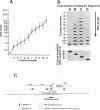
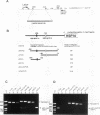
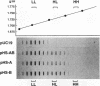
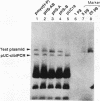
Abstract
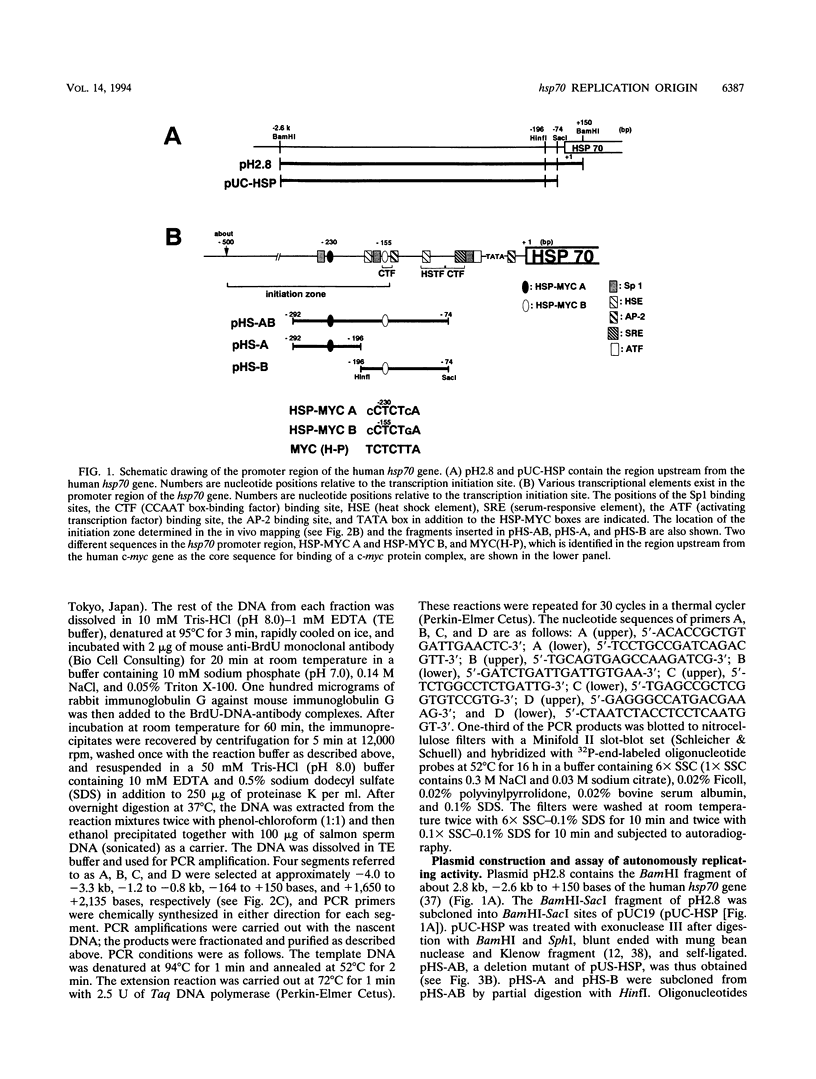
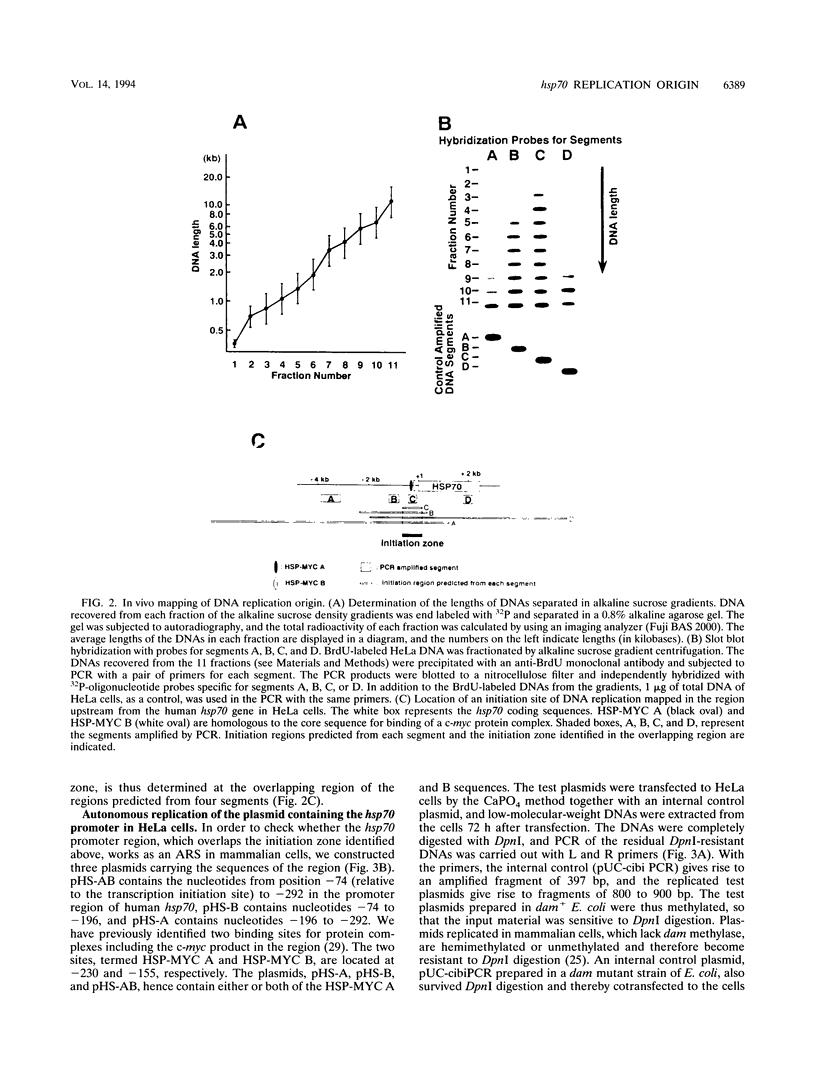
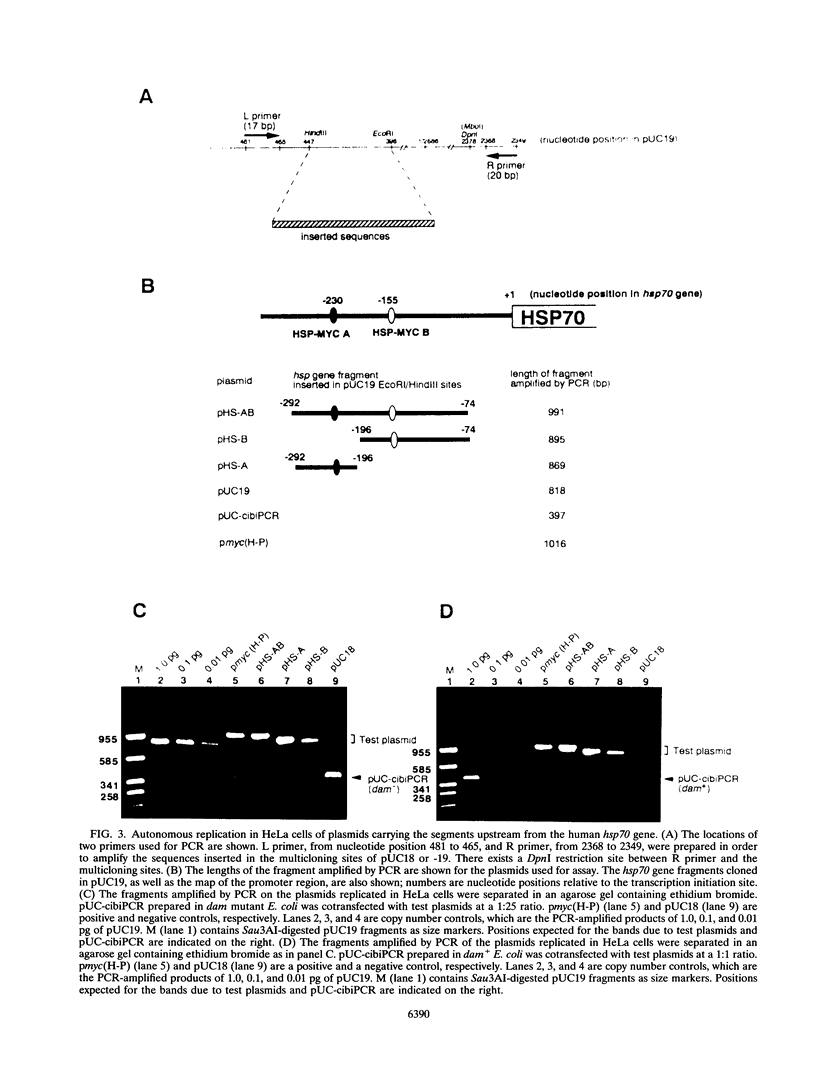
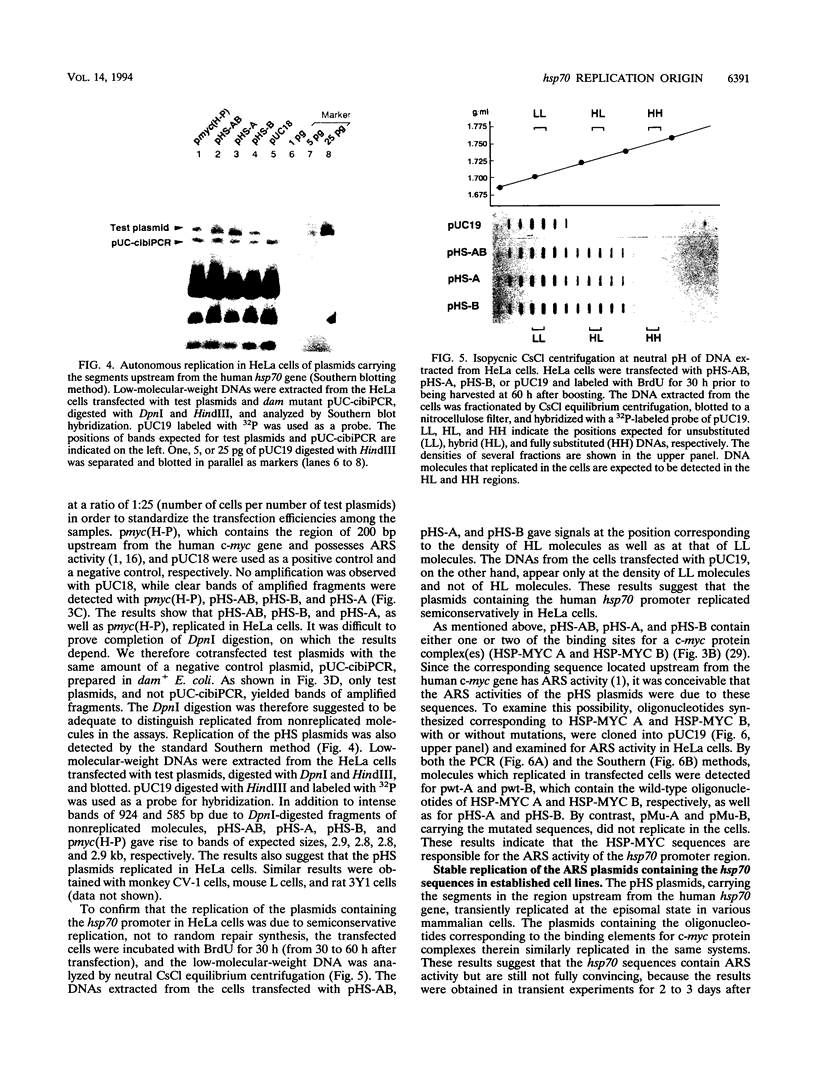
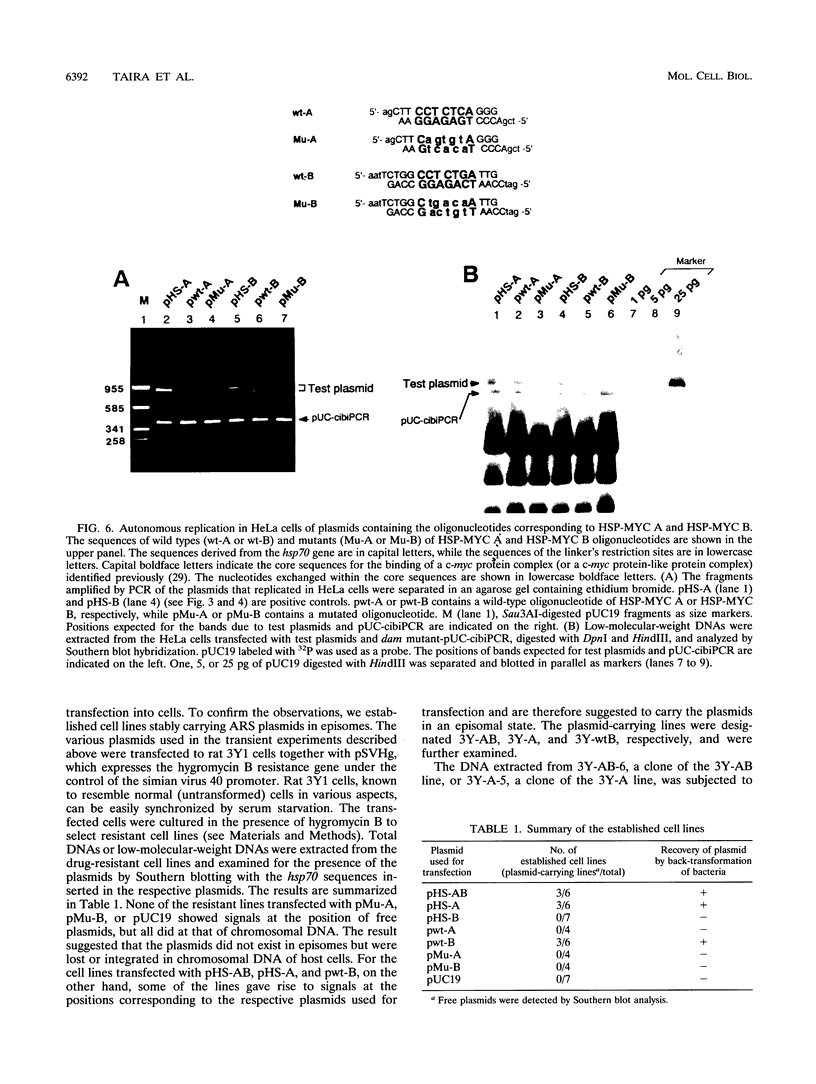
A general and sensitive method for the mapping of initiation sites of DNA replication in vivo, developed by Vassilev and Johnson, has revealed replication origins in the region of simian virus 40 ori, in the regions upstream from the human c-myc gene and downstream from the Chinese hamster dihydrofolate reductase gene, and in the enhancer region of the mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene. Here we report that the region containing the promoter of the human heat shock protein 70 (hsp70) gene was identified as a DNA replication origin in HeLa cells by this method. Several segments of the region were cloned into pUC19 and examined for autonomously replicating sequence (ARS) activity. The plasmids carrying the segments replicated episomally and semiconservatively when transfected into HeLa cells. The segments of ARS activity contained the sequences previously identified as binding sequences for a c-myc protein complex (T. Taira, Y. Negishi, F. Kihara, S. M. M. Iguchi-Ariga, and H. Ariga, Biochem. Biophys. Acta 1130:166-174, 1992). Mutations introduced within the c-myc protein complex binding sequences abolished the ARS activity. Moreover, the ARS plasmids stably replicated at episomal state for a long time in established cell lines. The results suggest that the promoter region of the human hsp70 gene plays a role in DNA replication as well as in transcription.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ariga H., Imamura Y., Iguchi-Ariga S. M. DNA replication origin and transcriptional enhancer in c-myc gene share the c-myc protein binding sequences. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4273–4279. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08613.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ariga H., Itani T., Iguchi-Ariga S. M. Autonomous replicating sequences from mouse cells which can replicate in mouse cells in vivo and in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):1–6. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ariizumi K., Wang Z., Tucker P. W. Immunoglobulin heavy chain enhancer is located near or in an initiation zone of chromosomal DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3695–3699. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biamonti G., Giacca M., Perini G., Contreas G., Zentilin L., Weighardt F., Guerra M., Della Valle G., Saccone S., Riva S. The gene for a novel human lamin maps at a highly transcribed locus of chromosome 19 which replicates at the onset of S-phase. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;12(8):3499–3506. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.8.3499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caddle M. S., Lussier R. H., Heintz N. H. Intramolecular DNA triplexes, bent DNA and DNA unwinding elements in the initiation region of an amplified dihydrofolate reductase replicon. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jan 5;211(1):19–33. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90008-A. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll S. M., DeRose M. L., Kolman J. L., Nonet G. H., Kelly R. E., Wahl G. M. Localization of a bidirectional DNA replication origin in the native locus and in episomally amplified murine adenosine deaminase loci. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 May;13(5):2971–2981. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.5.2971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L. Transcriptional elements as components of eukaryotic origins of DNA replication. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):635–638. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90398-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falaschi A., Biamonti G., Cobianchi F., Csordas-Toth E., Faulkner G., Giacca M., Pedacchia D., Perini G., Riva S., Tribioli C. Presence of transcription signals in two putative DNA replication origins of human cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Dec 20;951(2-3):430–442. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90117-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Held P. G., Heintz N. H. Eukaryotic replication origins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Apr 6;1130(3):235–246. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(92)90435-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iguchi-Ariga S. M., Ariga H. Concerted mechanism of DNA replication and transcription. Cell Struct Funct. 1989 Dec;14(6):649–651. doi: 10.1247/csf.14.649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iguchi-Ariga S. M., Ogawa N., Ariga H. Identification of the initiation region of DNA replication in the murine immunoglobulin heavy chain gene and possible function of the octamer motif as a putative DNA replication origin in mammalian cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Feb 20;1172(1-2):73–81. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(93)90271-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iguchi-Ariga S. M., Okazaki T., Itani T., Ogata M., Sato Y., Ariga H. An initiation site of DNA replication with transcriptional enhancer activity present upstream of the c-myc gene. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3135–3142. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03180.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Kadonaga J. T., Rosenfeld P. J., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. A cellular DNA-binding protein that activates eukaryotic transcription and DNA replication. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90358-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolluri R., Torrey T. A., Kinniburgh A. J. A CT promoter element binding protein: definition of a double-strand and a novel single-strand DNA binding motif. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 11;20(1):111–116. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.1.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kominami R., Muramatsu M., Moriwaki K. A mouse type 2 Alu sequence (M2) is mobile in the genome. Nature. 1983 Jan 6;301(5895):87–89. doi: 10.1038/301087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M. E., Piette J., Yaniv M., Tang W. J., Folk W. R. Activation of the polyomavirus enhancer by a murine activator protein 1 (AP1) homolog and two contiguous proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5839–5843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McWhinney C., Leffak M. Autonomous replication of a DNA fragment containing the chromosomal replication origin of the human c-myc gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 11;18(5):1233–1242. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.5.1233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami Y., Satake M., Yamaguchi-Iwai Y., Sakai M., Muramatsu M., Ito Y. The nuclear protooncogenes c-jun and c-fos as regulators of DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3947–3951. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negishi Y., Iguchi-Ariga S. M., Ariga H. Protein complexes bearing myc-like antigenicity recognize two distinct DNA sequences. Oncogene. 1992 Mar;7(3):543–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill E. A., Fletcher C., Burrow C. R., Heintz N., Roeder R. G., Kelly T. J. Transcription factor OTF-1 is functionally identical to the DNA replication factor NF-III. Science. 1988 Sep 2;241(4870):1210–1213. doi: 10.1126/science.3413485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peden K. W., Pipas J. M., Pearson-White S., Nathans D. Isolation of mutants of an animal virus in bacteria. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1392–1396. doi: 10.1126/science.6251547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruijn G. J., van Driel W., van Miltenburg R. T., van der Vliet P. C. Promoter and enhancer elements containing a conserved sequence motif are recognized by nuclear factor III, a protein stimulating adenovirus DNA replication. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3771–3778. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02712.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruijn G. J., van Driel W., van der Vliet P. C. Nuclear factor III, a novel sequence-specific DNA-binding protein from HeLa cells stimulating adenovirus DNA replication. Nature. 1986 Aug 14;322(6080):656–659. doi: 10.1038/322656a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudo K., Ogata M., Sato Y., Iguchi-Ariga S. M., Ariga H. Cloned origin of DNA replication in c-myc gene can function and be transmitted in transgenic mice in an episomal state. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 25;18(18):5425–5432. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.18.5425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taira T., Negishi Y., Kihara F., Iguchi-Ariga S. M., Ariga H. c-myc protein complex binds to two sites in human hsp70 promoter region. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Mar 24;1130(2):166–174. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(92)90524-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tóth E. C., Marusic L., Ochem A., Patthy A., Pongor S., Giacca M., Falaschi A. Interactions of USF and Ku antigen with a human DNA region containing a replication origin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 11;21(14):3257–3263. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.14.3257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassilev L. T., Burhans W. C., DePamphilis M. L. Mapping an origin of DNA replication at a single-copy locus in exponentially proliferating mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4685–4689. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassilev L., Johnson E. M. An initiation zone of chromosomal DNA replication located upstream of the c-myc gene in proliferating HeLa cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4899–4904. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassilev L., Johnson E. M. Mapping initiation sites of DNA replication in vivo using polymerase chain reaction amplification of nascent strand segments. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 11;17(19):7693–7705. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.19.7693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldman G. M., Lupton S., Kamen R. Polyomavirus enhancer contains multiple redundant sequence elements that activate both DNA replication and gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):649–658. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verrijzer C. P., Kal A. J., Van der Vliet P. C. The DNA binding domain (POU domain) of transcription factor oct-1 suffices for stimulation of DNA replication. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1883–1888. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08314.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe S., Yamaguchi N. Deletion analysis of a replication origin of human cytomegalovirus by a novel assay system with a combination of microinjection and polymerase chain reaction. Virology. 1993 Jan;192(1):332–335. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu B., Hunt C., Morimoto R. Structure and expression of the human gene encoding major heat shock protein HSP70. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;5(2):330–341. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.2.330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]