Abstract
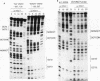
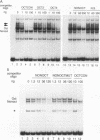
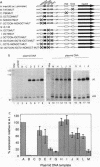
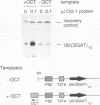
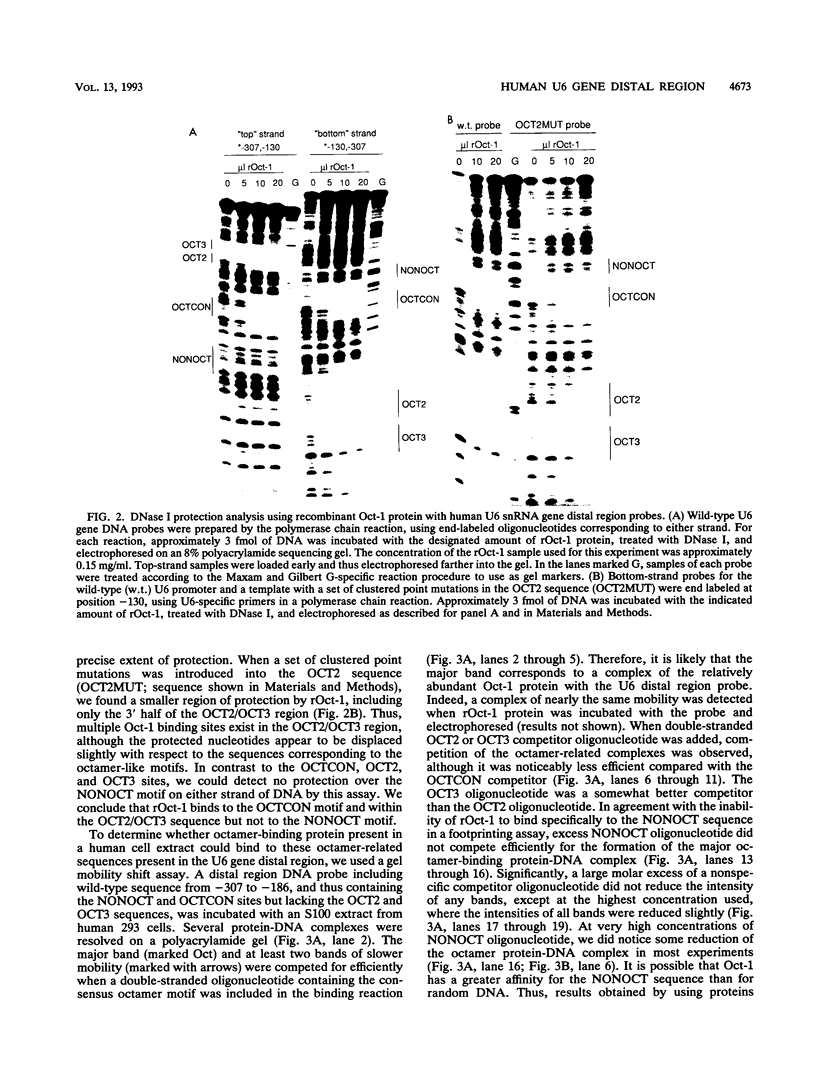
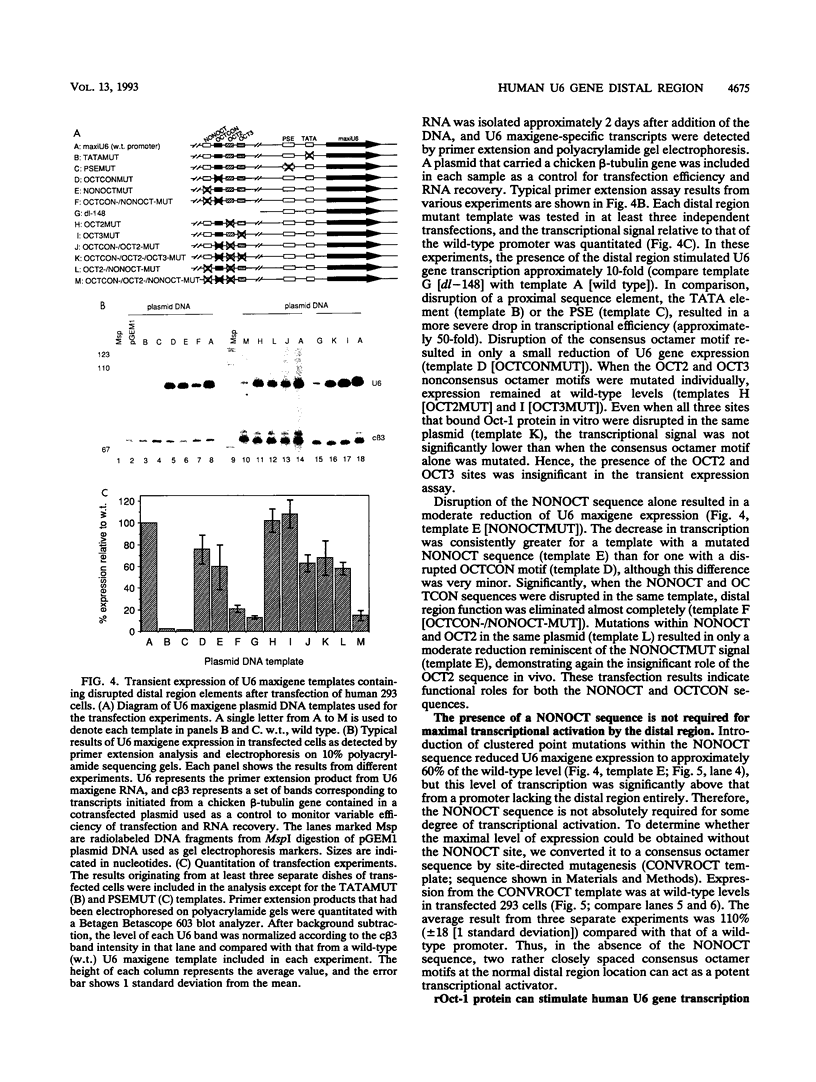
The promoters of vertebrate U6 small nuclear RNA genes contain a distal control region whose presence results in at least an eightfold level of transcriptional activation in vivo. Previous transfection experiments have demonstrated that most of the distal control region of a human U6 gene resides in a restriction fragment located from -244 to -149 relative to the transcriptional start site. Three octamer-related motifs that bind recombinant Oct-1 transcription factor in vitro exist in this segment of DNA. However, transfection of human 293 cells with various plasmid templates in which these Oct-1 binding sites had been disrupted individually or in combination showed that only the consensus octamer motif located between positions -221 to -214 was functional. Even so, the consensus octamer motif mutant template was expressed at only a moderately reduced level relative to the wild-type promoter. When another octamer-related sequence located nearby, one that did not bind Oct-1 in vitro, was disrupted along with the perfect octamer site, expression was reduced fivefold in transfected cells. A factor that binds this functional, nonconsensus octamer site (NONOCT) was detected in crude cellular extracts. However, the NONOCT sequence was not essential for activation, since its disruption caused only a 40% reduction in U6 gene expression, and mutagenesis to convert the NONOCT sequence to a consensus octamer motif restored wild-type expression. Furthermore, in vitro transcription of a human U6 proximal promoter joined to a single copy of the octamer motif was stimulated by the addition of recombinant Oct-1 protein.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ach R. A., Weiner A. M. Cooperation between CCAAT and octamer motifs in the distal sequence element of the rat U3 small nucleolar RNA promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 11;19(15):4209–4218. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.15.4209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ares M., Jr, Chung J. S., Giglio L., Weiner A. M. Distinct factors with Sp1 and NF-A specificities bind to adjacent functional elements of the human U2 snRNA gene enhancer. Genes Dev. 1987 Oct;1(8):808–817. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.8.808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ares M., Jr, Mangin M., Weiner A. M. Orientation-dependent transcriptional activator upstream of a human U2 snRNA gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1560–1570. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bark C., Weller P., Zabielski J., Janson L., Pettersson U. A distant enhancer element is required for polymerase III transcription of a U6 RNA gene. Nature. 1987 Jul 23;328(6128):356–359. doi: 10.1038/328356a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbon P., Murgo S., Ebel J. P., Krol A., Tebb G., Mattaj L. W. A common octamer motif binding protein is involved in the transcription of U6 snRNA by RNA polymerase III and U2 snRNA by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):71–79. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung C. H., Fan Q. N., Stumph W. E. Structural requirements for the functional activity of a U1 snRNA gene enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jan 25;21(2):281–287. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.2.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciliberto G., Palla F., Tebb G., Mattaj I. W., Philipson L. Properties of a U1 RNA enhancer-like sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 25;15(6):2403–2416. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.6.2403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlberg J. E., Lund E. How does III x II make U6? Science. 1991 Dec 6;254(5037):1462–1463. doi: 10.1126/science.1962205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlberg J. E., Schenborn E. T. The human U1 snRNA promoter and enhancer do not direct synthesis of messenger RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):5827–5840. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.5827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das G., Henning D., Wright D., Reddy R. Upstream regulatory elements are necessary and sufficient for transcription of a U6 RNA gene by RNA polymerase III. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):503–512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02838.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goomer R. S., Kunkel G. R. The transcriptional start site for a human U6 small nuclear RNA gene is dictated by a compound promoter element consisting of the PSE and the TATA box. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Sep 25;20(18):4903–4912. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.18.4903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janson L., Bark C., Pettersson U. Identification of proteins interacting with the enhancer of human U2 small nuclear RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):4997–5016. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.4997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janson L., Pettersson U. Cooperative interactions between transcription factors Sp1 and OTF-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4732–4736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Tjian R. Affinity purification of sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5889–5893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazmaier M., Tebb G., Mattaj I. W. Functional characterization of X. laevis U5 snRNA genes. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3071–3078. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02614.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinert H., Assert R., Benecke B. J. A single base pair deletion from the inactive octamer-like motif of the 7S K distal sequence element brings full functionality in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):23872–23877. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinert H., Bredow S., Benecke B. J. Expression of a human 7S K RNA gene in vivo requires a novel pol III upstream element. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):711–718. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08164.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel G. R., Danzeiser D. A. Formation of a template committed complex on the promoter of a gene for the U6 small nuclear RNA from the human requires multiple sequence elements, including the distal region. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):14250–14258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel G. R., Pederson T. Transcription of a human U6 small nuclear RNA gene in vivo withstands deletion of intragenic sequences but not of an upstream TATATA box. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7371–7379. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel G. R., Pederson T. Upstream elements required for efficient transcription of a human U6 RNA gene resemble those of U1 and U2 genes even though a different polymerase is used. Genes Dev. 1988 Feb;2(2):196–204. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.2.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel G. R. RNA polymerase III transcription of genes that lack internal control regions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jan 17;1088(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90146-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lescure A., Tebb G., Mattaj I. W., Krol A., Carbon P. A factor with Sp1 DNA-binding specificity stimulates Xenopus U6 snRNA in vivo transcription by RNA polymerase III. J Mol Biol. 1992 Nov 20;228(2):387–394. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90828-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobo S. M., Lister J., Sullivan M. L., Hernandez N. The cloned RNA polymerase II transcription factor IID selects RNA polymerase III to transcribe the human U6 gene in vitro. Genes Dev. 1991 Aug;5(8):1477–1489. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.8.1477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., Lienhard S., Jiricny J., De Robertis E. M. An enhancer-like sequence within the Xenopus U2 gene promoter facilitates the formation of stable transcription complexes. Nature. 1985 Jul 11;316(6024):163–167. doi: 10.1038/316163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy S., Di Liegro C., Melli M. The in vitro transcription of the 7SK RNA gene by RNA polymerase III is dependent only on the presence of an upstream promoter. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):81–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90012-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy S., Moorefield B., Pieler T. Common mechanisms of promoter recognition by RNA polymerases II and III. Trends Genet. 1989 Apr;5(4):122–126. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90043-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy S., Pierani A., Scheidereit C., Melli M., Roeder R. G. Purified octamer binding transcription factors stimulate RNA polymerase III--mediated transcription of the 7SK RNA gene. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1071–1080. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90763-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy S., Yoon J. B., Gerster T., Roeder R. G. Oct-1 and Oct-2 potentiate functional interactions of a transcription factor with the proximal sequence element of small nuclear RNA genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):3247–3261. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.3247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myslinski E., Krol A., Carbon P. Optimal tRNA((Ser)Sec) gene activity requires an upstream SPH motif. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 25;20(2):203–209. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.2.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer J. M., Folk W. R. Unraveling the complexities of transcription by RNA polymerase III. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Aug;15(8):300–304. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy R. Transcription of a U6 small nuclear RNA gene in vitro. Transcription of a mouse U6 small nuclear RNA gene in vitro by RNA polymerase III is dependent on transcription factor(s) different from transcription factors IIIA, IIIB, and IIIC. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):15980–15984. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roebuck K. A., Szeto D. P., Green K. P., Fan Q. N., Stumph W. E. Octamer and SPH motifs in the U1 enhancer cooperate to activate U1 RNA gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):341–352. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roebuck K. A., Walker R. J., Stumph W. E. Multiple functional motifs in the chicken U1 RNA gene enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4185–4193. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savino R., Hitti Y., Gerbi S. A. Genes for Xenopus laevis U3 small nuclear RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Oct 25;20(20):5435–5442. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.20.5435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmen K. A., Bernués J., Parry H. D., Stunnenberg H. G., Berkenstam A., Cavallini B., Egly J. M., Mattaj I. W. TFIID is required for in vitro transcription of the human U6 gene by RNA polymerase III. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1853–1862. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07711.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skuzeski J. M., Lund E., Murphy J. T., Steinberg T. H., Burgess R. R., Dahlberg J. E. Synthesis of human U1 RNA. II. Identification of two regions of the promoter essential for transcription initiation at position +1. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8345–8352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm R. A., Das G., Herr W. The ubiquitous octamer-binding protein Oct-1 contains a POU domain with a homeo box subdomain. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1582–1599. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Grossniklaus U., Herr W., Hernandez N. Activation of the U2 snRNA promoter by the octamer motif defines a new class of RNA polymerase II enhancer elements. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1764–1778. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Lai J. S., Herr W. Promoter-selective activation domains in Oct-1 and Oct-2 direct differential activation of an snRNA and mRNA promoter. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):755–767. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90150-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tebb G., Mattaj I. W. The Xenopus laevis U2 gene distal sequence element (enhancer) is composed of four subdomains that can act independently and are partly functionally redundant. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1682–1690. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldschmidt R., Seifart K. H. TFIIA is required for in vitro transcription of mammalian U6 genes by RNA polymerase III. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16359–16364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldschmidt R., Wanandi I., Seifart K. H. Identification of transcription factors required for the expression of mammalian U6 genes in vitro. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2595–2603. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07801.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller P., Bark C., Janson L., Pettersson U. Transcription analysis of a human U4C gene: involvement of transcription factors novel to snRNA gene expression. Genes Dev. 1988 Nov;2(11):1389–1399. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.11.1389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinaga S. K., L'Etoile N. D., Berk A. J. Purification and characterization of transcription factor IIIC2. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10726–10731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamrod Z., Stumph W. E. U4B snRNA gene enhancer activity requires functional octamer and SPH motifs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7323–7330. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]