Abstract
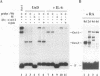
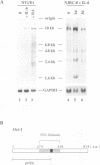
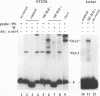
The nuclear signaling by the pleiotropic cytokine interleukin-6 (IL-6) has been investigated in human embryonal carcinoma cells and T cells. We show that Oct-1, a ubiquitously expressed octamer-binding protein known to be regulated posttranslationally, can also be regulated at the levels of mRNA and protein synthesis by IL-6 and by retinoic acid (RA) in human embryonal carcinoma cells. NF-IL6, an IL-6-inducible transcription factor of the C/EBP family, can confer this regulation and is itself regulated by both signals. The abundance and the molar ratios of the three forms of NF-IL6, corresponding to peptides initiated in frame from different AUGs of the same NF-IL6 mRNA species, are regulated by IL-6 and by RA. These results suggest that the two signal transduction pathways overlap in human embryonal carcinoma cells and that Oct-1 may be downstream of NF-IL6 in the shared regulatory cascade. Enhanced Oct-1 synthesis correlates with one of the functions of Oct-1, i.e., stimulation of adenovirus DNA replication. This provides an example of a possible functional consequence of IL-6 and RA signaling that is mediated by NF-IL6 and Oct-1 regulation.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akira S., Isshiki H., Sugita T., Tanabe O., Kinoshita S., Nishio Y., Nakajima T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. A nuclear factor for IL-6 expression (NF-IL6) is a member of a C/EBP family. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1897–1906. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08316.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. W. Retinoic acid induces neuronal differentiation of a cloned human embryonal carcinoma cell line in vitro. Dev Biol. 1984 Jun;103(2):285–293. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90316-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbon P., Murgo S., Ebel J. P., Krol A., Tebb G., Mattaj L. W. A common octamer motif binding protein is involved in the transcription of U6 snRNA by RNA polymerase III and U2 snRNA by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):71–79. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descombes P., Chojkier M., Lichtsteiner S., Falvey E., Schibler U. LAP, a novel member of the C/EBP gene family, encodes a liver-enriched transcriptional activator protein. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1541–1551. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descombes P., Schibler U. A liver-enriched transcriptional activator protein, LAP, and a transcriptional inhibitory protein, LIP, are translated from the same mRNA. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):569–579. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90531-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooley T. P., Miranda M., Jones N. C., DePamphilis M. L. Transactivation of the adenovirus EIIa promoter in the absence of adenovirus E1A protein is restricted to mouse oocytes and preimplantation embryos. Development. 1989 Dec;107(4):945–956. doi: 10.1242/dev.107.4.945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher C., Heintz N., Roeder R. G. Purification and characterization of OTF-1, a transcription factor regulating cell cycle expression of a human histone H2b gene. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):773–781. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90100-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearing D. P., Comeau M. R., Friend D. J., Gimpel S. D., Thut C. J., McGourty J., Brasher K. K., King J. A., Gillis S., Mosley B. The IL-6 signal transducer, gp130: an oncostatin M receptor and affinity converter for the LIF receptor. Science. 1992 Mar 13;255(5050):1434–1437. doi: 10.1126/science.1542794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerster T., Roeder R. G. A herpesvirus trans-activating protein interacts with transcription factor OTF-1 and other cellular proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6347–6351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatfield L., Hearing P. Redundant elements in the adenovirus type 5 inverted terminal repeat promote bidirectional transcription in vitro and are important for virus growth in vivo. Virology. 1991 Sep;184(1):265–276. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90843-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Sturm R. A., Clerc R. G., Corcoran L. M., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A., Ingraham H. A., Rosenfeld M. G., Finney M., Ruvkun G. The POU domain: a large conserved region in the mammalian pit-1, oct-1, oct-2, and Caenorhabditis elegans unc-86 gene products. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1513–1516. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibi M., Murakami M., Saito M., Hirano T., Taga T., Kishimoto T. Molecular cloning and expression of an IL-6 signal transducer, gp130. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1149–1157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90411-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imperiale M. J., Kao H. T., Feldman L. T., Nevins J. R., Strickland S. Common control of the heat shock gene and early adenovirus genes: evidence for a cellular E1A-like activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 May;4(5):867–874. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.5.867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip N. Y., Nye S. H., Boulton T. G., Davis S., Taga T., Li Y., Birren S. J., Yasukawa K., Kishimoto T., Anderson D. J. CNTF and LIF act on neuronal cells via shared signaling pathways that involve the IL-6 signal transducing receptor component gp130. Cell. 1992 Jun 26;69(7):1121–1132. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90634-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Thangue N. B., Rigby P. W. An adenovirus E1A-like transcription factor is regulated during the differentiation of murine embryonal carcinoma stem cells. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):507–513. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90453-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaBella F., Sive H. L., Roeder R. G., Heintz N. Cell-cycle regulation of a human histone H2b gene is mediated by the H2b subtype-specific consensus element. Genes Dev. 1988 Jan;2(1):32–39. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.1.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavery D. J., Chen-Kiang S. Adenovirus E1A and E1B genes are regulated posttranscriptionally in human lymphoid cells. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5349–5359. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5349-5359.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee V. M., Andrews P. W. Differentiation of NTERA-2 clonal human embryonal carcinoma cells into neurons involves the induction of all three neurofilament proteins. J Neurosci. 1986 Feb;6(2):514–521. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-02-00514.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord K. A., Abdollahi A., Thomas S. M., DeMarco M., Brugge J. S., Hoffman-Liebermann B., Liebermann D. A. Leukemia inhibitory factor and interleukin-6 trigger the same immediate early response, including tyrosine phosphorylation, upon induction of myeloid leukemia differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4371–4379. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo Y., Fujii H., Gerster T., Roeder R. G. A novel B cell-derived coactivator potentiates the activation of immunoglobulin promoters by octamer-binding transcription factors. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):231–241. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90352-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattila P. S., Ullman K. S., Fiering S., Emmel E. A., McCutcheon M., Crabtree G. R., Herzenberg L. A. The actions of cyclosporin A and FK506 suggest a novel step in the activation of T lymphocytes. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4425–4433. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07893.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima K., Wall R. Interleukin-6 signals activating junB and TIS11 gene transcription in a B-cell hybridoma. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1409–1418. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson C. C., Braithwaite A. W., Silvestro M., Bellett A. J. Defective expression of adenovirus genes during early infection of undifferentiated OTF963 embryonal carcinoma cells. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4329–4337. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4329-4337.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson C. C., Braithwaite A. W., Silvestro M., Bellett A. J. E1a-dependent expression of adenovirus genes in OTF963 embryonal carcinoma cells: role of E1a-induced differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):8041–8045. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.8041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill E. A., Fletcher C., Burrow C. R., Heintz N., Roeder R. G., Kelly T. J. Transcription factor OTF-1 is functionally identical to the DNA replication factor NF-III. Science. 1988 Sep 2;241(4870):1210–1213. doi: 10.1126/science.3413485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto K., Okazawa H., Okuda A., Sakai M., Muramatsu M., Hamada H. A novel octamer binding transcription factor is differentially expressed in mouse embryonic cells. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):461–472. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90597-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poli V., Mancini F. P., Cortese R. IL-6DBP, a nuclear protein involved in interleukin-6 signal transduction, defines a new family of leucine zipper proteins related to C/EBP. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):643–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90459-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruijn J. M., van der Vliet P. C., Dathan N. A., Mattaj I. W. Anti-OTF-1 antibodies inhibit NFIII stimulation of in vitro adenovirus DNA replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):1845–1863. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.1845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raynal M. C., Liu Z. Y., Hirano T., Mayer L., Kishimoto T., Chen-Kiang S. Interleukin 6 induces secretion of IgG1 by coordinated transcriptional activation and differential mRNA accumulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):8024–8028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.8024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts S. B., Segil N., Heintz N. Differential phosphorylation of the transcription factor Oct1 during the cell cycle. Science. 1991 Aug 30;253(5023):1022–1026. doi: 10.1126/science.1887216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosner M. H., Vigano M. A., Ozato K., Timmons P. M., Poirier F., Rigby P. W., Staudt L. M. A POU-domain transcription factor in early stem cells and germ cells of the mammalian embryo. Nature. 1990 Jun 21;345(6277):686–692. doi: 10.1038/345686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein J. L., Johnson D., DeLoia J. A., Skowronski J., Solter D., Knowles B. Gene expression during preimplantation mouse development. Genes Dev. 1992 Jul;6(7):1190–1201. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.7.1190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh T., Nakamura S., Taga T., Matsuda T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T., Kaziro Y. Induction of neuronal differentiation in PC12 cells by B-cell stimulatory factor 2/interleukin 6. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3546–3549. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt R. M., Bruyns E., Snodgrass H. R. Hematopoietic development of embryonic stem cells in vitro: cytokine and receptor gene expression. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):728–740. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber E., Matthias P., Müller M. M., Schaffner W. Identification of a novel lymphoid specific octamer binding protein (OTF-2B) by proteolytic clipping bandshift assay (PCBA). EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4221–4229. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03319.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R., Dressler G. R., Balling R., Rohdewohld H., Gruss P. Oct-4: a germline-specific transcription factor mapping to the mouse t-complex. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2185–2195. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07388.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segil N., Roberts S. B., Heintz N. Mitotic phosphorylation of the Oct-1 homeodomain and regulation of Oct-1 DNA binding activity. Science. 1991 Dec 20;254(5039):1814–1816. doi: 10.1126/science.1684878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Sen R., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. A nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence motif in transcriptional control elements of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):154–158. doi: 10.1038/319154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sive H. L., Heintz N., Roeder R. G. Multiple sequence elements are required for maximal in vitro transcription of a human histone H2B gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3329–3340. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sive H. L., Roeder R. G. Interaction of a common factor with conserved promoter and enhancer sequences in histone H2B, immunoglobulin, and U2 small nuclear RNA (snRNA) genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6382–6386. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spergel J. M., Chen-Kiang S. Interleukin 6 enhances a cellular activity that functionally substitutes for E1A protein in transactivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6472–6476. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spergel J. M., Hsu W., Akira S., Thimmappaya B., Kishimoto T., Chen-Kiang S. NF-IL6, a member of the C/EBP family, regulates E1A-responsive promoters in the absence of E1A. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):1021–1030. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.1021-1030.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm R. A., Das G., Herr W. The ubiquitous octamer-binding protein Oct-1 contains a POU domain with a homeo box subdomain. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1582–1599. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Lai J. S., Herr W. Promoter-selective activation domains in Oct-1 and Oct-2 direct differential activation of an snRNA and mRNA promoter. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):755–767. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90150-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullman K. S., Flanagan W. M., Edwards C. A., Crabtree G. R. Activation of early gene expression in T lymphocytes by Oct-1 and an inducible protein, OAP40. Science. 1991 Oct 25;254(5031):558–562. doi: 10.1126/science.1683003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegner M., Cao Z., Rosenfeld M. G. Calcium-regulated phosphorylation within the leucine zipper of C/EBP beta. Science. 1992 Apr 17;256(5055):370–373. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5055.370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki K., Taga T., Hirata Y., Yawata H., Kawanishi Y., Seed B., Taniguchi T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. Cloning and expression of the human interleukin-6 (BSF-2/IFN beta 2) receptor. Science. 1988 Aug 12;241(4867):825–828. doi: 10.1126/science.3136546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]