Abstract
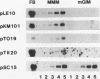
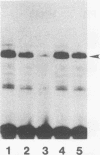
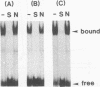
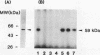
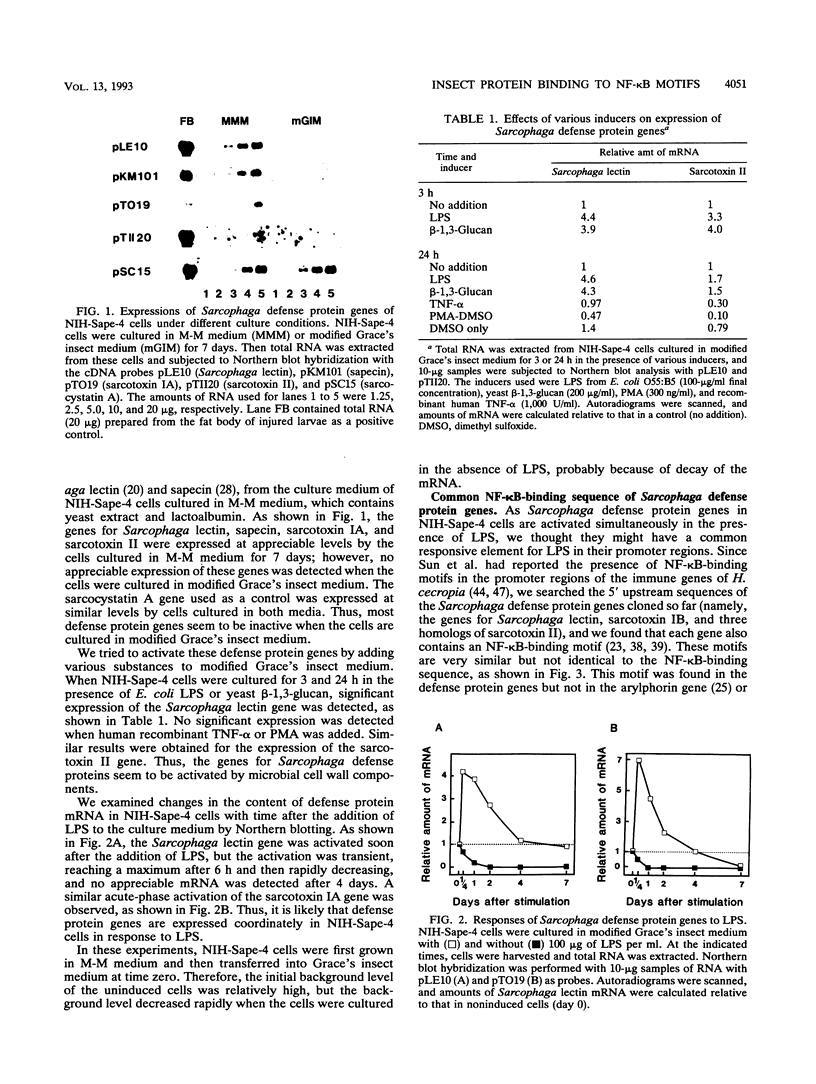
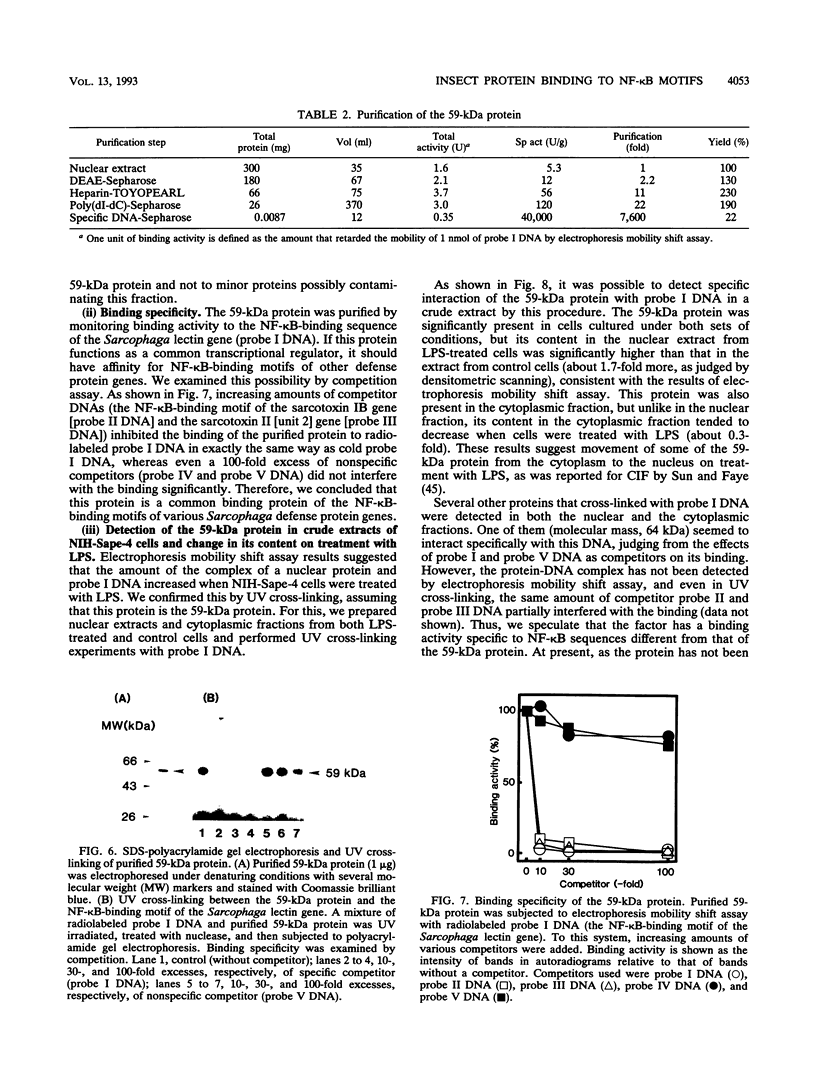
Various Sarcophaga peregrina (flesh fly) defense protein genes were shown to be activated when NIH-Sape-4 cells were cultured with bacterial lipopolysaccharides or beta-1,3-glucan. The 5' upstream regions of the defense protein genes were found to have common motifs showing similarity to the mammalian NF-kappa B-binding consensus sequence. A protein with affinity to the NF-kappa B-binding motif of the Sarcophaga lectin promoter was identified and purified to near homogeneity. This 59-kDa protein also bound to the NF-kappa B-binding motifs of other defense protein genes, e.g., sarcotoxin I and sarcotoxin II genes. This protein was found in both the cytoplasmic and the nuclear fractions of the cells, and it appeared to migrate from the cytoplasm to the nucleus on treatment of the cells with lipopolysaccharides. This 59-kDa protein is probably a transcriptional regulator of the genes for defense proteins of S. peregrina.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ando K., Natori S. Molecular cloning, sequencing, and characterization of cDNA for sarcotoxin IIA, an inducible antibacterial protein of Sarcophaga peregrina (flesh fly). Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 8;27(5):1715–1721. doi: 10.1021/bi00405a050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ando K., Okada M., Natori S. Purification of sarcotoxin II, antibacterial proteins of Sarcophaga peregrina (flesh fly) larvae. Biochemistry. 1987 Jan 13;26(1):226–230. doi: 10.1021/bi00375a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. I kappa B: a specific inhibitor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Science. 1988 Oct 28;242(4878):540–546. doi: 10.1126/science.3140380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boman H. G. Antibacterial peptides: key components needed in immunity. Cell. 1991 Apr 19;65(2):205–207. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90154-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boman H. G., Faye I., Gudmundsson G. H., Lee J. Y., Lidholm D. A. Cell-free immunity in Cecropia. A model system for antibacterial proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Oct 1;201(1):23–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16252.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boman H. G., Hultmark D. Cell-free immunity in insects. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:103–126. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.000535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler R., Bergmann A., Hiromi Y., Nüsslein-Volhard C. cactus, a gene involved in dorsoventral pattern formation of Drosophila, is related to the I kappa B gene family of vertebrates. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):613–621. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90595-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Gifford A. M., Riviere L. R., Tempst P., Nolan G. P., Baltimore D. Cloning of the p50 DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B: homology to rel and dorsal. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1019–1029. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90276-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Tjian R. Affinity purification of sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5889–5893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanai A., Natori S. Analysis of a gene cluster for sarcotoxin II, a group of antibacterial proteins of Sarcophaga peregrina. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6114–6122. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanai A., Natori S. Cloning of gene cluster for sarcotoxin I, antibacterial proteins of Sarcophaga peregrina. FEBS Lett. 1989 Dec 4;258(2):199–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81652-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami K., Scheidereit C., Roeder R. G. Identification and purification of a human immunoglobulin-enhancer-binding protein (NF-kappa B) that activates transcription from a human immunodeficiency virus type 1 promoter in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4700–4704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd S. Characterization of the Drosophila cactus locus and analysis of interactions between cactus and dorsal proteins. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):623–635. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90596-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieran M., Blank V., Logeat F., Vandekerckhove J., Lottspeich F., Le Bail O., Urban M. B., Kourilsky P., Baeuerle P. A., Israël A. The DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B is identical to factor KBF1 and homologous to the rel oncogene product. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1007–1018. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90275-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. W., Matsumoto N., Komano H., Natori S. Stage-specific detection of a DNA-binding protein for the storage protein gene of Sarcophaga peregrina. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jun 1;1008(1):79–84. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(89)90172-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi A., Hirai H., Kubo T., Ueno K., Nakanishi Y., Natori S. Cloning and in vitro transcription of the Sarcophaga lectin gene. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Dec 22;1009(3):244–250. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(89)90109-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komano H., Kasama E., Nagasawa Y., Nakanishi Y., Matsuyama K., Ando K., Natori S. Purification of Sarcophaga (fleshfly) lectin and detection of sarcotoxins in the culture medium of NIH-Sape-4, an embryonic cell line of Sarcophaga peregrina. Biochem J. 1987 Nov 15;248(1):217–222. doi: 10.1042/bj2480217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komano H., Mizuno D., Natori S. Purification of lectin induced in the hemolymph of Sarcophaga peregrina larvae on injury. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 10;255(7):2919–2924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kylsten P., Samakovlis C., Hultmark D. The cecropin locus in Drosophila; a compact gene cluster involved in the response to infection. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):217–224. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08098.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M. J., Baltimore D. NF-kappa B: a pleiotropic mediator of inducible and tissue-specific gene control. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):227–229. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90833-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto N., Nakanishi Y., Natori S. Homologies of nucleotide sequences in the 5'-end regions of two developmentally regulated genes of Sarcophaga peregrina. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2685–2698. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto N., Okada M., Takahashi H., Ming Q. X., Nakajima Y., Nakanishi Y., Komano H., Natori S. Molecular cloning of a cDNA and assignment of the C-terminal of sarcotoxin IA, a potent antibacterial protein of Sarcophaga peregrina. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 1;239(3):717–722. doi: 10.1042/bj2390717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto N., Sekimizu K., Soma G., Ohmura Y., Andoh T., Nakanishi Y., Obinata M., Natori S. Structural analysis of a developmentally regulated 25-kDa protein gene of Sarcophaga peregrina. J Biochem. 1985 May;97(5):1501–1508. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama K., Natori S. Purification of three antibacterial proteins from the culture medium of NIH-Sape-4, an embryonic cell line of Sarcophaga peregrina. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):17112–17116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nanbu R., Nakajima Y., Ando K., Natori S. Novel feature of expression of the sarcotoxin IA gene in development of Sarcophaga peregrina. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jan 29;150(2):540–544. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90427-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada M., Natori S. Purification and characterization of an antibacterial protein from haemolymph of Sarcophaga peregrina (flesh-fly) larvae. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 1;211(3):727–734. doi: 10.1042/bj2110727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichhart J. M., Meister M., Dimarcq J. L., Zachary D., Hoffmann D., Ruiz C., Richards G., Hoffmann J. A. Insect immunity: developmental and inducible activity of the Drosophila diptericin promoter. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1469–1477. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05191.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Suzuki T., Ueno K., Kubo T., Natori S. Molecular cloning of cDNA for sarcocystatin A and analysis of the expression of the sarcocystatin A gene during development of Sarcophaga peregrina. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 21;28(4):1749–1755. doi: 10.1021/bi00430a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samakovlis C., Asling B., Boman H. G., Gateff E., Hultmark D. In vitro induction of cecropin genes--an immune response in a Drosophila blood cell line. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Nov 16;188(3):1169–1175. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91354-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreck R., Rieber P., Baeuerle P. A. Reactive oxygen intermediates as apparently widely used messengers in the activation of the NF-kappa B transcription factor and HIV-1. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2247–2258. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07761.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Inducibility of kappa immunoglobulin enhancer-binding protein Nf-kappa B by a posttranslational mechanism. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):921–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90807-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiraishi A., Natori S. Humoral mediator-dependent activation of the Sarcophaga lectin gene. FEBS Lett. 1988 May 9;232(1):163–166. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80409-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staal F. J., Roederer M., Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A. Intracellular thiols regulate activation of nuclear factor kappa B and transcription of human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9943–9947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama H., Natori S. A novel mechanism of Sarcophaga lectin gene expression. Possible involvement of oxidation of the sulfhydryl group of a fat-body protein. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Sep 1;200(2):495–500. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16210.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun S. C., Asling B., Faye I. Organization and expression of the immunoresponsive lysozyme gene in the giant silk moth, Hyalophora cecropia. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6644–6649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun S. C., Faye I. Affinity purification and characterization of CIF, an insect immunoresponsive factor with NF-kappa B-like properties. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1992 Sep;103(1):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(92)90436-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun S. C., Faye I. Cecropia immunoresponsive factor, an insect immunoresponsive factor with DNA-binding properties similar to nuclear-factor kappa B. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Mar 1;204(2):885–892. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16708.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun S. C., Lindström I., Lee J. Y., Faye I. Structure and expression of the attacin genes in Hyalophora cecropia. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Feb 26;196(1):247–254. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15811.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi H., Komano H., Kawaguchi N., Kitamura N., Nakanishi S., Natori S. Cloning and sequencing of cDNA of Sarcophaga peregrina humoral lectin induced on injury of the body wall. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):12228–12233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabel U., Schreck R., Baeuerle P. A. DNA binding of purified transcription factor NF-kappa B. Affinity, specificity, Zn2+ dependence, and differential half-site recognition. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):252–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]