Abstract
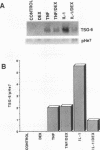
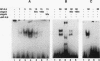
Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin-1 (IL-1) activate transcription of the TSG-6 gene in normal human fibroblasts through a promoter region (-165 to -58) that encompasses an AP-1 and a NF-IL6 site. We show by deletion analysis and substitution mutagenesis that both sites are necessary for activation by TNF-alpha. Activation by IL-1 requires the NF-IL6 site and is enhanced by the AP-1 site. These results suggest that the NF-IL6 and AP-1 family transcription factors functionally cooperate to mediate TNF-alpha and IL-1 signals. Consistent with this possibility, IL-1 and TNF-alpha markedly increase the binding of Fos and Jun to the AP-1 site, and NF-IL6 activates the native TSG-6 promoter. Activation by NF-IL6 requires an intact NF-IL6 site and is modulated by the ratio of activator to inhibitor NF-IL6 isoforms that are translated from different in-frame AUGs. However, the inhibitor isoform can also bind to the AP-1 site and repress AP-1 site-mediated transcription. The finding that the inhibitor isoform antagonizes activation of the native TSG-6 promoter by IL-1 and TNF-alpha suggests that NF-IL6 has a physiologic role in these cytokine responses. Thus, the functionally distinct NF-IL6 isoforms cooperate with Fos and Jun to positively and negatively regulate the native TSG-6 promoter by TNF-alpha and IL-1.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akira S., Isshiki H., Nakajima T., Kinoshita S., Nishio Y., Hashimoto S., Natsuka S., Kishimoto T. A nuclear factor for the IL-6 gene (NF-IL6). Chem Immunol. 1992;51:299–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akira S., Isshiki H., Sugita T., Tanabe O., Kinoshita S., Nishio Y., Nakajima T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. A nuclear factor for IL-6 expression (NF-IL6) is a member of a C/EBP family. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1897–1906. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08316.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Allegretto E. A., Okino S. T., Hattori K., Boyle W. J., Hunter T., Karin M. Oncogene jun encodes a sequence-specific trans-activator similar to AP-1. Nature. 1988 Mar 10;332(6160):166–171. doi: 10.1038/332166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Karin M. The role of Jun, Fos and the AP-1 complex in cell-proliferation and transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Dec 10;1072(2-3):129–157. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(91)90011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babich A., Feldman L. T., Nevins J. R., Darnell J. E., Jr, Weinberger C. Effect of adenovirus on metabolism of specific host mRNAs: transport control and specific translational discrimination. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;3(7):1212–1221. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.7.1212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengal E., Ransone L., Scharfmann R., Dwarki V. J., Tapscott S. J., Weintraub H., Verma I. M. Functional antagonism between c-Jun and MyoD proteins: a direct physical association. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):507–519. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90187-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohmann D., Bos T. J., Admon A., Nishimura T., Vogt P. K., Tjian R. Human proto-oncogene c-jun encodes a DNA binding protein with structural and functional properties of transcription factor AP-1. Science. 1987 Dec 4;238(4832):1386–1392. doi: 10.1126/science.2825349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen-Kiang S., Hsu W., Natkunam Y., Zhang X. Nuclear signaling by interleukin-6. Curr Opin Immunol. 1993 Feb;5(1):124–128. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(93)90091-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu R., Boyle W. J., Meek J., Smeal T., Hunter T., Karin M. The c-Fos protein interacts with c-Jun/AP-1 to stimulate transcription of AP-1 responsive genes. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):541–552. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90076-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Franza B. R., Jr Fos and Jun: the AP-1 connection. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):395–397. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90024-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng W. P., Nickoloff J. A. Site-directed mutagenesis of virtually any plasmid by eliminating a unique site. Anal Biochem. 1992 Jan;200(1):81–88. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(92)90280-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descombes P., Chojkier M., Lichtsteiner S., Falvey E., Schibler U. LAP, a novel member of the C/EBP gene family, encodes a liver-enriched transcriptional activator protein. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1541–1551. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descombes P., Schibler U. A liver-enriched transcriptional activator protein, LAP, and a transcriptional inhibitory protein, LIP, are translated from the same mRNA. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):569–579. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90531-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond M. I., Miner J. N., Yoshinaga S. K., Yamamoto K. R. Transcription factor interactions: selectors of positive or negative regulation from a single DNA element. Science. 1990 Sep 14;249(4974):1266–1272. doi: 10.1126/science.2119054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentz R., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Abate C., Curran T. Parallel association of Fos and Jun leucine zippers juxtaposes DNA binding domains. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1695–1699. doi: 10.1126/science.2494702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein L. A., Zhou D. F., Picker L. J., Minty C. N., Bargatze R. F., Ding J. F., Butcher E. C. A human lymphocyte homing receptor, the hermes antigen, is related to cartilage proteoglycan core and link proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):1063–1072. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90639-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu W., Chen-Kiang S. Convergent regulation of NF-IL6 and Oct-1 synthesis by interleukin-6 and retinoic acid signaling in embryonal carcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2515–2523. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu W., Kerppola T. K., Chen P. L., Curran T., Chen-Kiang S. Fos and Jun repress transcription activation by NF-IL6 through association at the basic zipper region. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):268–276. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isshiki H., Akira S., Tanabe O., Nakajima T., Shimamoto T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. Constitutive and interleukin-1 (IL-1)-inducible factors interact with the IL-1-responsive element in the IL-6 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2757–2764. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain J., McCaffrey P. G., Miner Z., Kerppola T. K., Lambert J. N., Verdine G. L., Curran T., Rao A. The T-cell transcription factor NFATp is a substrate for calcineurin and interacts with Fos and Jun. Nature. 1993 Sep 23;365(6444):352–355. doi: 10.1038/365352a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerppola T. K., Curran T. Fos-Jun heterodimers and Jun homodimers bend DNA in opposite orientations: implications for transcription factor cooperativity. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):317–326. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90621-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerppola T. K., Luk D., Curran T. Fos is a preferential target of glucocorticoid receptor inhibition of AP-1 activity in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3782–3791. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita S., Akira S., Kishimoto T. A member of the C/EBP family, NF-IL6 beta, forms a heterodimer and transcriptionally synergizes with NF-IL6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1473–1476. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The DNA binding domain of the rat liver nuclear protein C/EBP is bipartite. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1681–1688. doi: 10.1126/science.2494700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeClair K. P., Blanar M. A., Sharp P. A. The p50 subunit of NF-kappa B associates with the NF-IL6 transcription factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):8145–8149. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le J., Vilcek J. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1: cytokines with multiple overlapping biological activities. Lab Invest. 1987 Mar;56(3):234–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. H., Klampfer L., Shows T. B., Vilcek J. Transcriptional regulation of TSG6, a tumor necrosis factor- and interleukin-1-inducible primary response gene coding for a secreted hyaluronan-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 25;268(9):6154–6160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. H., Lee G. W., Ziff E. B., Vilcek J. Isolation and characterization of eight tumor necrosis factor-induced gene sequences from human fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):1982–1988. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. H., Wisniewski H. G., Vilcek J. A novel secretory tumor necrosis factor-inducible protein (TSG-6) is a member of the family of hyaluronate binding proteins, closely related to the adhesion receptor CD44. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(2):545–557. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.2.545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. X., Vilcek J. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 cause a rapid and transient stimulation of c-fos and c-myc mRNA levels in human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):11908–11911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsusaka T., Fujikawa K., Nishio Y., Mukaida N., Matsushima K., Kishimoto T., Akira S. Transcription factors NF-IL6 and NF-kappa B synergistically activate transcription of the inflammatory cytokines, interleukin 6 and interleukin 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):10193–10197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.10193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz R., Ziff E. cAMP stimulates the C/EBP-related transcription factor rNFIL-6 to trans-locate to the nucleus and induce c-fos transcription. Genes Dev. 1991 Oct;5(10):1754–1766. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.10.1754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima T., Kinoshita S., Sasagawa T., Sasaki K., Naruto M., Kishimoto T., Akira S. Phosphorylation at threonine-235 by a ras-dependent mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade is essential for transcription factor NF-IL6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2207–2211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishio Y., Isshiki H., Kishimoto T., Akira S. A nuclear factor for interleukin-6 expression (NF-IL6) and the glucocorticoid receptor synergistically activate transcription of the rat alpha 1-acid glycoprotein gene via direct protein-protein interaction. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1854–1862. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raynal M. C., Liu Z. Y., Hirano T., Mayer L., Kishimoto T., Chen-Kiang S. Interleukin 6 induces secretion of IgG1 by coordinated transcriptional activation and differential mRNA accumulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):8024–8028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.8024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman C., Platero J. S., Shuman J., Calame K. Ig/EBP-1: a ubiquitously expressed immunoglobulin enhancer binding protein that is similar to C/EBP and heterodimerizes with C/EBP. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1404–1415. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spergel J. M., Chen-Kiang S. Interleukin 6 enhances a cellular activity that functionally substitutes for E1A protein in transactivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6472–6476. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spergel J. M., Hsu W., Akira S., Thimmappaya B., Kishimoto T., Chen-Kiang S. NF-IL6, a member of the C/EBP family, regulates E1A-responsive promoters in the absence of E1A. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):1021–1030. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.1021-1030.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamenkovic I., Amiot M., Pesando J. M., Seed B. A lymphocyte molecule implicated in lymph node homing is a member of the cartilage link protein family. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):1057–1062. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90638-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein B., Baldwin A. S., Jr, Ballard D. W., Greene W. C., Angel P., Herrlich P. Cross-coupling of the NF-kappa B p65 and Fos/Jun transcription factors produces potentiated biological function. EMBO J. 1993 Oct;12(10):3879–3891. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06066.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein B., Cogswell P. C., Baldwin A. S., Jr Functional and physical associations between NF-kappa B and C/EBP family members: a Rel domain-bZIP interaction. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):3964–3974. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.3964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R., Tjian R. Leucine repeats and an adjacent DNA binding domain mediate the formation of functional cFos-cJun heterodimers. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1689–1694. doi: 10.1126/science.2494701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallejo M., Ron D., Miller C. P., Habener J. F. C/ATF, a member of the activating transcription factor family of DNA-binding proteins, dimerizes with CAAT/enhancer-binding proteins and directs their binding to cAMP response elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4679–4683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vietor I., Schwenger P., Li W., Schlessinger J., Vilcek J. Tumor necrosis factor-induced activation and increased tyrosine phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase in human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 5;268(25):18994–18999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilcek J., Lee T. H. Tumor necrosis factor. New insights into the molecular mechanisms of its multiple actions. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7313–7316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt P. K., Bos T. J., Doolittle R. F. Homology between the DNA-binding domain of the GCN4 regulatory protein of yeast and the carboxyl-terminal region of a protein coded for by the oncogene jun. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3316–3319. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegner M., Cao Z., Rosenfeld M. G. Calcium-regulated phosphorylation within the leucine zipper of C/EBP beta. Science. 1992 Apr 17;256(5055):370–373. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5055.370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski H. G., Burgess W. H., Oppenheim J. D., Vilcek J. TSG-6, an arthritis-associated hyaluronan binding protein, forms a stable complex with the serum protein inter-alpha-inhibitor. Biochemistry. 1994 Jun 14;33(23):7423–7429. doi: 10.1021/bi00189a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski H. G., Maier R., Lotz M., Lee S., Klampfer L., Lee T. H., Vilcek J. TSG-6: a TNF-, IL-1-, and LPS-inducible secreted glycoprotein associated with arthritis. J Immunol. 1993 Dec 1;151(11):6593–6601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]