Abstract
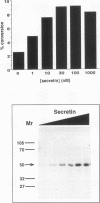
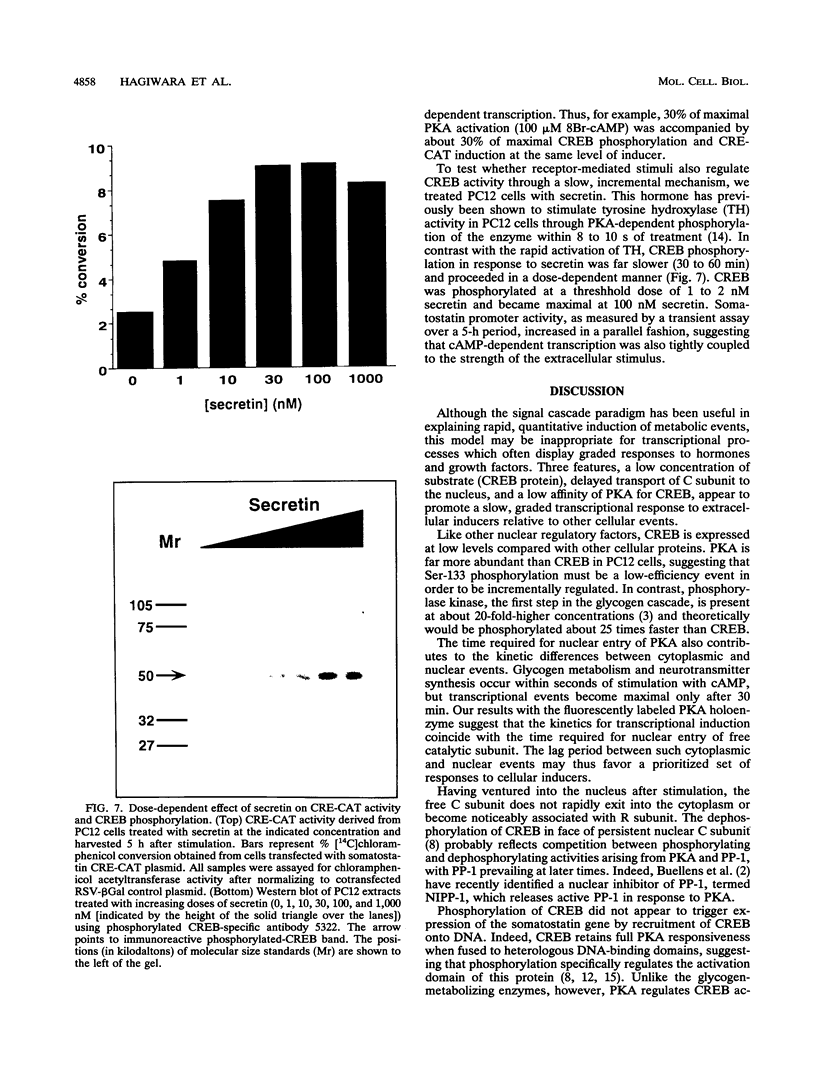
Cyclic AMP (cAMP) regulates a number of eukaryotic genes by mediating the protein kinase A (PKA)-dependent phosphorylation of the CREB transcription factor at Ser-133. In this study, we test the hypothesis that the stoichiometry and kinetics of CREB phosphorylation are determined by the liberation and subsequent translocation of PKA catalytic subunit (C subunit) into the nucleus. Using fluorescence imaging techniques, we observed that PKA was activated in a stimulus-dependent fashion that led to nuclear entry of C subunit over a 30-min period. The degree of CREB phosphorylation, assessed with antiserum specific for CREB phosphorylated at Ser-133, correlated with the amount of PKA liberated. The time course of phosphorylation closely paralleled the nuclear entry of the catalytic subunit. There was a linear relationship between the subsequent induction of the cAMP-responsive somatostatin gene and the degree of CREB phosphorylation, suggesting that each event--kinase activation, CREB phosphorylation, and transcriptional induction--was tightly coupled to the next. In contrast to other PKA-mediated cellular responses which are rapid and quantitative, the slow, incremental regulation of CREB activity by cAMP suggests that multifunctional kinases like PKA may coordinate cellular responses by dictating the kinetics and stoichiometry of phosphorylation for key substrates like CREB.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams S. R., Harootunian A. T., Buechler Y. J., Taylor S. S., Tsien R. Y. Fluorescence ratio imaging of cyclic AMP in single cells. Nature. 1991 Feb 21;349(6311):694–697. doi: 10.1038/349694a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beullens M., Van Eynde A., Stalmans W., Bollen M. The isolation of novel inhibitory polypeptides of protein phosphatase 1 from bovine thymus nuclei. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16538–16544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. Protein phosphorylation and the control of glycogen metabolism in skeletal muscle. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1983 Jul 5;302(1108):13–25. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1983.0034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colbran J. L., Roach P. J., Fiol C. J., Dixon J. E., Andrisani O. M., Corbin J. D. cAMP-dependent protein kinase, but not the cGMP-dependent enzyme, rapidly phosphorylates delta-CREB, and a synthetic delta-CREB peptide. Biochem Cell Biol. 1992 Oct-Nov;70(10-11):1277–1282. doi: 10.1139/o92-174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulkes N. S., Borrelli E., Sassone-Corsi P. CREM gene: use of alternative DNA-binding domains generates multiple antagonists of cAMP-induced transcription. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):739–749. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90503-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez G. A., Montminy M. R. Cyclic AMP stimulates somatostatin gene transcription by phosphorylation of CREB at serine 133. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):675–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez G. A., Yamamoto K. K., Fischer W. H., Karr D., Menzel P., Biggs W., 3rd, Vale W. W., Montminy M. R. A cluster of phosphorylation sites on the cyclic AMP-regulated nuclear factor CREB predicted by its sequence. Nature. 1989 Feb 23;337(6209):749–752. doi: 10.1038/337749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara M., Alberts A., Brindle P., Meinkoth J., Feramisco J., Deng T., Karin M., Shenolikar S., Montminy M. Transcriptional attenuation following cAMP induction requires PP-1-mediated dephosphorylation of CREB. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):105–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90537-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai T. W., Liu F., Coukos W. J., Green M. R. Transcription factor ATF cDNA clones: an extensive family of leucine zipper proteins able to selectively form DNA-binding heterodimers. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2083–2090. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp B. E., Graves D. J., Benjamini E., Krebs E. G. Role of multiple basic residues in determining the substrate specificity of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):4888–4894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamers W. H., Hanson R. W., Meisner H. M. cAMP stimulates transcription of the gene for cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase in rat liver nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5137–5141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. Q., Yun Y. D., Hoeffler J. P., Habener J. F. Cyclic-AMP-responsive transcriptional activation of CREB-327 involves interdependent phosphorylated subdomains. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4455–4465. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07896.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Nichols M., Weih F., Schmid W., DeVack C., Kowenz-Leutz E., Luckow B., Boshart M., Schütz G. Phosphorylation of CREB affects its binding to high and low affinity sites: implications for cAMP induced gene transcription. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3337–3346. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05412.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roskoski R., Jr, White L., Knowlton R., Roskoski L. M. Regulation of tyrosine hydroxylase activity in rat PC12 cells by neuropeptides of the secretin family. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;36(6):925–931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheng M., Thompson M. A., Greenberg M. E. CREB: a Ca(2+)-regulated transcription factor phosphorylated by calmodulin-dependent kinases. Science. 1991 Jun 7;252(5011):1427–1430. doi: 10.1126/science.1646483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan J. M., Rivier J., Corrigan A. Z., McClintock R., Campen C. A., Jolley D., Voglmayr J. K., Bardin C. W., Rivier C., Vale W. Detection and purification of inhibin using antisera generated against synthetic peptide fragments. Methods Enzymol. 1989;168:588–617. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)68044-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]