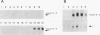Abstract
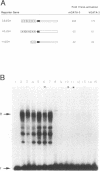
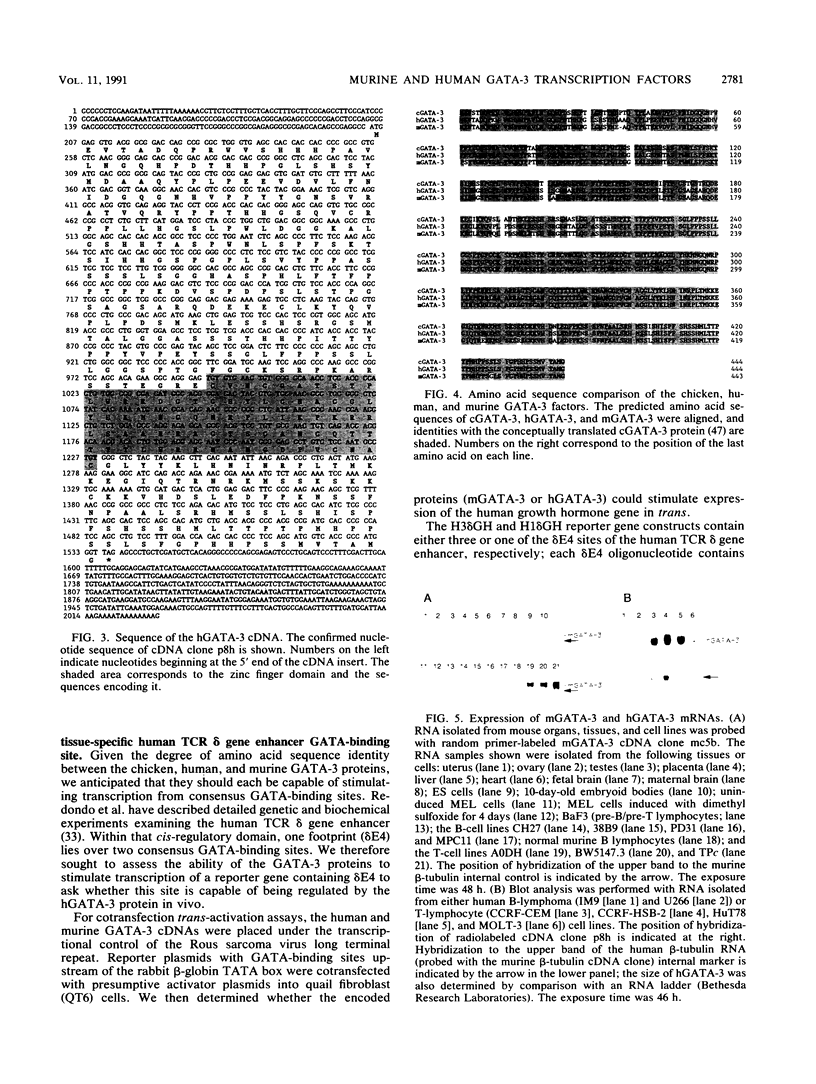
A family of transcriptional activators has recently been identified in chickens; these transcriptional activators recognize a common consensus motif (WGATAR) through a conserved C4 zinc finger DNA-binding domain. One of the members of this multigene family, cGATA-3, is most abundantly expressed in the T-lymphocyte cell lineage. Analysis of human and murine GATA-3 factors shows a striking degree of amino acid sequence identity and similar patterns of tissue specificity of expression in these three organisms. The murine and human factors are abundantly expressed in a variety of human and murine T-cell lines and can activate transcription through a tissue-specific GATA-binding site identified within the human T-cell receptor delta gene enhancer. We infer that the murine and human GATA-3 proteins play a central and highly conserved role in vertebrate T-cell-specific transcriptional regulation.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arst H. N., Jr, Kudla B., Martinez-Rossi N., Caddick M. X., Sibley S., Davies R. W. Aspergillus and mouse share a new class of 'zinc finger' protein. Trends Genet. 1989 Sep;5(9):291–291. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90105-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerc R. G., Corcoran L. M., LeBowitz J. H., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. The B-cell-specific Oct-2 protein contains POU box- and homeo box-type domains. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1570–1581. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descombes P., Chojkier M., Lichtsteiner S., Falvey E., Schibler U. LAP, a novel member of the C/EBP gene family, encodes a liver-enriched transcriptional activator protein. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1541–1551. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doe C. Q., Hiromi Y., Gehring W. J., Goodman C. S. Expression and function of the segmentation gene fushi tarazu during Drosophila neurogenesis. Science. 1988 Jan 8;239(4836):170–175. doi: 10.1126/science.2892267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson B. M., Nickol J. M., Jackson P. D., Felsenfeld G. Analysis of the tissue-specific enhancer at the 3' end of the chicken adult beta-globin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4786–4790. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Felsenfeld G. The erythroid-specific transcription factor Eryf1: a new finger protein. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):877–885. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90940-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Reitman M., Felsenfeld G. An erythrocyte-specific DNA-binding factor recognizes a regulatory sequence common to all chicken globin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5976–5980. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu Y. H., Marzluf G. A. nit-2, the major nitrogen regulatory gene of Neurospora crassa, encodes a protein with a putative zinc finger DNA-binding domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1056–1065. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallarda J. L., Foley K. P., Yang Z. Y., Engel J. D. The beta-globin stage selector element factor is erythroid-specific promoter/enhancer binding protein NF-E4. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12A):1845–1859. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12a.1845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguère V., Hollenberg S. M., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Functional domains of the human glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):645–652. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90339-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschalk L. R., Leiden J. M. Identification and functional characterization of the human T-cell receptor beta gene transcriptional enhancer: common nuclear proteins interact with the transcriptional regulatory elements of the T-cell receptor alpha and beta genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5486–5495. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He X., Treacy M. N., Simmons D. M., Ingraham H. A., Swanson L. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Expression of a large family of POU-domain regulatory genes in mammalian brain development. Nature. 1989 Jul 6;340(6228):35–41. doi: 10.1038/340035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., Adashi E. Y., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Isolation of a recombinant copy of the gene encoding C/EBP. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):786–800. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lum L. S., Sultzman L. A., Kaufman R. J., Linzer D. I., Wu B. J. A cloned human CCAAT-box-binding factor stimulates transcription from the human hsp70 promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6709–6717. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. I., Orkin S. H. Transcriptional activation and DNA binding by the erythroid factor GF-1/NF-E1/Eryf 1. Genes Dev. 1990 Nov;4(11):1886–1898. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.11.1886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. I., Tsai S. F., Orkin S. H. Increased gamma-globin expression in a nondeletion HPFH mediated by an erythroid-specific DNA-binding factor. Nature. 1989 Mar 30;338(6214):435–438. doi: 10.1038/338435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. I., Zon L. I., Mutter G., Orkin S. H. Expression of an erythroid transcription factor in megakaryocytic and mast cell lineages. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):444–447. doi: 10.1038/344444a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignotte V., Eleouet J. F., Raich N., Romeo P. H. Cis- and trans-acting elements involved in the regulation of the erythroid promoter of the human porphobilinogen deaminase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6548–6552. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscovici C., Moscovici M. G., Jimenez H., Lai M. M., Hayman M. J., Vogt P. K. Continuous tissue culture cell lines derived from chemically induced tumors of Japanese quail. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):95–103. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller C. R., Maire P., Schibler U. DBP, a liver-enriched transcriptional activator, is expressed late in ontogeny and its tissue specificity is determined posttranscriptionally. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):279–291. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90808-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M. M., Ruppert S., Schaffner W., Matthias P. A cloned octamer transcription factor stimulates transcription from lymphoid-specific promoters in non-B cells. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):544–551. doi: 10.1038/336544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto K., Okazawa H., Okuda A., Sakai M., Muramatsu M., Hamada H. A novel octamer binding transcription factor is differentially expressed in mouse embryonic cells. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):461–472. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90597-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H. Globin gene regulation and switching: circa 1990. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):665–672. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90133-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins N. D., Nicolas R. H., Plumb M. A., Goodwin G. H. The purification of an erythroid protein which binds to enhancer and promoter elements of haemoglobin genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 25;17(4):1299–1314. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.4.1299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plumb M., Frampton J., Wainwright H., Walker M., Macleod K., Goodwin G., Harrison P. GATAAG; a cis-control region binding an erythroid-specific nuclear factor with a role in globin and non-globin gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 11;17(1):73–92. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Cohen D. R., Curran T., Bos T. J., Vogt P. K., Bohmann D., Tjian R., Franza B. R., Jr Fos-associated protein p39 is the product of the jun proto-oncogene. Science. 1988 May 20;240(4855):1010–1016. doi: 10.1126/science.3130660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
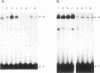
- Redondo J. M., Hata S., Brocklehurst C., Krangel M. S. A T cell-specific transcriptional enhancer within the human T cell receptor delta locus. Science. 1990 Mar 9;247(4947):1225–1229. doi: 10.1126/science.2156339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddle R. D., Yamamoto M., Engel J. D. Expression of delta-aminolevulinate synthase in avian cells: separate genes encode erythroid-specific and nonspecific isozymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):792–796. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romeo P. H., Prandini M. H., Joulin V., Mignotte V., Prenant M., Vainchenker W., Marguerie G., Uzan G. Megakaryocytic and erythrocytic lineages share specific transcription factors. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):447–449. doi: 10.1038/344447a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosner M. H., Vigano M. A., Ozato K., Timmons P. M., Poirier F., Rigby P. W., Staudt L. M. A POU-domain transcription factor in early stem cells and germ cells of the mammalian embryo. Nature. 1990 Jun 21;345(6277):686–692. doi: 10.1038/345686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder K., Lau L. F., Nathans D. A gene activated by growth factors is related to the oncogene v-jun. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1487–1491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro C., Mermod N., Andrews P. C., Tjian R. A family of human CCAAT-box-binding proteins active in transcription and DNA replication: cloning and expression of multiple cDNAs. Nature. 1988 Jul 21;334(6179):218–224. doi: 10.1038/334218a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R., Ruppert S., Suzuki N., Chowdhury K., Gruss P. New type of POU domain in germ line-specific protein Oct-4. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):435–439. doi: 10.1038/344435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm R. A., Das G., Herr W. The ubiquitous octamer-binding protein Oct-1 contains a POU domain with a homeo box subdomain. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1582–1599. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda J., Cheng A., Mauxion F., Nelson C. A., Newberry R. D., Sha W. C., Sen R., Loh D. Y. Functional analysis of the murine T-cell receptor beta enhancer and characteristics of its DNA-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5027–5035. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trainor C. D., Evans T., Felsenfeld G., Boguski M. S. Structure and evolution of a human erythroid transcription factor. Nature. 1990 Jan 4;343(6253):92–96. doi: 10.1038/343092a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. F., Martin D. I., Zon L. I., D'Andrea A. D., Wong G. G., Orkin S. H. Cloning of cDNA for the major DNA-binding protein of the erythroid lineage through expression in mammalian cells. Nature. 1989 Jun 8;339(6224):446–451. doi: 10.1038/339446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall L., deBoer E., Grosveld F. The human beta-globin gene 3' enhancer contains multiple binding sites for an erythroid-specific protein. Genes Dev. 1988 Sep;2(9):1089–1100. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.9.1089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. B., Dorfman D. M., Orkin S. H. A nonerythroid GATA-binding protein is required for function of the human preproendothelin-1 promoter in endothelial cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4854–4862. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winoto A., Baltimore D. A novel, inducible and T cell-specific enhancer located at the 3' end of the T cell receptor alpha locus. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):729–733. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03432.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto M., Ko L. J., Leonard M. W., Beug H., Orkin S. H., Engel J. D. Activity and tissue-specific expression of the transcription factor NF-E1 multigene family. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1650–1662. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zon L. I., Tsai S. F., Burgess S., Matsudaira P., Bruns G. A., Orkin S. H. The major human erythroid DNA-binding protein (GF-1): primary sequence and localization of the gene to the X chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):668–672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]