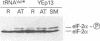Abstract
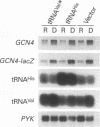
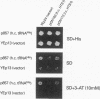
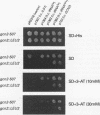
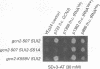
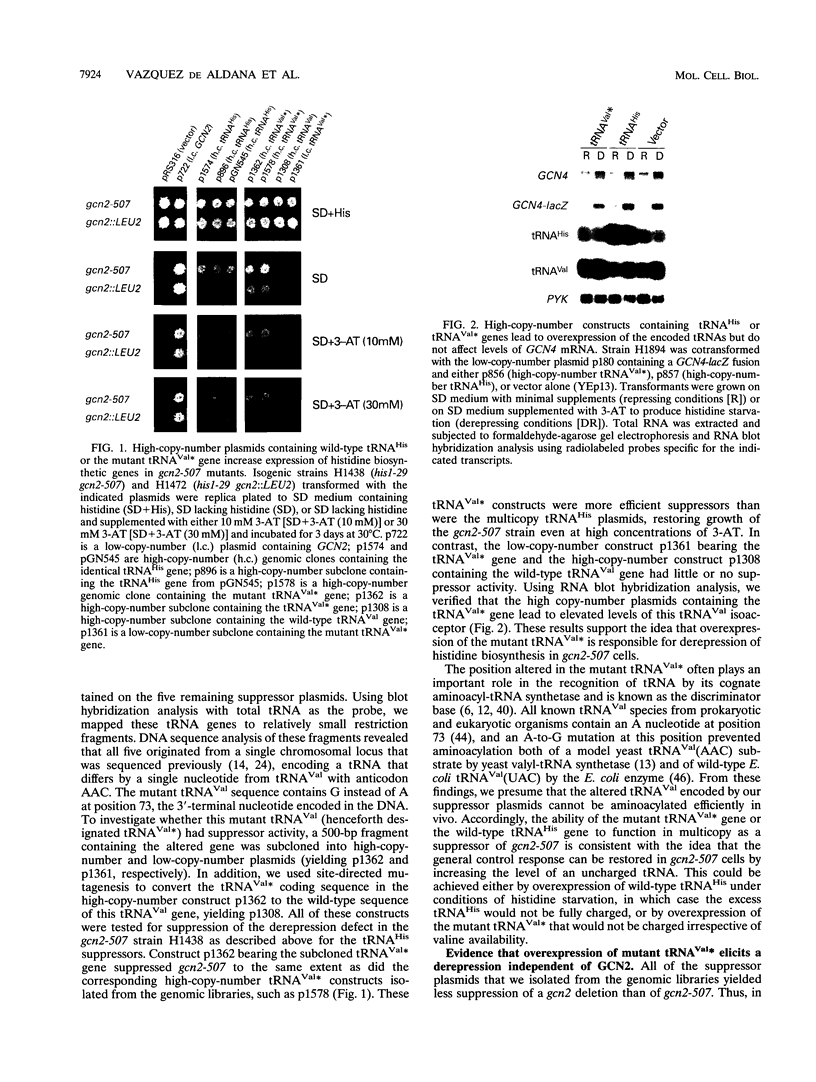
GCN2 is a protein kinase that stimulates translation of GCN4 mRNA in amino acid-starved cells by phosphorylating the alpha subunit of translation initiation factor 2 (eIL-2). We isolated multicopy plasmids that overcome the defective derepression of GCN4 and its target genes caused by the leaky mutation gcn2-507. One class of plasmids contained tRNA(His) genes and conferred efficient suppression only when cells were starved for histidine; these plasmids suppressed a gcn2 deletion much less efficiently than they suppressed gcn2-507. This finding indicates that the reduction in GCN4 expression caused by gcn2-507 can be overcome by elevating tRNA(His) expression under conditions in which the excess tRNA cannot be fully aminoacylated. The second class of suppressor plasmids all carried the same gene encoding a mutant form of tRNA(Val) (AAC) with an A-to-G transition at the 3' encoded nucleotide, a mutation shown previously to reduce aminoacylation of tRNA(Val) in vitro. In contrast to the wild-type tRNA(His) genes, the mutant tRNA(Val) gene efficiently suppressed a gcn2 deletion, and this suppression was independent of the phosphorylation site on eIF-2 alpha (Ser-51). Overexpression of the mutant tRNA(Val) did, however, stimulate GCN4 expression at the translational level. We propose that the multicopy mutant tRNA(Val) construct leads to an accumulation of uncharged tRNA(Val) that derepresses GCN4 translation through a pathway that does not involve GCN2 or eIF-2 alpha phosphorylation. This GCN2-independent pathway was also stimulated to a lesser extent by the multicopy tRNA(His) constructs in histidine-deprived cells. Because the mutant tRNA(Val) exacerbated the slow-growth phenotype associated with eIF-2 alpha hyperphosphorylation by an activated GCN2c kinase, we suggest that the GCN2-independent derepression mechanism involves down-regulation of eIF-2 activity.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boeke J. D., Trueheart J., Natsoulis G., Fink G. R. 5-Fluoroorotic acid as a selective agent in yeast molecular genetics. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:164–175. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54076-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushman J. L., Asuru A. I., Matts R. L., Hinnebusch A. G. Evidence that GCD6 and GCD7, translational regulators of GCN4, are subunits of the guanine nucleotide exchange factor for eIF-2 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1920–1932. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Botstein D. Two differentially regulated mRNAs with different 5' ends encode secreted with intracellular forms of yeast invertase. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90384-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cigan A. M., Bushman J. L., Boal T. R., Hinnebusch A. G. A protein complex of translational regulators of GCN4 mRNA is the guanine nucleotide-exchange factor for translation initiation factor 2 in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5350–5354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cigan A. M., Pabich E. K., Donahue T. F. Mutational analysis of the HIS4 translational initiator region in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;8(7):2964–2975. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.7.2964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cusack S., Berthet-Colominas C., Härtlein M., Nassar N., Leberman R. A second class of synthetase structure revealed by X-ray analysis of Escherichia coli seryl-tRNA synthetase at 2.5 A. Nature. 1990 Sep 20;347(6290):249–255. doi: 10.1038/347249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dever T. E., Chen J. J., Barber G. N., Cigan A. M., Feng L., Donahue T. F., London I. M., Katze M. G., Hinnebusch A. G. Mammalian eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha kinases functionally substitute for GCN2 protein kinase in the GCN4 translational control mechanism of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4616–4620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dever T. E., Feng L., Wek R. C., Cigan A. M., Donahue T. F., Hinnebusch A. G. Phosphorylation of initiation factor 2 alpha by protein kinase GCN2 mediates gene-specific translational control of GCN4 in yeast. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):585–596. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90193-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dholakia J. N., Wahba A. J. Phosphorylation of the guanine nucleotide exchange factor from rabbit reticulocytes regulates its activity in polypeptide chain initiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):51–54. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelberg D., Klein C., Martinetto H., Struhl K., Karin M. The UV response involving the Ras signaling pathway and AP-1 transcription factors is conserved between yeast and mammals. Cell. 1994 May 6;77(3):381–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90153-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriani G., Delarue M., Poch O., Gangloff J., Moras D. Partition of tRNA synthetases into two classes based on mutually exclusive sets of sequence motifs. Nature. 1990 Sep 13;347(6289):203–206. doi: 10.1038/347203a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frugier M., Florentz C., Giegé R. Anticodon-independent aminoacylation of an RNA minihelix with valine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):3990–3994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.3990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gokhman I., Zamir A. The nucleotide sequence of the ferrochelatase and tRNA(val) gene region from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 25;18(20):6130–6130. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.20.6130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershey J. W. Translational control in mammalian cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:717–755. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.003441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnebusch A. G. A hierarchy of trans-acting factors modulates translation of an activator of amino acid biosynthetic genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2349–2360. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnebusch A. G. Evidence for translational regulation of the activator of general amino acid control in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6442–6446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnebusch A. G., Fink G. R. Positive regulation in the general amino acid control of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5374–5378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnebusch A. G., Fink G. R. Repeated DNA sequences upstream from HIS1 also occur at several other co-regulated genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):5238–5247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki G., Fraenkel D. G. Cloning of yeast glycolysis genes by complementation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Oct 15;108(3):1107–1122. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)92114-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupitza G., Thireos G. Translational activation of GCN4 mRNA in a cell-free system is triggered by uncharged tRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4375–4378. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labbe-Bois R. The ferrochelatase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Sequence, disruption, and expression of its structural gene HEM15. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 5;265(13):7278–7283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanker S., Bushman J. L., Hinnebusch A. G., Trachsel H., Mueller P. P. Autoregulation of the yeast lysyl-tRNA synthetase gene GCD5/KRS1 by translational and transcriptional control mechanisms. Cell. 1992 Aug 21;70(4):647–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90433-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucchini G., Hinnebusch A. G., Chen C., Fink G. R. Positive regulatory interactions of the HIS4 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;4(7):1326–1333. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.7.1326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messenguy F., Delforge J. Role of transfer ribonucleic acids in the regulation of several biosyntheses in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 16;67(2):335–339. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10696.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meussdoerffer F., Fink G. R. Structure and expression of two aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase genes from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6293–6299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller P. F., Hinnebusch A. G. Sequences that surround the stop codons of upstream open reading frames in GCN4 mRNA determine their distinct functions in translational control. Genes Dev. 1989 Aug;3(8):1217–1225. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.8.1217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller P. P., Hinnebusch A. G. Multiple upstream AUG codons mediate translational control of GCN4. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):201–207. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90384-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K. A., Tatchell K. The structure of transposable yeast mating type loci. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):753–764. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80051-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natsoulis G., Hilger F., Fink G. R. The HTS1 gene encodes both the cytoplasmic and mitochondrial histidine tRNA synthetases of S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):235–243. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90740-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negrutskii B. S., Deutscher M. P. A sequestered pool of aminoacyl-tRNA in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3601–3604. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parent S. A., Fenimore C. M., Bostian K. A. Vector systems for the expression, analysis and cloning of DNA sequences in S. cerevisiae. Yeast. 1985 Dec;1(2):83–138. doi: 10.1002/yea.320010202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez M., Wek R. C., Hinnebusch A. G. Ribosome association of GCN2 protein kinase, a translational activator of the GCN4 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3027–3036. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez M., Wek R. C., Vazquez de Aldana C. R., Jackson B. M., Freeman B., Hinnebusch A. G. Mutations activating the yeast eIF-2 alpha kinase GCN2: isolation of alleles altering the domain related to histidyl-tRNA synthetases. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5801–5815. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussou I., Thireos G., Hauge B. M. Transcriptional-translational regulatory circuit in Saccharomyces cerevisiae which involves the GCN4 transcriptional activator and the GCN2 protein kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2132–2139. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruff M., Krishnaswamy S., Boeglin M., Poterszman A., Mitschler A., Podjarny A., Rees B., Thierry J. C., Moras D. Class II aminoacyl transfer RNA synthetases: crystal structure of yeast aspartyl-tRNA synthetase complexed with tRNA(Asp). Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1682–1689. doi: 10.1126/science.2047877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprinzl M., Hartmann T., Weber J., Blank J., Zeidler R. Compilation of tRNA sequences and sequences of tRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989;17 (Suppl):r1–172. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.suppl.r1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K., Stinchcomb D. T., Scherer S., Davis R. W. High-frequency transformation of yeast: autonomous replication of hybrid DNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1035–1039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura K., Himeno H., Asahara H., Hasegawa T., Shimizu M. Identity determinants of E. coli tRNA(Val). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jun 14;177(2):619–623. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91833-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. W., Ott J., Eckstein F. The rapid generation of oligonucleotide-directed mutations at high frequency using phosphorothioate-modified DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 20;13(24):8765–8785. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.24.8765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzamarias D., Roussou I., Thireos G. Coupling of GCN4 mRNA translational activation with decreased rates of polypeptide chain initiation. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):947–954. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90333-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez de Aldana C. R., Hinnebusch A. G. Mutations in the GCD7 subunit of yeast guanine nucleotide exchange factor eIF-2B overcome the inhibitory effects of phosphorylated eIF-2 on translation initiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 May;14(5):3208–3222. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.5.3208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wek R. C., Cannon J. F., Dever T. E., Hinnebusch A. G. Truncated protein phosphatase GLC7 restores translational activation of GCN4 expression in yeast mutants defective for the eIF-2 alpha kinase GCN2. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5700–5710. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wek R. C., Jackson B. M., Hinnebusch A. G. Juxtaposition of domains homologous to protein kinases and histidyl-tRNA synthetases in GCN2 protein suggests a mechanism for coupling GCN4 expression to amino acid availability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4579–4583. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wek R. C., Ramirez M., Jackson B. M., Hinnebusch A. G. Identification of positive-acting domains in GCN2 protein kinase required for translational activation of GCN4 expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2820–2831. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh G. I., Proud C. G. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 is rapidly inactivated in response to insulin and phosphorylates eukaryotic initiation factor eIF-2B. Biochem J. 1993 Sep 15;294(Pt 3):625–629. doi: 10.1042/bj2940625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wente S. R., Rout M. P., Blobel G. A new family of yeast nuclear pore complex proteins. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(4):705–723. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.4.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams N. P., Hinnebusch A. G., Donahue T. F. Mutations in the structural genes for eukaryotic initiation factors 2 alpha and 2 beta of Saccharomyces cerevisiae disrupt translational control of GCN4 mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7515–7519. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimmer C., Doye V., Grandi P., Nehrbass U., Hurt E. C. A new subclass of nucleoporins that functionally interact with nuclear pore protein NSP1. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):5051–5061. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05612.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Rey F., Donahue T. F., Fink G. R. The histidine tRNA genes of yeast. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8175–8182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]