Abstract
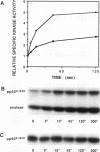
Thrombin stimulation of platelets induces a transient increase in the specific activity of pp60c-src followed by a redistribution of pp60c-src to the Triton X-100-insoluble, cytoskeleton-rich fraction. Concomitant with the observed increase in pp60c-src activity was a rapid dephosphorylation of tyrosine 527 in 10 to 15% of pp60c-src molecules. In addition, we found that pp60c-src from the Triton-insoluble fraction was phosphorylated on tyrosine 416, the autophosphorylation site which is phosphorylated in activated oncogenic variants of pp60src. Furthermore, in platelets from patients with Glanzmann's thrombasthenia (which are deficient in the integrin receptor GPIIb-IIIa), pp60c-src was not translocated to the Triton-insoluble fraction, and there was a sustained increase in pp60c-src activity following thrombin treatment. These results suggest that pp60c-src is rapidly activated in thrombin-stimulated platelets, potentially by a protein tyrosine phosphatase, before it translocates to a cytoskeletal fraction, where many of its potential substrates are found. The evidence that the cytoskeletal association of pp60c-src is dependent upon engagement of the integrin receptor GPIIb-IIIa suggests that integrin-cytoskeletal complexes may serve to compartmentalize and anchor activated enzymes involved in signal transduction.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolen J. B., Thiele C. J., Israel M. A., Yonemoto W., Lipsich L. A., Brugge J. S. Enhancement of cellular src gene product associated tyrosyl kinase activity following polyoma virus infection and transformation. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):767–777. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90272-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkhardt A. L., Brunswick M., Bolen J. B., Mond J. J. Anti-immunoglobulin stimulation of B lymphocytes activates src-related protein-tyrosine kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7410–7414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burridge K., Turner C. E., Romer L. H. Tyrosine phosphorylation of paxillin and pp125FAK accompanies cell adhesion to extracellular matrix: a role in cytoskeletal assembly. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(4):893–903. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.4.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Auger K. R., Carpenter C., Duckworth B., Graziani A., Kapeller R., Soltoff S. Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):281–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90639-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll R. C., Butler R. G., Morris P. A., Gerrard J. M. Separable assembly of platelet pseudopodal and contractile cytoskeletons. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):385–393. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90236-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright C. A., Kaplan P. L., Cooper J. A., Hunter T., Eckhart W. Altered sites of tyrosine phosphorylation in pp60c-src associated with polyomavirus middle tumor antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1562–1570. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Gould K. L., Cartwright C. A., Hunter T. Tyr527 is phosphorylated in pp60c-src: implications for regulation. Science. 1986 Mar 21;231(4744):1431–1434. doi: 10.1126/science.2420005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., King C. S. Dephosphorylation or antibody binding to the carboxy terminus stimulates pp60c-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4467–4477. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A. Activation of the pp60c-src kinase by middle T antigen binding or by dephosphorylation. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1471–1477. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03805.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R., Hanafusa H. Local mutagenesis of Rous sarcoma virus: the major sites of tyrosine and serine phosphorylation of pp60src are dispensable for transformation. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):597–607. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90392-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis S., Lu M. L., Lo S. H., Lin S., Butler J. A., Druker B. J., Roberts T. M., An Q., Chen L. B. Presence of an SH2 domain in the actin-binding protein tensin. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):712–715. doi: 10.1126/science.1708917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhar A., Shukla S. D. Involvement of pp60c-src in platelet-activating factor-stimulated platelets. Evidence for translocation from cytosol to membrane. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):18797–18801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferracini R., Brugge J. Analysis of mutant forms of the c-src gene product containing a phenylalanine substitution for tyrosine 416. Oncogene Res. 1990;5(3):205–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrell J. E., Jr, Martin G. S. Platelet tyrosine-specific protein phosphorylation is regulated by thrombin. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3603–3610. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. E. Linkage of a membrane skeleton to integral membrane glycoproteins in human platelets. Identification of one of the glycoproteins as glycoprotein Ib. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1673–1683. doi: 10.1172/JCI112153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frojmovic M., Wong T., van de Ven T. Dynamic measurements of the platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb-IIIa receptor for fibrinogen by flow cytometry. I. Methodology, theory and results for two distinct activators. Biophys J. 1991 Apr;59(4):815–827. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82294-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui Y., O'Brien M. C., Hanafusa H. Deletions in the SH2 domain of p60v-src prevent association with the detergent-insoluble cellular matrix. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1207–1213. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden A., Brugge J. S., Shattil S. J. Role of platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb-IIIa in agonist-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of platelet proteins. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 2):3117–3127. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.3117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden A., Brugge J. S. Thrombin treatment induces rapid changes in tyrosine phosphorylation in platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):901–905. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grondin P., Plantavid M., Sultan C., Breton M., Mauco G., Chap H. Interaction of pp60c-src, phospholipase C, inositol-lipid, and diacyglycerol kinases with the cytoskeletons of thrombin-stimulated platelets. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15705–15709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan J. L., Shalloway D. Regulation of focal adhesion-associated protein tyrosine kinase by both cellular adhesion and oncogenic transformation. Nature. 1992 Aug 20;358(6388):690–692. doi: 10.1038/358690a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan J. L., Trevithick J. E., Hynes R. O. Fibronectin/integrin interaction induces tyrosine phosphorylation of a 120-kDa protein. Cell Regul. 1991 Nov;2(11):951–964. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.11.951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutkind J. S., Lacal P. M., Robbins K. C. Thrombin-dependent association of phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase with p60c-src and p59fyn in human platelets. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3806–3809. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamaguchi M., Hanafusa H. Association of p60src with Triton X-100-resistant cellular structure correlates with morphological transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2312–2316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horak I. D., Corcoran M. L., Thompson P. A., Wahl L. M., Bolen J. B. Expression of p60fyn in human platelets. Oncogene. 1990 Apr;5(4):597–602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvath A. R., Muszbek L., Kellie S. Translocation of pp60c-src to the cytoskeleton during platelet aggregation. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):855–861. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05123.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M. M., Bolen J. B., Barnwell J. W., Shattil S. J., Brugge J. S. Membrane glycoprotein IV (CD36) is physically associated with the Fyn, Lyn, and Yes protein-tyrosine kinases in human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7844–7848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iba H., Takeya T., Cross F. R., Hanafusa T., Hanafusa H. Rous sarcoma virus variants that carry the cellular src gene instead of the viral src gene cannot transform chicken embryo fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4424–4428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jove R., Hanafusa H. Cell transformation by the viral src oncogene. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:31–56. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.000335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiecik T. E., Johnson P. J., Shalloway D. Regulation by the autophosphorylation site in overexpressed pp60c-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4541–4546. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiecik T. E., Shalloway D. Activation and suppression of pp60c-src transforming ability by mutation of its primary sites of tyrosine phosphorylation. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90756-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. A., Anderson D., Moran M. F., Ellis C., Pawson T. SH2 and SH3 domains: elements that control interactions of cytoplasmic signaling proteins. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):668–674. doi: 10.1126/science.1708916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg L. J., Earp H. S., Turner C. E., Prockop C., Juliano R. L. Signal transduction by integrins: increased protein tyrosine phosphorylation caused by clustering of beta 1 integrins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8392–8396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg L., Earp H. S., Parsons J. T., Schaller M., Juliano R. L. Cell adhesion or integrin clustering increases phosphorylation of a focal adhesion-associated tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 25;267(33):23439–23442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G. The signal transduction induced by thrombin in human platelets. FEBS Lett. 1990 Aug 1;268(2):400–404. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81293-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipfert L., Haimovich B., Schaller M. D., Cobb B. S., Parsons J. T., Brugge J. S. Integrin-dependent phosphorylation and activation of the protein tyrosine kinase pp125FAK in platelets. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(4):905–912. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.4.905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsich L. A., Lewis A. J., Brugge J. S. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies that recognize the transforming proteins of avian sarcoma viruses. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):352–360. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.352-360.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb D. M., Woolford J., Beemon K. pp60c-src has less affinity for the detergent-insoluble cellular matrix than do pp60v-src and other viral protein-tyrosine kinases. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2420–2427. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2420-2427.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostergaard H. L., Shackelford D. A., Hurley T. R., Johnson P., Hyman R., Sefton B. M., Trowbridge I. S. Expression of CD45 alters phosphorylation of the lck-encoded tyrosine protein kinase in murine lymphoma T-cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8959–8963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostergaard H. L., Trowbridge I. S. Coclustering CD45 with CD4 or CD8 alters the phosphorylation and kinase activity of p56lck. J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):347–350. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Jennings L. K., Edwards H. H. Identification of membrane proteins mediating the interaction of human platelets. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jul;86(1):77–86. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piwnica-Worms H., Saunders K. B., Roberts T. M., Smith A. E., Cheng S. H. Tyrosine phosphorylation regulates the biochemical and biological properties of pp60c-src. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90757-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussel R. R., Brodeur S. R., Shalloway D., Laudano A. P. Selective binding of activated pp60c-src by an immobilized synthetic phosphopeptide modeled on the carboxyl terminus of pp60c-src. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10696–10700. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuh S. M., Brugge J. S. Investigation of factors that influence phosphorylation of pp60c-src on tyrosine 527. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2465–2471. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shattil S. J., Brugge J. S. Protein tyrosine phosphorylation and the adhesive functions of platelets. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;3(5):869–879. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90062-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw A., Thomas M. L. Coordinate interactions of protein tyrosine kinases and protein tyrosine phosphatases in T-cell receptor-mediated signalling. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;3(5):862–868. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90061-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder M. A., Bishop J. M., Colby W. W., Levinson A. D. Phosphorylation of tyrosine-416 is not required for the transforming properties and kinase activity of pp60v-src. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):891–901. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90074-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veillette A., Bookman M. A., Horak E. M., Samelson L. E., Bolen J. B. Signal transduction through the CD4 receptor involves the activation of the internal membrane tyrosine-protein kinase p56lck. Nature. 1989 Mar 16;338(6212):257–259. doi: 10.1038/338257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonemoto W., Filson A. J., Queral-Lustig A. E., Wang J. Y., Brugge J. S. Detection of phosphotyrosine-containing proteins in polyomavirus middle tumor antigen-transformed cells after treatment with a phosphotyrosine phosphatase inhibitor. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):905–913. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., Fry M. J., Waterfield M. D., Jaken S., Liao L., Fox J. E., Rittenhouse S. E. Activated phosphoinositide 3-kinase associates with membrane skeleton in thrombin-exposed platelets. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4686–4692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. K., Huang D. P., Qiu D. K., Chiu J. F. The expression of c-myc and c-N-ras in human cirrhotic livers, hepatocellular carcinomas and liver tissue surrounding the tumors. Oncogene. 1990 Jun;5(6):909–914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]