Abstract
We showed previously that DNA replication initiates at multiple sites in the 5-kb histone gene repeating unit in early embryos of Drosophila melanogaster. The present report shows evidence that replication in the same chromosomal region initiates at multiple sites in tissue culture cells as well. First, we analyzed replication intermediates by the two-dimensional gel electrophoretic replicon mapping method and detected bubble-form replication intermediates for all fragments restricted at different sites in the repeating unit. Second, we analyzed bromodeoxyuridine-labeled nascent strands amplified by the polymerase chain reaction method and detected little differences in the size distribution of nascent strands specific to six short segments located at different sites in the repeating unit. These results strongly suggest that DNA replication initiates at multiple sites located within the repeating unit. We also found several replication pause sites located at 5' upstream regions of some histone genes.
Full text
PDF




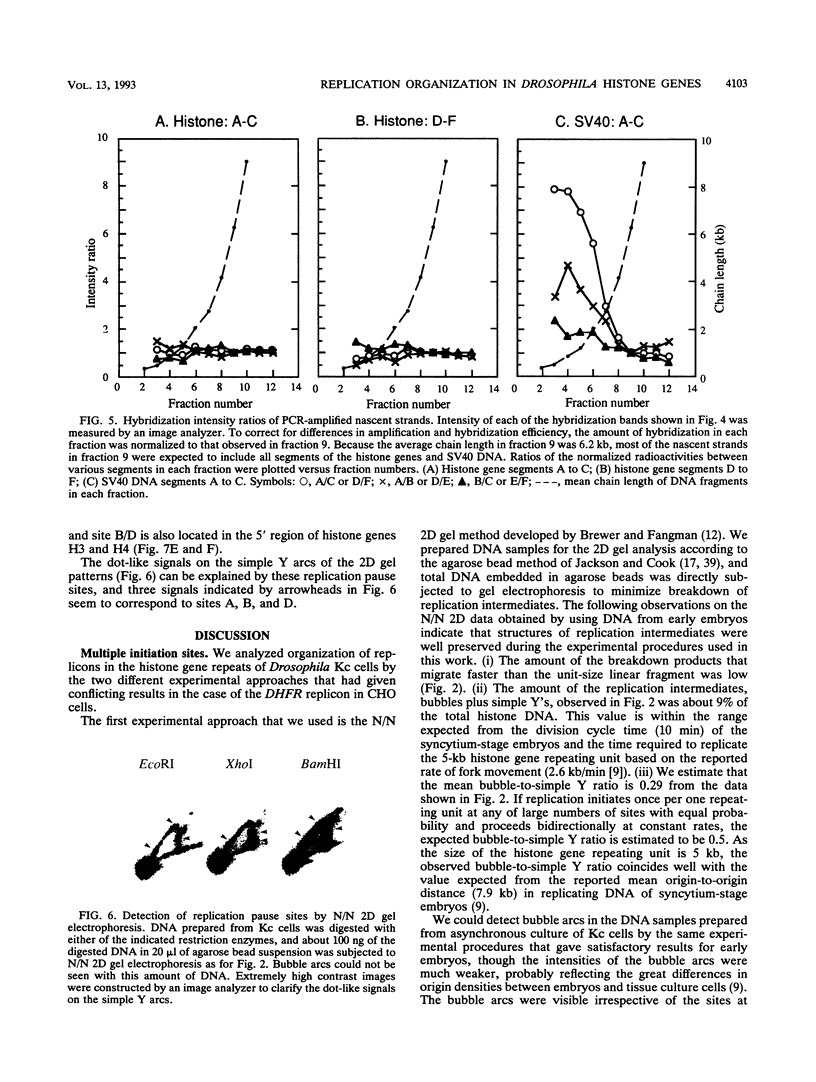



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amati B. B., Gasser S. M. Chromosomal ARS and CEN elements bind specifically to the yeast nuclear scaffold. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):967–978. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90111-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amati B., Gasser S. M. Drosophila scaffold-attached regions bind nuclear scaffolds and can function as ARS elements in both budding and fission yeasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5442–5454. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambrosio L., Schedl P. Two discrete modes of histone gene expression during oogenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1985 Sep;111(1):220–231. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90447-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amemiya Y., Miyahara J. Imaging plate illuminates many fields. Nature. 1988 Nov 3;336(6194):89–90. doi: 10.1038/336089a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell S. P., Stillman B. ATP-dependent recognition of eukaryotic origins of DNA replication by a multiprotein complex. Nature. 1992 May 14;357(6374):128–134. doi: 10.1038/357128a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benbow R. M., Zhao J., Larson D. D. On the nature of origins of DNA replication in eukaryotes. Bioessays. 1992 Oct;14(10):661–670. doi: 10.1002/bies.950141004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blow J. J., Laskey R. A. Initiation of DNA replication in nuclei and purified DNA by a cell-free extract of Xenopus eggs. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):577–587. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90622-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal A. B., Kriegstein H. J., Hogness D. S. The units of DNA replication in Drosophila melanogaster chromosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:205–223. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowiec J. A., Dean F. B., Bullock P. A., Hurwitz J. Binding and unwinding--how T antigen engages the SV40 origin of DNA replication. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):181–184. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90730-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bramhill D., Kornberg A. A model for initiation at origins of DNA replication. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):915–918. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90102-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer B. J., Fangman W. L. A replication fork barrier at the 3' end of yeast ribosomal RNA genes. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):637–643. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer B. J., Fangman W. L. The localization of replication origins on ARS plasmids in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):463–471. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90642-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinton B. T., Caddle M. S., Heintz N. H. Position and orientation-dependent effects of a eukaryotic Z-triplex DNA motif on episomal DNA replication in COS-7 cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 15;266(8):5153–5161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burhans W. C., Vassilev L. T., Caddle M. S., Heintz N. H., DePamphilis M. L. Identification of an origin of bidirectional DNA replication in mammalian chromosomes. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):955–965. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90270-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burhans W. C., Vassilev L. T., Wu J., Sogo J. M., Nallaseth F. S., DePamphilis M. L. Emetine allows identification of origins of mammalian DNA replication by imbalanced DNA synthesis, not through conservative nucleosome segregation. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4351–4360. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb05013.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bénard M., Pierron G. Mapping of a Physarum chromosomal origin of replication tightly linked to a developmentally-regulated profilin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jul 11;20(13):3309–3315. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.13.3309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. R. A general method for preparing intact nuclear DNA. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1837–1842. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02056.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross D. P., Sang J. H. Cell culture of individual Drosophila embryos. I. Development of wild-type cultures. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1978 Jun;45:161–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delidakis C., Kafatos F. C. Amplification enhancers and replication origins in the autosomal chorion gene cluster of Drosophila. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):891–901. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03450.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhar V., Schildkraut C. L. Role of EBNA-1 in arresting replication forks at the Epstein-Barr virus oriP family of tandem repeats. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):6268–6278. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.6268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diffley J. F., Stillman B. The initiation of chromosomal DNA replication in eukaryotes. Trends Genet. 1990 Dec;6(12):427–432. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90305-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkwel P. A., Hamlin J. L. Initiation of DNA replication in the dihydrofolate reductase locus is confined to the early S period in CHO cells synchronized with the plant amino acid mimosine. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):3715–3722. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.3715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkwel P. A., Vaughn J. P., Hamlin J. L. Mapping of replication initiation sites in mammalian genomes by two-dimensional gel analysis: stabilization and enrichment of replication intermediates by isolation on the nuclear matrix. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):3850–3859. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.3850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar B. A., Schubiger G. Parameters controlling transcriptional activation during early Drosophila development. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):871–877. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90009-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson B. M., Brewer B. J., Reynolds A. E., Fangman W. L. A yeast origin of replication is activated late in S phase. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):507–515. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90468-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gahn T. A., Schildkraut C. L. The Epstein-Barr virus origin of plasmid replication, oriP, contains both the initiation and termination sites of DNA replication. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):527–535. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90433-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser S. M., Laemmli U. K. Cohabitation of scaffold binding regions with upstream/enhancer elements of three developmentally regulated genes of D. melanogaster. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):521–530. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90877-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudette M. F., Benbow R. M. Replication forks are underrepresented in chromosomal DNA of Xenopus laevis embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5953–5957. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenfeder S. A., Newlon C. S. Replication forks pause at yeast centromeres. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):4056–4066. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.4056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamlin J. L. Mammalian origins of replication. Bioessays. 1992 Oct;14(10):651–659. doi: 10.1002/bies.950141002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harland R. M., Laskey R. A. Regulated replication of DNA microinjected into eggs of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):761–771. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90439-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heck M. M., Spradling A. C. Multiple replication origins are used during Drosophila chorion gene amplification. J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;110(4):903–914. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.4.903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hereford L. M., Osley M. A., Ludwig T. R., 2nd, McLaughlin C. S. Cell-cycle regulation of yeast histone mRNA. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):367–375. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90326-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman J. A., Spotila L. D., Nawotka K. A., el-Assouli S. M., Davis L. R. The in vivo replication origin of the yeast 2 microns plasmid. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):473–481. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90643-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyrien O., Méchali M. Plasmid replication in Xenopus eggs and egg extracts: a 2D gel electrophoretic analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Apr 11;20(7):1463–1469. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.7.1463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal M. A., Plumb M., Stein J., Stein G., Schildkraut C. L. Coordinate replication of members of the multigene family of core and H1 human histone genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7723–7727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishimi Y., Claude A., Bullock P., Hurwitz J. Complete enzymatic synthesis of DNA containing the SV40 origin of replication. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19723–19733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D. A., Cook P. R. A general method for preparing chromatin containing intact DNA. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):913–918. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03718.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi T., Hidaka M., Nishizawa M., Horiuchi T. Identification of a site required for DNA replication fork blocking activity in the rRNA gene cluster in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Jun;233(3):355–362. doi: 10.1007/BF00265431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krysan P. J., Calos M. P. Replication initiates at multiple locations on an autonomously replicating plasmid in human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1464–1472. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifton R. P., Goldberg M. L., Karp R. W., Hogness D. S. The organization of the histone genes in Drosophila melanogaster: functional and evolutionary implications. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):1047–1051. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linskens M. H., Huberman J. A. Organization of replication of ribosomal DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4927–4935. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linskens M. H., Huberman J. A. The two faces of higher eukaryotic DNA replication origins. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):845–847. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90258-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahbubani H. M., Paull T., Elder J. K., Blow J. J. DNA replication initiates at multiple sites on plasmid DNA in Xenopus egg extracts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Apr 11;20(7):1457–1462. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.7.1457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo Y., Yamazaki T. tRNA derived insertion element in histone gene repeating unit of Drosophila melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 11;17(1):225–238. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.1.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirkovitch J., Mirault M. E., Laemmli U. K. Organization of the higher-order chromatin loop: specific DNA attachment sites on nuclear scaffold. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90208-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Méchali M., Kearsey S. Lack of specific sequence requirement for DNA replication in Xenopus eggs compared with high sequence specificity in yeast. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):55–64. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90526-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller F., Grummt F. Mapping eukaryotic replication origins in vivo by size analysis of purified nascent DNA strands. DNA Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;10(2):149–157. doi: 10.1089/dna.1991.10.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saigo K., Millstein L., Thomas C. A., Jr The organization of Drosophila melanogaster histone genes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 2):815–827. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinomiya T., Ina S. Analysis of chromosomal replicons in early embryos of Drosophila melanogaster by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 25;19(14):3935–3941. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.14.3935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umek R. M., Linskens M. H., Kowalski D., Huberman J. A. New beginnings in studies of eukaryotic DNA replication origins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jan 23;1007(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(89)90123-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassilev L. T., Burhans W. C., DePamphilis M. L. Mapping an origin of DNA replication at a single-copy locus in exponentially proliferating mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4685–4689. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassilev L., Johnson E. M. An initiation zone of chromosomal DNA replication located upstream of the c-myc gene in proliferating HeLa cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4899–4904. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassilev L., Johnson E. M. Mapping initiation sites of DNA replication in vivo using polymerase chain reaction amplification of nascent strand segments. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 11;17(19):7693–7705. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.19.7693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughn J. P., Dijkwel P. A., Hamlin J. L. Replication initiates in a broad zone in the amplified CHO dihydrofolate reductase domain. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):1075–1087. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90071-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker S. S., Malik A. K., Eisenberg S. Analysis of the interactions of functional domains of a nuclear origin of replication from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 25;19(22):6255–6262. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.22.6255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu J., Newlon C. S., Huberman J. A. Localization of a DNA replication origin and termination zone on chromosome III of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4733–4741. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]