Abstract
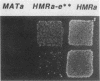
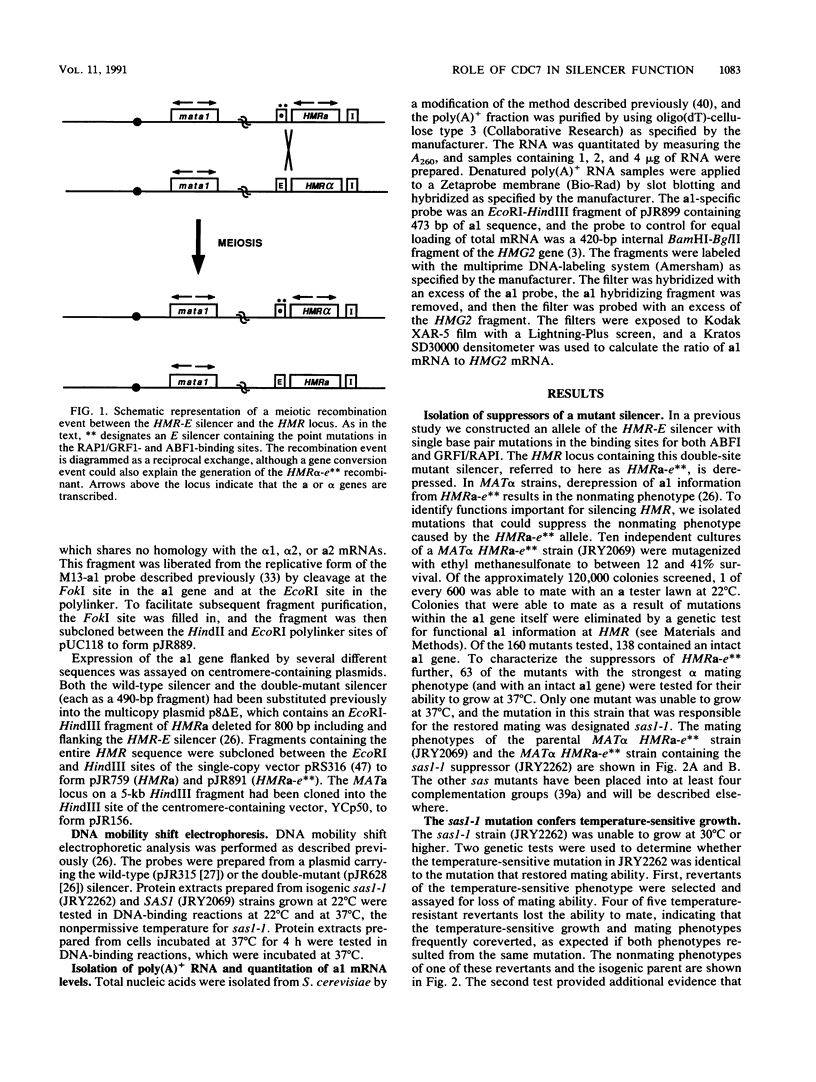
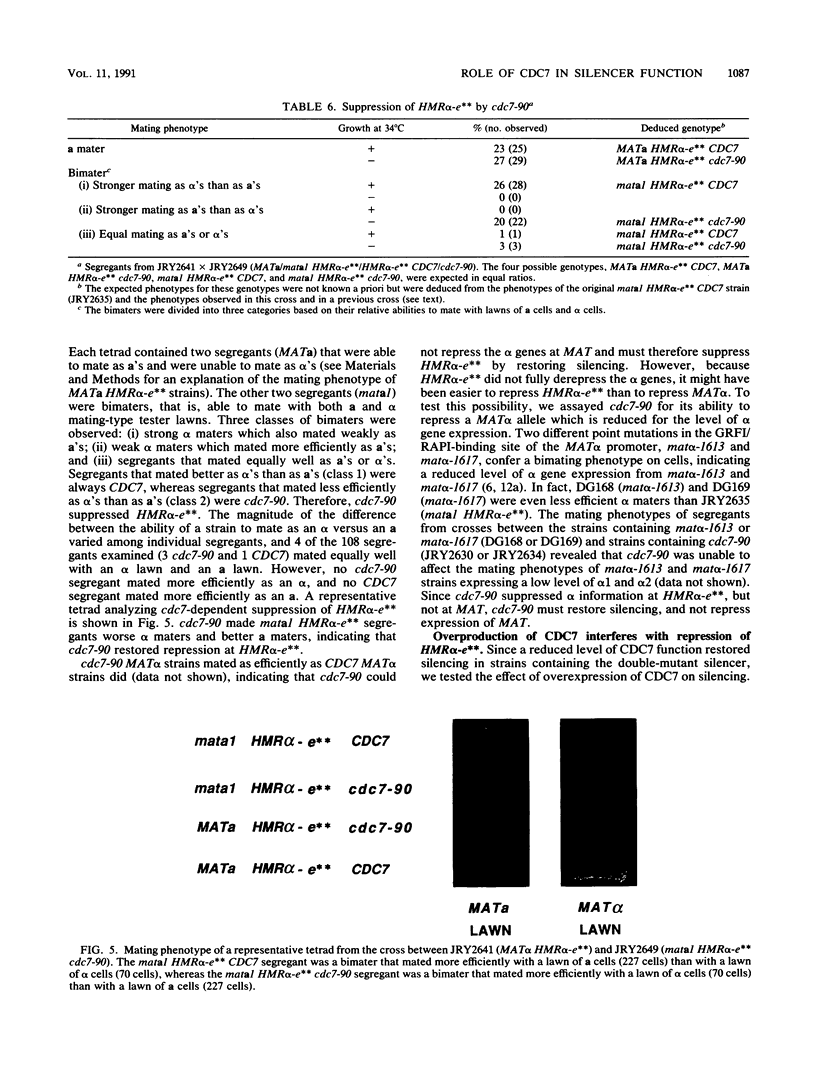
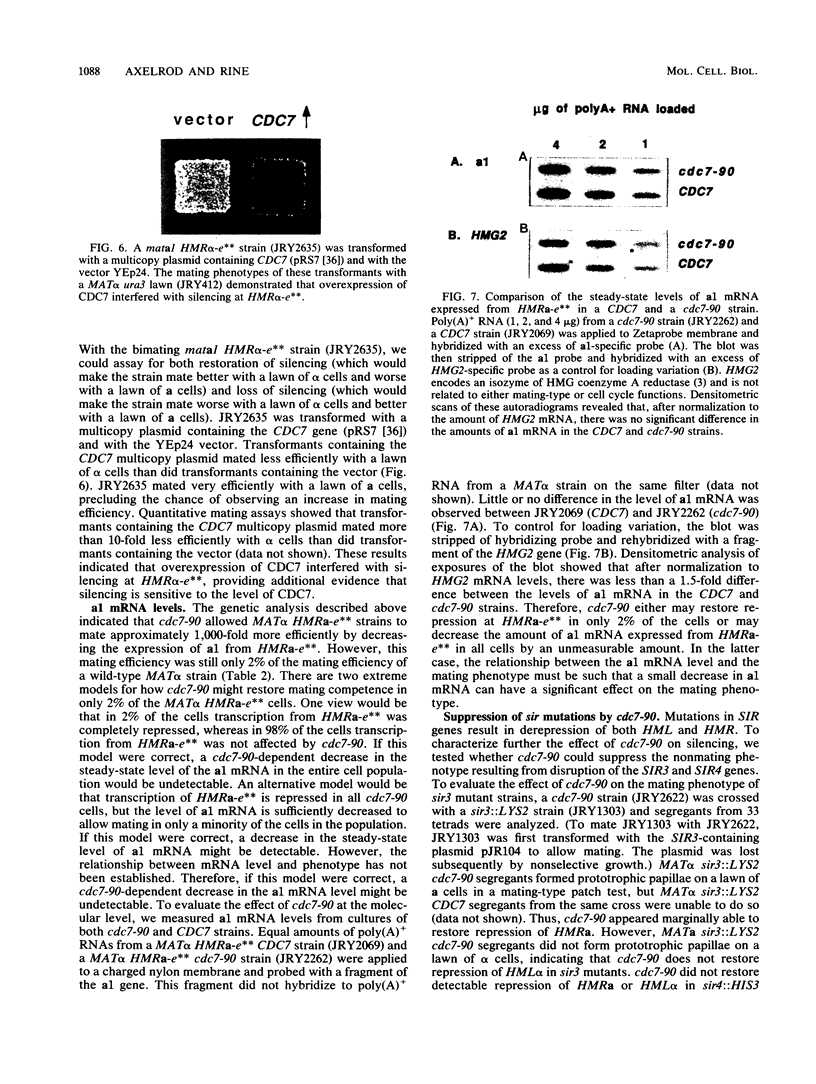
The mating-type genes at MAT in Saccharomyces cerevisiae are expressed, whereas the same genes located at HML and HMR are transcriptionally repressed. The DNA element responsible for repression at HMR has been termed a silencer and contains an autonomous replication sequence, a binding site for GRFI/RAPI, and a binding site for ABFI. A double-mutant HMR-E silencer that contains single nucleotide substitutions in both the GRFI/RAPI- and ABFI-binding sites no longer binds either factor in vitro, nor represses transcription at HMR in vivo. In MAT alpha cells, this derepression of a information results in a nonmating phenotype. Second-site suppressor mutations were isolated that restored the alpha mating phenotype to MAT alpha cells containing the double-mutant silencer. One of these suppressors, designated sas1-1, conferred a temperature-sensitive lethal phenotype to the cell. SAS1 was found to be identical to CDC7, a gene which encodes a protein kinase required for the initiation of DNA replication. This new allele of CDC7 was designated cdc7-90. cdc7-90 restored the alpha mating phenotype by restoring silencing. The original allele of CDC7, isolated on the basis of the cell cycle phenotype it confers, also restored silencing, and overexpression of CDC7 interfered with silencing. cdc7-90 did not restore detectable binding of GRFI/RAPI or ABFI to the double-mutant silencer in vitro. These results indicate that a reduced level of CDC7 function restores silencing to a locus defective in binding two factors normally required for silencing.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham J., Nasmyth K. A., Strathern J. N., Klar A. J., Hicks J. B. Regulation of mating-type information in yeast. Negative control requiring sequences both 5' and 3' to the regulated region. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jul 5;176(3):307–331. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90492-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balazs I., Brown E. H., Schildkraut C. L. The temporal order of replication of some DNA cistrons. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:239–245. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basson M. E., Thorsness M., Finer-Moore J., Stroud R. M., Rine J. Structural and functional conservation between yeast and human 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductases, the rate-limiting enzyme of sterol biosynthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3797–3808. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand A. H., Breeden L., Abraham J., Sternglanz R., Nasmyth K. Characterization of a "silencer" in yeast: a DNA sequence with properties opposite to those of a transcriptional enhancer. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90059-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand A. H., Micklem G., Nasmyth K. A yeast silencer contains sequences that can promote autonomous plasmid replication and transcriptional activation. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):709–719. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90094-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman A. R., Kimmerly W. J., Rine J., Kornberg R. D. Two DNA-binding factors recognize specific sequences at silencers, upstream activating sequences, autonomously replicating sequences, and telomeres in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):210–225. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman A. R., Lue N. F., Kornberg R. D. Connections between transcriptional activators, silencers, and telomeres as revealed by functional analysis of a yeast DNA-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5086–5099. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark-Adams C. D., Norris D., Osley M. A., Fassler J. S., Winston F. Changes in histone gene dosage alter transcription in yeast. Genes Dev. 1988 Feb;2(2):150–159. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.2.150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culotti J., Hartwell L. H. Genetic control of the cell division cycle in yeast. 3. Seven genes controlling nuclear division. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Aug;67(2):389–401. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(71)90424-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Della Seta F., Ciafré S. A., Marck C., Santoro B., Presutti C., Sentenac A., Bozzoni I. The ABF1 factor is the transcriptional activator of the L2 ribosomal protein genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2437–2441. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diffley J. F., Stillman B. Similarity between the transcriptional silencer binding proteins ABF1 and RAP1. Science. 1989 Nov 24;246(4933):1034–1038. doi: 10.1126/science.2511628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman J. B., Hicks J. B., Broach J. R. Identification of sites required for repression of a silent mating type locus in yeast. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 5;178(4):815–834. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90313-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartler S. M., Riggs A. D. Mammalian X-chromosome inactivation. Annu Rev Genet. 1983;17:155–190. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.17.120183.001103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman M. A. The chromatin domain as a unit of gene regulation. Bioessays. 1988 Aug-Sep;9(2-3):50–55. doi: 10.1002/bies.950090204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han M., Kim U. J., Kayne P., Grunstein M. Depletion of histone H4 and nucleosomes activates the PHO5 gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2221–2228. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03061.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harashima S., Miller A. M., Tanaka K., Kusumoto K., Tanaka K., Mukai Y., Nasmyth K., Oshima Y. Mating-type control in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: isolation and characterization of mutants defective in repression by a1-alpha 2. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4523–4530. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H. Three additional genes required for deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):966–974. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.966-974.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatton K. S., Dhar V., Brown E. H., Iqbal M. A., Stuart S., Didamo V. T., Schildkraut C. L. Replication program of active and inactive multigene families in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2149–2158. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herskowitz I. A regulatory hierarchy for cell specialization in yeast. Nature. 1989 Dec 14;342(6251):749–757. doi: 10.1038/342749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herskowitz I. Life cycle of the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Dec;52(4):536–553. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.4.536-553.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingsworth R. E., Jr, Sclafani R. A. DNA metabolism gene CDC7 from yeast encodes a serine (threonine) protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6272–6276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmquist G. P. Role of replication time in the control of tissue-specific gene expression. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Feb;40(2):151–173. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. M., Kayne P. S., Kahn E. S., Grunstein M. Genetic evidence for an interaction between SIR3 and histone H4 in the repression of the silent mating loci in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6286–6290. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassir Y., Hicks J. B., Herskowitz I. SAD mutation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is an extra a cassette. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):871–880. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayne P. S., Kim U. J., Han M., Mullen J. R., Yoshizaki F., Grunstein M. Extremely conserved histone H4 N terminus is dispensable for growth but essential for repressing the silent mating loci in yeast. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):27–39. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90006-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmerly W. J., Rine J. Replication and segregation of plasmids containing cis-acting regulatory sites of silent mating-type genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae are controlled by the SIR genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4225–4237. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmerly W., Buchman A., Kornberg R., Rine J. Roles of two DNA-binding factors in replication, segregation and transcriptional repression mediated by a yeast silencer. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2241–2253. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03064.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klar A. J., Strathern J. N., Hicks J. B. A position-effect control for gene transposition: state of expression of yeast mating-type genes affects their ability to switch. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):517–524. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90070-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird C. D. Proposed mechanism of inheritance and expression of the human fragile-X syndrome of mental retardation. Genetics. 1987 Nov;117(3):587–599. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.3.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Megee P. C., Morgan B. A., Mittman B. A., Smith M. M. Genetic analysis of histone H4: essential role of lysines subject to reversible acetylation. Science. 1990 Feb 16;247(4944):841–845. doi: 10.1126/science.2106160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermod N., O'Neill E. A., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. The proline-rich transcriptional activator of CTF/NF-I is distinct from the replication and DNA binding domain. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):741–753. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90108-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. M. The yeast MATa1 gene contains two introns. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1061–1065. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01927.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer R. K., Schild D. Genetic map of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Dec;44(4):519–571. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.4.519-571.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Njagi G. D., Kilbey B. J. cdc7-1 a temperature sensitive cell-cycle mutant which interferes with induced mutagenesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(4):478–481. doi: 10.1007/BF00337951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pillus L., Rine J. Epigenetic inheritance of transcriptional states in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):637–647. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90009-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds A. E., McCarroll R. M., Newlon C. S., Fangman W. L. Time of replication of ARS elements along yeast chromosome III. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4488–4494. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rine J., Herskowitz I. Four genes responsible for a position effect on expression from HML and HMR in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1987 May;116(1):9–22. doi: 10.1093/genetics/116.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schild D., Byers B. Meiotic effects of DNA-defective cell division cycle mutations of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Chromosoma. 1978 Dec 21;70(1):109–130. doi: 10.1007/BF00292220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M., Migeon B. R. Asynchronous replication of homologous loci on human active and inactive X chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3685–3689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnell R., Rine J. A position effect on the expression of a tRNA gene mediated by the SIR genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):494–501. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sclafani R. A., Patterson M., Rosamond J., Fangman W. L. Differential regulation of the yeast CDC7 gene during mitosis and meiosis. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):293–300. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore D., Nasmyth K. Purification and cloning of a DNA binding protein from yeast that binds to both silencer and activator elements. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90095-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer F., Gerring S. L., Connelly C., Hieter P. Mitotic chromosome transmission fidelity mutants in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1990 Feb;124(2):237–249. doi: 10.1093/genetics/124.2.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathern J. N., Klar A. J., Hicks J. B., Abraham J. A., Ivy J. M., Nasmyth K. A., McGill C. Homothallic switching of yeast mating type cassettes is initiated by a double-stranded cut in the MAT locus. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):183–192. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90418-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathern J., Hicks J., Herskowitz I. Control of cell type in yeast by the mating type locus. The alpha 1-alpha 2 hypothesis. J Mol Biol. 1981 Apr 15;147(3):357–372. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90488-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K., Stinchcomb D. T., Scherer S., Davis R. W. High-frequency transformation of yeast: autonomous replication of hybrid DNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1035–1039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umek R. M., Linskens M. H., Kowalski D., Huberman J. A. New beginnings in studies of eukaryotic DNA replication origins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jan 23;1007(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(89)90123-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]