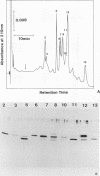
Abstract
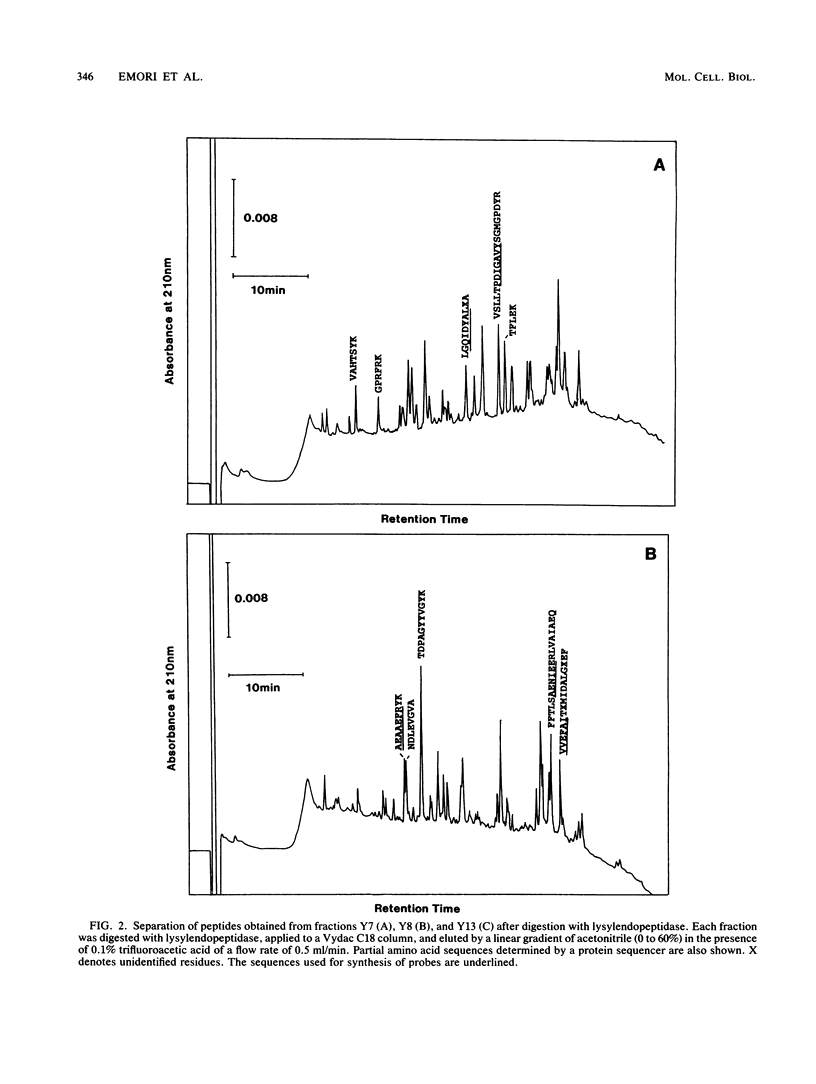
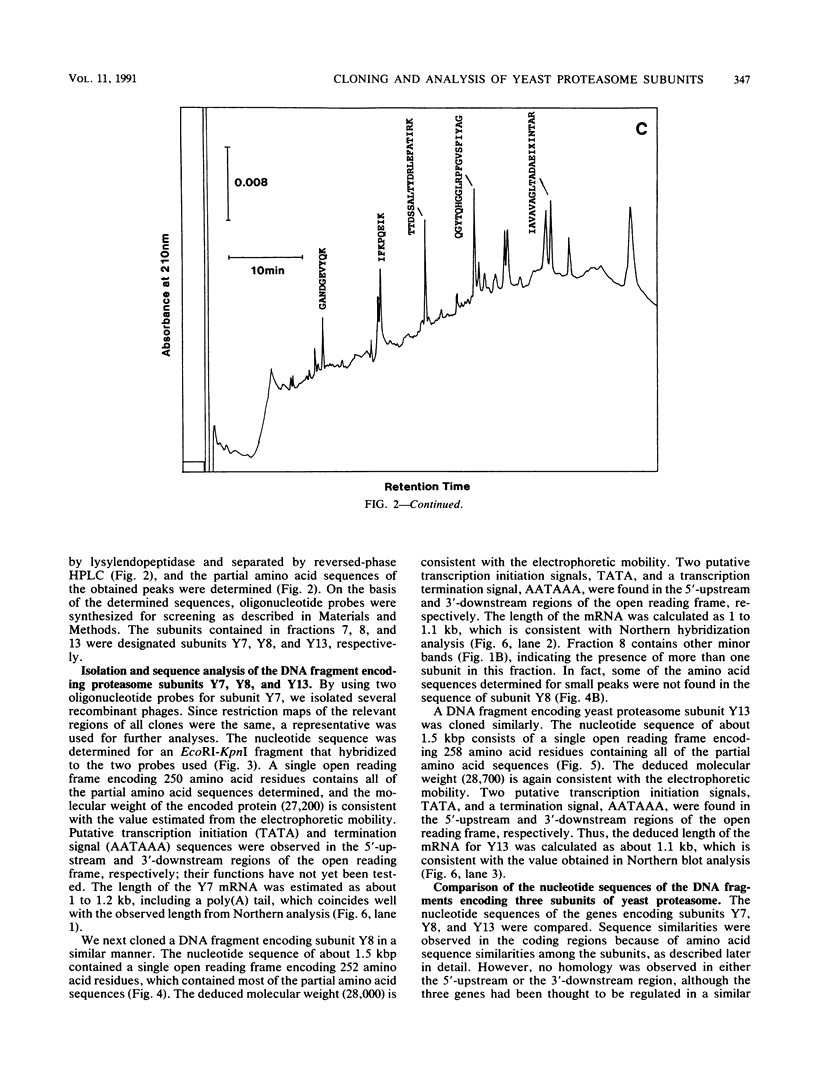
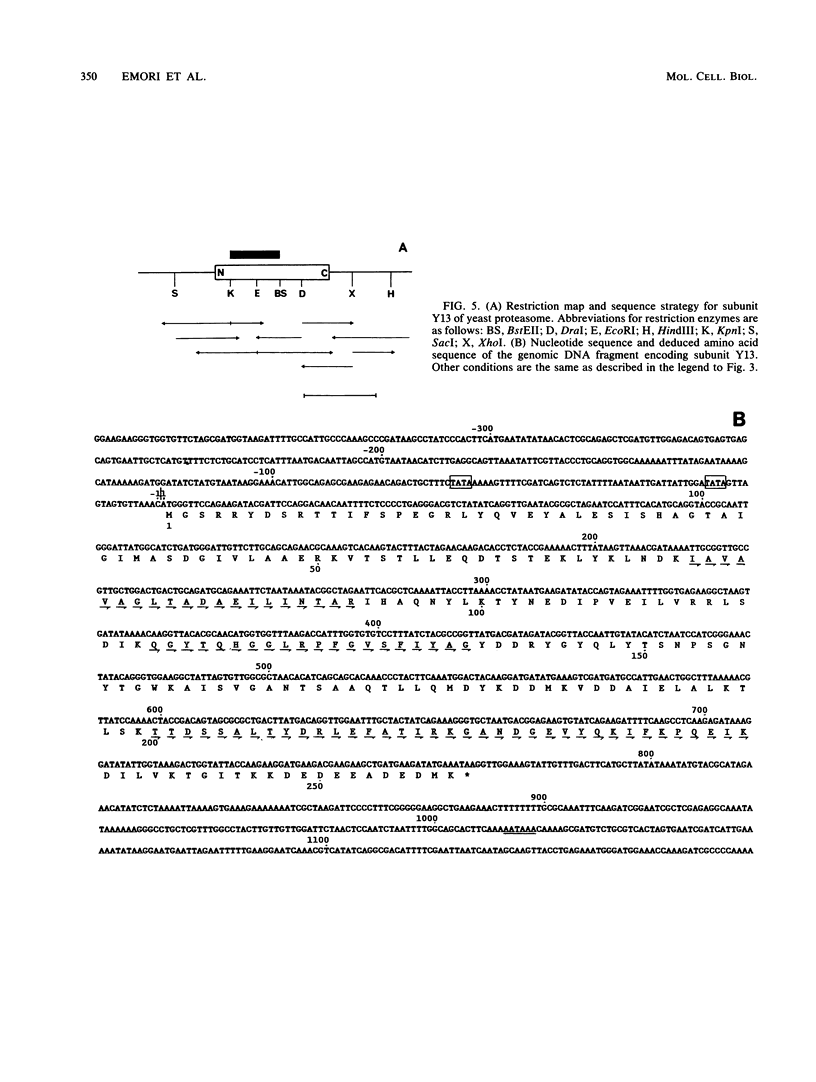
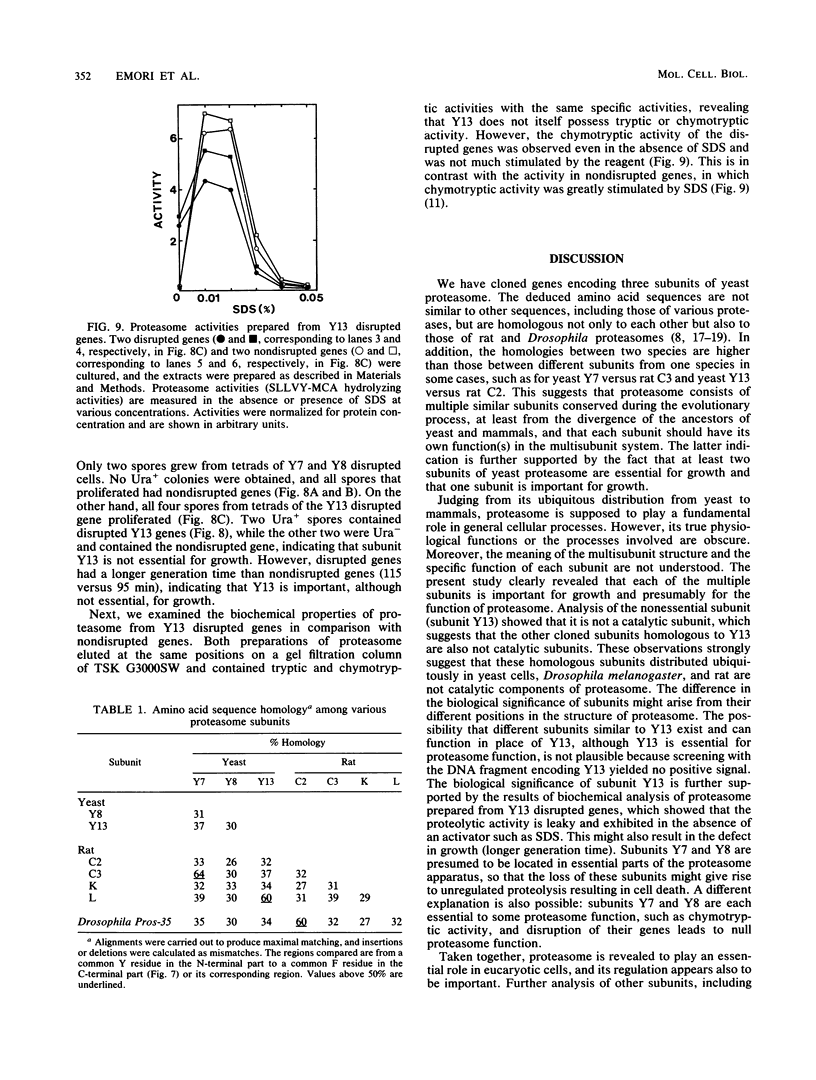
The genes encoding three subunits of Saccharomyces cerevisiae proteasome were cloned and sequenced. The deduced amino acid sequences were homologous not only to each other (30 to 40% identity) but also to those of rat and Drosophila proteasomes (25 to 65% identity). However, none of these sequences showed any similarity to any other known sequences, including various proteases, suggesting that these proteasome subunits may constitute a unique gene family. Gene disruption analyses revealed that two of the three subunits (subunits Y7 and Y8) are essential for growth, indicating that the proteasome and its individual subunits play an indispensable role in fundamental biological processes. On the other hand, subunit Y13 is not essential; haploid cells with a disrupted Y13 gene can proliferate, although the doubling time is longer than that of cells with nondisrupted genes. In addition, biochemical analysis revealed that proteasome prepared from the Y13 disrupted cells contains tryptic and chymotryptic activities equivalent to those of nondisrupted cells, indicating that the Y13 subunit is not essential for tryptic or chymotryptic activity. However, the chymotryptic activity of the Y13 disrupted cells is not dependent on sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), an activator of proteasome, since nearly full activity was observed in the absence of SDS. Thus, the activity in proteasome of the Y13 disrupted cells might result in unregulated intracellular proteolysis, thus leading to the prolonged cell cycle. These results indicate that cloned proteasome subunits having similar sequences to the yeast Y13 subunit are structural, but not catalytic, components of proteasome. It is also suggested that two subunits (Y7 and Y8) might occupy positions essential to proteasome structure or activity, whereas subunit Y13 is in a nonessential but important position.
Full text
PDF
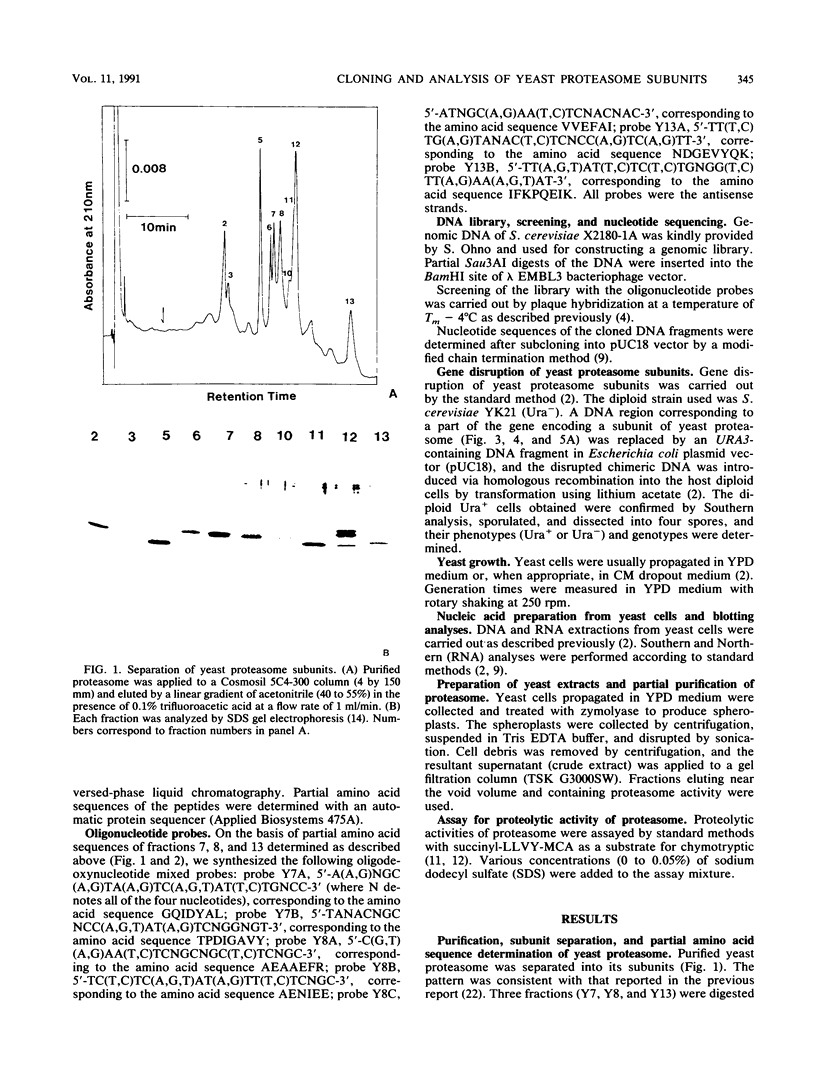




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arrigo A. P., Tanaka K., Goldberg A. L., Welch W. J. Identity of the 19S 'prosome' particle with the large multifunctional protease complex of mammalian cells (the proteasome). Nature. 1988 Jan 14;331(6152):192–194. doi: 10.1038/331192a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond J. S., Butler P. E. Intracellular proteases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:333–364. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emori Y., Kawasaki H., Imajoh S., Kawashima S., Suzuki K. Isolation and sequence analysis of cDNA clones for the small subunit of rabbit calcium-dependent protease. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9472–9476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkenburg P. E., Haass C., Kloetzel P. M., Niedel B., Kopp F., Kuehn L., Dahlmann B. Drosophila small cytoplasmic 19S ribonucleoprotein is homologous to the rat multicatalytic proteinase. Nature. 1988 Jan 14;331(6152):190–192. doi: 10.1038/331190a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara T., Tanaka K., Kumatori A., Shin S., Yoshimura T., Ichihara A., Tokunaga F., Aruga R., Iwanaga S., Kakizuka A. Molecular cloning of cDNA for proteasomes (multicatalytic proteinase complexes) from rat liver: primary structure of the largest component (C2). Biochemistry. 1989 Sep 5;28(18):7332–7340. doi: 10.1021/bi00444a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grainger J. L., Winkler M. M. The sea urchin multicatalytic protease: purification, biochemical analysis, subcellular distribution, and relationship to snRNPs. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):675–683. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haass C., Pesold-Hurt B., Multhaup G., Beyreuther K., Kloetzel P. M. The PROS-35 gene encodes the 35 kd protein subunit of Drosophila melanogaster proteasome. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2373–2379. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08366.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Sakaki Y. Dideoxy sequencing method using denatured plasmid templates. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):232–238. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90403-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hough R., Pratt G., Rechsteiner M. Purification of two high molecular weight proteases from rabbit reticulocyte lysate. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):8303–8313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiura S., Sano M., Kamakura K., Sugita H. Isolation of two forms of the high-molecular-mass serine protease, ingensin, from porcine skeletal muscle. FEBS Lett. 1985 Sep 9;189(1):119–123. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80854-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiura S., Sugita H. Ingensin, a high-molecular-mass alkaline protease from rabbit reticulocyte. J Biochem. 1986 Sep;100(3):753–763. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a121768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiura S., Yamamoto T., Nojima M., Sugita H. Ingensin, a fatty acid-activated serine proteinase from rat liver cytosol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jul 16;882(3):305–310. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(86)90252-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martins de Sa C., Grossi de Sa M. F., Akhayat O., Broders F., Scherrer K., Horsch A., Schmid H. P. Prosomes. Ubiquity and inter-species structural variation. J Mol Biol. 1986 Feb 20;187(4):479–493. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90328-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivett A. J. The multicatalytic proteinase of mammalian cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Jan;268(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90558-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura T., Tanaka K., Kumatori A., Yamada F., Tsurumi C., Fujiwara T., Ichihara A., Tokunaga F., Aruga R., Iwanaga S. cDNA cloning and sequencing of component C5 of proteasomes from rat hepatoma cells. FEBS Lett. 1990 May 7;264(1):91–94. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80773-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Fujiwara T., Kumatori A., Shin S., Yoshimura T., Ichihara A., Tokunaga F., Aruga R., Iwanaga S., Kakizuka A. Molecular cloning of cDNA for proteasomes from rat liver: primary structure of component C3 with a possible tyrosine phosphorylation site. Biochemistry. 1990 Apr 17;29(15):3777–3785. doi: 10.1021/bi00467a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Ii K., Ichihara A., Waxman L., Goldberg A. L. A high molecular weight protease in the cytosol of rat liver. I. Purification, enzymological properties, and tissue distribution. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 15;261(32):15197–15203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Kumatori A., Ii K., Ichihara A. Direct evidence for nuclear and cytoplasmic colocalization of proteasomes (multiprotease complexes) in liver. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Apr;139(1):34–41. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041390107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Tamura T., Kumatori A., Kwak T. H., Chung C. H., Ichihara A. Separation of yeast proteasome subunits. Immunoreactivity with antibodies against ATP-dependent protease Ti from Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Nov 15;164(3):1253–1261. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91804-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Yoshimura T., Ichihara A., Ikai A., Nishigai M., Morimoto Y., Sato M., Tanaka N., Katsube Y., Kameyama K. Molecular organization of a high molecular weight multi-protease complex from rat liver. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 20;203(4):985–996. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90123-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Yoshimura T., Kumatori A., Ichihara A., Ikai A., Nishigai M., Kameyama K., Takagi T. Proteasomes (multi-protease complexes) as 20 S ring-shaped particles in a variety of eukaryotic cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):16209–16217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Nojima M., Ishiura S., Sugita H. Purification of the two forms of the high-molecular-weight neutral proteinase ingensin from rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jul 16;882(3):297–304. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(86)90251-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]