Abstract
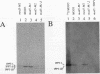
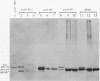
MOD5 is one of several genes that code for enzymes found in mitochondria and another cellular compartment. Like other such genes, it contains two in-frame ATGs that could be used to produce two proteins, differing from each other by an amino-terminal extension. Certain other genes produce heterogeneous mRNAs with some 5' ends falling upstream of the longest open reading frame and some 5' ends falling between the first and second ATGs. In these cases, selection of transcription start sites appears to play a significant role in translation start site selection. MOD5, in contrast, produces mRNAs with 5' ends that all fall upstream of both ATGs. To determine how MOD5 encodes isozymes that are located in different cellular compartments and to determine whether they differ in structure, we constructed MOD5 and MOD5-COXIV fusions with mutations of the first, second, or both ATGs. The effect of these alterations on protein production, tRNA modification, and cellular location was assessed. Both the first and second ATGs are used to produce MOD5 protein in vivo, but only the long form of the protein is imported into mitochondria. Thus, the first 11 amino acids present on the amino-terminal extended protein are necessary for mitochondrial import. Surprisingly, this extension does not promote complete import of the long form of the protein, but rather a functional pool of the extended protein remains in the cytoplasm. The amino-terminal extension is also unusual because it is probably not proteolytically removed upon import and therefore does not constitute part of a mitochondrial presequence.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ades I. Z., Butow R. A. The products of mitochondria-bound cytoplasmic polysomes in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9918–9924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ades I. Z., Butow R. A. The transport of proteins into yeast mitochondria. Kinetics and pools. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9925–9935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attardi G., Schatz G. Biogenesis of mitochondria. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:289–333. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.001445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beltzer J. P., Chang L. F., Hinkkanen A. E., Kohlhaw G. B. Structure of yeast LEU4. The 5' flanking region contains features that predict two modes of control and two productive translation starts. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):5160–5167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beltzer J. P., Morris S. R., Kohlhaw G. B. Yeast LEU4 encodes mitochondrial and nonmitochondrial forms of alpha-isopropylmalate synthase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):368–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatton B., Walter P., Ebel J. P., Lacroute F., Fasiolo F. The yeast VAS1 gene encodes both mitochondrial and cytoplasmic valyl-tRNA synthetases. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):52–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daum G., Böhni P. C., Schatz G. Import of proteins into mitochondria. Cytochrome b2 and cytochrome c peroxidase are located in the intermembrane space of yeast mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):13028–13033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dihanich M. E., Najarian D., Clark R., Gillman E. C., Martin N. C., Hopper A. K. Isolation and characterization of MOD5, a gene required for isopentenylation of cytoplasmic and mitochondrial tRNAs of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):177–184. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowhan W., Bibus C. R., Schatz G. The cytoplasmically-made subunit IV is necessary for assembly of cytochrome c oxidase in yeast. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):179–184. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02334.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilers M., Schatz G. Binding of a specific ligand inhibits import of a purified precursor protein into mitochondria. Nature. 1986 Jul 17;322(6076):228–232. doi: 10.1038/322228a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis S. R., Hopper A. K., Martin N. C. Amino-terminal extension generated from an upstream AUG codon increases the efficiency of mitochondrial import of yeast N2,N2-dimethylguanosine-specific tRNA methyltransferases. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1611–1620. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis S. R., Hopper A. K., Martin N. C. Amino-terminal extension generated from an upstream AUG codon is not required for mitochondrial import of yeast N2,N2-dimethylguanosine-specific tRNA methyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5172–5176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis S. R., Morales M. J., Li J. M., Hopper A. K., Martin N. C. Isolation and characterization of the TRM1 locus, a gene essential for the N2,N2-dimethylguanosine modification of both mitochondrial and cytoplasmic tRNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9703–9709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabian G. R., Hess S. M., Hopper A. K. srd1, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae suppressor of the temperature-sensitive pre-rRNA processing defect of rrp1-1. Genetics. 1990 Mar;124(3):497–504. doi: 10.1093/genetics/124.3.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gangloff S. P., Marguet D., Lauquin G. J. Molecular cloning of the yeast mitochondrial aconitase gene (ACO1) and evidence of a synergistic regulation of expression by glucose plus glutamate. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3551–3561. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough J. A., Murray N. E. Sequence diversity among related genes for recognition of specific targets in DNA molecules. J Mol Biol. 1983 May 5;166(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N., Alexander H., Olson A., Alexander S., Shinnick T. M., Sutcliffe J. G., Lerner R. A. Immunogenic structure of the influenza virus hemagglutinin. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90202-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hase T., Müller U., Riezman H., Schatz G. A 70-kd protein of the yeast mitochondrial outer membrane is targeted and anchored via its extreme amino terminus. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3157–3164. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02274.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Woods K. R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3824–3828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper A. K., Schultz L. D., Shapiro R. A. Processing of intervening sequences: a new yeast mutant which fails to excise intervening sequences from precursor tRNAs. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):741–751. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80050-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper A. K., Traglia H. M., Dunst R. W. The yeast RNA1 gene product necessary for RNA processing is located in the cytosol and apparently excluded from the nucleus. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):309–321. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurt D. J., Wang S. S., Lin Y. H., Hopper A. K. Cloning and characterization of LOS1, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene that affects tRNA splicing. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1208–1216. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurt E. C., Müller U., Schatz G. The first twelve amino acids of a yeast mitochondrial outer membrane protein can direct a nuclear-coded cytochrome oxidase subunit to the mitochondrial inner membrane. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3509–3518. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04110.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilmartin J. V., Adams A. E. Structural rearrangements of tubulin and actin during the cell cycle of the yeast Saccharomyces. J Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;98(3):922–933. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.3.922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. L., Campbell J. L. Cloning of Saccharomyces cerevisiae DNA replication genes: isolation of the CDC8 gene and two genes that compensate for the cdc8-1 mutation. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Oct;3(10):1730–1737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.10.1730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laten H., Gorman J., Bock R. M. Isopentenyladenosine deficient tRNA from an antisuppressor mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Nov;5(11):4329–4342. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.11.4329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. M., Hopper A. K., Martin N. C. N2,N2-dimethylguanosine-specific tRNA methyltransferase contains both nuclear and mitochondrial targeting signals in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;109(4 Pt 1):1411–1419. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.4.1411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin N. C., Hopper A. K. Isopentenylation of both cytoplasmic and mitochondrial tRNA is affected by a single nuclear mutation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):10562–10565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Najarian D., Dihanich M. E., Martin N. C., Hopper A. K. DNA sequence and transcript mapping of MOD5: features of the 5' region which suggest two translational starts. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):185–191. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda T., Funai T., Ichiyama A. Generation from a single gene of two mRNAs that encode the mitochondrial and peroxisomal serine:pyruvate aminotransferase of rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 5;265(13):7513–7519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid G. A., Schatz G. Import of proteins into mitochondria. Extramitochondrial pools and post-translational import of mitochondrial protein precursors in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):13062–13067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz L. D., Hofmann K. J., Mylin L. M., Montgomery D. L., Ellis R. W., Hopper J. E. Regulated overproduction of the GAL4 gene product greatly increases expression from galactose-inducible promoters on multi-copy expression vectors in yeast. Gene. 1987;61(2):123–133. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90107-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki T., Sato M., Yoshida T., Tuboi S. Rat liver mitochondrial and cytosolic fumarases with identical amino acid sequences are encoded from a single gene. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):2581–2586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tropschug M., Nicholson D. W., Hartl F. U., Köhler H., Pfanner N., Wachter E., Neupert W. Cyclosporin A-binding protein (cyclophilin) of Neurospora crassa. One gene codes for both the cytosolic and mitochondrial forms. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14433–14440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu M., Tzagoloff A. Mitochondrial and cytoplasmic fumarases in Saccharomyces cerevisiae are encoded by a single nuclear gene FUM1. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):12275–12282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Loon A. P., Brändli A. W., Pesold-Hurt B., Blank D., Schatz G. Transport of proteins to the mitochondrial intermembrane space: the 'matrix-targeting' and the 'sorting' domains in the cytochrome c1 presequence. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2433–2439. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02522.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Mitochondrial targeting sequences may form amphiphilic helices. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1335–1342. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04364.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]