Abstract
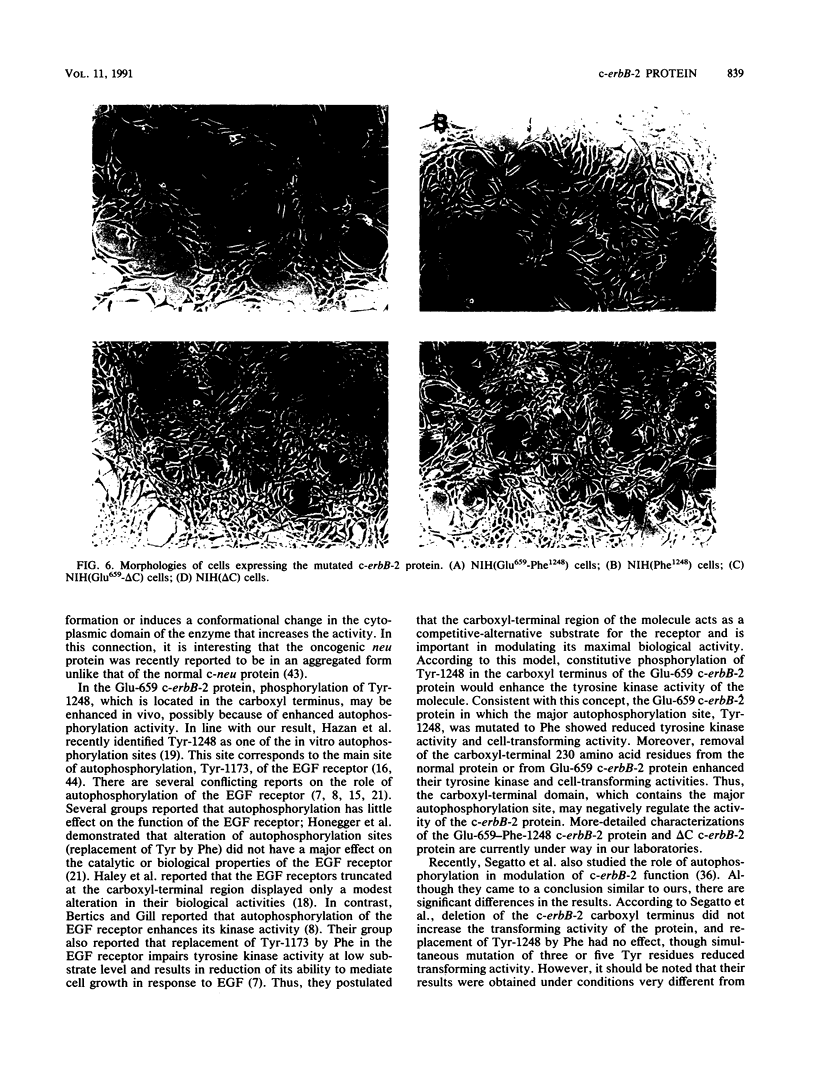
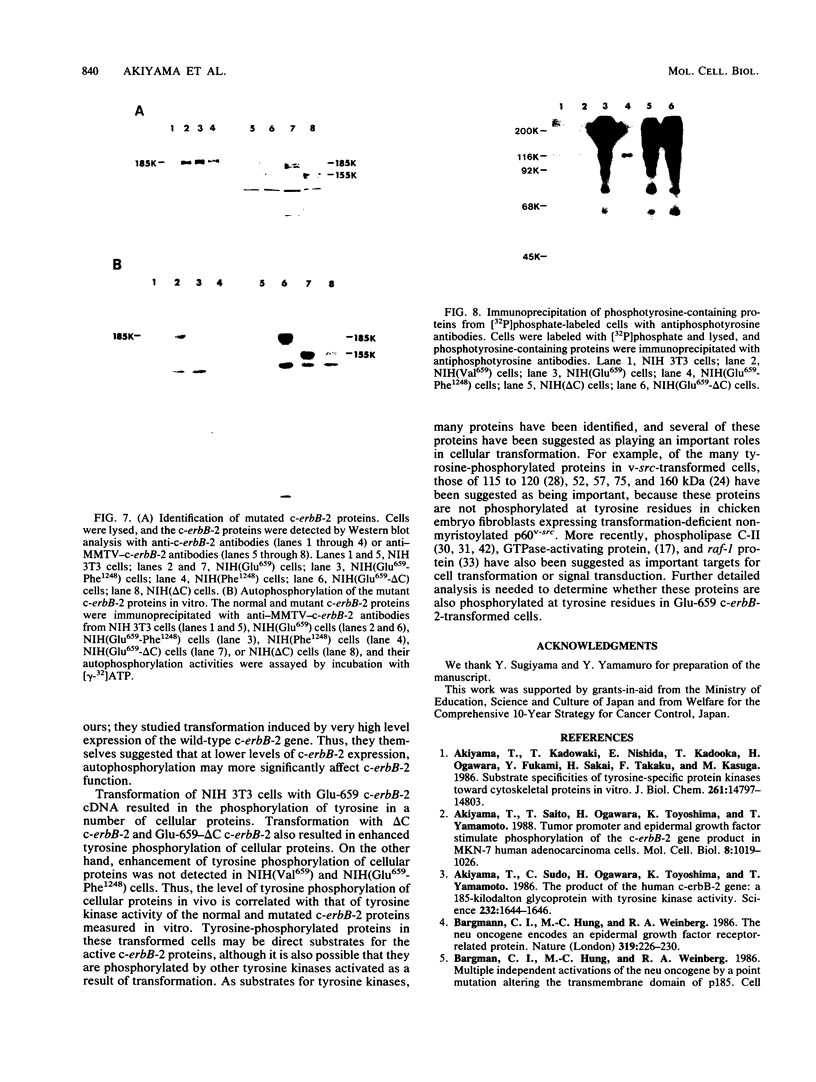
The mutant c-erbB-2 protein with Glu instead of Val-659 exhibited transforming activity in NIH 3T3 cells. This protein showed enhanced tyrosine kinase activity in vitro and enhanced autophosphorylation at Tyr-1248 located proximal to the carboxyl terminus. Enhanced tyrosine phosphorylation of several cellular proteins was detected in cells expressing the Glu-659 c-erbB-2 protein. Introduction of an additional mutation at the ATP-binding site (Lys-753 to Met) of this protein resulted in abolition of its transforming ability. These data indicate that the transforming potential of c-erbB-2 is closely correlated with elevated tyrosine kinase activity of the gene product. To investigate the role of autophosphorylation in cell transformation, we introduced an additional mutation at the autophosphorylation site of the Glu-659 c-erbB-2 protein (Tyr-1248 to Phe). This mutant protein exhibited lower tyrosine kinase activity and lower transforming activity. On the other hand, when the carboxyl-terminal 230 amino acid residues were deleted from the c-erbB-2 protein, the tyrosine kinase activity and cell-transforming activity of the protein were enhanced. Thus, the carboxyl-terminal domain, which contains the major autophosphorylation site, Tyr-1248, may regulate cellular transformation negatively and autophosphorylation may eliminate this negative regulation.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyama T., Kadowaki T., Nishida E., Kadooka T., Ogawara H., Fukami Y., Sakai H., Takaku F., Kasuga M. Substrate specificities of tyrosine-specific protein kinases toward cytoskeletal proteins in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14797–14803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama T., Saito T., Ogawara H., Toyoshima K., Yamamoto T. Tumor promoter and epidermal growth factor stimulate phosphorylation of the c-erbB-2 gene product in MKN-7 human adenocarcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1019–1026. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama T., Sudo C., Ogawara H., Toyoshima K., Yamamoto T. The product of the human c-erbB-2 gene: a 185-kilodalton glycoprotein with tyrosine kinase activity. Science. 1986 Jun 27;232(4758):1644–1646. doi: 10.1126/science.3012781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargmann C. I., Hung M. C., Weinberg R. A. The neu oncogene encodes an epidermal growth factor receptor-related protein. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):226–230. doi: 10.1038/319226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargmann C. I., Weinberg R. A. Oncogenic activation of the neu-encoded receptor protein by point mutation and deletion. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2043–2052. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03044.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertics P. J., Chen W. S., Hubler L., Lazar C. S., Rosenfeld M. G., Gill G. N. Alteration of epidermal growth factor receptor activity by mutation of its primary carboxyl-terminal site of tyrosine self-phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 15;263(8):3610–3617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertics P. J., Gill G. N. Self-phosphorylation enhances the protein-tyrosine kinase activity of the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14642–14647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biswas R., Basu M., Sen-Majumdar A., Das M. Intrapeptide autophosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor: regulation of kinase catalytic function by receptor dimerization. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 2;24(14):3795–3802. doi: 10.1021/bi00335a056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böni-Schnetzler M., Rubin J. B., Pilch P. F. Structural requirements for the transmembrane activation of the insulin receptor kinase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 15;261(32):15281–15287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W. S., Lazar C. S., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y., Gill G. N., Rosenfeld M. G. Requirement for intrinsic protein tyrosine kinase in the immediate and late actions of the EGF receptor. 1987 Aug 27-Sep 2Nature. 328(6133):820–823. doi: 10.1038/328820a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou C. K., Dull T. J., Russell D. S., Gherzi R., Lebwohl D., Ullrich A., Rosen O. M. Human insulin receptors mutated at the ATP-binding site lack protein tyrosine kinase activity and fail to mediate postreceptor effects of insulin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1842–1847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coussens L., Yang-Feng T. L., Liao Y. C., Chen E., Gray A., McGrath J., Seeburg P. H., Libermann T. A., Schlessinger J., Francke U. Tyrosine kinase receptor with extensive homology to EGF receptor shares chromosomal location with neu oncogene. Science. 1985 Dec 6;230(4730):1132–1139. doi: 10.1126/science.2999974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Fiore P. P., Pierce J. H., Kraus M. H., Segatto O., King C. R., Aaronson S. A. erbB-2 is a potent oncogene when overexpressed in NIH/3T3 cells. Science. 1987 Jul 10;237(4811):178–182. doi: 10.1126/science.2885917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Parker P., Waterfield M. D. Autophosphorylation sites on the epidermal growth factor receptor. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):483–485. doi: 10.1038/311483a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Waterfield M. D., Parker P. J. Autophosphorylation and protein kinase C phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Effect on tyrosine kinase activity and ligand binding affinity. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14538–14546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis C., Moran M., McCormick F., Pawson T. Phosphorylation of GAP and GAP-associated proteins by transforming and mitogenic tyrosine kinases. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):377–381. doi: 10.1038/343377a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haley J. D., Hsuan J. J., Waterfield M. D. Analysis of mammalian fibroblast transformation by normal and mutated human EGF receptors. Oncogene. 1989 Mar;4(3):273–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazan R., Margolis B., Dombalagian M., Ullrich A., Zilberstein A., Schlessinger J. Identification of autophosphorylation sites of HER2/neu. Cell Growth Differ. 1990 Jan;1(1):3–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H., Betsholtz C., Claesson-Welsh L., Westermark B. Subversion of growth regulatory pathways in malignant transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Nov 25;907(3):219–244. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(87)90007-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honegger A., Dull T. J., Bellot F., Van Obberghen E., Szapary D., Schmidt A., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Biological activities of EGF-receptor mutants with individually altered autophosphorylation sites. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3045–3052. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03169.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadowaki T., Kasuga M., Tobe K., Takaku F., Nishida E., Sakai H., Koyasu S., Yahara I., Toyoshima K., Yamamoto T. A Mr = 190,000 glycoprotein phosphorylated on tyrosine residues in epidermal growth factor stimulated KB cells is the product of the c-erbB-2 gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Apr 29;144(2):699–704. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Sefton B. M. Identification of multiple novel polypeptide substrates of the v-src, v-yes, v-fps, v-ros, and v-erb-B oncogenic tyrosine protein kinases utilizing antisera against phosphotyrosine. Oncogene. 1988 Apr;2(4):305–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. R., Kraus M. H., Aaronson S. A. Amplification of a novel v-erbB-related gene in a human mammary carcinoma. Science. 1985 Sep 6;229(4717):974–976. doi: 10.1126/science.2992089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokai Y., Cohen J. A., Drebin J. A., Greene M. I. Stage- and tissue-specific expression of the neu oncogene in rat development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8498–8501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koland J. G., Cerione R. A. Growth factor control of epidermal growth factor receptor kinase activity via an intramolecular mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 15;263(5):2230–2237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder M. E., Burr J. G. Nonmyristoylated p60v-src fails to phosphorylate proteins of 115-120 kDa in chicken embryo fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2608–2612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupu R., Colomer R., Zugmaier G., Sarup J., Shepard M., Slamon D., Lippman M. E. Direct interaction of a ligand for the erbB2 oncogene product with the EGF receptor and p185erbB2. Science. 1990 Sep 28;249(4976):1552–1555. doi: 10.1126/science.2218496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Rhee S. G., Felder S., Mervic M., Lyall R., Levitzki A., Ullrich A., Zilberstein A., Schlessinger J. EGF induces tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-II: a potential mechanism for EGF receptor signaling. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1101–1107. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90047-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisenhelder J., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G., Hunter T. Phospholipase C-gamma is a substrate for the PDGF and EGF receptor protein-tyrosine kinases in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1109–1122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori S., Akiyama T., Yamada Y., Morishita Y., Sugawara I., Toyoshima K., Yamamoto T. C-erbB-2 gene product, a membrane protein commonly expressed on human fetal epithelial cells. Lab Invest. 1989 Jul;61(1):93–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. K., Kaplan D. R., Rapp U., Roberts T. M. Signal transduction from membrane to cytoplasm: growth factors and membrane-bound oncogene products increase Raf-1 phosphorylation and associated protein kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8855–8859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang D. T., Sharma B. R., Shafer J. A. Purification of the catalytically active phosphorylated form of insulin receptor kinase by affinity chromatography with O-phosphotyrosyl-binding antibodies. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Oct;242(1):176–186. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90491-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike L. J., Gallis B., Casnellie J. E., Bornstein P., Krebs E. G. Epidermal growth factor stimulates the phosphorylation of synthetic tyrosine-containing peptides by A431 cell membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1443–1447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segatto O., Lonardo F., Pierce J. H., Bottaro D. P., Di Fiore P. P. The role of autophosphorylation in modulation of erbB-2 transforming function. New Biol. 1990 Feb;2(2):187–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semba K., Kamata N., Toyoshima K., Yamamoto T. A v-erbB-related protooncogene, c-erbB-2, is distinct from the c-erbB-1/epidermal growth factor-receptor gene and is amplified in a human salivary gland adenocarcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6497–6501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slamon D. J., Clark G. M., Wong S. G., Levin W. J., Ullrich A., McGuire W. L. Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science. 1987 Jan 9;235(4785):177–182. doi: 10.1126/science.3798106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. F., Heffernan P. A., Weinberg R. A. p185, a product of the neu proto-oncogene, is a receptorlike protein associated with tyrosine kinase activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1729–1740. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. F., Kamps M. P., Cao H. Oncogenic activation of p185neu stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3969–3973. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. W., Ott J., Eckstein F. The rapid generation of oligonucleotide-directed mutations at high frequency using phosphorothioate-modified DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 20;13(24):8765–8785. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.24.8765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl M. I., Nishibe S., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G., Carpenter G. Epidermal growth factor stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-II independently of receptor internalization and extracellular calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1568–1572. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota J., Yamamoto T., Miyajima N., Toyoshima K., Nomura N., Sakamoto H., Yoshida T., Terada M., Sugimura T. Genetic alterations of the c-erbB-2 oncogene occur frequently in tubular adenocarcinoma of the stomach and are often accompanied by amplification of the v-erbA homologue. Oncogene. 1988 Mar;2(3):283–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota J., Yamamoto T., Toyoshima K., Terada M., Sugimura T., Battifora H., Cline M. J. Amplification of c-erbB-2 oncogene in human adenocarcinomas in vivo. Lancet. 1986 Apr 5;1(8484):765–767. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91782-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]