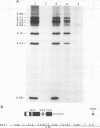
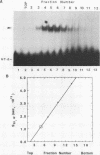
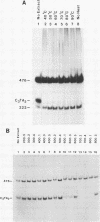
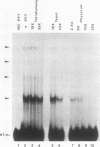
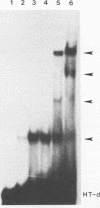
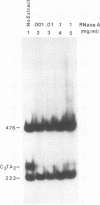
Abstract
We have partially purified a nuclear protein (PPT) from Physarum polycephalum that binds to the extrachromosomal ribosomal DNA telomeres of this acellular slime mold. Binding is specific for the (T2AG3)n telomere repeats, as evidenced by nitrocellulose filter binding assays, by gel mobility shift assays with both DNA fragments and double-stranded oligonucleotides, and by DNase I footprinting. PPT is remarkably heat stable, showing undiminished binding activity after incubation at 90 degrees C. It sediments at 1.2S, corresponding to a molecular weight of about 10,000 (for a globular protein), and its binding activity is undiminished by incubation with RNase, suggesting that it is not a ribonucleoprotein. We hypothesize that PPT plays a structural role in telomeres, perhaps preventing nucleolytic degradation or promoting telomere extension by a telomere-specific terminal transferase.
Full text
PDF


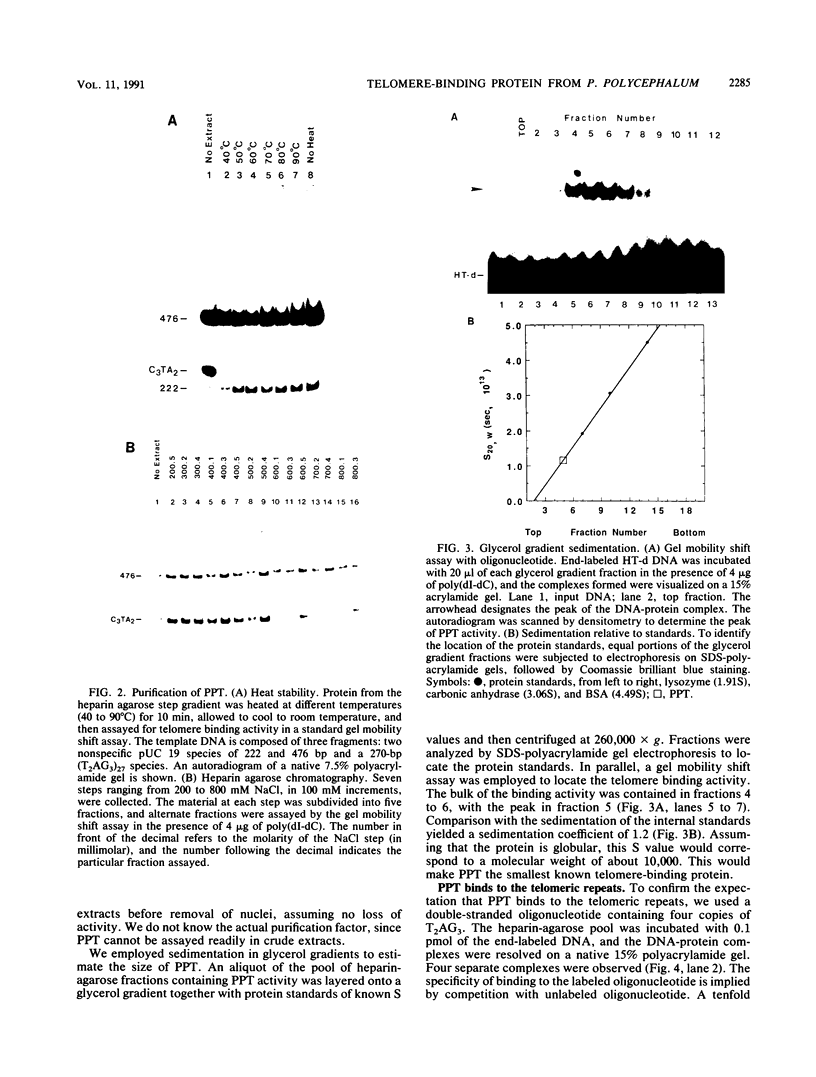





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berman J., Tachibana C. Y., Tye B. K. Identification of a telomere-binding activity from yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3713–3717. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H., Challoner P. B. Identification of a telomeric DNA sequence in Trypanosoma brucei. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):447–457. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90238-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H., Chiou S. S. Non-nucleosomal packaging of a tandemly repeated DNA sequence at termini of extrachromosomal DNA coding for rRNA in Tetrahymena. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2263–2267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H. The molecular structure of centromeres and telomeres. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:163–194. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman A. R., Lue N. F., Kornberg R. D. Connections between transcriptional activators, silencers, and telomeres as revealed by functional analysis of a yeast DNA-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5086–5099. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson M. J., Hartwell L. CDC17: an essential gene that prevents telomere elongation in yeast. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):249–257. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80120-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung M. K., Drivas D. T., Littau V. C., Johnson E. M. Protein tightly bound near the termini of the Physarum extrachromosomal rDNA palindrome. J Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;91(1):309–314. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.1.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad M. N., Wright J. H., Wolf A. J., Zakian V. A. RAP1 protein interacts with yeast telomeres in vivo: overproduction alters telomere structure and decreases chromosome stability. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):739–750. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90140-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DANIEL J. W., BABCOCK K. L., SIEVERT A. H., RUSCH H. P. ORGANIC REQUIREMENTS AND SYNTHETIC MEDIA FOR GROWTH OF THE MYXOMYCETE PHYSARUM POLYCEPHALUM. J Bacteriol. 1963 Aug;86:324–331. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.2.324-331.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferris P. J. Nucleotide sequence of the central non-transcribed spacer region of Physarum polycephalum rDNA. Gene. 1985;39(2-3):203–211. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90314-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferris P. J., Vogt V. M. Structure of the central spacer region of extrachromosomal ribosomal DNA in Physarum polycephalum. J Mol Biol. 1982 Aug 15;159(3):359–381. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90289-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forney J., Henderson E. R., Blackburn E. H. Identification of the telomeric sequence of the acellular slime molds Didymium iridis and Physarum polycephalum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 25;15(22):9143–9152. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.22.9143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschling D. E., Zakian V. A. Telomere proteins: specific recognition and protection of the natural termini of Oxytricha macronuclear DNA. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):195–205. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90442-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greider C. W., Blackburn E. H. A telomeric sequence in the RNA of Tetrahymena telomerase required for telomere repeat synthesis. Nature. 1989 Jan 26;337(6205):331–337. doi: 10.1038/337331a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greider C. W., Blackburn E. H. Identification of a specific telomere terminal transferase activity in Tetrahymena extracts. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):405–413. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90170-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greider C. W., Blackburn E. H. The telomere terminal transferase of Tetrahymena is a ribonucleoprotein enzyme with two kinds of primer specificity. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):887–898. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90576-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson E., Hardin C. C., Walk S. K., Tinoco I., Jr, Blackburn E. H. Telomeric DNA oligonucleotides form novel intramolecular structures containing guanine-guanine base pairs. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):899–908. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90577-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Kadonaga J. T., Rosenfeld P. J., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. A cellular DNA-binding protein that activates eukaryotic transcription and DNA replication. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90358-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Yamamoto K. R., Tjian R. Two distinct transcription factors bind to the HSV thymidine kinase promoter in vitro. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):559–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klobutcher L. A., Swanton M. T., Donini P., Prescott D. M. All gene-sized DNA molecules in four species of hypotrichs have the same terminal sequence and an unusual 3' terminus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3015–3019. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Z. P., Tye B. K. A yeast protein that binds to vertebrate telomeres and conserved yeast telomeric junctions. Genes Dev. 1991 Jan;5(1):49–59. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longtine M. S., Wilson N. M., Petracek M. E., Berman J. A yeast telomere binding activity binds to two related telomere sequence motifs and is indistinguishable from RAP1. Curr Genet. 1989 Oct;16(4):225–239. doi: 10.1007/BF00422108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundblad V., Szostak J. W. A mutant with a defect in telomere elongation leads to senescence in yeast. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):633–643. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90132-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lustig A. J., Kurtz S., Shore D. Involvement of the silencer and UAS binding protein RAP1 in regulation of telomere length. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):549–553. doi: 10.1126/science.2237406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lustig A. J., Petes T. D. Identification of yeast mutants with altered telomere structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1398–1402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin G. B. The human telomere terminal transferase enzyme is a ribonucleoprotein that synthesizes TTAGGG repeats. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):521–529. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90035-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyzis R. K., Buckingham J. M., Cram L. S., Dani M., Deaven L. L., Jones M. D., Meyne J., Ratliff R. L., Wu J. R. A highly conserved repetitive DNA sequence, (TTAGGG)n, present at the telomeres of human chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6622–6626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka Y., Thomas C. A., Jr The cohering telomeres of Oxytricha. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 11;15(21):8877–8898. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.21.8877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pluta A. F., Dani G. M., Spear B. B., Zakian V. A. Elaboration of telomeres in yeast: recognition and modification of termini from Oxytricha macronuclear DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1475–1479. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price C. M., Cech T. R. Properties of the telomeric DNA-binding protein from Oxytricha nova. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 24;28(2):769–774. doi: 10.1021/bi00428a053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price C. M., Cech T. R. Telomeric DNA-protein interactions of Oxytricha macronuclear DNA. Genes Dev. 1987 Oct;1(8):783–793. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.8.783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price C. M. Telomere structure in Euplotes crassus: characterization of DNA-protein interactions and isolation of a telomere-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3421–3431. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raghuraman M. K., Cech T. R. Assembly and self-association of oxytricha telomeric nucleoprotein complexes. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):719–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90018-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raghuraman M. K., Dunn C. J., Hicke B. J., Cech T. R. Oxytricha telomeric nucleoprotein complexes reconstituted with synthetic DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 12;17(11):4235–4253. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.11.4235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs A. D., Suzuki H., Bourgeois S. Lac repressor-operator interaction. I. Equilibrium studies. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 28;48(1):67–83. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90219-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechtman M. G. Characterization of telomere DNA from Neurospora crassa. Gene. 1990 Apr 16;88(2):159–165. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90027-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen D., Gilbert W. A sodium-potassium switch in the formation of four-stranded G4-DNA. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):410–414. doi: 10.1038/344410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen D., Gilbert W. Formation of parallel four-stranded complexes by guanine-rich motifs in DNA and its implications for meiosis. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):364–366. doi: 10.1038/334364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shampay J., Szostak J. W., Blackburn E. H. DNA sequences of telomeres maintained in yeast. Nature. 1984 Jul 12;310(5973):154–157. doi: 10.1038/310154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shippen-Lentz D., Blackburn E. H. Functional evidence for an RNA template in telomerase. Science. 1990 Feb 2;247(4942):546–552. doi: 10.1126/science.1689074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shippen-Lentz D., Blackburn E. H. Telomere terminal transferase activity from Euplotes crassus adds large numbers of TTTTGGGG repeats onto telomeric primers. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2761–2764. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoeman R. L., Wadle S., Scherbarth A., Traub P. The binding in vitro of the intermediate filament protein vimentin to synthetic oligonucleotides containing telomere sequences. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):18744–18749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore D., Nasmyth K. Purification and cloning of a DNA binding protein from yeast that binds to both silencer and activator elements. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90095-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Sen R., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. A nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence motif in transcriptional control elements of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):154–158. doi: 10.1038/319154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt V. M., Braun R. Structure of ribosomal DNA in Physarum polycephalum. J Mol Biol. 1976 Sep 25;106(3):567–587. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90252-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. S., Zakian V. A. Telomere-telomere recombination provides an express pathway for telomere acquisition. Nature. 1990 May 31;345(6274):456–458. doi: 10.1038/345456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson J. R., Raghuraman M. K., Cech T. R. Monovalent cation-induced structure of telomeric DNA: the G-quartet model. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):871–880. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90610-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu G. L., Bradley J. D., Attardi L. D., Blackburn E. H. In vivo alteration of telomere sequences and senescence caused by mutated Tetrahymena telomerase RNAs. Nature. 1990 Mar 8;344(6262):126–132. doi: 10.1038/344126a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahler A. M., Prescott D. M. Telomere terminal transferase activity in the hypotrichous ciliate Oxytricha nova and a model for replication of the ends of linear DNA molecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14B):6953–6972. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.6953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakian V. A. Structure and function of telomeres. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:579–604. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.003051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]