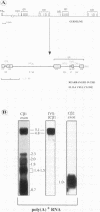
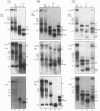
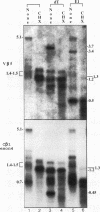
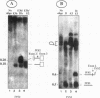
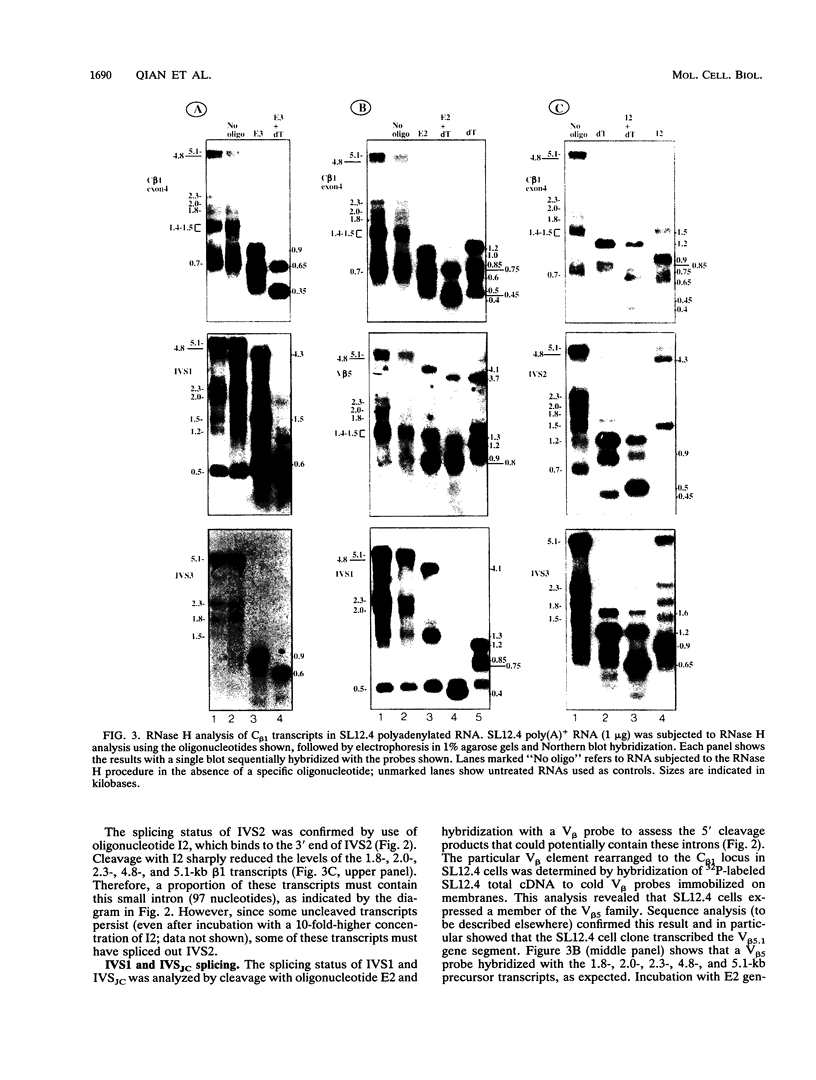
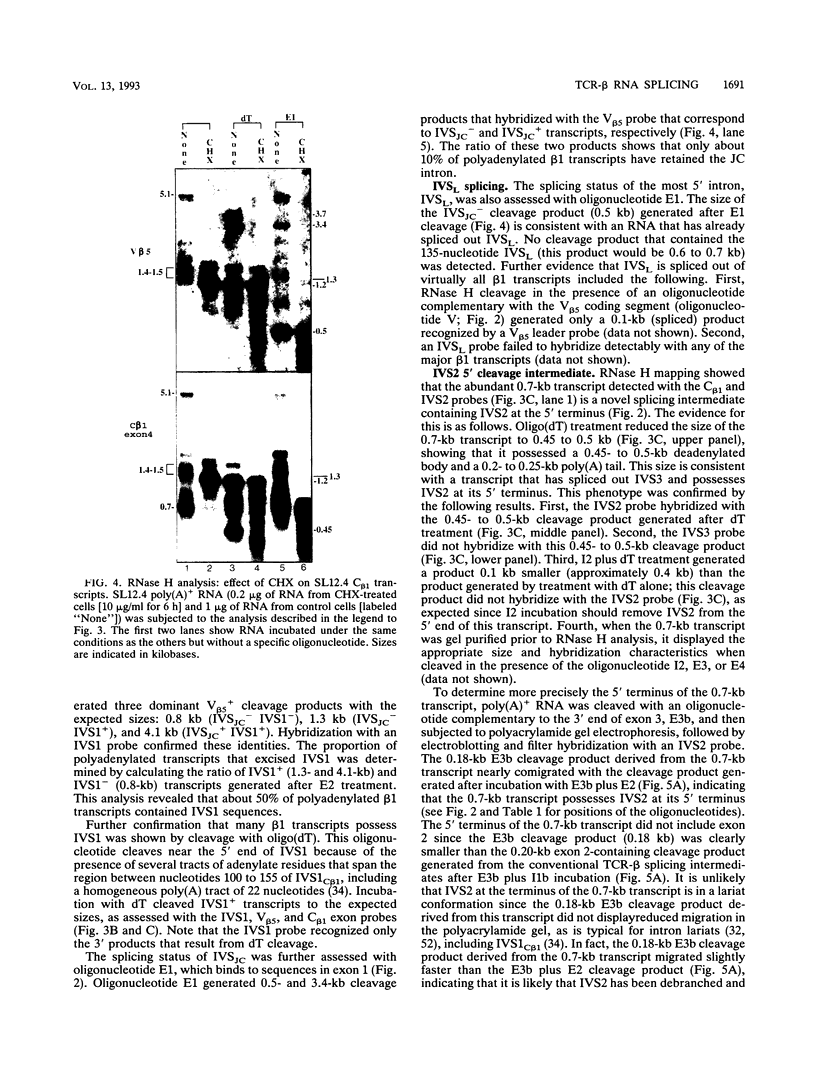
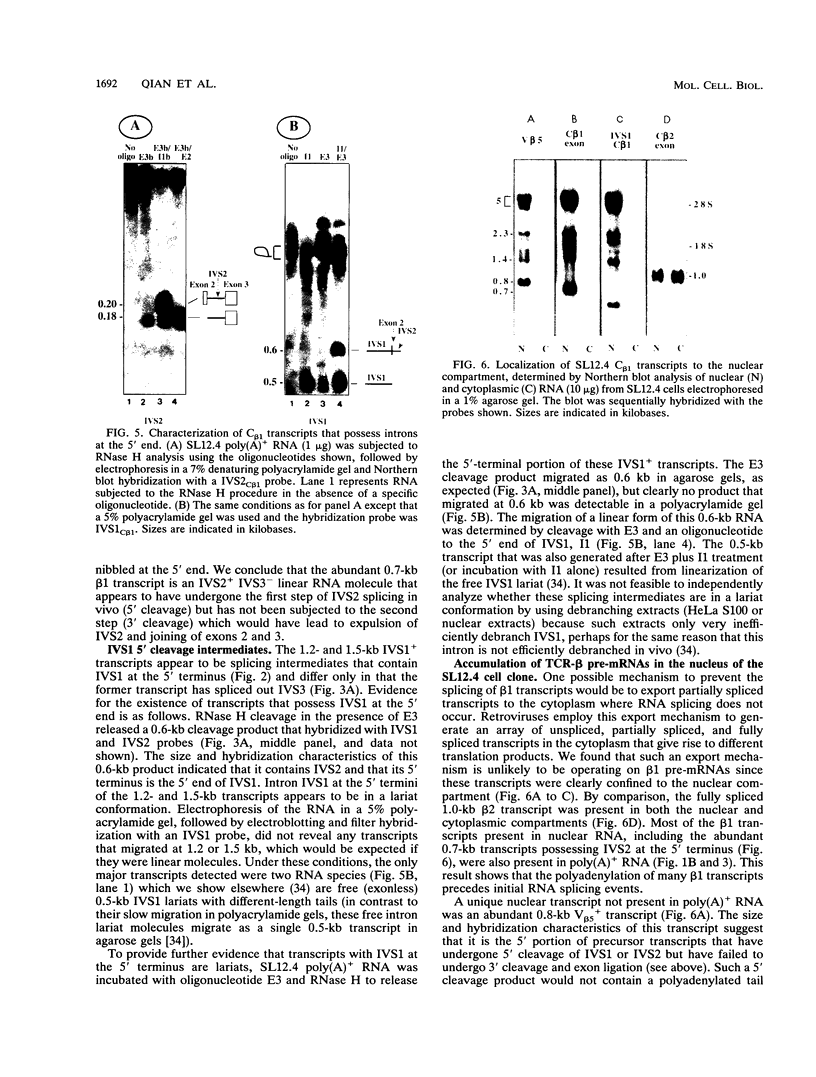
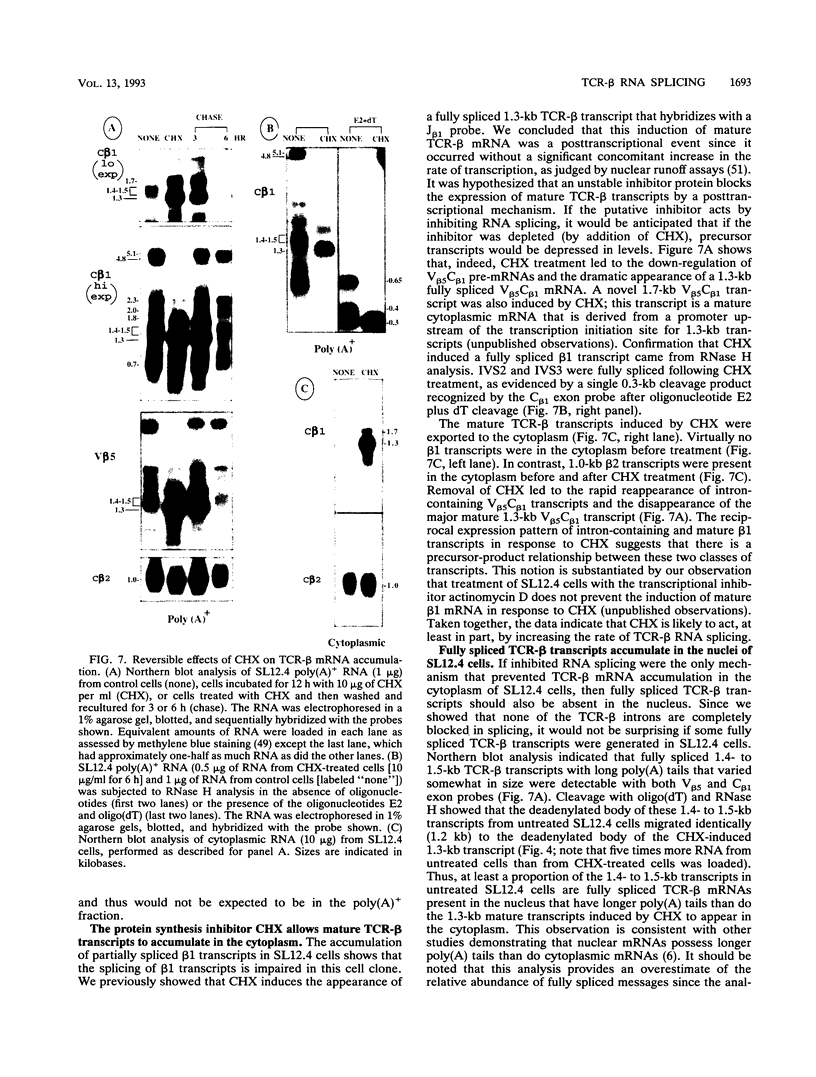
Abstract
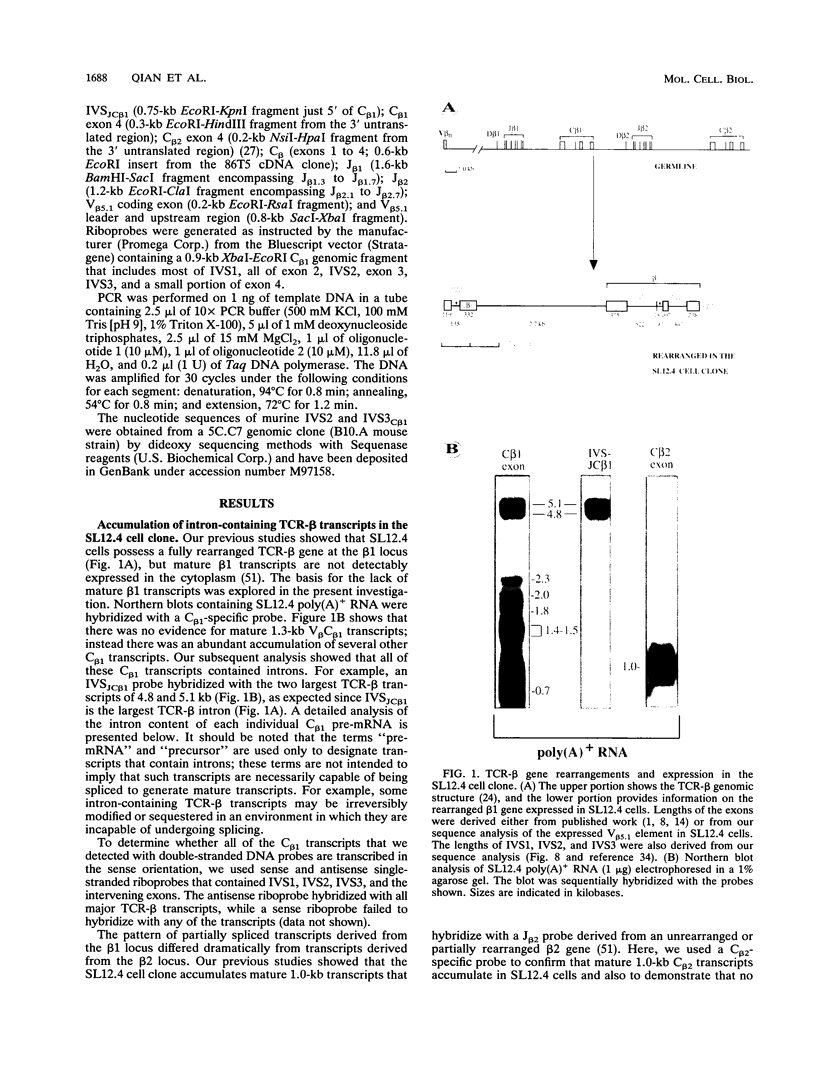
The expression of functional T cell receptor-beta (TCR-beta) transcripts requires the activation of programmed DNA rearrangement events. It is not clear whether other mechanisms dictate TCR-beta mRNA levels during thymic ontogeny. We examined the potential role of RNA splicing as a regulatory mechanism. As a model system, we used an immature T cell clone, SL12.4, that transcribes a fully rearranged TCR-beta gene but essentially lacks mature 1.3-kb TCR-beta transcripts in the cytoplasm. Abundant TCR-beta splicing intermediates accumulate in the nucleus of this cell clone. These splicing intermediates result from inefficient or inhibited excision of four of the five TCR-beta introns; the only intron that is efficiently spliced is the most 5' intron, IVSL. The focal point for the regulation appears to be IVS1C beta 1 and IVS2C beta 1, since unusual splicing intermediates that have cleaved the 5' splice site but not the 3' splice site of these two introns accumulate in vivo. The block in 3' splice site cleavage is of interest since sequence analysis reveals that these two introns possess canonical splice sites. A repressional mechanism involving a labile repressor protein may be responsible for the inhibition of RNA splicing since treatment of SL12.4 cells with the protein synthesis inhibitor cycloheximide reversibly induces a rapid and dramatic accumulation of fully spliced TCR-beta transcripts in the cytoplasm, concomitant with a decline in TCR-beta pre-mRNAs in the nucleus. This inducible system may be useful for future studies analyzing the underlying molecular mechanisms that regulate RNA splicing.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S. J., Chou H. S., Loh D. Y. A conserved sequence in the T-cell receptor beta-chain promoter region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3551–3554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashwell J. D., Klusner R. D. Genetic and mutational analysis of the T-cell antigen receptor. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:139–167. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.001035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. I kappa B: a specific inhibitor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Science. 1988 Oct 28;242(4878):540–546. doi: 10.1126/science.3140380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behlke M. A., Loh D. Y. Alternative splicing of murine T-cell receptor beta-chain transcripts. Nature. 1986 Jul 24;322(6077):379–382. doi: 10.1038/322379a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bingham P. M., Chou T. B., Mims I., Zachar Z. On/off regulation of gene expression at the level of splicing. Trends Genet. 1988 May;4(5):134–138. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90136-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawerman G., Diez J. Metabolism of the polyadenylate sequence of nuclear RNA and messenger RNA in mammalian cells. Cell. 1975 Jul;5(3):271–280. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90102-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer G. An A + U-rich element RNA-binding factor regulates c-myc mRNA stability in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2460–2466. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou H. S., Anderson S. J., Louie M. C., Godambe S. A., Pozzi M. R., Behlke M. A., Huppi K., Loh D. Y. Tandem linkage and unusual RNA splicing of the T-cell receptor beta-chain variable-region genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1992–1996. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clouet d'Orval B., d'Aubenton Carafa Y., Sirand-Pugnet P., Gallego M., Brody E., Marie J. RNA secondary structure repression of a muscle-specific exon in HeLa cell nuclear extracts. Science. 1991 Jun 28;252(5014):1823–1828. doi: 10.1126/science.2063195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent A. L., Fink P. J., Hedrick S. M. Characterization of an alternative exon of the murine T cell receptor beta-chain. Pattern of expression and evolutionary conservation. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 1;143(1):322–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doskow J. R., Wilkinson M. F. CD3-gamma, -delta, -epsilon, -zeta, T-cell receptor-alpha and -beta transcripts are independently regulated during thymocyte ontogeny and T-cell activation. Immunology. 1992 Nov;77(3):465–468. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emeson R. B., Hedjran F., Yeakley J. M., Guise J. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Alternative production of calcitonin and CGRP mRNA is regulated at the calcitonin-specific splice acceptor. Nature. 1989 Sep 7;341(6237):76–80. doi: 10.1038/341076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eng F. J., Warner J. R. Structural basis for the regulation of splicing of a yeast messenger RNA. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):797–804. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90387-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gattoni R., Chebli K., Himmelspach M., Stévenin J. Modulation of alternative splicing of adenoviral E1A transcripts: factors involved in the early-to-late transition. Genes Dev. 1991 Oct;5(10):1847–1858. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.10.1847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haars R., Kronenberg M., Gallatin W. M., Weissman I. L., Owen F. L., Hood L. Rearrangement and expression of T cell antigen receptor and gamma genes during thymic development. J Exp Med. 1986 Jul 1;164(1):1–24. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto Y., Maxam A. M., Greene M. I. Identification of tissue specific nuclear proteins: DNA sequence and protein binding regions in the T cell receptor beta J-C intron. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 25;18(10):3027–3033. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.10.3027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman A., Kappler J. W., Marrack P., Pullen A. M. Superantigens: mechanism of T-cell stimulation and role in immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:745–772. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.003525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue K., Hoshijima K., Sakamoto H., Shimura Y. Binding of the Drosophila sex-lethal gene product to the alternative splice site of transformer primary transcript. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):461–463. doi: 10.1038/344461a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson C., Mauxion F., Sen R. Identification of a functional NF-kappa B binding site in the murine T cell receptor beta 2 locus. J Exp Med. 1989 Nov 1;170(5):1737–1743. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.5.1737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishi H., Borgulya P., Scott B., Karjalainen K., Traunecker A., Kaufman J., von Boehmer H. Surface expression of the beta T cell receptor (TCR) chain in the absence of other TCR or CD3 proteins on immature T cells. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):93–100. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07924.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
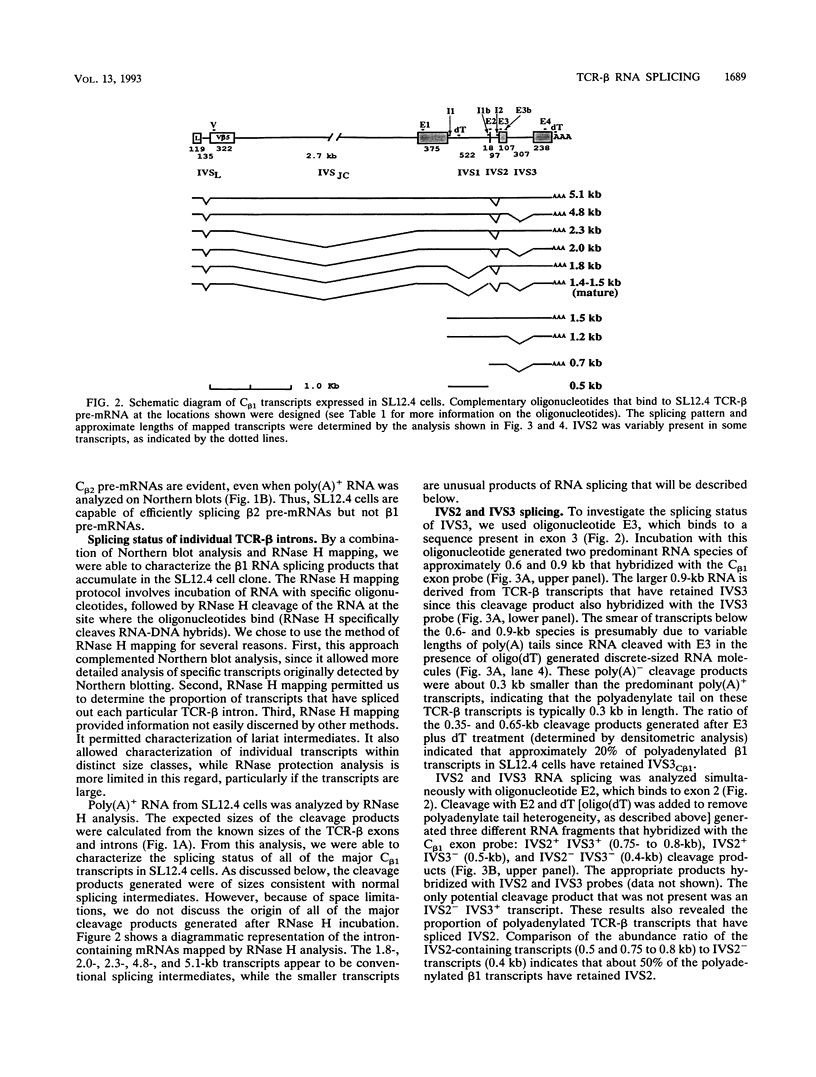
- Krainer A. R., Maniatis T., Ruskin B., Green M. R. Normal and mutant human beta-globin pre-mRNAs are faithfully and efficiently spliced in vitro. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):993–1005. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krimpenfort P., de Jong R., Uematsu Y., Dembic Z., Ryser S., von Boehmer H., Steinmetz M., Berns A. Transcription of T cell receptor beta-chain genes is controlled by a downstream regulatory element. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):745–750. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02871.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronenberg M., Siu G., Hood L. E., Shastri N. The molecular genetics of the T-cell antigen receptor and T-cell antigen recognition. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:529–591. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.002525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier E. R., Brown R. M., Kraig E. Binding of thymic factors to the conserved decanucleotide promoter element of the T-cell receptor V beta gene is developmentally regulated and is absent in SCID mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 15;88(18):8131–8135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.18.8131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLeod C. L., Minning L., Gold D. P., Terhorst C., Wilkinson M. Negative trans-regulation of T-cell antigen receptor/T3 complex mRNA expression in murine T-lymphoma somatic cell hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6989–6993. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malissen M., Minard K., Mjolsness S., Kronenberg M., Goverman J., Hunkapiller T., Prystowsky M. B., Yoshikai Y., Fitch F., Mak T. W. Mouse T cell antigen receptor: structure and organization of constant and joining gene segments encoding the beta polypeptide. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1101–1110. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90444-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattox W., Baker B. S. Autoregulation of the splicing of transcripts from the transformer-2 gene of Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):786–796. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougall S., Peterson C. L., Calame K. A transcriptional enhancer 3' of C beta 2 in the T cell receptor beta locus. Science. 1988 Jul 8;241(4862):205–208. doi: 10.1126/science.2968651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasim F. H., Spears P. A., Hoffmann H. M., Kuo H. C., Grabowski P. J. A Sequential splicing mechanism promotes selection of an optimal exon by repositioning a downstream 5' splice site in preprotachykinin pre-mRNA. Genes Dev. 1990 Jul;4(7):1172–1184. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.7.1172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Konarska M. M., Grabowski P. J., Hardy S. F., Sharp P. A. Lariat RNA's as intermediates and products in the splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Science. 1984 Aug 31;225(4665):898–903. doi: 10.1126/science.6206566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Punt J. A., Kubo R. T., Saito T., Finkel T. H., Kathiresan S., Blank K. J., Hashimoto Y. Surface expression of a T cell receptor beta (TCR-beta) chain in the absence of TCR-alpha, -delta, and -gamma proteins. J Exp Med. 1991 Oct 1;174(4):775–783. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.4.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian L., Vu M. N., Carter M., Wilkinson M. F. A spliced intron accumulates as a lariat in the nucleus of T cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Oct 25;20(20):5345–5350. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.20.5345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian L., Wilkinson M. DNA fragment purification: removal of agarose 10 minutes after electrophoresis. Biotechniques. 1991 Jun;10(6):736–738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein D. M., Saito H., Streuli M., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. The alternative splicing of the CD45 tyrosine phosphatase is controlled by negative regulatory trans-acting splicing factors. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):7139–7147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royer H. D., Reinherz E. L. Multiple nuclear proteins bind upstream sequences in the promotor region of a T-cell receptor beta-chain variable-region gene: evidence for tissue specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):232–236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimonkevitz R. P., Husmann L. A., Bevan M. J., Crispe I. N. Transient expression of IL-2 receptor precedes the differentiation of immature thymocytes. Nature. 1987 Sep 10;329(6135):157–159. doi: 10.1038/329157a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. W., Porro E. B., Patton J. G., Nadal-Ginard B. Scanning from an independently specified branch point defines the 3' splice site of mammalian introns. Nature. 1989 Nov 16;342(6247):243–247. doi: 10.1038/342243a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass H. R., Kisielow P., Kiefer M., Steinmetz M., von Boehmer H. Ontogeny of the T-cell antigen receptor within the thymus. Nature. 1985 Feb 14;313(6003):592–595. doi: 10.1038/313592a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sosnowski B. A., Belote J. M., McKeown M. Sex-specific alternative splicing of RNA from the transformer gene results from sequence-dependent splice site blockage. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):449–459. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90426-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda J., Cheng A., Mauxion F., Nelson C. A., Newberry R. D., Sha W. C., Sen R., Loh D. Y. Functional analysis of the murine T-cell receptor beta enhancer and characteristics of its DNA-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5027–5035. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talerico M., Berget S. M. Effect of 5' splice site mutations on splicing of the preceding intron. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6299–6305. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng J. C., Zollman S., Chain A. C., Laski F. A. Splicing of the Drosophila P element ORF2-ORF3 intron is inhibited in a human cell extract. Mech Dev. 1991 Aug;35(1):65–72. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(91)90042-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall R., Briskin M., Carter C., Govan H., Taylor A., Kincade P. A labile inhibitor blocks immunoglobulin kappa-light-chain-gene transcription in a pre-B leukemic cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):295–298. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson M. F., Doskow J., von Borstel R., 2nd, Fong A. M., MacLeod C. L. The expression of several T cell-specific and novel genes is repressed by trans-acting factors in immature T lymphoma clones. J Exp Med. 1991 Jul 1;174(1):269–280. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.1.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson M. F., MacLeod C. L. Induction of T-cell receptor-alpha and -beta mRNA in SL12 cells can occur by transcriptional and post-transcriptional mechanisms. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):101–109. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02788.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson M., Doskow J., Lindsey S. RNA blots: staining procedures and optimization of conditions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 11;19(3):679–679. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.3.679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeitlin S., Efstratiadis A. In vivo splicing products of the rabbit beta-globin pre-mRNA. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):589–602. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90466-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang Y. A., Goldstein A. M., Weiner A. M. UACUAAC is the preferred branch site for mammalian mRNA splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2752–2756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]