Abstract
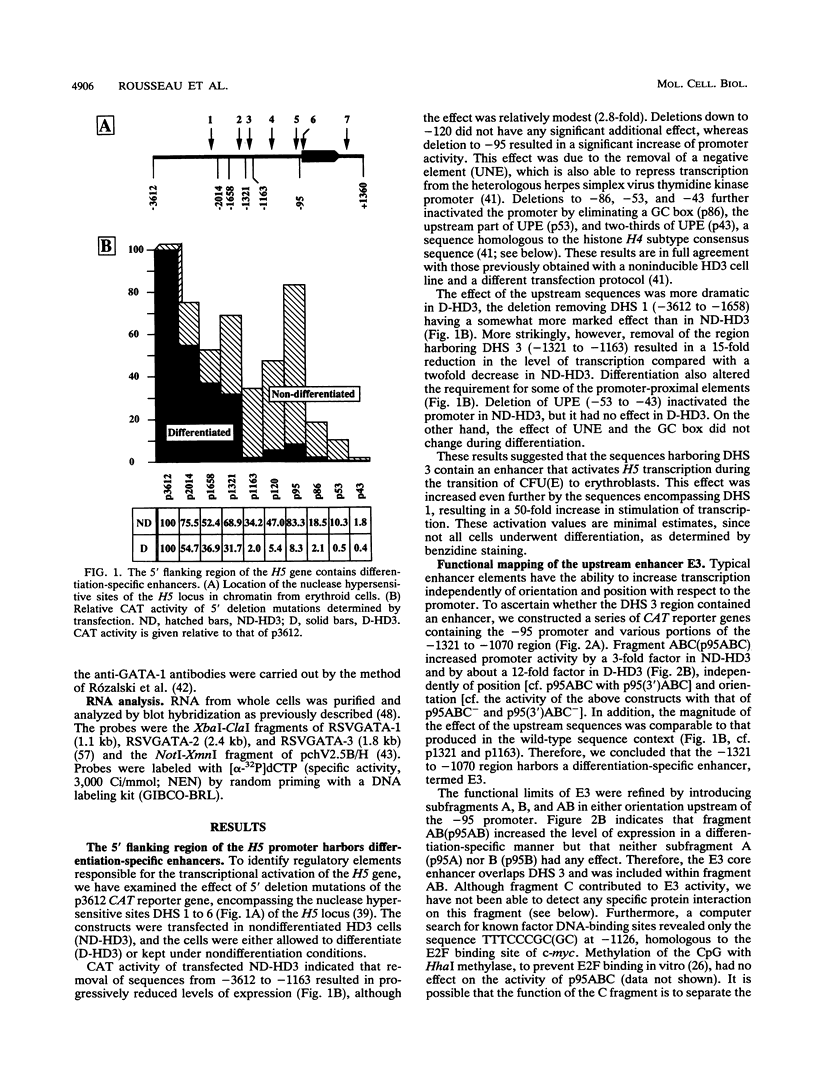
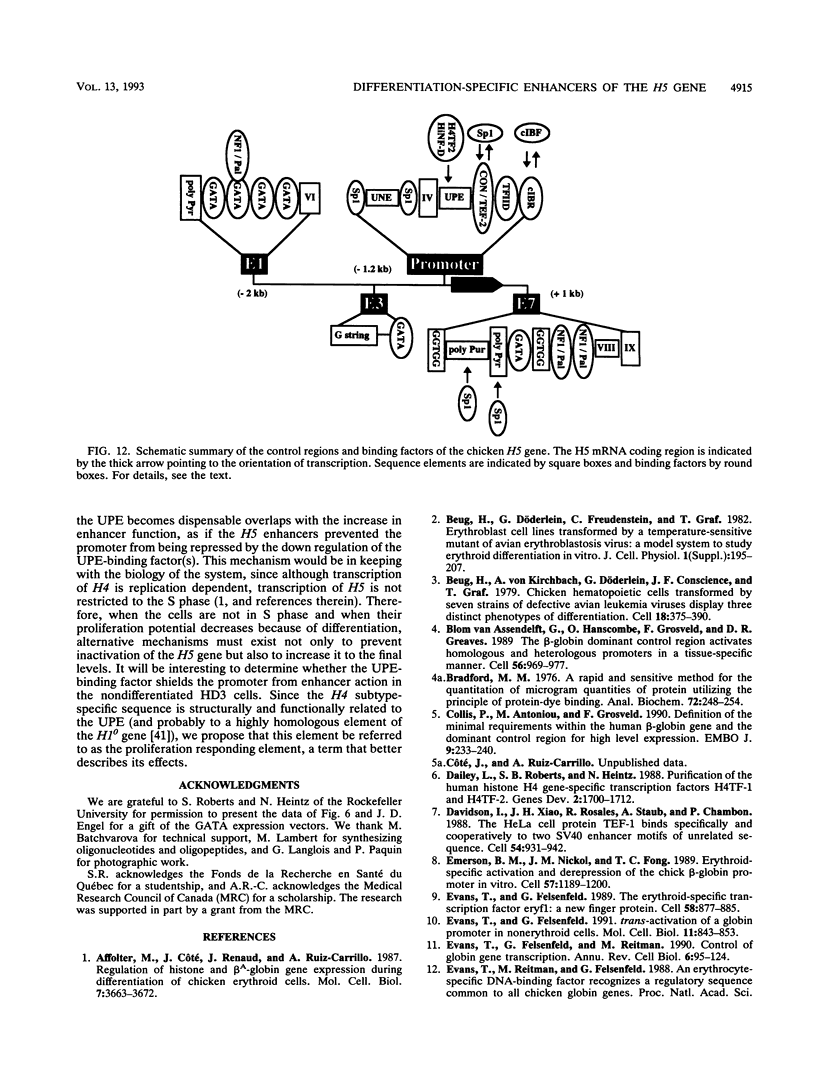
Histone H5, an early marker of the avian erythroid lineage, is expressed at low levels in early erythroid precursors and at higher levels in more mature cells. We show that the increase in H5 expression is due to transcriptional activation of the H5 gene following differentiation of precursor CFU(E). We have found and characterized two upstream enhancers, E1 (between -2233 and -1878 from the site of transcription initiation, +1) and E3 (between -1321 and -1163), and confirmed the presence of a downstream enhancer (C. D. Trainor, S. J. Stamler, and J. D. Engel, Nature [London] 328:827-830, 1987) E7 (between +846 and +1181) which are responsible for the increase in H5 gene transcription. The enhancers had a weak effect in nondifferentiated CFU(E) but a strong effect when the cells were induced to differentiate. Cooperation among the three enhancers, however, was not required for H5 gene activity in the differentiated cells. The enhancers contain binding sites for several ubiquitous and erythroid cell-specific nuclear proteins, including GATA-1, as demonstrated with GATA-1-specific antibodies. Although the GATA sites were required for enhancer function, the concentration of GATA-1, GATA-2, and GATA-3 decreased during cell differentiation, and overexpression of these factors had little effect on H5 transcription. Hence, the differentiation-specific effect of the enhancers is not mediated by changes in relative levels of the GATA factors. Functional analysis of the H5 promoter indicated that the requirement of several elements, including a GC box necessary for transcription enhancement, did not change during the early stages of CFU(E) differentiation. However, the UPE, a positive element in proliferating CFU(E) recognized by the transcription factor H4TF2, was dispensable in the differentiated cells. These results suggest that as the cells enter the final stages of differentiation, there is a reprogramming of the regulatory factors that control H5 transcription and that the enhancers rescue and increase the activity of the promoter.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Affolter M., Côté J., Renaud J., Ruiz-Carrillo A. Regulation of histone and beta A-globin gene expression during differentiation of chicken erythroid cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3663–3672. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beug H., Doederlein G., Freudenstein C., Graf T. Erythroblast cell lines transformed by a temperature-sensitive mutant of avian erythroblastosis virus: a model system to study erythroid differentiation in vitro. J Cell Physiol Suppl. 1982;1:195–207. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041130427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beug H., von Kirchbach A., Döderlein G., Conscience J. F., Graf T. Chicken hematopoietic cells transformed by seven strains of defective avian leukemia viruses display three distinct phenotypes of differentiation. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):375–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90057-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blom van Assendelft G., Hanscombe O., Grosveld F., Greaves D. R. The beta-globin dominant control region activates homologous and heterologous promoters in a tissue-specific manner. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):969–977. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90630-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collis P., Antoniou M., Grosveld F. Definition of the minimal requirements within the human beta-globin gene and the dominant control region for high level expression. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):233–240. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08100.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dailey L., Roberts S. B., Heintz N. Purification of the human histone H4 gene-specific transcription factors H4TF-1 and H4TF-2. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1700–1712. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson I., Xiao J. H., Rosales R., Staub A., Chambon P. The HeLa cell protein TEF-1 binds specifically and cooperatively to two SV40 enhancer motifs of unrelated sequence. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):931–942. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90108-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson B. M., Nickol J. M., Fong T. C. Erythroid-specific activation and derepression of the chick beta-globin promoter in vitro. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1189–1200. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90056-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Felsenfeld G., Reitman M. Control of globin gene transcription. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:95–124. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.000523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Felsenfeld G. The erythroid-specific transcription factor Eryf1: a new finger protein. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):877–885. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90940-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Felsenfeld G. trans-Activation of a globin promoter in nonerythroid cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):843–853. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallarda J. L., Foley K. P., Yang Z. Y., Engel J. D. The beta-globin stage selector element factor is erythroid-specific promoter/enhancer binding protein NF-E4. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12A):1845–1859. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12a.1845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronostajski R. M. Analysis of nuclear factor I binding to DNA using degenerate oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 25;14(22):9117–9132. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.22.9117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronostajski R. M. Site-specific DNA binding of nuclear factor I: effect of the spacer region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 24;15(14):5545–5559. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.14.5545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld F., van Assendelft G. B., Greaves D. R., Kollias G. Position-independent, high-level expression of the human beta-globin gene in transgenic mice. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90584-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guertin M., LaRue H., Bernier D., Wrange O., Chevrette M., Gingras M. C., Bélanger L. Enhancer and promoter elements directing activation and glucocorticoid repression of the alpha 1-fetoprotein gene in hepatocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1398–1407. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Cuadrado A., Rousseau S., Renaud J., Ruiz-Carrillo A. Repression of the H5 histone gene by a factor from erythrocytes that binds to the region of transcription initiation. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1857–1866. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05237.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N., Zernik M., Roeder R. G. The structure of the human histone genes: clustered but not tandemly repeated. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):661–668. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90092-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho I. C., Vorhees P., Marin N., Oakley B. K., Tsai S. F., Orkin S. H., Leiden J. M. Human GATA-3: a lineage-restricted transcription factor that regulates the expression of the T cell receptor alpha gene. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1187–1192. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08059.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holthuis J., Owen T. A., van Wijnen A. J., Wright K. L., Ramsey-Ewing A., Kennedy M. B., Carter R., Cosenza S. C., Soprano K. J., Lian J. B. Tumor cells exhibit deregulation of the cell cycle histone gene promoter factor HiNF-D. Science. 1990 Mar 23;247(4949 Pt 1):1454–1457. doi: 10.1126/science.247.4949.1454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson S. P., Tjian R. O-glycosylation of eukaryotic transcription factors: implications for mechanisms of transcriptional regulation. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90015-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joulin V., Bories D., Eléouet J. F., Labastie M. C., Chrétien S., Mattéi M. G., Roméo P. H. A T-cell specific TCR delta DNA binding protein is a member of the human GATA family. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1809–1816. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07706.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kageyama R., Merlino G. T., Pastan I. A transcription factor active on the epidermal growth factor receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5016–5020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kageyama R., Pastan I. Molecular cloning and characterization of a human DNA binding factor that represses transcription. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):815–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90605-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovesdi I., Reichel R., Nevins J. R. Role of an adenovirus E2 promoter binding factor in E1A-mediated coordinate gene control. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2180–2184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Bella F., Heintz N. Histone gene transcription factor binding in extracts of normal human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):5825–5831. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.5825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis C. D., Clark S. P., Felsenfeld G., Gould H. An erythrocyte-specific protein that binds to the poly(dG) region of the chicken beta-globin gene promoter. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):863–873. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney M. M., Parkinson A. A simple, non-chromatographic procedure to purify immunoglobulins from serum and ascites fluid. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Feb 11;96(2):271–278. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90324-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignotte V., Wall L., deBoer E., Grosveld F., Romeo P. H. Two tissue-specific factors bind the erythroid promoter of the human porphobilinogen deaminase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 11;17(1):37–54. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Timmons P. M., Hébert J. M., Rigby P. W., Tjian R. Transcription factor AP-2 is expressed in neural crest cell lineages during mouse embryogenesis. Genes Dev. 1991 Jan;5(1):105–119. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.1.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H. Globin gene regulation and switching: circa 1990. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):665–672. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90133-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins N. D., Nicolas R. H., Plumb M. A., Goodwin G. H. The purification of an erythroid protein which binds to enhancer and promoter elements of haemoglobin genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 25;17(4):1299–1314. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.4.1299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perucho M., Molgaard H. V., Shevack A., Pataryas T., Ruiz-Carrillo A. An improved method for the preparation of undegraded polysomes and active messenger RNA from immature chicken erythrocytes. Anal Biochem. 1979 Oct 1;98(2):464–471. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90168-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pevny L., Simon M. C., Robertson E., Klein W. H., Tsai S. F., D'Agati V., Orkin S. H., Costantini F. Erythroid differentiation in chimaeric mice blocked by a targeted mutation in the gene for transcription factor GATA-1. Nature. 1991 Jan 17;349(6306):257–260. doi: 10.1038/349257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipsen S., Talbot D., Fraser P., Grosveld F. The beta-globin dominant control region: hypersensitive site 2. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2159–2167. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07385.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plumb M., Frampton J., Wainwright H., Walker M., Macleod K., Goodwin G., Harrison P. GATAAG; a cis-control region binding an erythroid-specific nuclear factor with a role in globin and non-globin gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 11;17(1):73–92. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitman M., Felsenfeld G. Mutational analysis of the chicken beta-globin enhancer reveals two positive-acting domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6267–6271. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renaud J., Ruiz-Carrillo A. Fine analysis of the active H5 gene chromatin of chicken erythroid cells at different stages of differentiation. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):217–226. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90392-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts S. B., Emmons S. W., Childs G. Nucleotide sequences of Caenorhabditis elegans core histone genes. Genes for different histone classes share common flanking sequence elements. J Mol Biol. 1989 Apr 20;206(4):567–577. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90566-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau S., Renaud J., Ruiz-Carrillo A. Basal expression of the histone H5 gene is controlled by positive and negative cis-acting sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7495–7511. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Carrillo A., Affolter M., Renaud J. Genomic organization of the genes coding for the six main histones of the chicken: complete sequence of the H5 gene. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):843–859. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80191-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Carrillo A., Renaud J. Endonuclease G: a (dG)n X (dC)n-specific DNase from higher eukaryotes. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):401–407. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04769.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Vazquez R., Ruiz-Carillo A. Construction of chimeric plasmids containing histone H5 cDNA from hen erythrocyte. DNA sequence of a fragment derived from the 5' region of H5 mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 25;10(6):2093–2108. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.6.2093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rózalski M., Lafleur L., Ruiz-Carrillo A. Monoclonal antibodies against histone H5. Epitope mapping and binding to chromatin. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14379–14386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B., Sheen J. Y. A simple phase-extraction assay for chloramphenicol acyltransferase activity. Gene. 1988 Jul 30;67(2):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90403-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein G., Lian J., Stein J., Briggs R., Shalhoub V., Wright K., Pauli U., van Wijnen A. Altered binding of human histone gene transcription factors during the shutdown of proliferation and onset of differentiation in HL-60 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1865–1869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun J. M., Wiaderkiewicz R., Ruiz-Carrillo A. Histone H5 in the control of DNA synthesis and cell proliferation. Science. 1989 Jul 7;245(4913):68–71. doi: 10.1126/science.2740916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot D., Philipsen S., Fraser P., Grosveld F. Detailed analysis of the site 3 region of the human beta-globin dominant control region. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2169–2177. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07386.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trainor C. D., Stamler S. J., Engel J. D. Erythroid-specific transcription of the chicken histone H5 gene is directed by a 3' enhancer. 1987 Aug 27-Sep 2Nature. 328(6133):827–830. doi: 10.1038/328827a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. F., Strauss E., Orkin S. H. Functional analysis and in vivo footprinting implicate the erythroid transcription factor GATA-1 as a positive regulator of its own promoter. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):919–931. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall L., deBoer E., Grosveld F. The human beta-globin gene 3' enhancer contains multiple binding sites for an erythroid-specific protein. Genes Dev. 1988 Sep;2(9):1089–1100. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.9.1089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. W., Robins A. J., d'Andrea R., Wells J. R. Inverted duplication of histone genes in chicken and disposition of regulatory sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1369–1387. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitelaw E., Tsai S. F., Hogben P., Orkin S. H. Regulated expression of globin chains and the erythroid transcription factor GATA-1 during erythropoiesis in the developing mouse. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6596–6606. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiang M., Lu S. Y., Musso M., Karsenty G., Klein W. H. A G-string positive cis-regulatory element in the LpS1 promoter binds two distinct nuclear factors distributed non-uniformly in Lytechinus pictus embryos. Development. 1991 Dec;113(4):1345–1355. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.4.1345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao J. H., Davidson I., Macchi M., Rosales R., Vigneron M., Staub A., Chambon P. In vitro binding of several cell-specific and ubiquitous nuclear proteins to the GT-I motif of the SV40 enhancer. Genes Dev. 1987 Oct;1(8):794–807. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.8.794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto M., Ko L. J., Leonard M. W., Beug H., Orkin S. H., Engel J. D. Activity and tissue-specific expression of the transcription factor NF-E1 multigene family. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1650–1662. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenke M., Muñoz A., Sap J., Vennström B., Beug H. v-erbA oncogene activation entails the loss of hormone-dependent regulator activity of c-erbA. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):1035–1049. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90068-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]









