Abstract
CLK is a dual-specificity protein kinase capable of phosphorylating serine, threonine, and tyrosine residues. We have investigated the action of CLK by establishing stable PC12 cell lines capable of inducibly expressing CLK. Expression of CLK in stably transfected PC12 cells mimicked a number of nerve growth factor (NGF)-dependent events, including the morphological differentiation of these cells and the elaboration of neurites. Moreover, CLK expression enhanced the rate of NGF-mediated neurite outgrowth of these cells, indicating that CLK expression and NGF treatment activate similar signal transduction pathways. CLK expression, unlike NGF, was not able to promote PC12 cell survival in serum-free media, demonstrating that CLK only partially recapitulated the actions of NGF on these cells and that the biochemical pathways necessary for morphological differentiation can be stimulated without also stimulating those necessary for survival. Induction of CLK expression also resulted in the selective activation of protein kinases that are components of growth factor-stimulated signal transduction cascades, including ERK1, ERK2, pp90RSK, and S6PKII. Induction of CLK expression, however, did not stimulate pp70S6K or Fos kinase, two NGF-sensitive protein kinases. These data indicate that CLK action mediates the morphological differentiation of these cells through its capacity to independently stimulate signal transduction pathways normally employed by NGF.
Full text
PDF




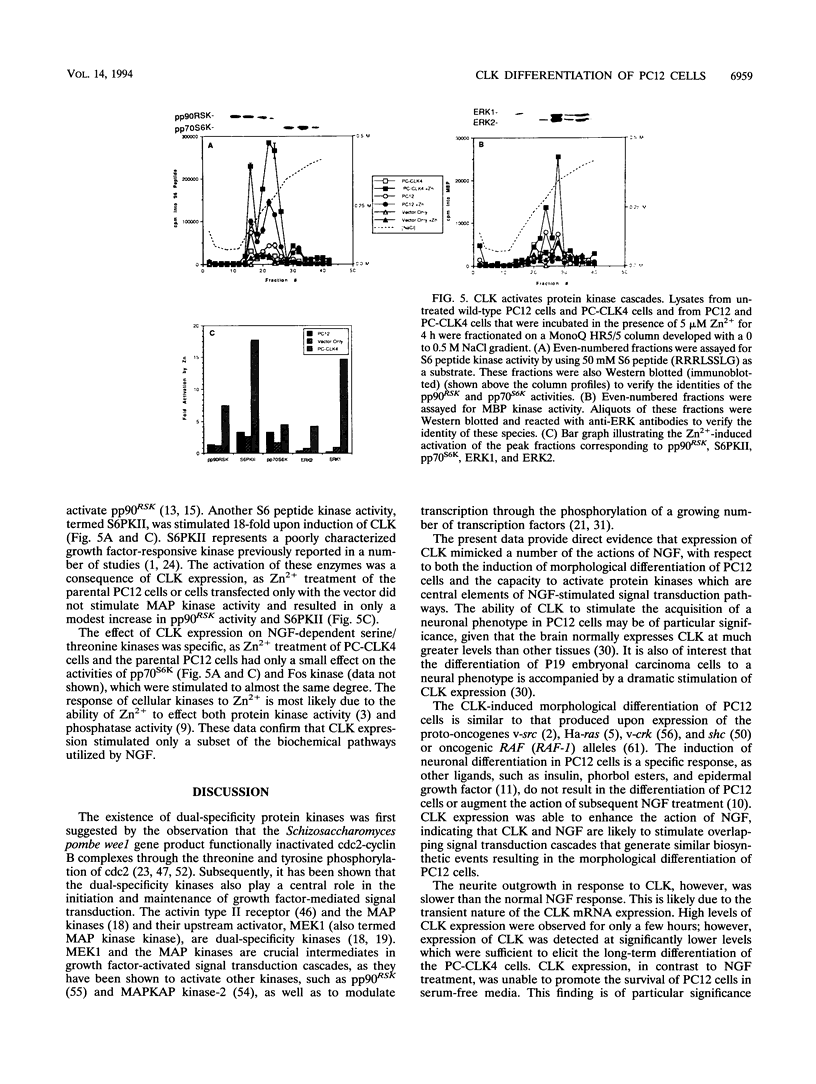


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahn N. G., Seger R., Bratlien R. L., Diltz C. D., Tonks N. K., Krebs E. G. Multiple components in an epidermal growth factor-stimulated protein kinase cascade. In vitro activation of a myelin basic protein/microtubule-associated protein 2 kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4220–4227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alemà S., Casalbore P., Agostini E., Tatò F. Differentiation of PC12 phaeochromocytoma cells induced by v-src oncogene. Nature. 1985 Aug 8;316(6028):557–559. doi: 10.1038/316557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alitalo K., Keski-Oja J., Bornstein P. Effects of Zn2+ ions on protein phosphorylation in epithelial cell membranes. J Cell Physiol. 1983 Jun;115(3):305–312. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041150314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballou L. M., Luther H., Thomas G. MAP2 kinase and 70K S6 kinase lie on distinct signalling pathways. Nature. 1991 Jan 24;349(6307):348–350. doi: 10.1038/349348a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Sagi D., Feramisco J. R. Microinjection of the ras oncogene protein into PC12 cells induces morphological differentiation. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):841–848. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90280-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-David Y., Letwin K., Tannock L., Bernstein A., Pawson T. A mammalian protein kinase with potential for serine/threonine and tyrosine phosphorylation is related to cell cycle regulators. EMBO J. 1991 Feb;10(2):317–325. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07952.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J., Chung J., Erikson E., Alcorta D. A., Erikson R. L. Distinct mechanisms for the activation of the RSK kinases/MAP2 kinase/pp90rsk and pp70-S6 kinase signaling systems are indicated by inhibition of protein synthesis. Cell Growth Differ. 1991 Jun;2(6):279–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulton T. G., Nye S. H., Robbins D. J., Ip N. Y., Radziejewska E., Morgenbesser S. D., DePinho R. A., Panayotatos N., Cobb M. H., Yancopoulos G. D. ERKs: a family of protein-serine/threonine kinases that are activated and tyrosine phosphorylated in response to insulin and NGF. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):663–675. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90098-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brautigan D. L., Bornstein P., Gallis B. Phosphotyrosyl-protein phosphatase. Specific inhibition by Zn. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6519–6522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstein D. E., Greene L. A. Evidence for RNA synthesis-dependent and -independent pathways in stimulation of neurite outgrowth by nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6059–6063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao M. V. Growth factor signaling: where is the specificity? Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):995–997. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90068-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung J., Chen R. H., Blenis J. Coordinate regulation of pp90rsk and a distinct protein-serine/threonine kinase activity that phosphorylates recombinant pp90rsk in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1868–1874. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung J., Kuo C. J., Crabtree G. R., Blenis J. Rapamycin-FKBP specifically blocks growth-dependent activation of and signaling by the 70 kd S6 protein kinases. Cell. 1992 Jun 26;69(7):1227–1236. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90643-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung J., Pelech S. L., Blenis J. Mitogen-activated Swiss mouse 3T3 RSK kinases I and II are related to pp44mpk from sea star oocytes and participate in the regulation of pp90rsk activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4981–4985. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke M. P., Abraham K. M., Forbush K. A., Perlmutter R. M. Regulation of T cell receptor signaling by a src family protein-tyrosine kinase (p59fyn). Cell. 1991 Apr 19;65(2):281–291. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90162-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke M. P., Perlmutter R. M. Expression of a novel form of the fyn proto-oncogene in hematopoietic cells. New Biol. 1989 Oct;1(1):66–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews C. M., Alessandrini A. A., Erikson R. L. Mouse Erk-1 gene product is a serine/threonine protein kinase that has the potential to phosphorylate tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8845–8849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews C. M., Erikson R. L. Purification of a murine protein-tyrosine/threonine kinase that phosphorylates and activates the Erk-1 gene product: relationship to the fission yeast byr1 gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):8205–8209. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Arcangelo G., Halegoua S. A branched signaling pathway for nerve growth factor is revealed by Src-, Ras-, and Raf-mediated gene inductions. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3146–3155. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. J. The mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathway. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 15;268(20):14553–14556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dichter M. A., Tischler A. S., Greene L. A. Nerve growth factor-induced increase in electrical excitability and acetylcholine sensitivity of a rat pheochromocytoma cell line. Nature. 1977 Aug 11;268(5620):501–504. doi: 10.1038/268501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Featherstone C., Russell P. Fission yeast p107wee1 mitotic inhibitor is a tyrosine/serine kinase. Nature. 1991 Feb 28;349(6312):808–811. doi: 10.1038/349808a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giugni T. D., Chen K., Cohen S. Activation of a cytosolic serine protein kinase by epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):18988–18995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass D. B., Masaracchia R. A., Feramisco J. R., Kemp B. E. Isolation of phosphorylated peptides and proteins on ion exchange papers. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jul 1;87(2):566–575. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90707-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., Aletta J. M., Rukenstein A., Green S. H. PC12 pheochromocytoma cells: culture, nerve growth factor treatment, and experimental exploitation. Methods Enzymol. 1987;147:207–216. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)47111-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M. Protein kinase catalytic domain sequence database: identification of conserved features of primary structure and classification of family members. Methods Enzymol. 1991;200:38–62. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)00126-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempstead B. L., Martin-Zanca D., Kaplan D. R., Parada L. F., Chao M. V. High-affinity NGF binding requires coexpression of the trk proto-oncogene and the low-affinity NGF receptor. Nature. 1991 Apr 25;350(6320):678–683. doi: 10.1038/350678a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe L. R., Leevers S. J., Gómez N., Nakielny S., Cohen P., Marshall C. J. Activation of the MAP kinase pathway by the protein kinase raf. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):335–342. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90361-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell B. W., Afar D. E., Lew J., Douville E. M., Icely P. L., Gray D. A., Bell J. C. STY, a tyrosine-phosphorylating enzyme with sequence homology to serine/threonine kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):568–572. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Karin M. The regulation of transcription by phosphorylation. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):375–387. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90162-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaggi R., Salmons B., Muellener D., Groner B. The v-mos and H-ras oncogene expression represses glucocorticoid hormone-dependent transcription from the mouse mammary tumor virus LTR. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2609–2616. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04541.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaiswal R. K., Moodie S. A., Wolfman A., Landreth G. E. The mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade is activated by B-Raf in response to nerve growth factor through interaction with p21ras. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;14(10):6944–6953. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.10.6944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaiswal R. K., Murphy M. B., Landreth G. E. Identification and characterization of a nerve growth factor-stimulated mitogen-activated protein kinase activator in PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 5;268(10):7055–7063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. W., Smith K. A. Molecular cloning of a novel human cdc2/CDC28-like protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3402–3407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Hempstead B. L., Martin-Zanca D., Chao M. V., Parada L. F. The trk proto-oncogene product: a signal transducing receptor for nerve growth factor. Science. 1991 Apr 26;252(5005):554–558. doi: 10.1126/science.1850549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Martin-Zanca D., Parada L. F. Tyrosine phosphorylation and tyrosine kinase activity of the trk proto-oncogene product induced by NGF. Nature. 1991 Mar 14;350(6314):158–160. doi: 10.1038/350158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R., Jing S. Q., Nanduri V., O'Rourke E., Barbacid M. The trk proto-oncogene encodes a receptor for nerve growth factor. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):189–197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90419-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kremer N. E., D'Arcangelo G., Thomas S. M., DeMarco M., Brugge J. S., Halegoua S. Signal transduction by nerve growth factor and fibroblast growth factor in PC12 cells requires a sequence of src and ras actions. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(3):809–819. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.3.809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakis J. M., App H., Zhang X. F., Banerjee P., Brautigan D. L., Rapp U. R., Avruch J. Raf-1 activates MAP kinase-kinase. Nature. 1992 Jul 30;358(6385):417–421. doi: 10.1038/358417a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landreth G. E., Smith D. S., McCabe C., Gittinger C. Characterization of a nerve growth factor-stimulated protein kinase in PC12 cells which phosphorylates microtubule-associated protein 2 and pp250. J Neurochem. 1990 Aug;55(2):514–523. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb04165.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane H. A., Fernandez A., Lamb N. J., Thomas G. p70s6k function is essential for G1 progression. Nature. 1993 May 13;363(6425):170–172. doi: 10.1038/363170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange-Carter C. A., Pleiman C. M., Gardner A. M., Blumer K. J., Johnson G. L. A divergence in the MAP kinase regulatory network defined by MEK kinase and Raf. Science. 1993 Apr 16;260(5106):315–319. doi: 10.1126/science.8385802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg R. A., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. Dual-specificity protein kinases: will any hydroxyl do? Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Mar;17(3):114–119. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90248-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moodie S. A., Willumsen B. M., Weber M. J., Wolfman A. Complexes of Ras.GTP with Raf-1 and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase. Science. 1993 Jun 11;260(5114):1658–1661. doi: 10.1126/science.8503013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Sugino K., Kurosawa N., Sawai M., Takio K., Eto Y., Iwashita S., Muramatsu M., Titani K., Sugino H. Isolation and characterization of activin receptor from mouse embryonal carcinoma cells. Identification of its serine/threonine/tyrosine protein kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 15;267(26):18924–18928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker L. L., Atherton-Fessler S., Lee M. S., Ogg S., Falk J. L., Swenson K. I., Piwnica-Worms H. Cyclin promotes the tyrosine phosphorylation of p34cdc2 in a wee1+ dependent manner. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1255–1263. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08067.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray L. B., Sturgill T. W. Insulin-stimulated microtubule-associated protein kinase is phosphorylated on tyrosine and threonine in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3753–3757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins D. J., Cheng M., Zhen E., Vanderbilt C. A., Feig L. A., Cobb M. H. Evidence for a Ras-dependent extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase (ERK) cascade. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6924–6928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozakis-Adcock M., McGlade J., Mbamalu G., Pelicci G., Daly R., Li W., Batzer A., Thomas S., Brugge J., Pelicci P. G. Association of the Shc and Grb2/Sem5 SH2-containing proteins is implicated in activation of the Ras pathway by tyrosine kinases. Nature. 1992 Dec 17;360(6405):689–692. doi: 10.1038/360689a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rukenstein A., Rydel R. E., Greene L. A. Multiple agents rescue PC12 cells from serum-free cell death by translation- and transcription-independent mechanisms. J Neurosci. 1991 Aug;11(8):2552–2563. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-08-02552.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Nurse P. Negative regulation of mitosis by wee1+, a gene encoding a protein kinase homolog. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):559–567. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90458-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Growth factor signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Neuron. 1992 Sep;9(3):383–391. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90177-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokoe D., Campbell D. G., Nakielny S., Hidaka H., Leevers S. J., Marshall C., Cohen P. MAPKAP kinase-2; a novel protein kinase activated by mitogen-activated protein kinase. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):3985–3994. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05492.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgill T. W., Ray L. B., Erikson E., Maller J. L. Insulin-stimulated MAP-2 kinase phosphorylates and activates ribosomal protein S6 kinase II. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):715–718. doi: 10.1038/334715a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S., Hattori S., Kurata T., Nagashima K., Fukui Y., Nakamura S., Matsuda M. Both the SH2 and SH3 domains of human CRK protein are required for neuronal differentiation of PC12 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):4409–4415. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.4409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor L. K., Marshak D. R., Landreth G. E. Identification of a nerve growth factor- and epidermal growth factor-regulated protein kinase that phosphorylates the protooncogene product c-Fos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):368–372. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas S. M., DeMarco M., D'Arcangelo G., Halegoua S., Brugge J. S. Ras is essential for nerve growth factor- and phorbol ester-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of MAP kinases. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1031–1040. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90075-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Aelst L., Barr M., Marcus S., Polverino A., Wigler M. Complex formation between RAS and RAF and other protein kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6213–6217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood K. W., Qi H., D'Arcangelo G., Armstrong R. C., Roberts T. M., Halegoua S. The cytoplasmic raf oncogene induces a neuronal phenotype in PC12 cells: a potential role for cellular raf kinases in neuronal growth factor signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5016–5020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood K. W., Sarnecki C., Roberts T. M., Blenis J. ras mediates nerve growth factor receptor modulation of three signal-transducing protein kinases: MAP kinase, Raf-1, and RSK. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1041–1050. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90076-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






