Abstract
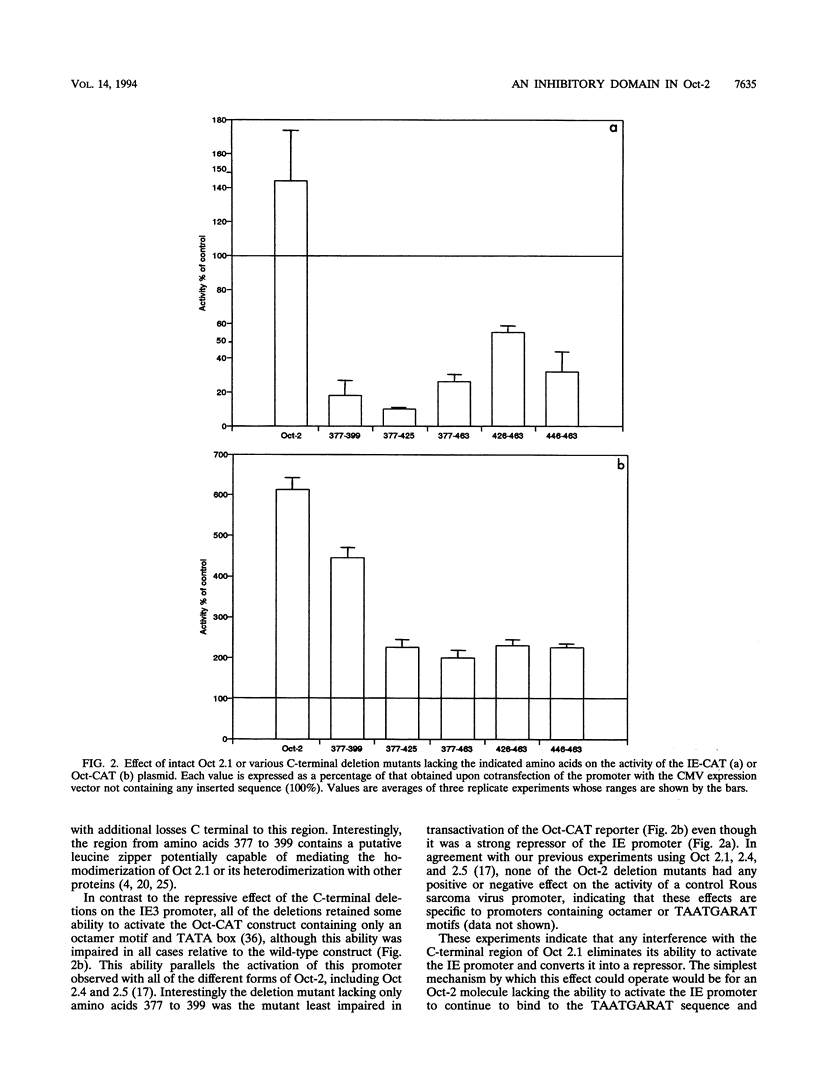
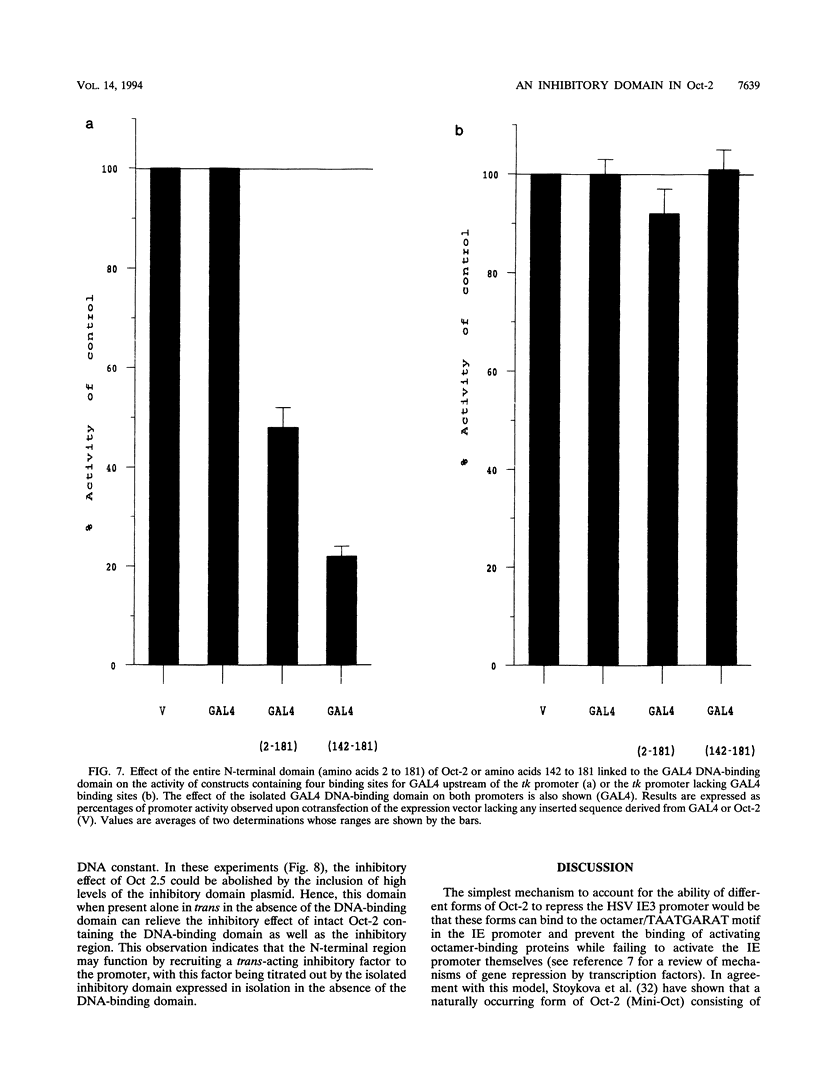
The B-cell form of the Oct-2 transcription factor Oct 2.1 can activate the herpes simplex virus immediate-early gene 3 (IE3) promoter, whereas the neuronally expressed Oct 2.4 and 2.5 forms of the protein, which contain a different C terminus, can repress this promoter. Here we show that partial or full deletion of the C terminus of Oct 2.1 in the presence of an intact N terminus results in a protein which can strongly repress the IE3 promoter. In contrast, deletion of the entire N terminus or a short region within it leaving the C terminus intact results in a very strong activator. Deletion of both N and C termini leaving only the isolated POU domain generates only a very weak repressor. The N-terminal region defined in this way can repress a heterologous promoter when linked to the DNA-binding domain of the GAL4 factor, indicating that it can function as an independent inhibitory domain. These results indicate that a specific region within the N terminus common to Oct 2.1, 2.4, and 2.5 plays a critical role in the ability of neuronally expressed forms of Oct-2 to repress the IE3 promoter but can do so only when the C-terminal region of Oct 2.1 is altered or deleted.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abken H., Reifenrath B. A procedure to standardize CAT reporter gene assay. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jul 11;20(13):3527–3527. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.13.3527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Annweiler A., Müller-Immerglück M., Wirth T. Oct2 transactivation from a remote enhancer position requires a B-cell-restricted activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):3107–3116. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.3107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerc R. G., Corcoran L. M., LeBowitz J. H., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. The B-cell-specific Oct-2 protein contains POU box- and homeo box-type domains. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1570–1581. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson S. J., Yoon S. O., Chikaraishi D. M., Lillycrop K. A., Latchman D. S. The Oct-2 transcription factor represses tyrosine hydroxylase expression via a heptamer TAATGARAT-like motif in the gene promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Mar 25;22(6):1023–1028. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.6.1023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent C. L., Lillycrop K. A., Estridge J. K., Thomas N. S., Latchman D. S. The B-cell and neuronal forms of the octamer-binding protein Oct-2 differ in DNA-binding specificity and functional activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):3925–3930. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.3925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerster T., Balmaceda C. G., Roeder R. G. The cell type-specific octamer transcription factor OTF-2 has two domains required for the activation of transcription. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1635–1643. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08283.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodbourn S. Negative regulation of transcriptional initiation in eukaryotes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jun 1;1032(1):53–77. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(90)90012-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han K., Manley J. L. Transcriptional repression by the Drosophila even-skipped protein: definition of a minimal repression domain. Genes Dev. 1993 Mar;7(3):491–503. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.3.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatzopoulos A. K., Stoykova A. S., Erselius J. R., Goulding M., Neuman T., Gruss P. Structure and expression of the mouse Oct2a and Oct2b, two differentially spliced products of the same gene. Development. 1990 Jun;109(2):349–362. doi: 10.1242/dev.109.2.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He X., Treacy M. N., Simmons D. M., Ingraham H. A., Swanson L. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Expression of a large family of POU-domain regulatory genes in mammalian brain development. Nature. 1989 Jul 6;340(6228):35–41. doi: 10.1038/340035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp L. M., Dent C. L., Latchman D. S. Octamer motif mediates transcriptional repression of HSV immediate-early genes and octamer-containing cellular promoters in neuronal cells. Neuron. 1990 Feb;4(2):215–222. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90096-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latchman D. S. Current status review: molecular biology of herpes simplex virus latency. J Exp Pathol (Oxford) 1990 Feb;71(1):133–141. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis E. J., Harrington C. A., Chikaraishi D. M. Transcriptional regulation of the tyrosine hydroxylase gene by glucocorticoid and cyclic AMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3550–3554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillycrop K. A., Dent C. L., Wheatley S. C., Beech M. N., Ninkina N. N., Wood J. N., Latchman D. S. The octamer-binding protein Oct-2 represses HSV immediate-early genes in cell lines derived from latently infectable sensory neurons. Neuron. 1991 Sep;7(3):381–390. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90290-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillycrop K. A., Estridge J. K., Latchman D. S. The octamer binding protein Oct-2 inhibits transactivation of the herpes simplex virus immediate-early genes by the virion protein Vmw65. Virology. 1993 Oct;196(2):888–891. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillycrop K. A., Latchman D. S. Alternative splicing of the Oct-2 transcription factor RNA is differentially regulated in neuronal cells and B cells and results in protein isoforms with opposite effects on the activity of octamer/TAATGARAT-containing promoters. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 15;267(35):24960–24965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACPHERSON I., STOKER M. Polyoma transformation of hamster cell clones--an investigation of genetic factors affecting cell competence. Virology. 1962 Feb;16:147–151. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90290-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Immerglück M. M., Schaffner W., Matthias P. Transcription factor Oct-2A contains functionally redundant activating domains and works selectively from a promoter but not from a remote enhancer position in non-lymphoid (HeLa) cells. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1625–1634. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08282.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M. M., Ruppert S., Schaffner W., Matthias P. A cloned octamer transcription factor stimulates transcription from lymphoid-specific promoters in non-B cells. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):544–551. doi: 10.1038/336544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Goding C. R. Herpes simplex virus regulatory elements and the immunoglobulin octamer domain bind a common factor and are both targets for virion transactivation. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):435–445. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80036-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M., Frame M. C., Campbell M. E. A complex formed between cell components and an HSV structural polypeptide binds to a viral immediate early gene regulatory DNA sequence. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):425–434. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Ptashne M. A vector for expressing GAL4(1-147) fusions in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7539–7539. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidereit C., Cromlish J. A., Gerster T., Kawakami K., Balmaceda C. G., Currie R. A., Roeder R. G. A human lymphoid-specific transcription factor that activates immunoglobulin genes is a homoeobox protein. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):551–557. doi: 10.1038/336551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R., Hatzopoulos A. K., Balling R., Suzuki N., Gruss P. A family of octamer-specific proteins present during mouse embryogenesis: evidence for germline-specific expression of an Oct factor. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2543–2550. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08392.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R., Ruppert S., Suzuki N., Chowdhury K., Gruss P. New type of POU domain in germ line-specific protein Oct-4. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):435–439. doi: 10.1038/344435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Y., Seto E., Chang L. S., Shenk T. Transcriptional repression by YY1, a human GLI-Krüppel-related protein, and relief of repression by adenovirus E1A protein. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):377–388. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90189-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Sen R., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. A nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence motif in transcriptional control elements of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):154–158. doi: 10.1038/319154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudt L. M., Singh H., Sen R., Wirth T., Sharp P. A., Baltimore D. A lymphoid-specific protein binding to the octamer motif of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):640–643. doi: 10.1038/323640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoykova A. S., Sterrer S., Erselius J. R., Hatzopoulos A. K., Gruss P. Mini-Oct and Oct-2c: two novel, functionally diverse murine Oct-2 gene products are differentially expressed in the CNS. Neuron. 1992 Mar;8(3):541–558. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90282-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Herr W. Differential transcriptional activation by Oct-1 and Oct-2: interdependent activation domains induce Oct-2 phosphorylation. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):375–386. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90589-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheatley S. C., Dent C. L., Wood J. N., Latchman D. S. A cellular factor binding to the TAATGARAT DNA sequence prevents the expression of the HSV immediate-early genes following infection of nonpermissive cell lines derived from dorsal root ganglion neurons. Exp Cell Res. 1991 May;194(1):78–82. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90132-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth T., Priess A., Annweiler A., Zwilling S., Oeler B. Multiple Oct2 isoforms are generated by alternative splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 11;19(1):43–51. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth T., Staudt L., Baltimore D. An octamer oligonucleotide upstream of a TATA motif is sufficient for lymphoid-specific promoter activity. Nature. 1987 Sep 10;329(6135):174–178. doi: 10.1038/329174a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. N., Bevan S. J., Coote P. R., Dunn P. M., Harmar A., Hogan P., Latchman D. S., Morrison C., Rougon G., Theveniau M. Novel cell lines display properties of nociceptive sensory neurons. Proc Biol Sci. 1990 Sep 22;241(1302):187–194. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1990.0084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]