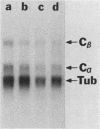
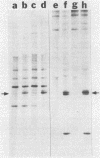
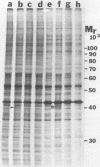
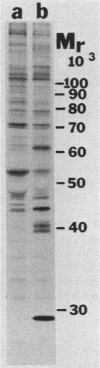
Abstract
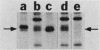
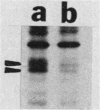
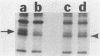
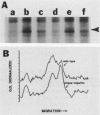
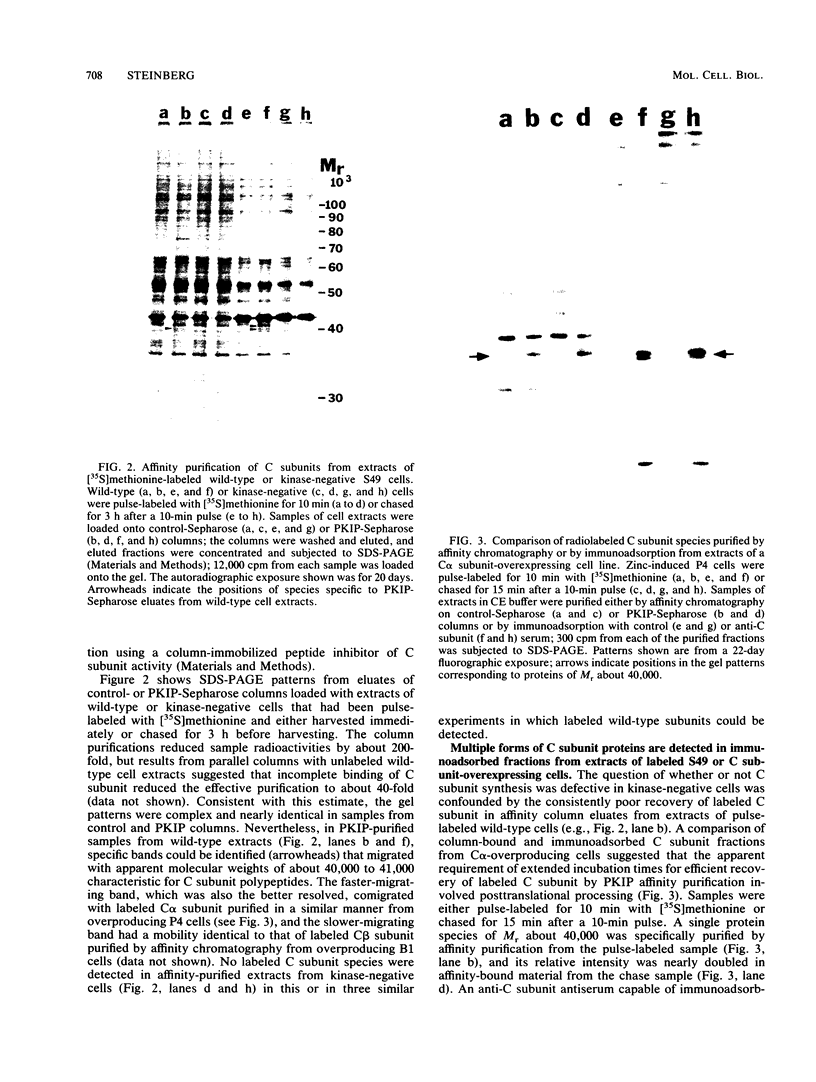
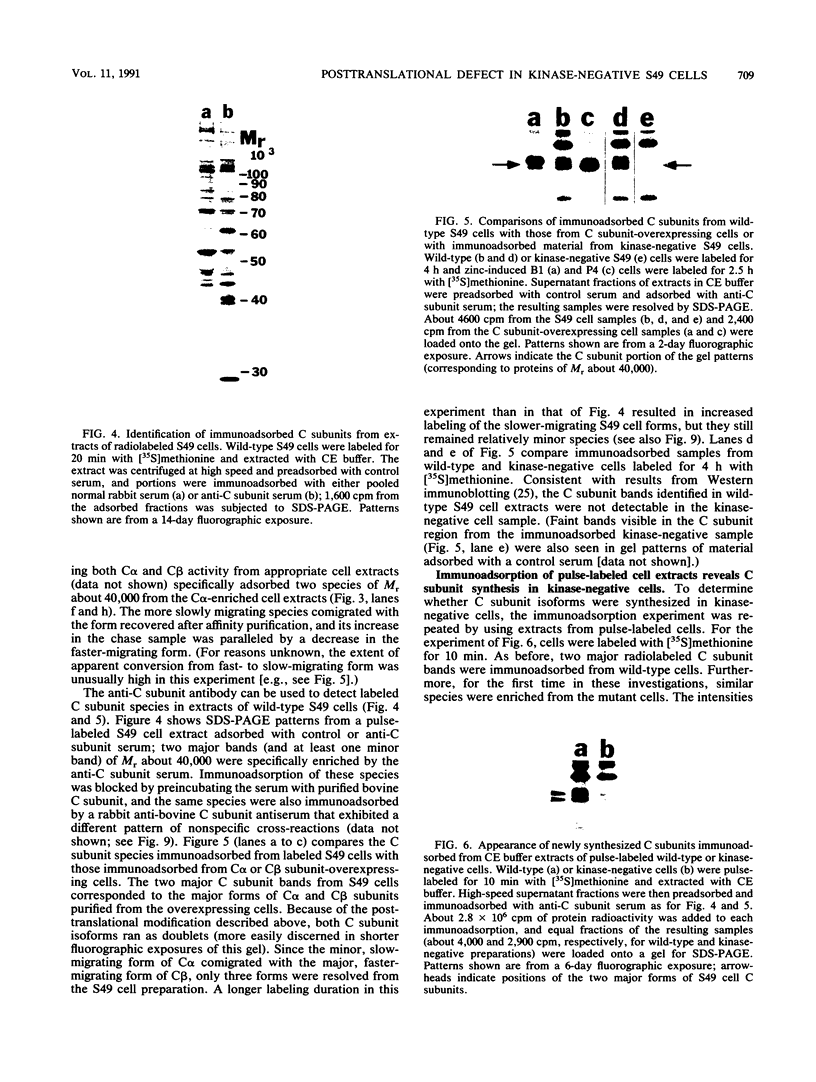
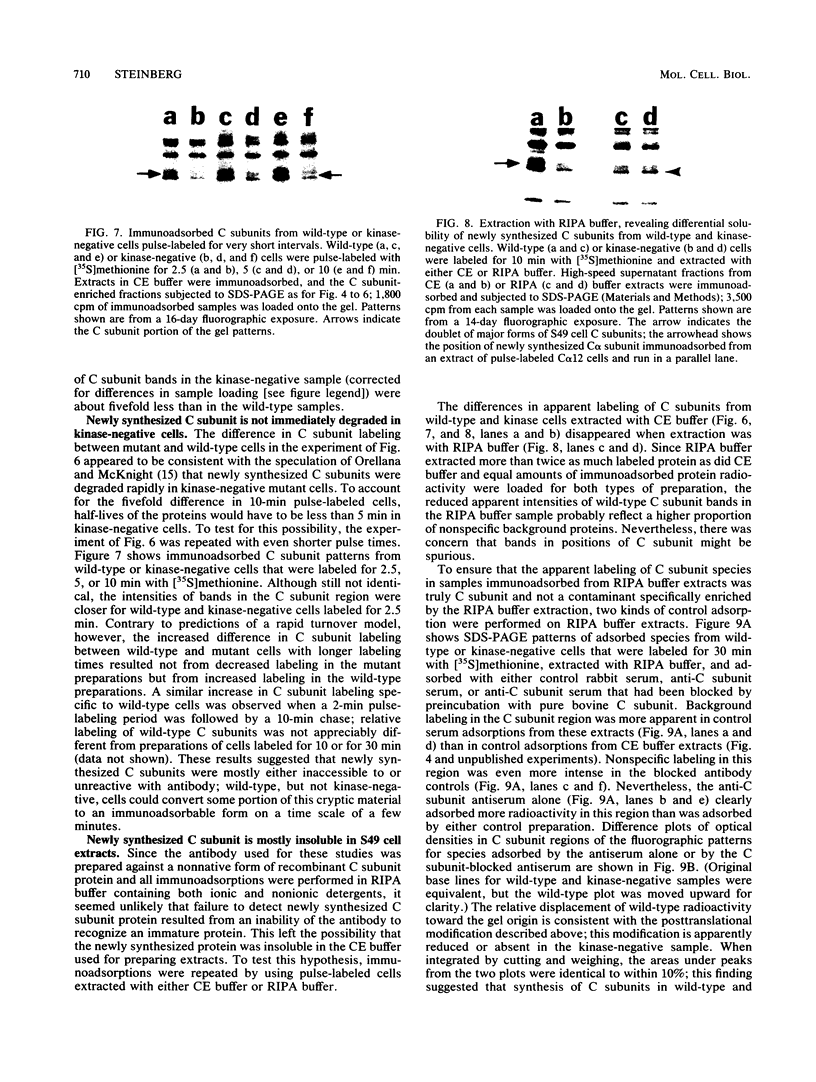
Kinase-negative mutants of S49 mouse lymphoma cells, which lack detectable catalytic (C) subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase, nevertheless contain cytoplasmic mRNAs for the two major forms of C subunit, C alpha and C beta. Investigation of the metabolism of C subunits in wild-type and mutant cells was undertaken to identify the step(s) at which C subunit expression was defective in kinase-negative cells. [35S]methionine-labeled C subunits from cytosolic fractions of wild-type S49 cells or C subunit-overexpressing cell lines were visualized by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis after purification by either affinity chromatography using a peptide inhibitor of C subunit as the ligand or immunoadsorption with an anti-C subunit antiserum. Immunoadsorption revealed electrophoretic forms of C alpha and C beta subunits that migrated faster than those detected in affinity-purified samples; this unexpected heterogeneity suggested that functional activation of C subunit may require posttranslational modification. Immunoadsorption of cytosolic fractions from wild-type cells labeled for various times with [35S]methionine revealed an additional posttranslational maturation step. The bulk of immunoadsorbable C subunit label in cells pulse-labeled for 5 min or less was in an insoluble fraction from which it could be solubilized with a detergent-containing buffer; solubilization of the newly synthesized material proceeded over an incubation period of about 10 min. The primary defect in kinase-negative cells appeared to be in this solubilization step, since about equal C subunit radioactivity was found in detergent extracts of wild-type and kinase-negative cells but very little was found in mutant cytosols. I speculate that an accessory factor required for proper folding of newly synthesized C subunit in defective in the kinase-negative cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng H. C., van Patten S. M., Smith A. J., Walsh D. A. An active twenty-amino-acid-residue peptide derived from the inhibitor protein of the cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 1;231(3):655–661. doi: 10.1042/bj2310655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg C. H., Ran W., Uhler M. D., McKnight G. S. A mutation in the catalytic subunit of protein kinase A prevents myristylation but does not inhibit biological activity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):20140–20146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman A. M., Blumenthal D. K., Krebs E. G. Protein serine/threonine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:567–613. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer G., Schmid F. X. The mechanism of protein folding. Implications of in vitro refolding models for de novo protein folding and translocation in the cell. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 6;29(9):2205–2212. doi: 10.1021/bi00461a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich U., Coffino P. Mutagenesis in S49 mouse lymphoma cells: induction of resistance to ouabain, 6-thioguanine, and dibutyryl cyclic AMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):679–683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman K. B., Steinberg R. A. Simplified method for selective amplification and direct sequencing of cDNAs. Biotechniques. 1989 Apr;7(4):326-8, 331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. A., Lee M. G., Cowan N. J. Five mouse tubulin isotypes and their regulated expression during development. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):852–861. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen S. R., Uhler M. D. Affinity purification of the C alpha and C beta isoforms of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18662–18666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orellana S. A., McKnight G. S. The S49 Kin- cell line transcribes and translates a functional mRNA coding for the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3048–3053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoji S., Ericsson L. H., Walsh K. A., Fischer E. H., Titani K. Amino acid sequence of the catalytic subunit of bovine type II adenosine cyclic 3',5'-phosphate dependent protein kinase. Biochemistry. 1983 Jul 19;22(15):3702–3709. doi: 10.1021/bi00284a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showers M. O., Maurer R. A. A cloned bovine cDNA encodes an alternate form of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 15;261(35):16288–16291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slice L. W., Taylor S. S. Expression of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):20940–20946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg R. A., Agard D. A. Turnover of regulatory subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase in S49 mouse lymphoma cells. Regulation by catalytic subunit and analogs of cyclic AMP. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):10731–10734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg R. A. Radiolabeling and detection methods for studying metabolism of regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase I in intact cultured cells. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:233–243. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99058-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg R. A., van Daalen Wetters T., Coffino P. Kinase-negative mutants of S49 mouse lymphoma cells carry a trans-dominant mutation affecting expression of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1351–1361. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90060-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhler M. D., Chrivia J. C., McKnight G. S. Evidence for a second isoform of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15360–15363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhler M. D., McKnight G. S. Expression of cDNAs for two isoforms of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):15202–15207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Daalen Wetters T., Murtaugh M. P., Coffino P. Revertants of a trans-dominant S49 mouse lymphoma mutant that affects expression of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):311–320. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90234-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]