Abstract
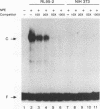
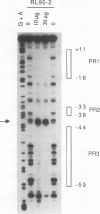
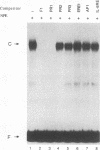
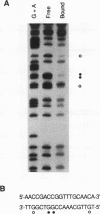
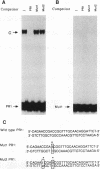
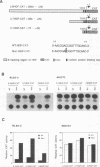
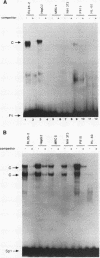
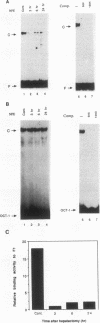
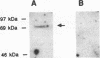
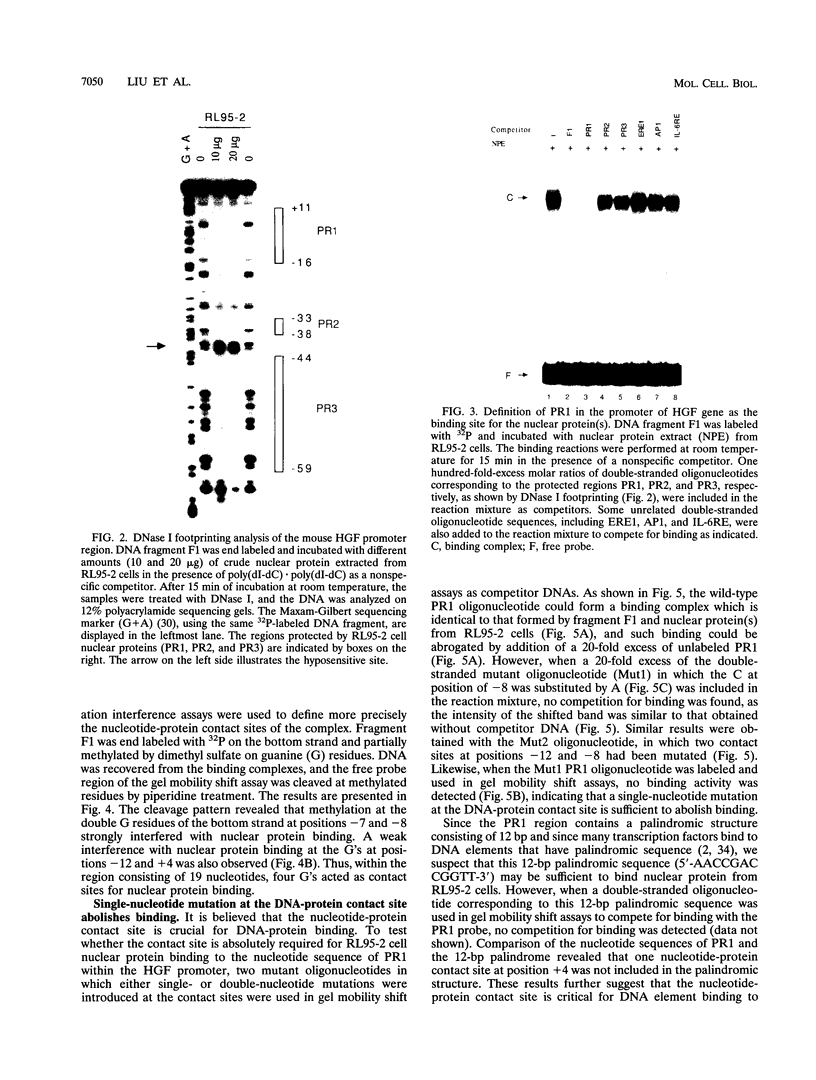
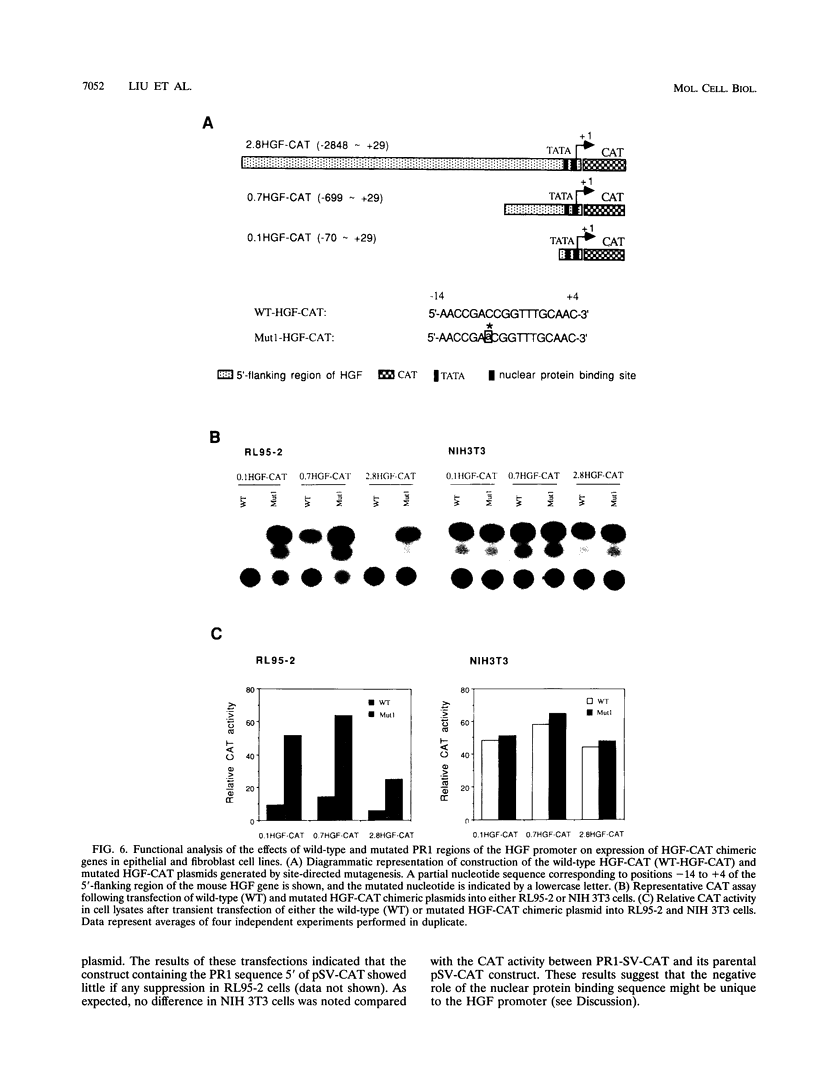
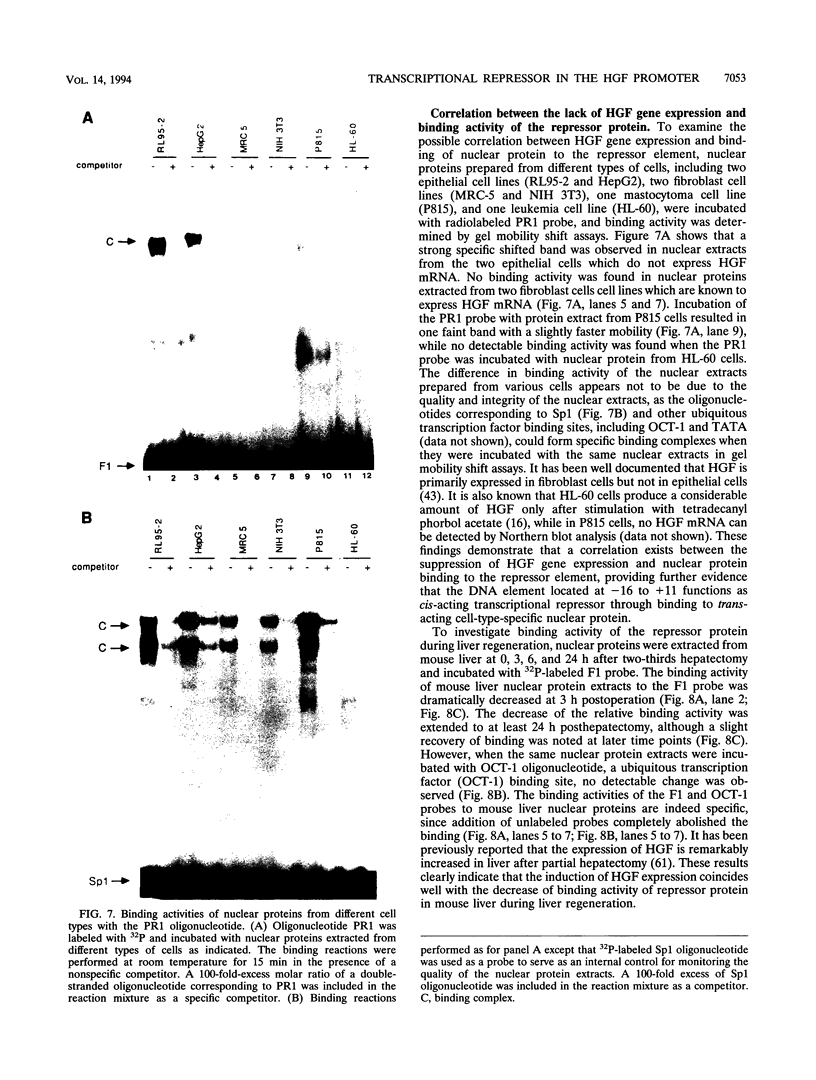
Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), a cytokine with multiple functions, exhibits cell-type-specific as well as cytokine- and steroid hormone-regulated expression. The HGF gene is known to be expressed predominately in mesenchymal but not in epithelial cells. In this study, we report the identification of a cell-type-specific transcriptional repressor in the promoter region of the mouse HGF gene, which is evidently responsible for the suppression of HGF expression in epithelial cells. Gel mobility shift assays and DNase I footprinting studies revealed that a 27-bp element (-16 to +11) around the transcription initiation site is responsible for the binding of a nuclear protein which is present in epithelial but not in mesenchymally derived cells. Further analysis of the binding activity of the DNA region with nuclear protein revealed that an approximately 19-bp sequence containing a unique palindromic structure (5'-AACCGACCGGTT-3') overlapped by a CAP box is essential for binding. Substitution of a single base (the contact site) within this region by site-directed mutagenesis resulted in total abrogation of the binding of the nuclear protein and a concomitant increase in the transcriptional activity of various lengths of HGF-chloramphenicol acetyltransferase fused genes when transfected into the epithelial cell line RL95-2 but not the mesenchymal cell line NIH 3T3. Southwestern (DNA-protein) analyses revealed that the nuclear protein which binds to this repressor element is a single polypeptide of approximately 70 kDa. Analysis of the nuclear extract prepared from regenerating mouse liver at various times after two-thirds partial hepatectomy by gel mobility shift assay revealed a substantial reduction (more than 75% within 3 h) in the binding of the repressor to its cognate binding site. Our results suggest that a cis-acting transcriptional repressor in the promoter region of the mouse HGF gene is involved in cell-type-specific regulation through binding to its cognate trans-acting protein which exists in epithelial cells but is absent in fibroblast cells.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baniahmad A., Steiner C., Köhne A. C., Renkawitz R. Modular structure of a chicken lysozyme silencer: involvement of an unusual thyroid hormone receptor binding site. Cell. 1990 May 4;61(3):505–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90532-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benezra R., Davis R. L., Lockshon D., Turner D. L., Weintraub H. The protein Id: a negative regulator of helix-loop-helix DNA binding proteins. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):49–59. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90214-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottaro D. P., Rubin J. S., Faletto D. L., Chan A. M., Kmiecik T. E., Vande Woude G. F., Aaronson S. A. Identification of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor as the c-met proto-oncogene product. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):802–804. doi: 10.1126/science.1846706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski S. The basics of basal transcription by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1994 Apr 8;77(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90226-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussolino F., Di Renzo M. F., Ziche M., Bocchietto E., Olivero M., Naldini L., Gaudino G., Tamagnone L., Coffer A., Comoglio P. M. Hepatocyte growth factor is a potent angiogenic factor which stimulates endothelial cell motility and growth. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(3):629–641. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.3.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao S. X., Gutman P. D., Dave H. P., Schechter A. N. Identification of a transcriptional silencer in the 5'-flanking region of the human epsilon-globin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5306–5309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Defrances M. C., Wolf H. K., Michalopoulos G. K., Zarnegar R. The presence of hepatocyte growth factor in the developing rat. Development. 1992 Oct;116(2):387–395. doi: 10.1242/dev.116.2.387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descombes P., Schibler U. A liver-enriched transcriptional activator protein, LAP, and a transcriptional inhibitory protein, LIP, are translated from the same mRNA. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):569–579. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90531-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond M. I., Miner J. N., Yoshinaga S. K., Yamamoto K. R. Transcription factor interactions: selectors of positive or negative regulation from a single DNA element. Science. 1990 Sep 14;249(4974):1266–1272. doi: 10.1126/science.2119054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao E., Alcorn J. L., Mendelson C. R. Identification of enhancers in the 5'-flanking region of the rabbit surfactant protein A (SP-A) gene and characterization of their binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 15;268(26):19697–19709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garzon R. J., Zehner Z. E. Multiple silencer elements are involved in regulating the chicken vimentin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;14(2):934–943. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.2.934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodbourn S., Maniatis T. Overlapping positive and negative regulatory domains of the human beta-interferon gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1447–1451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou X., Johnson A. C., Rosner M. R. Identification of an epidermal growth factor receptor transcriptional repressor. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 11;269(6):4307–4312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa M., Osada S., Okuda A., Muramatsu M. Silencer binding proteins function on multiple cis-elements in the glutathione transferase P gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 11;19(1):5–10. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.1.5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inaba M., Koyama H., Hino M., Okuno S., Terada M., Nishizawa Y., Nishino T., Morii H. Regulation of release of hepatocyte growth factor from human promyelocytic leukemia cells, HL-60, by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3, 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate, and dibutyryl cyclic adenosine monophosphate. Blood. 1993 Jul 1;82(1):53–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inostroza J. A., Mermelstein F. H., Ha I., Lane W. S., Reinberg D. Dr1, a TATA-binding protein-associated phosphoprotein and inhibitor of class II gene transcription. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):477–489. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90172-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson F. B., Krasnow M. A. Differential regulation of transcription preinitiation complex assembly by activator and repressor homeo domain proteins. Genes Dev. 1992 Nov;6(11):2177–2189. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.11.2177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kan M., Zhang G. H., Zarnegar R., Michalopoulos G., Myoken Y., McKeehan W. L., Stevens J. I. Hepatocyte growth factor/hepatopoietin A stimulates the growth of rat kidney proximal tubule epithelial cells (RPTE), rat nonparenchymal liver cells, human melanoma cells, mouse keratinocytes and stimulates anchorage-independent growth of SV-40 transformed RPTE. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jan 15;174(1):331–337. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90524-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr L. D., Inoue J., Davis N., Link E., Baeuerle P. A., Bose H. R., Jr, Verma I. M. The rel-associated pp40 protein prevents DNA binding of Rel and NF-kappa B: relationship with I kappa B beta and regulation by phosphorylation. Genes Dev. 1991 Aug;5(8):1464–1476. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.8.1464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kono S., Nagaike M., Matsumoto K., Nakamura T. Marked induction of hepatocyte growth factor mRNA in intact kidney and spleen in response to injury of distant organs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jul 31;186(2):991–998. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)90844-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li-Weber M., Eder A., Krafft-Czepa H., Krammer P. H. T cell-specific negative regulation of transcription of the human cytokine IL-4. J Immunol. 1992 Mar 15;148(6):1913–1918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y., Bell A. W., Michalopoulos G. K., Zarnegar R. The mouse hepatocyte growth factor-encoding gene: structural organization and evolutionary conservation. Gene. 1994 Jul 8;144(2):179–187. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90376-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y., Michalopoulos G. K., Zarnegar R. Structural and functional characterization of the mouse hepatocyte growth factor gene promoter. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 11;269(6):4152–4160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y., Yang N., Teng C. T. COUP-TF acts as a competitive repressor for estrogen receptor-mediated activation of the mouse lactoferrin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1836–1846. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher J. J. Cell-specific expression of hepatocyte growth factor in liver. Upregulation in sinusoidal endothelial cells after carbon tetrachloride. J Clin Invest. 1993 May;91(5):2244–2252. doi: 10.1172/JCI116451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto K., Tajima H., Okazaki H., Nakamura T. Negative regulation of hepatocyte growth factor gene expression in human lung fibroblasts and leukemic cells by transforming growth factor-beta 1 and glucocorticoids. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 15;267(35):24917–24920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisterernst M., Roeder R. G. Family of proteins that interact with TFIID and regulate promoter activity. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):557–567. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90530-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merino A., Madden K. R., Lane W. S., Champoux J. J., Reinberg D. DNA topoisomerase I is involved in both repression and activation of transcription. Nature. 1993 Sep 16;365(6443):227–232. doi: 10.1038/365227a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalopoulos G. K., Zarnegav R. Hepatocyte growth factor. Hepatology. 1992 Jan;15(1):149–155. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840150125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazawa K., Kitamura A., Kitamura N. Structural organization and the transcription initiation site of the human hepatocyte growth factor gene. Biochemistry. 1991 Sep 24;30(38):9170–9176. doi: 10.1021/bi00102a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montesano R., Matsumoto K., Nakamura T., Orci L. Identification of a fibroblast-derived epithelial morphogen as hepatocyte growth factor. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):901–908. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90363-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Teramoto H., Ichihara A. Purification and characterization of a growth factor from rat platelets for mature parenchymal hepatocytes in primary cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6489–6493. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naldini L., Vigna E., Narsimhan R. P., Gaudino G., Zarnegar R., Michalopoulos G. K., Comoglio P. M. Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) stimulates the tyrosine kinase activity of the receptor encoded by the proto-oncogene c-MET. Oncogene. 1991 Apr;6(4):501–504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noji S., Tashiro K., Koyama E., Nohno T., Ohyama K., Taniguchi S., Nakamura T. Expression of hepatocyte growth factor gene in endothelial and Kupffer cells of damaged rat livers, as revealed by in situ hybridization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Nov 30;173(1):42–47. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81018-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okajima A., Miyazawa K., Kitamura N. Characterization of the promoter region of the rat hepatocyte-growth-factor/scatter-factor gene. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Apr 1;213(1):113–119. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17740.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okajima A., Miyazawa K., Kitamura N. Primary structure of rat hepatocyte growth factor and induction of its mRNA during liver regeneration following hepatic injury. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Oct 24;193(2):375–381. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19349.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rong S., Bodescot M., Blair D., Dunn J., Nakamura T., Mizuno K., Park M., Chan A., Aaronson S., Vande Woude G. F. Tumorigenicity of the met proto-oncogene and the gene for hepatocyte growth factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;12(11):5152–5158. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.11.5152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin J. S., Bottaro D. P., Aaronson S. A. Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor and its receptor, the c-met proto-oncogene product. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Dec 23;1155(3):357–371. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(93)90015-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvetti A., Lilienbaum A., Li Z., Paulin D., Gazzolo L. Identification of a negative element in the human vimentin promoter: modulation by the human T-cell leukemia virus type I Tax protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):89–97. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savagner P., Miyashita T., Yamada Y. Two silencers regulate the tissue-specific expression of the collagen II gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6669–6674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seki T., Hagiya M., Shimonishi M., Nakamura T., Shimizu S. Organization of the human hepatocyte growth factor-encoding gene. Gene. 1991 Jun 30;102(2):213–219. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90080-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiota G., Rhoads D. B., Wang T. C., Nakamura T., Schmidt E. V. Hepatocyte growth factor inhibits growth of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):373–377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg E., Meyer D., Weidner K. M., Birchmeier C. Scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor and its receptor, the c-met tyrosine kinase, can mediate a signal exchange between mesenchyme and epithelia during mouse development. J Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;123(1):223–235. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.1.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoker M., Gherardi E., Perryman M., Gray J. Scatter factor is a fibroblast-derived modulator of epithelial cell mobility. Nature. 1987 May 21;327(6119):239–242. doi: 10.1038/327239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tajima H., Matsumoto K., Nakamura T. Hepatocyte growth factor has potent anti-proliferative activity in various tumor cell lines. FEBS Lett. 1991 Oct 21;291(2):229–232. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81291-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamai K., Li K., Uitto J. Identification of a DNA-binding protein (keratinocyte transcriptional protein-1) recognizing a keratinocyte-specific regulatory element in the 230-kDa bullous pemphigoid antigen gene. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):493–502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura M., Arakaki N., Tsubouchi H., Takada H., Daikuhara Y. Enhancement of human hepatocyte growth factor production by interleukin-1 alpha and -1 beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha by fibroblasts in culture. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 15;268(11):8140–8145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R., Maniatis T. Transcriptional activation: a complex puzzle with few easy pieces. Cell. 1994 Apr 8;77(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90227-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uehara Y., Kitamura N. Expression of a human hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor cDNA in MDCK epithelial cells influences cell morphology, motility, and anchorage-independent growth. J Cell Biol. 1992 May;117(4):889–894. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.4.889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf H. K., Zarnegar R., Oliver L., Michalopoulos G. K. Hepatocyte growth factor in human placenta and trophoblastic disease. Am J Pathol. 1991 Apr;138(4):1035–1043. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagita K., Matsumoto K., Sekiguchi K., Ishibashi H., Niho Y., Nakamura T. Hepatocyte growth factor may act as a pulmotrophic factor on lung regeneration after acute lung injury. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 5;268(28):21212–21217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee C. J., DeFrances M. C., Bell A., Bowen W., Petersen B., Michalopoulos G. K., Zarnegar R. Expression and characterization of biologically active human hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) by insect cells infected with HGF-recombinant baculovirus. Biochemistry. 1993 Aug 10;32(31):7922–7931. doi: 10.1021/bi00082a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarnegar R., DeFrances M. C., Kost D. P., Lindroos P., Michalopoulos G. K. Expression of hepatocyte growth factor mRNA in regenerating rat liver after partial hepatectomy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 May 31;177(1):559–565. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)92020-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarnegar R., Michalopoulos G. Purification and biological characterization of human hepatopoietin A, a polypeptide growth factor for hepatocytes. Cancer Res. 1989 Jun 15;49(12):3314–3320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarnegar R., Muga S., Rahija R., Michalopoulos G. Tissue distribution of hepatopoietin-A: a heparin-binding polypeptide growth factor for hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1252–1256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Klundert F. A., van Eldik G. J., Pieper F. R., Jansen H. J., Bloemendal H. Identification of two silencers flanking an AP-1 enhancer in the vimentin promoter. Gene. 1992 Dec 15;122(2):337–343. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90223-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]