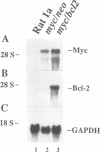
Abstract
The product of the c-myc proto-oncogene is an important positive regulator of cell growth and proliferation. Recently, c-Myc has also been demonstrated to be a potent inducer of apoptosis when expressed in the absence of serum or growth factors. To further examine Myc-induced apoptosis, we coexpressed the proto-oncogene bcl2, which has been shown to block apoptosis in other systems, with c-myc in serum-deprived Rat 1a fibroblasts. Here we report that ectopic expression of bcl2 specifically blocks apoptosis induced by constitutive c-myc expression. Constitutive c-myc expression in serum-deprived Rat 1a cells caused a > 15-fold increase in the number of dead cells, accompanied by DNA fragmentation. However, coexpression of bcl2 with c-myc in these cells led to a 10-fold increase in the number of live cells and a significant decrease in DNA fragmentation. Thus, Bcl-2 effectively inhibits Myc-induced apoptosis in serum-deprived Rat 1a fibroblasts without blocking entry into the cell cycle. These results imply that apoptosis serves as a protective mechanism to prevent tumorigenicity elicited by deregulated Myc expression. This protective mechanism is abrogated, however, by Bcl-2 and therefore may explain the synergism between Myc and Bcl-2 observed in certain tumor cells.
Full text
PDF
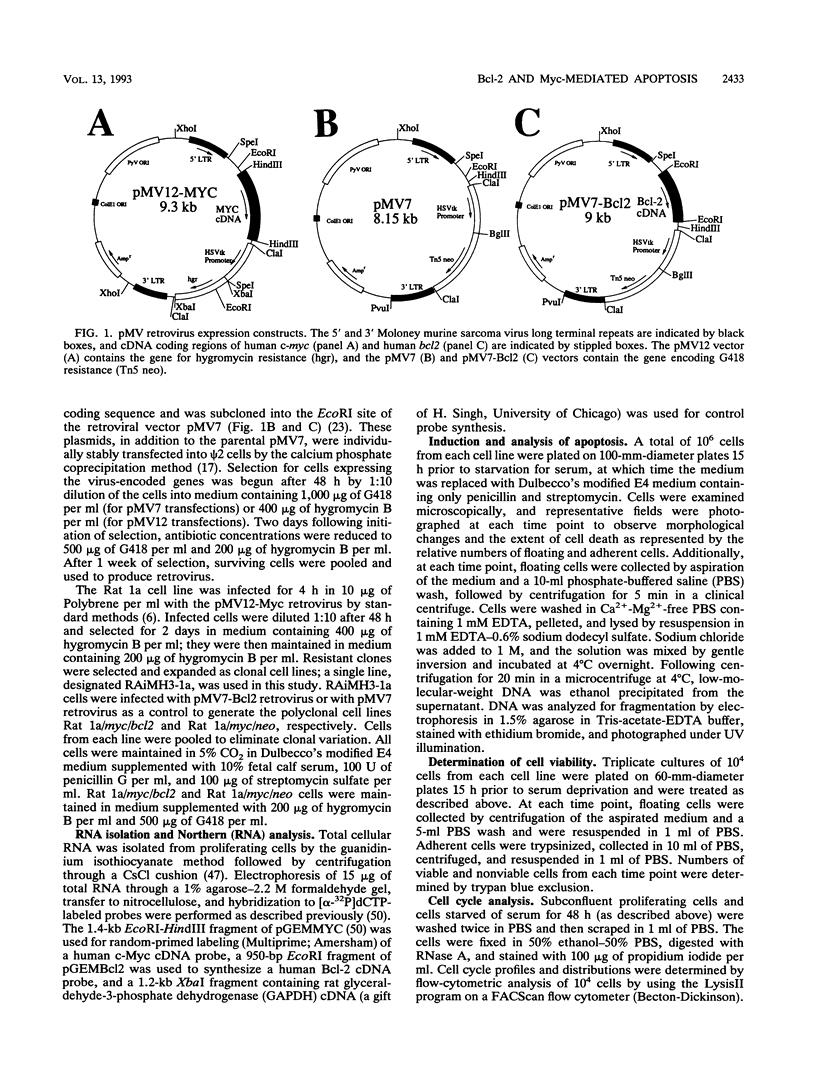

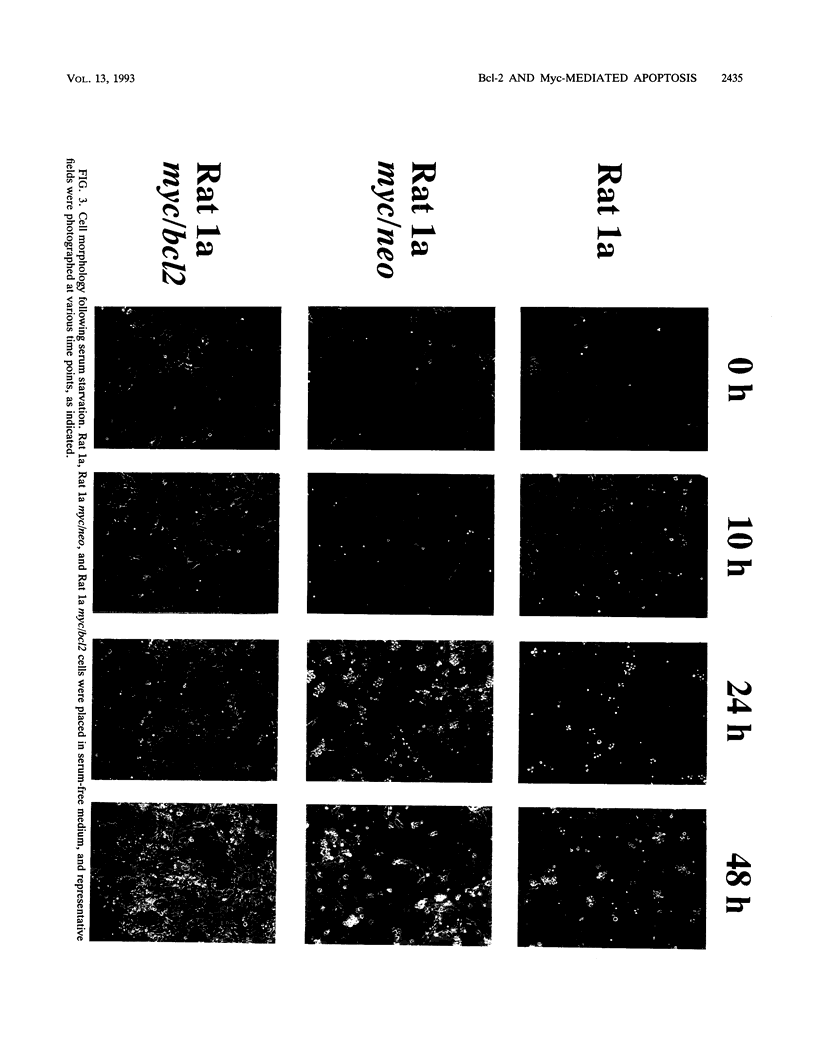
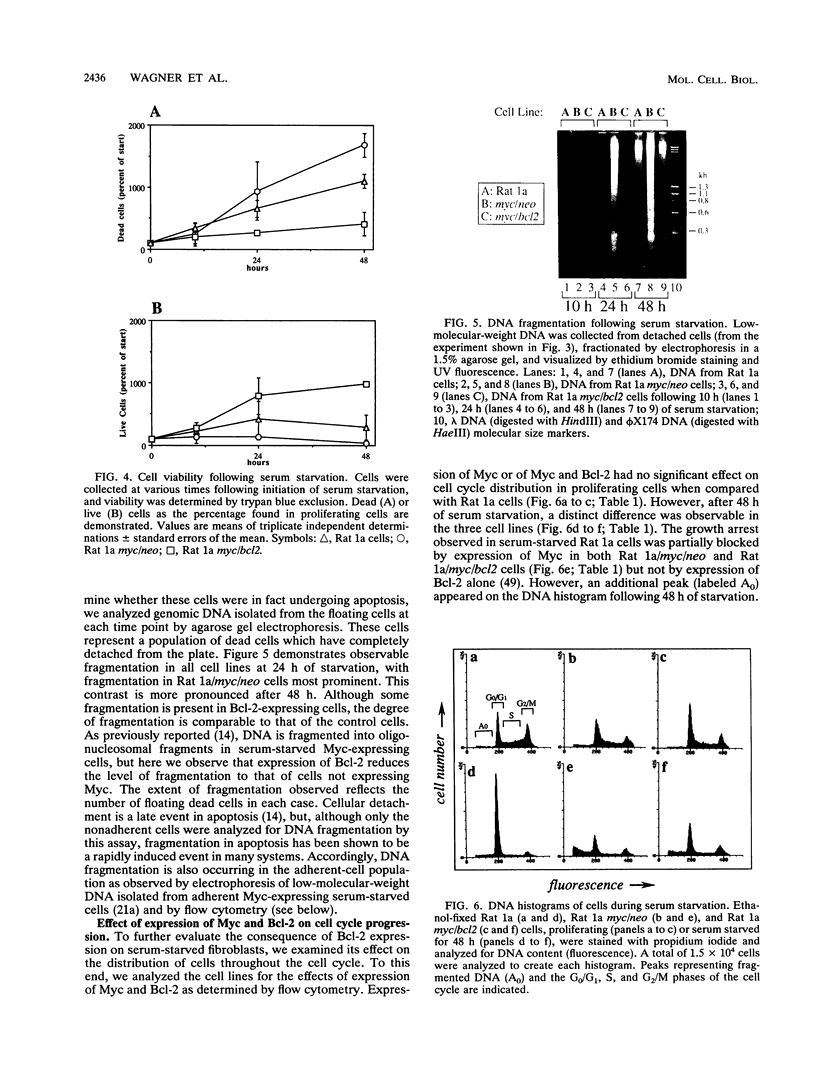
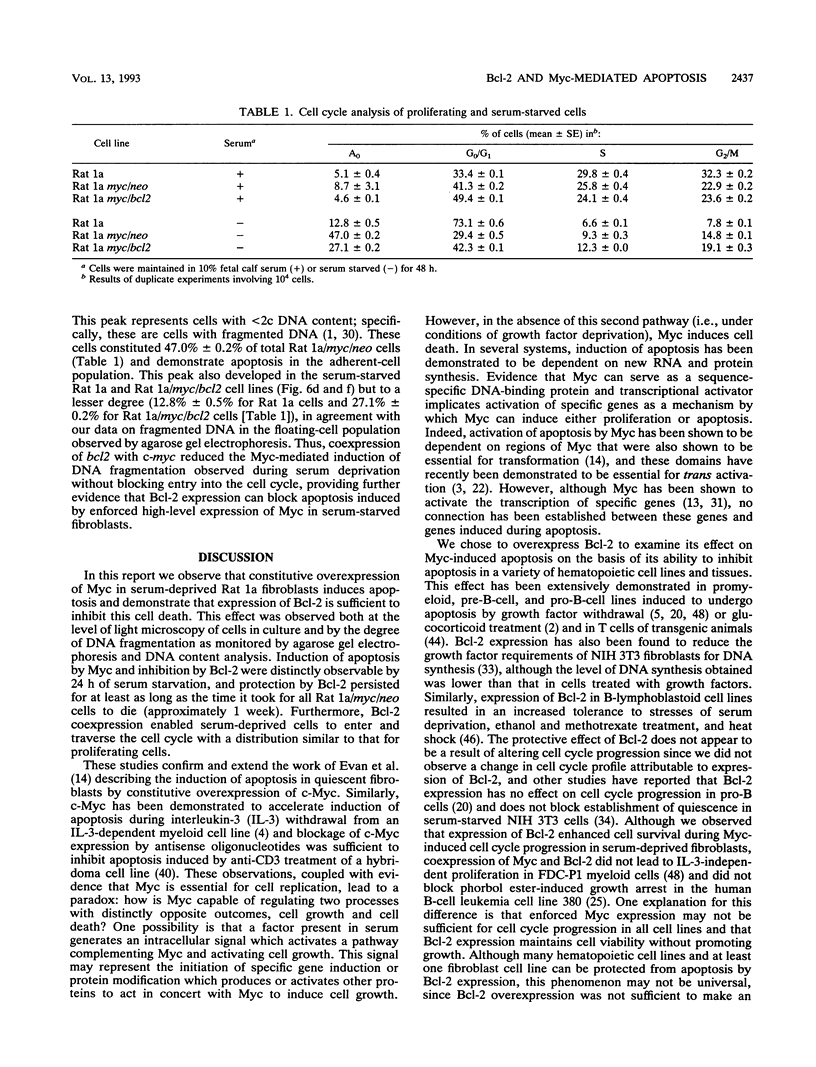



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Afanas'ev V. N., Korol B. A., Mantsygin YuA, Nelipovich P. A., Pechatnikov V. A., Umansky S. R. Flow cytometry and biochemical analysis of DNA degradation characteristic of two types of cell death. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jan 6;194(2):347–350. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80115-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alnemri E. S., Fernandes T. F., Haldar S., Croce C. M., Litwack G. Involvement of BCL-2 in glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis of human pre-B-leukemias. Cancer Res. 1992 Jan 15;52(2):491–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amin C., Wagner A. J., Hay N. Sequence-specific transcriptional activation by Myc and repression by Max. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):383–390. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Askew D. S., Ashmun R. A., Simmons B. C., Cleveland J. L. Constitutive c-myc expression in an IL-3-dependent myeloid cell line suppresses cell cycle arrest and accelerates apoptosis. Oncogene. 1991 Oct;6(10):1915–1922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. Molecular themes in oncogenesis. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):235–248. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90636-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissonnette R. P., Echeverri F., Mahboubi A., Green D. R. Apoptotic cell death induced by c-myc is inhibited by bcl-2. Nature. 1992 Oct 8;359(6395):552–554. doi: 10.1038/359552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borzillo G. V., Endo K., Tsujimoto Y. Bcl-2 confers growth and survival advantage to interleukin 7-dependent early pre-B cells which become factor independent by a multistep process in culture. Oncogene. 1992 May;7(5):869–876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen-Levy Z., Nourse J., Cleary M. L. The bcl-2 candidate proto-oncogene product is a 24-kilodalton integral-membrane protein highly expressed in lymphoid cell lines and lymphomas carrying the t(14;18) translocation. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):701–710. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Classon M., Henriksson M., Sümegi J., Klein G., Hammarskjöld M. L., Hammaskjöld M. L. Elevated c-myc expression facilitates the replication of SV40 DNA in human lymphoma cells. Nature. 1987 Nov 19;330(6145):272–274. doi: 10.1038/330272a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleary M. L., Smith S. D., Sklar J. Cloning and structural analysis of cDNAs for bcl-2 and a hybrid bcl-2/immunoglobulin transcript resulting from the t(14;18) translocation. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):19–28. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90362-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole M. D. The myc oncogene: its role in transformation and differentiation. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:361–384. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.002045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cory S. Activation of cellular oncogenes in hemopoietic cells by chromosome translocation. Adv Cancer Res. 1986;47:189–234. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60200-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalla-Favera R., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C. Onc gene amplification in promyelocytic leukaemia cell line HL-60 and primary leukaemic cells of the same patient. Nature. 1982 Sep 2;299(5878):61–63. doi: 10.1038/299061a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilers M., Schirm S., Bishop J. M. The MYC protein activates transcription of the alpha-prothymosin gene. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):133–141. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07929.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Wyllie A. H., Gilbert C. S., Littlewood T. D., Land H., Brooks M., Waters C. M., Penn L. Z., Hancock D. C. Induction of apoptosis in fibroblasts by c-myc protein. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):119–128. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90123-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanidi A., Harrington E. A., Evan G. I. Cooperative interaction between c-myc and bcl-2 proto-oncogenes. Nature. 1992 Oct 8;359(6395):554–556. doi: 10.1038/359554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. J., Allan G. J., Shanahan F., Vousden K. H., Crook T. p53 is frequently mutated in Burkitt's lymphoma cell lines. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):2879–2887. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07837.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finke J., Fritzen R., Ternes P., Trivedi P., Bross K. J., Lange W., Mertelsmann R., Dölken G. Expression of bcl-2 in Burkitt's lymphoma cell lines: induction by latent Epstein-Barr virus genes. Blood. 1992 Jul 15;80(2):459–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory C. D., Dive C., Henderson S., Smith C. A., Williams G. T., Gordon J., Rickinson A. B. Activation of Epstein-Barr virus latent genes protects human B cells from death by apoptosis. Nature. 1991 Feb 14;349(6310):612–614. doi: 10.1038/349612a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson S., Rowe M., Gregory C., Croom-Carter D., Wang F., Longnecker R., Kieff E., Rickinson A. Induction of bcl-2 expression by Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 protects infected B cells from programmed cell death. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1107–1115. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90007-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hockenbery D., Nuñez G., Milliman C., Schreiber R. D., Korsmeyer S. J. Bcl-2 is an inner mitochondrial membrane protein that blocks programmed cell death. Nature. 1990 Nov 22;348(6299):334–336. doi: 10.1038/348334a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iguchi-Ariga S. M., Itani T., Kiji Y., Ariga H. Possible function of the c-myc product: promotion of cellular DNA replication. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2365–2371. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02513.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato G. J., Barrett J., Villa-Garcia M., Dang C. V. An amino-terminal c-myc domain required for neoplastic transformation activates transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5914–5920. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschmeier P. T., Housey G. M., Johnson M. D., Perkins A. S., Weinstein I. B. Construction and characterization of a retroviral vector demonstrating efficient expression of cloned cDNA sequences. DNA. 1988 Apr;7(3):219–225. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretzner L., Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N. Myc and Max proteins possess distinct transcriptional activities. Nature. 1992 Oct 1;359(6394):426–429. doi: 10.1038/359426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lech K., Anderson K., Brent R. DNA-bound Fos proteins activate transcription in yeast. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):179–184. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90506-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makover D., Cuddy M., Yum S., Bradley K., Alpers J., Sukhatme V., Reed J. C. Phorbol ester-mediated inhibition of growth and regulation of proto-oncogene expression in the human T cell leukemia line JURKAT. Oncogene. 1991 Mar;6(3):455–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcu K. B., Bossone S. A., Patel A. J. myc function and regulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:809–860. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.004113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell T. J., Korsmeyer S. J. Progression from lymphoid hyperplasia to high-grade malignant lymphoma in mice transgenic for the t(14; 18). Nature. 1991 Jan 17;349(6306):254–256. doi: 10.1038/349254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nau M. M., Brooks B. J., Battey J., Sausville E., Gazdar A. F., Kirsch I. R., McBride O. W., Bertness V., Hollis G. F., Minna J. D. L-myc, a new myc-related gene amplified and expressed in human small cell lung cancer. Nature. 1985 Nov 7;318(6041):69–73. doi: 10.1038/318069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunez G., Seto M., Seremetis S., Ferrero D., Grignani F., Korsmeyer S. J., Dalla-Favera R. Growth- and tumor-promoting effects of deregulated BCL2 in human B-lymphoblastoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4589–4593. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pechatnikov V. A., Afanasyev V. N., Korol B. A., Korneev V. N., Rochev YuA, Umansky S. R. Flow cytometry analysis of DNA degradation in thymocytes of gamma-irradiated or hydrocortisone treated rats. Gen Physiol Biophys. 1986 Jun;5(3):273–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendergast G. C., Diamond L. E., Dahl D., Cole M. D. The c-myc-regulated gene mrl encodes plasminogen activator inhibitor 1. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1265–1269. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy C. D., Dasgupta P., Saikumar P., Dudek H., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Reddy E. P. Mutational analysis of Max: role of basic, helix-loop-helix/leucine zipper domains in DNA binding, dimerization and regulation of Myc-mediated transcriptional activation. Oncogene. 1992 Oct;7(10):2085–2092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. C., Cuddy M., Haldar S., Croce C., Nowell P., Makover D., Bradley K. BCL2-mediated tumorigenicity of a human T-lymphoid cell line: synergy with MYC and inhibition by BCL2 antisense. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3660–3664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. C., Haldar S., Croce C. M., Cuddy M. P. Complementation by BCL2 and C-HA-RAS oncogenes in malignant transformation of rat embryo fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4370–4374. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. C., Talwar H. S., Cuddy M., Baffy G., Williamson J., Rapp U. R., Fisher G. J. Mitochondrial protein p26 BCL2 reduces growth factor requirements of NIH3T3 fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1991 Aug;195(2):277–283. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90374-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. C., Tanaka S., Cuddy M. Cell cycle analysis of p26-BCL-2 protein levels in proliferating lymphoma and leukemia cell lines. Cancer Res. 1992 May 15;52(10):2802–2805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. C., Tsujimoto Y., Alpers J. D., Croce C. M., Nowell P. C. Regulation of bcl-2 proto-oncogene expression during normal human lymphocyte proliferation. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1295–1299. doi: 10.1126/science.3495884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnitzky D., Kimchi A. Deregulated c-myc expression abrogates the interferon- and interleukin 6-mediated G0/G1 cell cycle arrest but not other inhibitory responses in M1 myeloblastic cells. Cell Growth Differ. 1991 Jan;2(1):33–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rustgi A. K., Dyson N., Bernards R. Amino-terminal domains of c-myc and N-myc proteins mediate binding to the retinoblastoma gene product. Nature. 1991 Aug 8;352(6335):541–544. doi: 10.1038/352541a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw P., Bovey R., Tardy S., Sahli R., Sordat B., Costa J. Induction of apoptosis by wild-type p53 in a human colon tumor-derived cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4495–4499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Y., Glynn J. M., Guilbert L. J., Cotter T. G., Bissonnette R. P., Green D. R. Role for c-myc in activation-induced apoptotic cell death in T cell hybridomas. Science. 1992 Jul 10;257(5067):212–214. doi: 10.1126/science.1378649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small M. B., Hay N., Schwab M., Bishop J. M. Neoplastic transformation by the human gene N-myc. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1638–1645. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strasser A., Harris A. W., Cory S. bcl-2 transgene inhibits T cell death and perturbs thymic self-censorship. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):889–899. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90362-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., D'Amico D., Chiba I., Buchhagen D. L., Minna J. D. Identification of intronic point mutations as an alternative mechanism for p53 inactivation in lung cancer. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jul;86(1):363–369. doi: 10.1172/JCI114710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto Y. Stress-resistance conferred by high level of bcl-2 alpha protein in human B lymphoblastoid cell. Oncogene. 1989 Nov;4(11):1331–1336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Shine J., Chirgwin J., Pictet R., Tischer E., Rutter W. J., Goodman H. M. Rat insulin genes: construction of plasmids containing the coding sequences. Science. 1977 Jun 17;196(4296):1313–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.325648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaux D. L., Cory S., Adams J. M. Bcl-2 gene promotes haemopoietic cell survival and cooperates with c-myc to immortalize pre-B cells. Nature. 1988 Sep 29;335(6189):440–442. doi: 10.1038/335440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner A. J., Le Beau M. M., Diaz M. O., Hay N. Expression, regulation, and chromosomal localization of the Max gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):3111–3115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.3111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring P., Kos F. J., Müllbacher A. Apoptosis or programmed cell death. Med Res Rev. 1991 Mar;11(2):219–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams G. T. Programmed cell death: apoptosis and oncogenesis. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1097–1098. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90002-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams G. T., Smith C. A., McCarthy N. J., Grimes E. A. Apoptosis: final control point in cell biology. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;2(9):263–267. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90198-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman K. G., Magnusson K. P., Ramqvist T., Klein G. Mutant p53 detected in a majority of Burkitt lymphoma cell lines by monoclonal antibody PAb240. Oncogene. 1991 Sep;6(9):1633–1639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf D., Rotter V. Major deletions in the gene encoding the p53 tumor antigen cause lack of p53 expression in HL-60 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):790–794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H., Kerr J. F., Currie A. R. Cell death: the significance of apoptosis. Int Rev Cytol. 1980;68:251–306. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62312-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonish-Rouach E., Resnitzky D., Lotem J., Sachs L., Kimchi A., Oren M. Wild-type p53 induces apoptosis of myeloid leukaemic cells that is inhibited by interleukin-6. Nature. 1991 Jul 25;352(6333):345–347. doi: 10.1038/352345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]